文章编号:1004-0609(2014)10-2506-07
热变形粉末冶金Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金热处理过程的组织演变
赵 堃,刘 咏,黄 岚,刘 彬,李建波,梁霄鹏,贺跃辉
(中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:对锻造态的粉末冶金Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W(摩尔分数,%)合金进行后续热处理,研究热处理时间和热处理温度对合金组织演变的影响,利用扫描电镜及透射电镜对合金显微组织进行观察。结果表明:在1230~1260 ℃温度区间热处理可消除锻造态合金的少量β相。在该温度区间进行等时热处理时,随着热处理温度的升高,α晶粒和γ晶粒迅速长大,γ相体积分数急剧减小,且α晶粒趋于等轴化。合金在1260 ℃进行等温热处理时,热处理时间由0.5 h延长至6 h,α晶粒和γ晶粒迅速长大,γ相体积分数降低,继续延长热处理时间,显微组织没有明显的变化。通过计算可知,1260 ℃下α晶粒尺寸的极限值约为0.54 Dγ /Vγ(Dγ为γ晶粒尺寸;Vγ为γ晶粒体积分数)。
关键词:TiAl合金;热处理;组织演变;晶粒长大
中图分类号:TG111.7 文献标志码:A
Microstructure evolution of hot-deformed powder metallurgy Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W alloy during heat treatment
ZHAO Kun, LIU Yong, HUANG Lan, LIU Bin, LI Jian-bo, LIANG Xiao-peng, HE Yue-hui
(State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Powder metallurgy Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W (mole fraction, %) alloy was canned-forged and then heat-treated. The effects of heat treatment time and temperature on the alloy microstructure evolution were studied. The microstructures of as-forged alloy and heat-treated alloy were investigated by scanning and transmission microscopy. The results demonstrate that a few β grains in as-forged alloy are eliminated during heat treatments in the temperature range of 1230-1260 ℃. Isochronal annealing experiments show that the α grain size and γ grain size rapidly increase with increasing the temperature, while the volume fraction of γ phase steeply decreases and α grains become equiaxial. Isothermal annealing experiments at 1260 ℃ for 0.5-6 h reveal a sharp increase of α grain size and γ grain size with time. Meantime, the volume fraction of γ phase decreases. The microstructure of alloy shows no significant change during prolonging the annealing time. By calculation, the extreme α grain size at 1260 ℃ is approximately 0.54 Dγ /Vγ (Dγ is short for γ grain size and Vγ is short or the volume fraction of γ phase).
Key words: titanium aluminide alloy; heat treatment; microstructure evolution; grain growth
TiAl基合金由于具有高比强度、优异的高温强度和优良的抗氧化性能[1-8],在汽车及航空航天领域有着广泛的应用前景。TiAl基合金室温脆性大而且热加工变形能力差,极大地制约了其生产应用[9]。与铸造合金相比,粉末冶金TiAl基合金中不存在缩孔、疏松和偏析等缺陷,而且组织和化学成分更均匀,晶粒尺寸更细小,延性更高。目前,已采用热等静压工艺成功制备出Ti-47Al-2Cr-0.2Mo[2]、Ti-46Al-2Cr-2Nb-0.2B[10]、Ti-48Al- 2Mn-2Nb[11]和Ti-46Al-9Nb[12]等全致密合金坯体。
包套锻造作为一种机械热处理方式,常用于细化TiAl基合金的显微组织[13],以改善其室温脆性[14]。对锻造态TiAl基合金进行热处理,可得到均匀细小的再结晶组织。通过对再结晶晶粒尺寸的合理控制,可优化合金组织并提高其力学性能。通常以晶粒长大动力学作为指导热处理的理论依据,从而制定相应的加工工艺。因此,研究锻造态合金在热处理时的晶粒长大行为具有重要的实际意义。
研究表明,锻造态TiAl基合金在α单相区加热时,经历了单相α晶粒长大的过程[15],冷却至室温可获得全片层组织;锻造态TiAl合金在α+γ两相区加热时,冷却至室温可获得双态组织 ,该过程中合金中的γ晶粒会阻碍α晶粒的长大,使晶粒长大行为变得复杂[16]。在热处理后的冷却过程中,合金中的α相不发生长大,而发生α→α2+γ相变,高温下的α相转变为室温下的α2/γ片层晶团。故实验测得的α2/γ片层晶团尺寸即可代表高温时α相晶粒的尺寸。
与全片层组织相比,双态组织的TiAl基合金呈现更优异的塑性。双态组织的晶粒尺寸不仅影响材料在服役状态下的拉伸性能和疲劳性能,并且决定了后续加工的手段。研究者已对Ti-48Al-2Cr[16]、Ti-45.5- 2Nb-2Cr[17]、Ti-45Al-2Nb[18]和Ti-45Al-2Nb-0.4Mn[18]等体系双态组织晶粒长大动力学进行了探索。
与普通TiAl基合金相比,高铌TiAl基合金具有更优异的高温强度、抗氧化性能和抗蠕变性能[19-21],已受到了研究者的广泛关注。目前,对于高铌TiAl基合金体系的研究主要集中在铸态合金,对粉末冶金高铌TiAl基合金的组织演变的研究报道较少。本文作者选用一种自行设计的合金成分,采用热等静压法制备了Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金坯体,并对其进行包套锻造,研究锻造过程及后续热处理过程中合金的组织演变规律。
1 实验
实验材料选用名义成分为Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W的热等静压态合金。采用电火花线切割从热等静压坯体中切割下尺寸为d 50 mm×70 mm的小圆柱,以厚度为10 mm的不锈钢包套进行包裹。将带包套试样在1280 ℃下,以大于s-1的应变速率进行锻造处理,使其总变形量达到76%。由金相法测得锻造态TiAl基合金α转变温度(Tα)为1295 ℃。为研究热处理温度对合金组织的影响,在低于α转变温度的α+γ两相区以内选取1230 ℃、1240 ℃、1250 ℃和1260 ℃对合金进行4 h热处理(HT1~HT4);为探究热处理时间对合金组织演变的影响,在1260 ℃对合金进行0.5~8 h不同时间的热处理(HT4~HT9),具体工艺如表1所列。
表1 锻造态Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金的热处理工艺
Table 1 Different heat treatments of as-forged alloy

采用Rigaku D/max 2500型18 kW转靶X射线衍射仪对合金进行物相分析。在Nova Nano SEM 230高分辨场发射扫描电镜和JEM-2010型透射电子显微镜下观察合金的显微组织。在由α+γ两相区温度降至室温的过程中,合金中的α相不发生长大,仅发生α→α2+γ相变,生成α2/γ片层晶团,故实验测得的α2/γ片层晶团尺寸即可代表α+γ两相区内α晶粒的尺寸。采用面积法确定α和γ晶粒的平均尺寸。为了提高精确度,分别对每一试样中4个视野内的α相晶粒和γ相晶粒进行统计。利用Image plus软件计算SEM照片中γ相的体积分数。将γ片层中心点到相邻γ片层中心点的距离定义为片间距,对50对α2/γ片层进行统计可获得片层晶团的平均片间距。
2 实验结果
2.1 合金在锻造过程中的组织演变
对热等静压和锻造态Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金分别做XRD物相分析,其结果如图1所示。经比较发现,两者的物相未出现明显的差别,均由γ相和少量α2相组成。
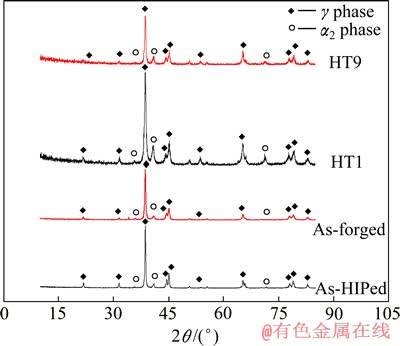
图1 热等静压态(as-HIPed),锻造态(as-forged)、热处理态(HT1、HT9) Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of as-HIPed, as-forged and heat-treated Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W alloy
图2所示为热等静压态及锻造态Ti-45Al-7Nb- 0.3W合金的BSE像。如图2(a)所示,热等静压态合金呈现典型的等轴晶,浅灰色α2相分布于深灰色γ相的三叉晶界处,γ晶粒尺寸在9~15 μm之间。热等静压态合金无孔隙,为晶粒细小的全致密材料,组织分析和物相分析结果吻合较好。图2(b)所示为锻造态合金的显微组织,垂直于锻造方向可见浅灰色带状组织,显示了典型的流线型变形组织特征,γ晶粒尺寸在6~10 μm之间。可见合金经锻造后得到由γ晶粒和α2/γ片层晶团组成的细小的双态组织,γ晶粒得到明显细化。在扫描电镜的高放大倍率下继续观察锻造态合金(见图2(c)),可发现少量亮白色颗粒,因其富含钨而与基体衬度不同,为β相。由于β相含量较少,因此在图1的XRD物相分析结果中未发现其衍射峰。
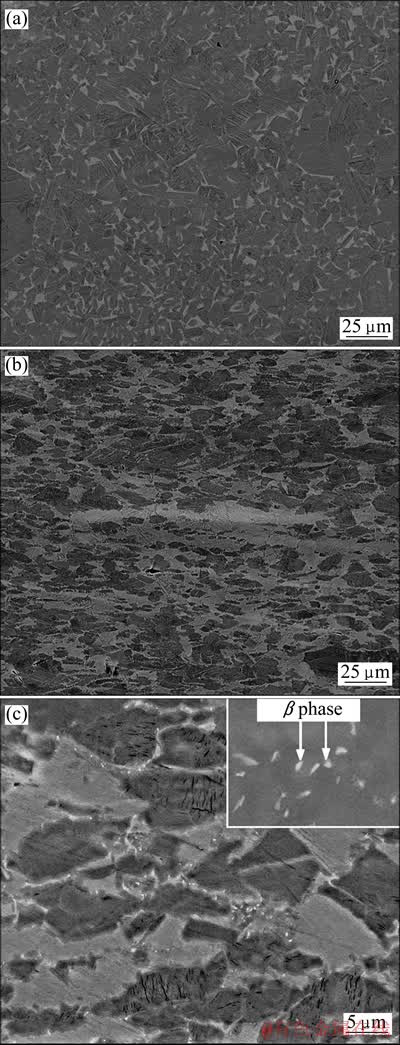
图2 热等静压态及锻造态Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金的BSE像
Fig. 2 SEM images of as-HIPed alloy(a) and as-forged((b), (c)) Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W alloy
2.2 合金在等时热处理的组织演变
图3所示为锻造态Ti-45Al-7Nb- 0.3W合金在1230、1240和1250 ℃热处理4 h后的显微组织。由图1物相分析结果可知,锻造态合金经1230 ℃热处理4 h(HT1)后,主要由α2和γ两相组成。由扫描电镜的背散射照片(见图3(a))可知,热处理态合金(HT1)由等轴的α2/γ片层晶团和γ晶粒组成,其中α2/γ片层晶团呈现浅灰色,γ晶粒呈现深灰色,两相界面平直清晰,锻造态合金中亮白色β相和浅灰色带状组织均得以消除。进一步将热处理温度升高至1240 ℃(见图3(b))和1250 ℃(见图3(c))时,α2/γ片层晶团由扁平状进一步趋向于等轴状。锻造态合金经过1230、1240和1250 ℃下热处理4 h后,两相的不均匀分布得以消除,合金转变为均匀的静态再结晶组织。
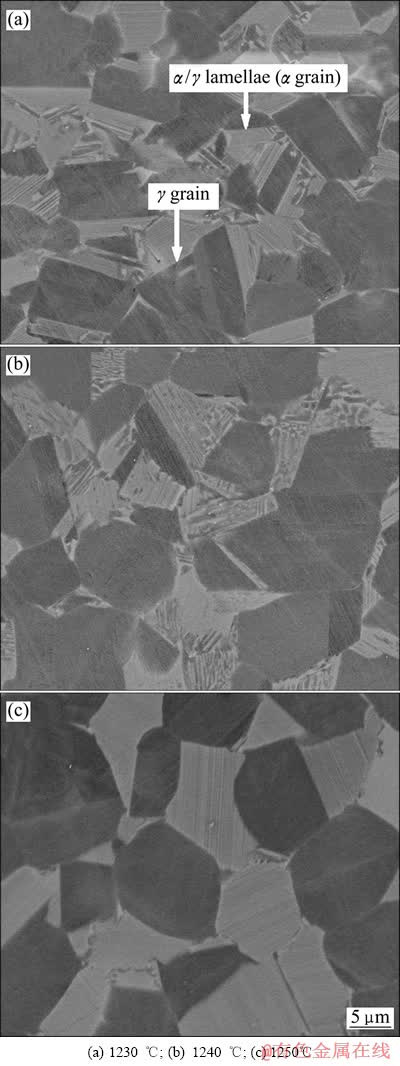
图3 不同温度保温4 h后Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金的SEM像
Fig. 3 SEM images of as-forged Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W alloy heat-treated at different temperatures for 4 h
锻造态Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金在等温热处理后的显微组织与热处理温度相关。用实验测得的α2/γ片层晶团尺寸表示α+γ两相区内α晶粒的尺寸。将α晶粒尺寸(Dα)、γ晶粒尺寸(Dγ)和γ相体积分数(Vγ)随温度的变化趋势如图4所示。在1230 ℃热处理4 h后,热处理态合金中γ晶粒的体积分数为72%,而Dα和Dγ分别为8.2和9.2 μm,Dα略小于Dγ。在该温度区间进行等时热处理实验时,随着热处理温度的升高,合金中的Dα和Dγ逐渐增大,而Vγ逐渐减小。
2.3 合金在等温热处理的组织演变
图5所示为锻造态Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金在
1260 ℃热处理0.5、1、4和6 h后空冷至室温后的显微组织。物相分析结果(见图1)表明,合金在1260 ℃经过8 h(HT9)热处理后,主要由α2和γ两相组成,该结果与1230 ℃下热处理4 h(HT1)的物相组成无明显差别,但两相相对含量发生变化。

图4 α晶粒尺寸、γ晶粒尺寸及γ相体积分数随热处理温度的变化
Fig. 4 Variation of α grain size (Dα), γ grain size (Dγ) and volume fraction of γ phase (Vγ)with annealing temperature

图5 1260 ℃不同保温时间后Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金的BSE像
Fig. 5 BSE images of Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W alloy heat-treated at 1260 ℃ for different times
图6所示为锻造态Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金在1260 ℃热处理4 h(HT4)后空冷至室温后的透射电镜明场像。经统计可知,片层晶团的平均片间距仅为51 nm。合金因发生静态再结晶,在α2/γ片层晶团周围(见图6),形成了无位错的γ晶粒。

图6 合金在1260 ℃下热处理4 h后的透射电镜明场像
Fig. 6 Bright-field TEM images of alloy heat-treated at 1260 ℃ for 4 h
对1260 ℃下不同热处理时间后合金的晶粒尺寸及相体积分数进行定量分析,其结果如图7所示。分析可知,Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金在等温热处理后的显微组织与热处理时间密切相关。α晶粒尺寸(Dα)在保温0.5 h时仅为6.0 μm,保温1 h时迅速升至6.8 μm,保温2 h时升至10.1 μm,保温4 h后长大速度变缓,稳定在13.5~14 μm之间。而γ晶粒尺寸(Dγ)在保温0.5 h时为7.1 μm,保温时间为4 h时晶粒尺寸升至12 μm,此后始终略小于Dα。γ晶粒的体积分数(Vγ)随保温时间(t)延长而降低,在保温时间大于6 h后趋于稳定。在保温时间大于6 h时后,合金显微组织基本不发生变化,因此,可将该合金在热处理6 h时的晶粒尺寸看作为1260 ℃下热处理的极限晶粒尺寸,α晶粒的极限晶粒尺寸为13.9 μm,γ晶粒的极限晶粒尺寸为13.4 μm。由此可见,TiAl基合金在α+γ双相区热处理,当热处理温度恒定时,γ相体积分数、α晶粒尺寸和γ相的晶粒尺寸都存在一个极限值,该实验结果与文献[15]中结果一致。
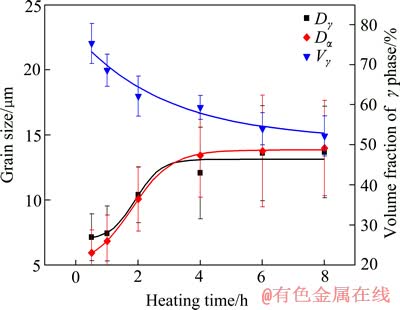
图7 α晶粒尺寸、γ晶粒尺寸及γ相体积分数随热处理时间的变化
Fig. 7 Variation of α grain size (Dα), γ grain size (Dγ) and volume fraction of γ phase (Vγ) with annealing time
3 分析与讨论
3.1 锻造过程中合金的组织演变
在锻造温度(1280 ℃)下,Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金中发生了α2+γ→α+γ相变,有序的α2相转变为无序的α相。在包套锻造过程中,合金在垂直于锻造方向产生正应变,在平行于锻造方向产生负应变,因此,α和γ晶粒在负应变方向被压扁,在两个正应变方向拉长。合金冷却至室温后,γ晶粒和α2/γ片层晶团仍成条带状分布(见图2(b)),其形成原因有两种:一方面,α相与γ相晶界处具有强烈的应力集中,存在大量的缺陷,α相优先在晶界形核并长大,再结晶后α相和γ相均变成等轴晶粒,其分布成带状;另一方面,热等静压坯体中的少量α相在变形后形成流线,可作为后续α相析出的核心,使α相和γ相成带状分布。在随后冷却过程中,从α相中析出γ片层,同时,α相发生有序化转变为α2相,最终形成α2/γ片层晶团。
在锻坯的转移、停留和锻造过程中,包套通过热辐射方式散失热量,锻坯借助包套的热传导散失热量,从而使锻坯及包套均产生一定温降,其温降最先从端角等包套的表面处开始。WANG等[22]在对TiAl基合金包套锻造的数值模拟中发现,包套可以降低锻坯的热量损失。在包套锻造过程中,锻坯中心区产生剧烈的塑性变形,使得该区域产生温升,使其温度高于锻造温度。如图8所示,合金在锻造温度(1280 ℃)下的平衡组成为α相和γ相。Nb元素扩大β相区向高铝区移动,使得图8中(β+α)/α相界降低至约1300 ℃。因此可以推测:锻饼中心区的温度高于1300 ℃,处于β+α相区,在后续的冷却过程中,β相因未溶解而保留下来。这一推测仍需下一步实验加以验证。
3.2 合金在热处理时的组织演变
锻造态合金在热处理时的组织变化主要包括β晶粒的消除、γ相的体积分数变化、α晶粒和γ晶粒的长大。
变形组织经过1230~1260 ℃热处理4 h后,β相晶粒消失。尽管W等β相偏析元素扩散激活能较高[23],具有较低的迁移速率,但是在1230~1260 ℃经过足够长的保温时间后,扩散得以充分进行,从而使β相消除。
热处理时,在发生静态再结晶及后续晶粒长大的过程中,会发生α2+γ→α+γ相变,从而改变了γ相的体积分数。如TiAl-8Nb伪二元相图(见图8)所示[24],1230~1260 ℃处于合金的α+γ两相区。根据杠杆定律可知,在α+γ两相区内,平衡组成中γ相的相对含量随着温度的升高而降低。本实验中等时热处理实验数据(见图4)与此规律相符。若在特定热处理温度下保温时间充分长,α相和γ相的相对量会达到由相图所确定的平衡值(见图7)。

图8 Ti-Al-8Nb伪二元相图和Ti-Al二元系相图[24]
Fig. 8 Pseudobinary phase diagram of Ti-Al-8Nb (full-line) and diagram of Ti-Al binary phase (dotted line)[24]
在大速率变形的包套锻造过程中,变形组织储存了大量应变能,为热处理时的静态再结晶提供了驱动力。经过1260 ℃热处理4 h后,无位错的γ相晶粒在α2/γ片层晶团的周围(见图6)形成,通过不断吞噬原有的高储能晶粒获得长大。最终,在α晶粒周围形成了长条状、少位错的γ再结晶晶粒(见图6)。冷却后,储存有大量应变能的合金逐渐转变为γ相再结晶晶粒和α2/γ片层晶团组成的静态再结晶组织。
合金在α+γ两相区热处理时,α晶粒和γ晶粒均经历了尺寸长大的过程。TiAl基合金中α晶粒长大的驱动力为界面能的减小和应变能的消除。当α晶粒长大的驱动力与晶界迁移的阻力达到平衡时,晶界迁移达到动态平衡,晶粒不再长大。该阻力是合金中的γ相钉扎晶界所产生的Zener钉扎力[17],如式(1)所示,
 (1)
(1)
式中:P为α晶粒晶界迁移的阻力;C为常数;γs为晶界能;Vγ为γ相的体积分数;Dγ为γ相的晶粒尺寸。由式(3)可以看出,α晶粒晶界迁移的阻力与γ相的尺寸呈反比,与γ相的体积分数成正比。因发生α2+γ→α+γ相变,γ相的体积分数随着热处理温度的升高而降低,使得γ相对α晶粒晶界迁移的阻力减小,α晶粒长大的速度增快 [16]。
等温热处理时锻造态TiAl基合金的α晶粒的晶粒尺寸的生长速度可用式(2)[17]描述:
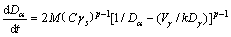 (2)
(2)
式中:M、C、k为常数;γs为晶界能;Vγ为γ相体积分数;Dα为α相的晶粒尺寸;Dγ为γ相的晶粒尺寸;p为晶粒长大因子。该式表明当dDα/dt=0,α晶粒不再长大,而趋近于其极限值kDγ/Vγ,该极限值取决于Vγ和Dγ。如图7所示,合金在1260 ℃热处理6 h后,α晶粒的尺寸变化不再明显,可认为其达到极限晶粒尺寸13.9 μm,即0.54 Dγ/Vγ。
第二相钉扎晶粒长大所得的极限尺寸可用Zener极限晶粒尺寸(DZ)进行描述:
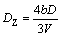 (3)
(3)
式中:D为第二相的尺寸;V为第二相的体积分数;b为系数,与材料本身相关。将γ相看作第二相,代入本实验中的数据得b的取值为0.41,与0.25<b<0.5[25]的取值范围相符。故认为本实验中α晶粒的极限值满足Zener极限晶粒尺寸。
4 结论
1) 经包套锻造后,Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3W合金转变为细小的双态组织,由γ相、α2相和少量β相组成,呈现典型的流线型组织特征。
2) 等时热处理时,随着热处理温度由1230 ℃升高至1260 ℃,α晶粒和γ晶粒迅速长大,γ相体积分数急剧减小,且α晶粒趋于等轴化,同时β相得到有效消除。
3) 在1260 ℃等温热处理时,随着热处理时间由0.5 h延长至6 h时,γ相体积分数减小,α晶粒尺寸和γ晶粒尺寸不断增大。γ相体积分数、α晶粒尺寸和γ晶粒尺寸均存在极限值。经计算可知,经1260 ℃热处理时,α晶粒尺寸的极限值为0.54 Dγ/Vγ,满足Zener极限晶粒尺寸。
REFERENCES
[1] LIU Jian-ping, SU Yan-qing, LUO Liang-shun, CHEN Hui, XU Yan-jin, GUO Jing-jie, FU Heng-zhi. Fabrication of wavy γ TiAl based sheet with foil metallurgy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(1): 72-77.
[2] LI Hui-zhong, ZENG Min, LIANG Xiao-peng, LI Zhou, LIU Yong. Flow behavior and processing map of PM Ti-47Al-2Cr-0.2Mo alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(4): 754-760.
[3] YANG Jie-ren, CHEN Rui-run, DING Hong-sheng, SU Yan-qing, HUANG Feng, GUO Jing-jie, FU Heng-zhi. Numerical calculation of flow field inside TiAl melt during rectangular cold crucible directional solidification[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(1): 157-163.
[4] KIM Y W. Gamma titanium aluminides: Their status and future[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1995, 47(7): 39-42.
[5] 陈玉勇, 韩建超, 肖树龙, 徐丽娟, 田 竟. 稀土Y在γ-TiAl基合金及其精密热成形中应用的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(5): 1241-1250.
CHEN Yu-yong, HAN Jian-chao, XIAO Shu-long, XU Li-juan, TIAN Jing. Research progress of rare earth yttrium application in γ-TiAl based alloys and precision thermal forming[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(5): 1241-1250.
[6] ABDALLAH Z, WHITTAKER M T, BACHE M R. High temperature creep behaviour in the γ titanium aluminide Ti-45Al-2Mn-2Nb[J]. Intermetallics, 2013, 38(1): 55-62.
[7] 卢 山, 李子然, 昝 祥. 晶界对近片层TiAl高温动态力学行为的数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(2): 379-387.
LU Shan, LI Zi-ran, ZAN Xiang. Numerical simulation of dynamic mechanical behavior of near lamellar TiAl at elevated temperature with influence of grain boundary[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(2): 379-387.
[8] CHEN Yan-fei, ZHENG Shun-qi, TU Jiang-ping, XIAO Shu-long, TIAN Jing, XU Li-juan, CHEN Yu-yong. Fracture characteristics of notched investment cast TiAl alloy through in situ SEM observation[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(10): 2389-2394.
[9] KIM Y W, DIMIDUK D M. Progress in the understanding of gamma titanium aluminides[J]. Journal of Materials, 1991, 43(8): 40-47.
[10] HABEL U, MCTIERNAN B. HIP temperature and properties of a gas-atomized γ-titanium aluminide alloy[J]. Intermetallics, 2004, 12(1): 63-68.
[11] ZHANG G, BLENKINSOP P A, WISE M L H. Phase transformations in HIPped Ti-48Al-2Mn- 2Nb powder during heat-treatments[J]. Intermetallics, 1996, 4(6): 447-455.
[12] GERLING R, BARTELS A, CLEMENS H, KESTLER H, SCHIMANSKY F P. Structural characterization and tensile properties of a high niobium containing gamma TiAl sheet obtained by powder metallurgical processing[J]. Intermetallics, 2004, 12(3): 275-280.
[13] 刘 咏, 黄伯云, 周科朝, 贺跃辉, 韦伟峰. TiAl基合金包套锻造工艺[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2000, 10(S1): s6-s9.
LIU Yong, HUANG Bai-yun, ZHOU Ke-chao, HE Yue-hui, WEI Wei-feng. Canned forging process of TiAl based alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2000, 10(S1): s6-s9.
[14] KIM Y W. Strength and ductility in TiAl alloy[J]. Intermetallics, 1998, 6(7/8): 623-628.
[15] NOVOSELOVA T, MALINOV S, SHA W. Experimental study of the effects of heat treatment on microstructure and grain size of a gamma TiAl alloy[J]. Intermetallics, 2003, 11(5): 491-499.
[16] 唐建成, 黄伯云, 刘文胜, 贺跃辉. 锻造TiAl基合金的晶粒长大及其动力学分析[J]. 金属学报, 2000, 36(1): 25-29.
TANG Jian-cheng, HUANG Bai-yun, LIU Wen-sheng, HE Yue-hui. Kinetics of grain growth in a forged TiAl-based alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2000, 36(1): 25-29.
[17] SEETHARAMAN V, SEMIATIN S L. Analysis of grain growth in a two-phase gamma titanium aluminide alloy[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1997, 28(4): 947-954.
[18] PRASAD U, CHATURVEDI M C. Grain coarsening in Ti-45Al based titanium aluminides at supertransus temperature and subsequent lamellar structure formation[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2004, 20(1): 87-92.
[19] LAMIRAND M, BONNENTIEN J L, FERRIERE G, GUERIN S, CHEVALIER J P. Relative effects of chromium and niobium on microstructure and mechanical properties as a function of oxygen content in TiAl alloys[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 56(5): 325-328.
[20] HUANG Z W, CONG T. Microstructure instability and embrittlement behaviour of an Al-lean, high-Nb γ-TiAl-based alloy subjected to a long-term thermal exposure in air[J]. Intermetallics, 2010, 18(1): 161-172.
[21] 沈 勇, 丁晓非, 王富刚, 谭 毅. 高铌TiAl基合金高温抗氧化性能研究[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2004, 24(4): 203-207.
SHEN Yong, DING Xiao-fei, WANG Fu-gang, TAN Yi. High-temperature oxidation resistance of high-Nb TiAl-based alloy[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2004, 24(4): 203-207.
[22] WANG Li, LIU Yong, ZHANG Wei, WANG Hui, LI Qi. Optimization of pack parameters for hot deformation of TiAl alloys[J]. Intermetallics, 2011, 19(1): 68-74.
[23] SEMIATIN S L, SEETHARAMAN V, DIMIDUK D M, ASHBEE K H G. Phase transformation behavior of gamma titanium aluminide during supertransus heat treatment[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1998, 29(1): 7-18.
[24] 张永刚, 韩雅芳, 陈国良, 郭建亭, 万晓景, 冯 涤. 金属间化合物结构材料[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2001: 778.
ZHANG Yong-gang, HAN Ya-fang, CHEN Guo-liang, GUO Jian-ting, WAN Xiao-jing, FENG Di. Structural intermetallics [M]. Beijing: National Defense Industrial Press, 2001: 778.
[25] HUMPHREYS F J, MATHERLY M. Recrystallization and related annealing phenomena[M]. Netherlands: ELSEVIER, 2004: 359.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2011CB605505);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51174233)
收稿日期:2013-12-10;修订日期:2014-07-20
通信作者:黄 岚,副教授,博士;电话:15973118718;E-mail: hazefog2013@yahoo.com