新型Ti-22Al-25Nb-1Mo-1V-1Zr-0.2Si合金的显微组织演变与蠕变变形行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第2期
论文作者:何永胜 胡锐 罗文忠 何涛 赖运金 杜玉俊 刘向宏
文章页码:313 - 321
关键词:Ti2AlNb基合金;显微组织演变;热处理;蠕变变形行为
Key words:Ti2AlNb-based alloy; microstructure evolution; heat treatment; creep deformation behavior
摘 要:采用扫描电镜和透射电镜等分析手段研究新型Ti-22Al-25Nb-1Mo-1V-1Zr-0.2Si (摩尔分数,%)合金经不同时效热处理调控的显微组织演变与650 °C、150 MPa下的蠕变变形行为。结果表明,合金的初始显微组织由α2、B2和O相构成。显微组织对热处理温度非常敏感,随着热处理温度的提高,合金的初始显微组织发生改变,其析出的板条O相的厚度增加,长度变短。而合金的抗蠕变性能与显微组织特征参数和板条O相的体积分数有关,板条O相的厚度增加是蠕变强度提高的主要原因。
Abstract: The microstructural evolution and creep deformation behavior which were adjusted and controlled by age treatment of a novel Ti-22Al-25Nb-1Mo-1V-1Zr-0.2Si (mole fraction, %) alloy, were investigated. The microstructures were obtained at different heat treatment temperatures and analyzed by SEM and TEM techniques. The creep behavior of the alloy was studied at 650 °C, 150 MPa for 100 h in air. The results showed that the initial microstructure mainly contained lath-like α2, B2, and O phases. The precipitated O phase was sensitive to aging temperature. With the aging temperature increasing, the thickness of the precipitated O phase was also increased, and the length was shortened. The creep resistance of this alloy was relevant to the morphology and volume faction of the lamellar O phase. The increase of lamellar O phase in thickness was the main reason for the improved creep properties.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 313-321
Yong-sheng HE1,2, Rui HU1, Wen-zhong LUO2, Tao HE1,2, Yun-jin LAI2, Yu-jun DU2, Xiang-hong LIU2
1. State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China;
2. Western Superconducting Technologies Co., Ltd., Shaanxi Province Engineering Laboratory for Aerial Material, Xi’an 710018, China
Received 24 February 2018; accepted 12 October 2018
Abstract: The microstructural evolution and creep deformation behavior which were adjusted and controlled by age treatment of a novel Ti-22Al-25Nb-1Mo-1V-1Zr-0.2Si (mole fraction, %) alloy, were investigated. The microstructures were obtained at different heat treatment temperatures and analyzed by SEM and TEM techniques. The creep behavior of the alloy was studied at 650 °C, 150 MPa for 100 h in air. The results showed that the initial microstructure mainly contained lath-like α2, B2, and O phases. The precipitated O phase was sensitive to aging temperature. With the aging temperature increasing, the thickness of the precipitated O phase was also increased, and the length was shortened. The creep resistance of this alloy was relevant to the morphology and volume faction of the lamellar O phase. The increase of lamellar O phase in thickness was the main reason for the improved creep properties.
Key words: Ti2AlNb-based alloy; microstructure evolution; heat treatment; creep deformation behavior
1 Introduction
Ti2AlNb based alloys have received considerable attention as the potential high-temperature structure materials because of their higher specific strength, greater fracture toughness, and better workability than conventional Ti3Al based intermetallic alloys [1,2]. So far, several Ti2AlNb alloys have been developed, such as Ti-22Al-22Nb-2W [3], Ti-22Al-27Nb-3Ta [4], and Ti-22Al-25Nb [5]. Among these alloys, the Ti-22Al- 25Nb alloy is recognized as a prototypical alloy owing to the better comprehensive properties [6-8]. However, the Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy still has some drawbacks in terms of creep and oxidation resistance. These become the major obstacles for the application in the aerospace industry. Hence, it is rather important to improve the oxidation and creep resistance of the Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy.
In Ti2AlNb alloys, the O phase can dissolve a great fraction of β (bcc phase) stabilizers by solid solution [9]. So it is possible to improve the oxidation and creep resistance of the Ti2AlNb alloy by adding the β (bcc phase) stabilizers. TANG et al [10] found that the addition of Mo can improve both the oxidation and creep resistance of the alloy. Recent works revealed that the addition of Si can also improve the oxidation resistance of Ti3Al alloy [11]. The combination of the addition of Mo and Si is more effective for improving the high temperature oxidation and creep resistance of Ti3Al alloy than that of alloying alone [12]. DANG et al [13] found that the addition of Zr can improve the oxidation resistance of Ti-22Al-27Nb alloy at 800 °C. GERMANN et al [14] proved that the addition of Zr is beneficial to creep strength without deterioration of other mechanical properties. V element is effective in improving the room-temperature ductility of Ti2AlNb alloy [15]. However, the previous researches on alloying have focused mainly on the effect of individual alloying element on the microstructure and properties of Ti2AlNb based alloys. A few works were focused on the synergetic influences of multi-elements alloying. On the basis of previous works, the authors design a Ti2AlNb based alloy with the composition of Ti-22Al-25Nb-1Mo-1V-1Zr-0.2Si preliminarily in order to obtain excellent comprehensive properties. It has been proved that this multi-compositional Ti2AlNb alloy indeed exhibited an excellent oxidation resistance [16], but its creep property is not clear yet.
The creep resistance of the alloys strongly depended on the microstructure features (i.e., morphology, grain size, and volume fraction of each phase) [17]. Microstructure of Ti2AlNb based alloy is further influenced by heat treatment condition. The effects of heat treatment condition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti2AlNb based alloy are very important and have been widely reported [18,19]. WANG et al [18,19] found that Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy with the lamellar microstructure showed the best room temperature and elevated tensile strength and creep resistance. The lamellar size and volume fraction were mainly controlled by aging temperatures [20,21]. Thus, to obtain superior mechanical properties of the alloy, it is believed that adjustment and controlling of the microstructure parameters by aging treatment are very important. ZHANG et al [22] found that the lamellar microstructure of Ti-22Al-26Nb-1Zr was coarsening with the long-term aging treatment, and it exhibited microstructural instability during the long-term aging process. But for a novel multi-compositional Ti2AlNb based alloy, the microstructure evolution and the corresponding creep properties after different aging treatments are not well known. The objective of the present work is to develop a new multi-compositional Ti2AlNb alloy with excellent creep properties and to investigate the microstructure instability of the alloy at different aging temperatures.
2 Experimental
Sponge Ti and other master alloys were used to prepare the experimental material with the nominal composition of Ti-22Al-25Nb-1V-1Mo-1Zr-0.2Si (mole fraction, %). The raw materials were blended and then melted by consumable vacuum arc melting. To ensure the compositional homogeneity, the ingot was re-melted three times, and the final ingot with a diameter of 520 mm and a height of 1500 mm was obtained. In order to get the designed lamellar microstructure, the ingot was hot forged in β phase region by multi-pass forging process. The forged microstructures, comprising of α2, B2 and O phases after heat treatment could be seen in Fig. 1(a). It exhibited the typical bimodal size lamellar O microstructures with coarser-lath and fine-lamellar O phase precipitates from the B2 phase matrix. The deformed alloy was then machined to be d20 mm × 200 mm cylinders. The specimens were solution treated at 975 °C for 90 min followed by water cooling (Fig. 1(b)). It can be seen that the fine-lamellar O phase was dissolved into B2 matrix.
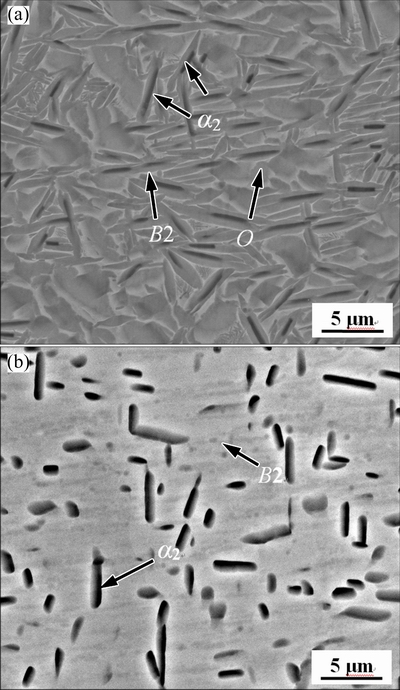

Fig. 1 Back-scattered electron images of alloy forged at 1080 °C (a) and solid solution treated at 975 °C for 1.5 h (b)
The specimens were solution-treated at 975 °C and then age-treated between 750 and 900 °C at intervals of 50 °C for 6 h by air cooling. The heat-treated specimens were marked as HT1, HT2, HT3, and HT4, respectively (Table 1). After that, cylindrical creep specimens with a diameter of 18 mm and a gauge length of 180 mm were machined. Creep tests were performed at 650 °C under the applied stress of 150 MPa on a multi-functional electronic relaxation creep testing machine equipped with a three-zone furnace. The temperature of the sample was measured by three thermocouples closely attached to the upper, middle and lower section of the specimen, respectively. The creep strains were continuously measured using a linear variable differential transducer (LVDT) extensometer having a strain resolution of ±0.1 μm. The acquisition of time-elongation data was accomplished through a computer program. Microstructure observation was carried out by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM, S4800). The volume fraction and grain size were determined by the Image-Pro Plus software. Constituent phases of the alloys were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM-200CX).
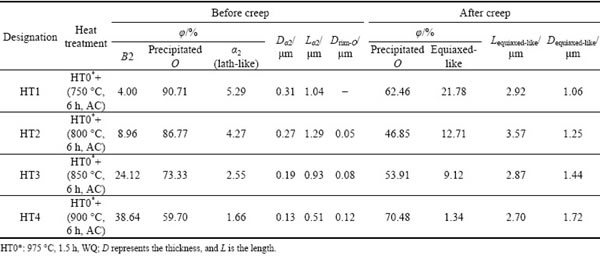
Table 1 Microstructural characteristics of investigated Ti2AlNb alloys after different heat treatments
3 Results
3.1 Microstructural evolution
The XRD patterns of alloys after different heat treatments (from HT1 to HT4) are shown in Fig. 2. It can be seen that the constituent phases of the alloys are B2 and O phases, and no α2 phase was detected. The above results are consistent with the Ti-Al-Nb phase diagram depicted by HELLWIG et al [23]. As the aging temperature increased, the intensity of (200)B2 slightly increased (Fig. 2). This indicated that the volume fraction of B2 phase increased while the volume fraction of O phase decreased. Noted that the maximum volume fraction of B2 phase was obtained at the aging temperature of 900 °C.
Figure 3 shows the BSE images of the alloys after different heat treatments (from HT1 to HT4). The black, grey, and bright areas represent the α2, O, and B2 phases, respectively. Obviously, many black short lath-like α2 phase precipitates were dispersed in the gray matrix. TEM observation and selected area diffraction pattern further confirm that these short lath-like particles are α2 phases (Fig. 4). The α2 phase has a hexagonal close-packed crystal structure, which is in accordance with the observation by WANG et al [20]. The α2 phase region was presented during cooling after forging, thus the formation of α2 phase is unavoidable in the final microstructure. Noted that once α2 phase was formed during the forging process or solution-treatment in α2+B2+O field, the α2 phase is quite stable and it cannot transform into O phase at lower temperatures. On the other hand, the α2 phase and O phase have similar structure, thus it is rather difficult to distinguish the difference of α2 phase and O phase by XRD.
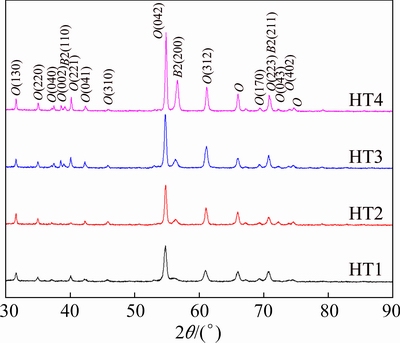
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of multi-compositional Ti2AlNb alloy after being aged at different temperatures
The statistical data of the volume fraction and morphology of the constituent phases in the investigated Ti2AlNb based alloy obtained at different aging temperatures are listed in Table 1. The volume fraction of O phase (Precipitated O) in HT1 sample is 90%. As the aging temperature increased to 800 °C (HT2 sample), the volume fraction of B2 phases and the length of lath α2 phases (Lα2) also increased, but the total volume fraction of O phases and the thickness of lath α2 phases (Dα2) decreased. This suggests that O phase was evolved into the bright B2 phase, hence the volume fraction of O phase was decreased. Compared to HT1 sample, it is also worth noting that some rim-O phases formed through the peritectoid reaction B2+α2→O [24], which slightly precipitated around α2 phase, leading to an increase in the thickness of rim-O phases (Drim-O). Subsequently, as the aging temperature increased to 850 °C (HT3), α2 phase was dissolved into rim-O phase, and rim-O phase around α2 phase became thicker. When the alloy was age-treated at 900 °C (HT4), some α2 phases have already embedded in rim-O phase and dissolved gradually into O phase, and finally these rim-O phases transformed into a lath grain.
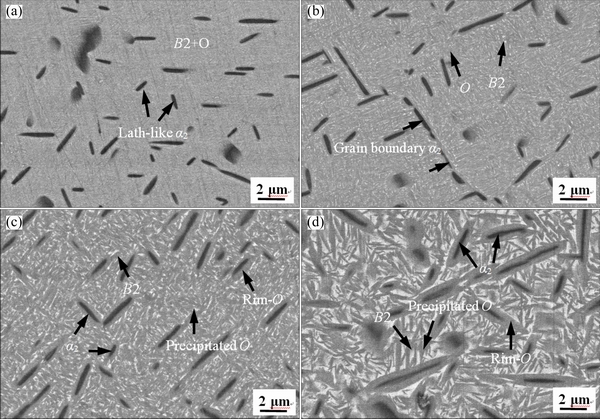
Fig. 3 Microstructures of multi-compositional Ti2AlNb alloy solution-treated at 975 °C and aged for 6 h at 750 °C (a), 800 °C (b), 850 °C (c) and 900 °C (d)
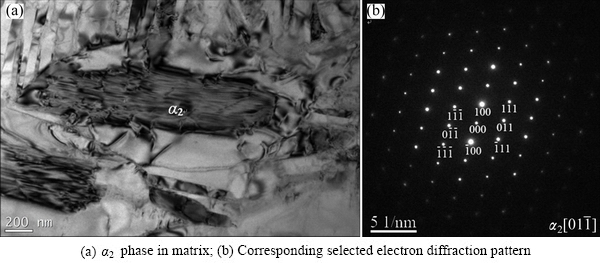
Fig. 4 Bright field micrograph of multi-compositional Ti2AlNb alloy solution-treated at 975 °C and aged at 750 °C for 6 h
3.2 Creep behaviors of alloy
The creep behaviors of the multi-compositional alloyed Ti2AlNb-based alloys after heat treatment were studied in this work. Figure 5 shows the curves of the five alloys tested at 650 °C, 150 MPa for 100 h. It can be seen that each plot possesses the typical primary or transient creep stage followed by a steady-state stage. No obvious tertiary creep stage is observed. The shape of creep curves is essentially the same, the creep rate increases initially, and then keeps a roughly steady value at the secondary stage. There are some differences on creep deformation rate during the steady-state stage. The creep rate of steady-state stage for HT4 specimen is 2.78×10-9 s-1, and that for Ti-22Al-25Nb specimen is 1.39×10-8 s-1. The creep rate of the other three (HT1, HT2 and HT3) is about 5.56×10-9 s-1, and nearly the same. It is demonstrated that the HT4 specimen has the best creep resistance at 650 °C, 150 MPa. Moreover, the steady creep rate of the multi-compositional alloyed Ti2AlNb-based alloys specimen is lower than that of the Ti-22Al-25Nb specimen under the same condition.
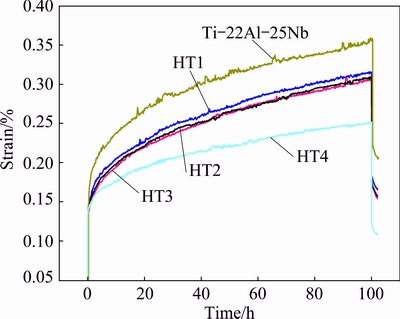
Fig. 5 Creep curves of HT1, HT2, HT3 and HT4 samples tested at 650 °C and 150 MPa for 100 h
3.3 Microstructure after creep
The microstructures of crept samples were analyzed to understand the effect of creep deformation on the microstructural instability. Figure 6 shows the XRD patterns of the four alloys after creep. It is found that the constituent phases of all the alloys are B2 and O phases, and no α2 phase is detected. The above results are consistent with the XRD results before creep. Figure 7(a) depicts the microstructure of the HT1 sample after creep test. There are significant differences in morphology and size. It can be seen that the previous short lath-like morphology is retained, but the amount of the lath-like phase is obviously increased. The volume fraction of short lath-like α2 phase was approximately 5.29% before creep, but after creep, the lath-like phase has already increased to approximately 21.78%, which is nearly four times (Table 1). Furthermore, the initial lath-like α2 phase becomes thicker in width and shorter in length; the average diameter of lath-like O phases in width is increased from 1.06 μm to 1.72 μm. The finer acicular phase can also be clearly observed, and the volume fraction of these acicular precipitated O distributed in the matrix is measured to be 62.46%.
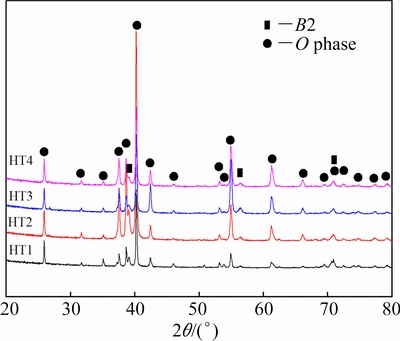
Fig. 6 XRD patterns of multi-compositional Ti2AlNb alloys (aged) after creep
TEM observation and selected area diffraction pattern confirmed that after creep the constitute phases are α2, B2 and O phases (Fig. 8). The lath-like particles are no longer a sole α2 phase, they are a mixture of α2+O phase. This indicates that through a long-time creep, α2→O transformation takes place. Figures 7(b), (e) and (f) show the crept microstructures of the HT2, HT3 and HT4 samples. It can be seen that some lath O phases have already dissolved into the matrix, but the thickness of the lath-like phase is coarsening at the same time. The volume fractions of equiaxed phase in the HT2, HT3 and HT4 samples were 12.71%, 9.12%, and 1.34%, respectively (Table 1).
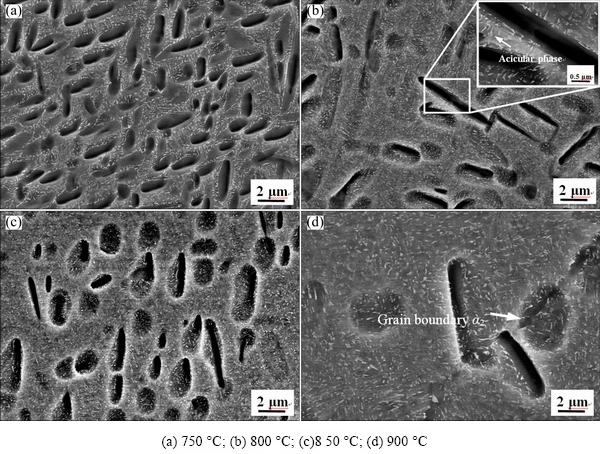
Fig. 7 Crept microstructures of multi-compositional Ti2AlNb alloys at different aging treatment temperatures
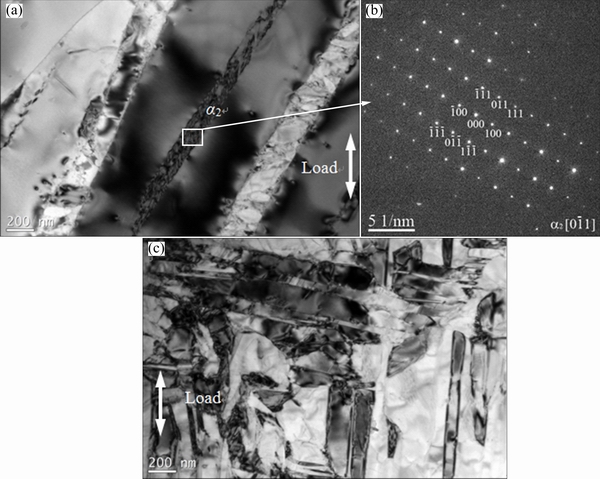
Fig. 8 Bright-field TEM images of HT4 (a) and corresponding SAED image of HT4 specimen (b), and HT1 (c) specimens
4 Discussion
4.1 Effect of aging treatment on initial microstructure
As aforementioned above, the morphology and volume fraction of initial microstructure under different aging treatments have great differences. With the age treatment temperature increasing, the transformation of α2 to O phases occurred. Although it takes a long time for the transformation, the supersaturating of vanadium and molybdenum and so on as strong β stabilizing elements was accelerated with the advance of aging temperature. Thus, the content of niobium in α2 phase was increased and unstable. According to the investigation of WU et al [25], as the niobium element reached a critical value, α2 phase can be changed from the HCP lattice type to the orthorhombic. It is a phase transformation from α2 phase to rim-O phase. Besides the formation of rim-O phase, due to the temperature of aging treatment located in the O+B2 two-phase region, with the aging treatment temperature increasing, the diffusion of elements in the alloy was accelerated. The precipitated O phase was preferentially nucleated at the grain boundaries, leading to the coarsening of the lamellar O phase through the element pipeline diffusion [26]. When the alloy was heat treated in the O+B2 region, the O-phase was precipitated as lamellar from the B2 matrix. The matrix exhibits an O+B2 two-phase lamellar microstructure. And the thickness of lath O was increased as the aging temperature increased. Hence it can be seen that as the aging treatment temperature increased, the volume fraction of the O phase decreased, while the size and volume fraction of the B2 phase increased. The largest size of acicular O phase occurred at 900 °C and the finest size was displayed at 750 °C (Fig. 3(a)).
4.2 Effect of age-treated microstructures on creep property
It has been reported that the creep behavior is relevant to microstructure. Hence it is necessary to research the effect of microstructure variation on creep behavior. According to GOGIA et al [27], O and α2 phases exhibit better creep resistance than that of B2 phase and the increase of the thickness of lath O phase is beneficial to the improvement of the creep resistance. For four typical microstructures, as the aging treatment temperature increased, the width of primary lath O phase became coarser. Similar to previous conclusions, the HT4 specimen owns the coarsest lamellar O phase, while the creep resistance is the highest. In order to investigate the effect of microstructure on creep behavior, the microstructure after creep test was analyzed by TEM. Figure 8 shows the BF and SAED images of the HT1 and HT4 specimens after creep test. HT4 specimen shows higher content in the O phase, and the thickness of coarse-lamellar O phase is about 550.7 nm. It can also be seen that the primary α2 particle was elongated along the direction of the tensile axis. However, the HT1 specimen shows a high content of fine acicular O phase with a thickness of about 97.3 nm. That is to say, the thicker the lath O phase, the better the creep resistance.
Due to high aging treatment temperature, the microstructure of HT4 specimen after creep test shows coarser lamellar O phase. From the TEM analysis of lamellar O phase in Fig. 8, it can be seen that the dislocation density of coarser lamellar O phase was very low. This means that the movement of dislocations in the coarser-lamellar O-phase is not as active in the fine-lamellar O-phase during creep deformation at 650 °C, so the creep resistance of the coarser lamellar O-phase is higher than that of the fine-lamellar O-phase. The quantity of coarser lamellar O-phase in HT4 is more than that in HT1. Thus, HT4 has the highest creep resistance.
4.3 Effect of creep on microstructure instability
The morphology and volume fraction of phases have been changed greatly after creep for the Ti2AlNb-based alloy. From the observations of the microstructure after creep test in Fig. 7, it is found that the lath O phase was equiaxed after a long period of high temperature creep. In creep deformation, the phase structure, phase morphology and the B2 grain size are also important factors for improving creep resistance of alloys [28]. The creep properties are mainly related to the microstructures which are decided by the temperature and stress. In current research, the creep process except the influence of stress and temperature can be deemed as an age treatment again. Thus, the B2 grain size after creep test has a little change. The principal variation of microstructure in creep process is the spheroidization of α2/O phase. When deformed in the creep process, this alloy exhibited strong microstructure instability including dynamic phase transformation, coarsening and globularization of O-phase lamellae.
Besides the spheroidization of lamellar O phase during the creep process, the creep has also a profound effect on the α2 phase decomposition. Although the aging treatment temperature is higher than the deformation temperature of creep, the decomposition of α2 phase has not finished or not completely finished during aging treatment. Through the TEM analysis of samples after creep test, during the creep process, the α2 phase decomposition occurred. The phase structure of the α2 phase and O phase is very similar. The O-phase usually nucleated with a single variant and two or three variants within the primary α2-phases and the crystallographic variants originated from the nucleation of the phase on particular habit planes [29]. Because there are three possible 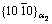 planes and two possible
planes and two possible 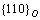 planes with a common
planes with a common  or
or 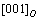 direction, theoretically six variants of the O-phase can occur in the α2 matrix [1,30]. This O phase has an orientation relationship to the parent α2 phase [1,29],
direction, theoretically six variants of the O-phase can occur in the α2 matrix [1,30]. This O phase has an orientation relationship to the parent α2 phase [1,29], 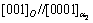 and
and 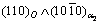 =1.5° with a habit plane of
=1.5° with a habit plane of 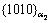 . On previous researches, WU and HWANG [29] have found the α2 phase decomposition in heat treatment. WANG et al [20] have also discovered the α2 phase decomposition with different thermo-processing and heat treatment. However, the α2 phase decomposition which occurred in creep processing has rare reports. It is indicated that the aging temperature is not the only reason for the decomposition of α2 phase. Creep stress has an important role in phase decomposition. The microstructure of HT4 was formed at higher age treatment temperature, so low potential barrier was required for dislocation climbing. Therefore, the internal dislocations in α2 phase are stacked in the stacking fault. The Nb elements which diffused into the stacking fault made the transformation of α2 to O phase.
. On previous researches, WU and HWANG [29] have found the α2 phase decomposition in heat treatment. WANG et al [20] have also discovered the α2 phase decomposition with different thermo-processing and heat treatment. However, the α2 phase decomposition which occurred in creep processing has rare reports. It is indicated that the aging temperature is not the only reason for the decomposition of α2 phase. Creep stress has an important role in phase decomposition. The microstructure of HT4 was formed at higher age treatment temperature, so low potential barrier was required for dislocation climbing. Therefore, the internal dislocations in α2 phase are stacked in the stacking fault. The Nb elements which diffused into the stacking fault made the transformation of α2 to O phase.
In summary, the formation of the O-phase was the result of niobium diffusion. As a result of a phase separation reaction in which the α2 phase containing niobium separates into niobium lean and rich regions. Niobium rich regions are closer to the Ti2AlNb composition to transform into O phase [20]. The driving force is distortion energy of niobium solution in the α2 phases. The α2 phase is in equilibrium with the B2 phase at high temperature but is in equilibrium with the O phase at lower temperature, that is, the O phase may be formed through a decomposition reaction: α2→ α2(Nb-lean)+O(Nb-rich).
5 Conclusions
(1) The effects of aging temperature on the microstructure and creep property of a Ti-22Al-25Nb- 1V-1Mo-1Zr-0.2Si alloy were investigated. The initial microstructure of the alloy consisted mainly of lath-like α2, B2, and O phases. With the aging treatment temperature increasing, the precipitate size of lamellar O phase was increased. The precipitated O phase was preferentially nucleated at grain boundaries, resulting in coarsening of the constituent phase.
(2) In terms of the creep behavior, the HT4 specimen has the best creep resistance at 650 °C and 150 MPa. The steady creep rate of the multi- compositional alloyed Ti2AlNb-based alloy specimen is lower than that of the Ti-22Al-25Nb specimen under the same condition. From the results of effect of aging treatment temperature on creep properties, as the aging treatment temperature increased, the creep resistance increased. The creep properties of alloys were concerned with the microstructures. The morphology and volume fraction of phases after creep test were changed greatly. The most distinctive feature is the spheroidization of O phase ascribed to the temperature and stress during the creep process.
References
[1] BANERJEE D, GOGIA A K, NANDI T K, JOSHI V A. A new ordered orthorhombic phase in a Ti3Al-Nb alloy [J]. Acta Metallurgical, 1988, 36(4): 871-882.
[2] ZHANG Qin-chai, CHEN Ming-he, WANG Hui, WANG Ning, OUYANG Jin-dong, LI Xin-xiao. Thermal deformation behavior and mechanism of intermetallic alloy Ti2AlNb [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(3): 722-728.
[3] TANG F, EMURA S, HAGIWARA M. Tensile properties of tungsten-modified orthorhombic Ti-22Al-20Nb-2W alloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2001, 44(4): 671-676.
[4] MAO Yong, LI Shi-qiong, ZHANG Jian-wei, PENG Ji-hua, ZOU Dun-xu, ZHONG Zeng-yong. Microstructure and tensile properties of orthorhombic Ti-Al-Nb-Ta alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2000, 8(5-6): 659-662.
[5] QIN Chun, YAO Ze-kun, NING Yong-quan, SHI Zhi-feng, GUO Hong-zhen. Hot deformation behavior of TC11/Ti-22Al-25Nb dual-alloy in isothermal compression [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(7): 2195-2205.
[6] CHENG Yun-jun, LI Shi-qiong, LIANG Xiao-bo, ZHANG Jian-wei. Effect of deformed microstructure on mechanical properties of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(s3): 2058-2061.
[7] JIA Jian-bo, ZHANG Kai-feng, JIANG Shao-song. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy fabricated by vacuum hot pressing sintering [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 616: 93-98.
[8] WANG Y X, ZHANG K F. LI B Y. Microstructure and high temperature tensile properties of Ti22Al25Nb [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 608 (25): 229-233.
[9] MAO Y, HAGIWARA M, EMURA S. Creep behavior and tensile properties of Mo- and Fe-added orthorhombic Ti-22Al-11Nb- 2Mo-1Fe alloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57(3): 261-264.
[10] TANG F, NAKAZAWA S, HAGIWARA M. The effect of quaternary additions on the microstructures and mechanical properties of orthorhombic Ti2AlNb-based alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, S329-331(6): 492-498.
[11] WU J S, ZHANG LT, WANG F, JIANG K, QIU G H. The individual effects of niobium and silicon on the oxidation behaviour of Ti3Al based alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2000, 8(1): 19-28.
[12] SUN Yu-feng, CAO Chun-xiao, CAO Jing-xia, YANG Ming-gao. Oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of Ti3Al-Nb-Mo-Si alloys [J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica (English Letters), 1995, 8(4-6): 577-582.
[13] DANG Wei, LI Jin-shan, ZHANG Tie-bang, KOU Hong-chao. Oxidation behavior of Zr-containing Ti2AlNb-based alloy at 800 °C [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(3): 783-790.
[14] GERMANN L, BANERJEE D, GUEDOU J Y, STRUDEL J L. Effect of composition on the mechanical properties of newly developed Ti2AlNb-based titanium aluminide [J]. Intermetallics, 2005,13 (9): 920-924.
[15] CHO W, THOMPSON A W, WILLIAMS J C. Creep behavior of Ti-25Al-10Nb-3V-1Mo [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1990, 21(2): 641-651.
[16] HE Yong-shen, HU Rui, LUO Wen-zhong, HE Tao, LIU Xiang-hong. Oxidation behavior of a multi-element alloyed Ti2AlNb-based alloy with improved oxidation resistance from 650 °C to 850 °C [J]. Rare Metals, 2018, 37(10): 838-845.
[17] KUMPFERT J. Intermetallic alloys based on orthorhombic titanium aluminide [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2001, 3(11): 851-861.
[18] WANG Wei, ZENG Wei-dong, LI Dong, ZHU Bin, ZHENG Yong-ping, LIANG Xiao-bo. Microstructural evolution and tensile behavior of Ti2AlNb alloys based α2-phase decomposition [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 662: 120-128.
[19] WANG Wei, ZENG Wei-dong, XUE Chen, LIANG Xiao-bo, ZHANG Jian-wei. Microstructural evolution, creep, and tensile behavior of a Ti-22Al-25Nb (at%) orthorhombic alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 603: 176-184.
[20] WANG Wei, ZENG Wei-dong, XUE Chen, LIANG Xiao-bo, ZHANG Jian-wei. Microstructure control and mechanical properties from isothermal forging and heat treatment of Ti-22Al-25Nb (at. %) orthorhombic alloy [J]. Intermetallics, 2015, 56(4): 79-86.
[21] XUE Chen, ZENG Wei-dong, WANG Wei, LIANG Xiao-bo, ZHANG Jian-wei. Quantitative analysis on microstructure evolution and tensile property for the isothermally forged Ti2AlNb based alloy during heat treatment [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 573(3): 183-189.
[22] ZHANG Tie-bang, HUAGN Gang, HU Rui, LI Jin-shan. Microstructural stability of long term aging treated Ti-22Al-26Nb- 1Zr orthorhombic titanium aluminide [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25 (8): 2549-2555.
[23] HELLWIG A, PALM M, INDEN G. Phase equilibria in the Al-Nb-Ti system at high temperatures [J]. Intermetallics, 1998, 6(2): 79-94.
[24] BOEHLERT C J, MIRACLE D B. The creep behavior of Ti-Al-Nb O+Bcc orthorhombic alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1999, 30A(9): 2349-2367.
[25] WU Y, ZHEN L, YANG D Z, MAO J F. TEM observation of the α2/O interface in a Ti3Al-Nb Alloy [J]. Materials Letters, 1997, 32(S5-6): 319-323.
[26] GUSTAFSON A, HATTESTRAND M. Coarsening of precipitates in an advanced creep resistant 9% chromium steel quantitative microscopy and simulations [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 333(1-2): 279-286.
[27] GOGIA A K, NANDY T K, BANERJEE D, CARISEY T, STRUDEL J L, FRANCHET J M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of orthorhombic alloys in the Ti-Al-Nb System [J]. Intermetallics, 1998, 6(7-8): 741-748.
[28] MOMENI A, DEHGHANI K. Characterization of hot deformation behavior of 410 martensitic stainless steel using constitutive equations and processing maps [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A [J]. 2010, 527(21-22): 5467-5473.
[29] WU Y, HWANG S K. O-phase and carbides precipitation in intermetallics based on Ti-Al [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2001, 7(3): 191-199.
[30] MURALEEDHARAN K, BANERJEE D. The α2-to-O transformation in Ti-Al-Nb alloys [J]. Philosophical Magazine A, 1995, 71(71): 1011-1036.
何永胜1,2,胡 锐1,罗文忠2,何 涛1,2,赖运金2,杜玉俊2,刘向宏2
1. 西北工业大学 凝固技术国家重点实验室,西安 710072;
2. 西部超导材料科技股份有限公司 陕西省航空材料工程实验室,西安 710018
摘 要:采用扫描电镜和透射电镜等分析手段研究新型Ti-22Al-25Nb-1Mo-1V-1Zr-0.2Si (摩尔分数,%)合金经不同时效热处理调控的显微组织演变与650 °C、150 MPa下的蠕变变形行为。结果表明,合金的初始显微组织由α2、B2和O相构成。显微组织对热处理温度非常敏感,随着热处理温度的提高,合金的初始显微组织发生改变,其析出的板条O相的厚度增加,长度变短。而合金的抗蠕变性能与显微组织特征参数和板条O相的体积分数有关,板条O相的厚度增加是蠕变强度提高的主要原因。
关键词:Ti2AlNb基合金;显微组织演变;热处理;蠕变变形行为
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (51601146) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2017M613234) supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
Corresponding author: Rui HU; Tel/Fax: +86-29-88491764; E-mail: nwpuhys@sina.com, rhu@nwpu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)64941-1

