氧化钛纳米陶瓷的制备及其结构与力学性能
冶银平1, 2,李建功2,陈建敏1,周惠娣1
(中国科学院兰州化学物理研究所 固体润滑国家重点实验室,甘肃 兰州,730000;
2. 兰州大学 材料科学与工程研究所,甘肃 兰州,730000)
摘 要:为探讨在无压烧结过程中TiO2纳米陶瓷的致密化与晶粒长大的关系以及纳米陶瓷的结构对其力学性能的影响,采用溶胶-凝胶技术制备的不同颗粒粒径的TiO2纳米粉体经冷压成型后无压烧结TiO2纳米陶瓷。研究结果表明:利用相变辅助无压烧结方法在800 ℃烧结获得了晶粒粒径小于60 nm、相对密度超过95%的TiO2纳米块体陶瓷;当800 ℃以下烧结时,TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度随烧结温度的升高而快速增大,而TiO2纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒粒径随烧结温度升高则缓慢长大;当大于800 ℃的温度烧结时,TiO2纳米陶瓷的致密化加快,但陶瓷的晶粒粒径则快速长大。TiO2纳米陶瓷的显微硬度主要取决于TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度和平均晶粒粒径,即纳米氧化钛陶瓷的相对密度越大,晶粒粒径越小,则显微硬度越大。
关键词:TiO2纳米陶瓷;晶粒生长;致密化;显微硬度
中图分类号:TQ174 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2008)04-0682-06
Preparation, microstructures and mechanical properties of TiO2 nanoceramics
YE Yin-ping1, 2, LI Jian-gong2, CHEN Jian-min1, ZHOU Hui-di1
(1. State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000, China;
2. Institute of Materials Science and Engineering, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China)
Abstract: In order to inquire into the processes of densification versus grain growth and the effect of the microstructure on the mechanical property of the TiO2 nanoceramics, the TiO2 nanopowders with various mean particle sizes synthesized by sol-gel method were used to sinter bulk TiO2 nanoceramics. The results show that the bulk TiO2 nanoceramics with an average grain size of less than 60 nm and a relative density over 95% are prepared by a phase-transformation-assisted pressureless sintering method at 800 ℃. The relative density of the TiO2 nanoceramics increases rapidly whereas the average grain size increases slowly with the increase of sintering temperature below 800 ℃. The higher sintering temperature above 800 ℃ enhances the densification of the TiO2 nanoceramics, but increases intensively the average grain size of the TiO2 nanoceramics. The Vickers microhardness of the TiO2 nanoceramics is mainly related to the relative density and average grain size of the TiO2 nanoceramics. Namely, the Vickers microhardness increases with the increase of relative density and the decrease of the average grain size.
Key words: TiO2 nanoceramics; grain growth; densification; microhardness
氧化钛(TiO2)是一类重要的无机功能材料,在诸多领域中有着广泛和潜在的应用前景,如用于制造功能陶瓷﹑传感材料﹑高级涂料和催化剂等[1-3]。通常TiO2粗晶陶瓷不作为结构陶瓷使用,因为粗晶粒TiO2陶瓷的强度较低。当TiO2陶瓷的晶粒非常细小,甚至达到纳米数量级时,TiO2陶瓷的力学性能得到显著改善[4],甚至在室温下就可发生塑性变形[5-6]。为了在促进致密化的同时抑制晶粒的长大,Kear等[7-10]采用各种烧结工艺制备纳米陶瓷,如热压烧结、高压/低温烧结等,获得了较好的结果。然而,由于这些烧结工艺制备条件苛刻,不但增加了陶瓷的制备成本,而且所得到的纳米陶瓷的体积很小,使得纳米陶瓷的性能很难准确测定,更不用说制成实用的器件。而另一方面,最具有商业价值的常规无压烧结(大气环境下的无压烧结)工艺,在这一领域的应用进展缓慢,这极大地制约了纳米陶瓷的广泛应用。然而,采用常规无压烧结方法制备TiO2纳米陶瓷时,在坯体达到90%致密度 之前,晶粒长大非常缓慢,而在90%致密度之后晶粒长大异常迅速[4, 11],这为制备高致密度﹑细晶粒的TiO2纳米陶瓷带来很大困难。因此,有关纳米氧化钛陶瓷烧结特性的研究是近年来陶瓷领域的研究热点 之一[12-13]。
在TiO2体系中,锐钛矿向金红石相的转变是一个由亚稳态向稳态的不可逆转过程[14],这种相变过程对TiO2陶瓷的致密化和晶粒长大非常重要。如Kumar等[15]直接将TiO2凝胶在锐钛矿-金红石相转变温度(约600 ℃)附近进行烧结,制备了平均晶粒粒径小于60 nm、致密度大于99 %的氧化钛纳米陶瓷涂层,这为TiO2纳米陶瓷的常规无压烧结指出了一条新的途径。在此,本文作者采用溶胶-凝胶技术制备TiO2纳米粉体,经冷压成型后研究无压烧结TiO2纳米陶瓷,考察纳米粉体特征﹑成型压力﹑烧结温度和相变在无压烧结过程中对TiO2纳米陶瓷的结构、平均晶粒粒径、致密化和显微硬的影响。
1 实 验
1.1 粉体制备
以钛酸丁酯为原料,在乙醇的水溶液中进行水解、缩聚反应后得到凝胶,凝胶干燥后经煅烧制得TiO2纳米粉体。煅烧温度的升温速率为10 ℃/min。
1.2 生坯成型
采用常规的轴向冷压成型方法制备TiO2生坯,成型压力分别为500,720和920 MPa,保压时间为5 min。生坯是直径为15 mm、厚度为1~2 mm的柱状薄片。
1.3 纳米粉体和陶瓷表征
用D/Max-240型X射线衍射仪对纳米粉体和纳米陶瓷的物相组成进行分析,通过X射线衍射峰的宽化,利用Scherrer公式计算纳米粉体的平均颗粒粒径和纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒粒径;用JEM-1200EX型透射电子显微镜(TEM)对纳米粉体和陶瓷晶粒的形貌和微结构进行观察;陶瓷坯体的相对密度采用阿基米德法测定。
2 结果与分析
2.1 粉体的结构与颗粒粒径
图1所示为TiO2干凝胶粉经不同温度煅烧后的XRD谱。可见,经300 ℃煅烧后的TiO2粉体已出现TiO2锐钛矿相的特征衍射峰,但经300 ℃煅烧后的粉体呈黑色,表明粉体仍含有未分解的有机物,经400 ℃煅烧后粉体呈白色,并且具有完整的锐钛矿相特征衍射峰。经550 ℃煅烧后粉体中有金红石相,当煅烧温度大于600 ℃时,TiO2已完全转化为金红石相。图2所示为经400 ℃和500 ℃煅烧后TiO2粉体的形貌照片。可见,所制备的粉体为球状颗粒,颗粒粒径分布比较均匀,且团聚较轻,平均颗粒粒径分别为15 nm和28 nm,此结果与利用XRD衍射峰的宽化,通过Scherrer公式估算的结果是一致的。
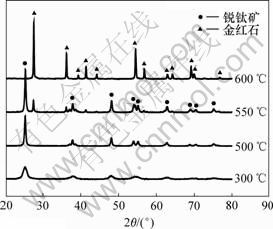
图1 在不同温度下煅烧2 h所得的TiO2纳米粉体的XRD谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of TiO2 nanopowders calcinated at different temperatures for 2 h

(a) 400 ℃; (b) 500 ℃
图2 经400 ℃和500 ℃煅烧2 h后得到TiO2纳米粉体的TEM照片
Fig.2 TEM micrographs of TiO2 nanopowders calcinated at 400 ℃ and 500 ℃
2.2 生坯烧结与晶粒生长
烧结是制备陶瓷最关键的步骤之一。对纳米陶瓷来说,烧结尤为重要。因为在烧结促进陶瓷致密化的过程中,总是伴随着晶粒的快速长大。本实验烧结时的升温速率为10 ℃/min。图3所示为于800 ℃/2 h烧结的TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度随TiO2纳米粉体平均颗粒粒径变化的关系。可见,粉体的平均颗粒粒径为15~40 nm时,TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度随着粉体平均颗粒粒径的增大而减小,也就是说,在相同烧结条件下平均颗粒较小的粉体更容易致密化。粉体颗粒越粗,比表面积越小,本征表面能驱动力就越小;而颗粒越细,比表面积越大,本征表面能驱动力就越大。这也是实际烧结中小颗粒粉体比大颗粒粉体易于烧结的原因。然而,用平均颗粒粒径为7 nm的粉体制备的TiO2纳米陶瓷其相对密度(90%)反而比平均颗粒粒径为15 nm的粉体制备的TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度(96%)低,这个反常的结果可以从初始粉体的特征得到解释。经300 ℃煅烧获得的平均颗粒粒径为7 nm的粉体呈黑色,表明粉体中有未被燃烧的有机物质存在,这些残余的有机物在陶瓷的烧结过程中被燃烧分解,但同时在陶瓷中留下大量的气孔,导致所烧结的陶瓷相对密度降低。从图3还可以看出,TiO2陶瓷的相对密度随着成型压力的增加而提高,这是因为通过较高的成型压力可以获得较高密度的生坯,在相同烧结条件下,高密度的生坯更容易致密化。

图3 在800 ℃烧结的TiO2纳米陶瓷相对密度随TiO2纳米粉体的平均颗粒粒径变化的关系
Fig.3 Relationship between relative density of TiO2 nanoceramics sintered at 800 ℃ and mean particle size of starting TiO2 nanopowders
图4所示为TiO2陶瓷的相对密度随烧结温度变化的关系。可见,TiO2陶瓷的相对密度随着烧结温度的升高而增大;在烧结温度小于800 ℃时,相对密度随烧结温度升高增大较快;当烧结温度超过800 ℃时,相对密度的增加程度减慢。因为烧结温度越高,颗粒内原子扩散系数越大,而且按指数规律迅速增大,烧结进行得越迅速;在烧结后期阶段,当闭气孔球化、缩小或消失,陶瓷烧结体已接近完全致密,虽然此时陶瓷密度进一步增加,但密度的增加幅度开始减慢。在800 ℃烧结时,TiO2陶瓷的相对密度已超过95%。同样,TiO2陶瓷的相对密度随成型压力的增加而增 大。在较高的成型压力下不仅可以获得较高密度的生坯,而且在压制生坯时,高压可以压碎粉体中团聚体,使生坯中的气孔变小和气孔粒径分布变窄[16]。去除小气孔比去除大气孔需要较低的烧结温度和较短的烧结时间。因此,高压通常被用于制备细晶粒纳米陶瓷。

初始粉体的平均颗粒粒径为15 nm
图4 TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度随烧结温度变化的关系
Fig.4 Relationship between relative density of TiO2 nanoceramics and sintering temperature
尽管TiO2纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒粒径也随烧结温度升高而增大,但是,TiO2纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒粒径随烧结温度的变化却不同于相对密度随烧结温度的变化。图5所示为TiO2纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒大小随烧结温度变化的关系。可见,在烧结温度低于800 ℃时,随烧结温度升高晶粒长大很慢;当在烧结温度高于800 ℃时,晶粒开始快速长大。另外,TiO2纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒粒径随成型压力的增大而减小,在800 ℃烧结720 MPa压力成型的生坯获得的TiO2纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒粒径不到60 nm。图6所示是成型压力为720 MPa时生坯在800 ℃烧结所制得的TiO2纳米陶瓷的TEM照片。从TEM照片上可以看到所制备的TiO2纳米陶瓷没有残余的气孔,是典型的最后烧结阶段的陶瓷结构,晶粒为多面体的等轴晶粒,平均晶粒粒径约为100 nm,这比通过相应的XRD衍射峰宽化经Scherrer公式估算的平均晶粒粒径大。此结果与Hahn等[11]和Kumar[15]报道的结果一致。Hahn等[11]认为在TEM照片上观察到的晶粒可能是多个单个晶粒构成的。

初始粉体的平均颗粒粒径为15 nm
图5 TiO2纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒粒径随烧结温度变化的关系
Fig.5 Relationship between average grain size of TiO2 nanoceramics and sintering temperature
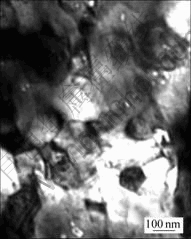
初始粉体的平均颗粒粒径为15 nm
图6 烧结成型压力为720 MPa的生坯在800 ℃烧结所制得的TiO2纳米陶瓷的TEM照片
Fig.6 TEM micrograph of TiO2 nanoceramics pressed at 720 MPa and sintered at 800 ℃
2.3 TiO2纳米陶瓷的力学性能
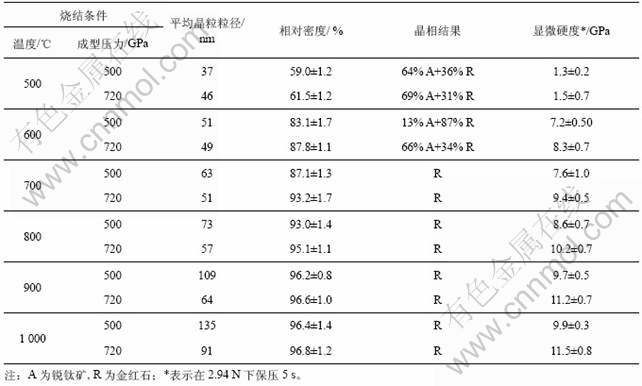
表1所示为由不同平均颗粒粒径的初始TiO2纳米粉体成型的生坯经800 ℃烧结2 h所获得的TiO2纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒大小、相组成、相对密度和显微硬度。从表1可以看出,经800 ℃/2 h的烧结所获得的TiO2纳米陶瓷仅仅由金红石相结构组成,而且其平均晶粒粒径都在100 nm以下。TiO2纳米陶瓷的显微硬度与陶瓷的相对密度和平均晶粒粒径有着密切的对应关系,即TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度越高,其显微硬度越大,而在相对密度接近相等的条件下,TiO2纳米陶瓷平均晶粒粒径越小,其显微硬度越大。表2所示为在不同温度下烧结2 h所获得的TiO2纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒大小、相组成、相对密度和显微硬度值。从表2可以看出,在500 ℃和600 ℃烧结的TiO2纳米陶瓷由锐钛矿相和金红石相组成,当烧结温度大于700 ℃时,烧结的TiO2纳米陶瓷仅仅由金红石相组成,而且烧结的TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度和显微硬度随着烧结温度升高而大幅度增加,特别是当烧结温度大于800 ℃时,TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度都超过90%,其显微硬度超过8 GPa。TiO2纳米陶瓷的显微硬度不仅与其相对密度有密切的对应关系,即随着TiO2纳米陶瓷相对密度的增大,其显微硬度增大;而且与其平均晶粒大小也有非常密切的对应关系,即在TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度接近相等的条件下,TiO2纳米陶瓷平均晶粒粒径越小,其显微硬度越大。
表1 于800 ℃烧结2 h得到的TiO2纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒粒径、相结构、相对密度和显微硬度
Table 1 Average grain size, phase structure, relative density and vickers microhardness of TiO2 nanoceramics sintering at
800 ℃ for 2 h

通常,TiO2粗晶陶瓷的显微硬度小于5 GPa[4],TiO2纳米陶瓷的显微硬度是粗晶陶瓷显微硬度的2倍多。与TiO2粗晶陶瓷相比,TiO2纳米陶瓷具有高硬度的原因应归结于TiO2陶瓷的纳米结构。由于纳米陶瓷晶粒粒径减小,晶界的密度大幅度增加,高密度的晶界可导致晶粒取向杂乱以及界面的体积分数和强度增加[17]。对于纳米陶瓷材料,其硬度提高可用Hall-Petch关系来解释。根据Hall-Petch关系,晶粒粒径减小,将导致纳米陶瓷的硬度显著提高。
表2 在不同温度下烧结的TiO2纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒粒径、相对密度、相结构和显微硬度
Table 2 Average grain size, phase structure, relative density and vickers microhardness of TiO2 nanoceramics sintered at different temperatures
3 结 论
a. 利用相变辅助的无压烧结方法在800 ℃烧结获得平均晶粒粒径小于60 nm、相对密度超过95%的TiO2纳米陶瓷。
b. 髙的成型压力抑制了烧结过程中锐钛矿相向金红石相的转变,而且使锐钛矿相向金红石相的转变温度由粉体的600 ℃提高到700℃,从而扩展了TiO2陶瓷在烧结过程中晶粒缓慢长大的温度范围。
c. 当烧结温度低于800 ℃时,TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度随烧结温度的升高而快速增大,但TiO2纳米陶瓷的平均晶粒粒径随烧结温度的升高而缓慢长大;若继续升高烧结温度,尽管TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度会继续增大,但是,陶瓷的平均晶粒粒径则快速长大。
d. TiO2纳米陶瓷的显微硬度主要取决于TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度和平均晶粒粒径,即TiO2纳米陶瓷的相对密度越大、晶粒粒径越小,则显微硬度就越大。
参考文献:
[1] Yang J, Mei S, Ferreira J M F. Hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2 nanopowders from tetraalkylammonium hydroxide peptized sols[J]. Mater Sci Eng, 2001, C15(1/2): 183-185.
[2] Haro-Poniatowski E, Rodriguez-Talavera R, De la Craz Heredia M, et al. Crystallization of nanosized titania particles prepared by the sol-gel process[J]. J Mater Res, 1994, 9(8): 2102-2108.
[3] Birkefeld L D, Azad A M, Akbar S A. Carbon monoxide and hydrogen detection by anatase modification of titanium dioxide[J]. J Am Ceram Soc, 1992, 75(75): 2964-2968.
[4] Siegel R W, Ramasamy S, Hahn H, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and properties of nanophase TiO2 [J]. J Mater Res, 1988, 3(6): 1367-1372.
[5] Karch J, Birringer R, Gleiter H. Ceramics ductile at low temperature[J]. Nature, 1987, 330(6148): 556-558.
[6] Hahn H, Averback R S. High temperature mechanical properties of nanostructured ceramics[J]. Nanostruct Mater, 1992, 1(1): 95-100.
[7] Kear B K, Colaizzi J, Mayo W E, et al. On the processing of nanocrystalline and nanocomposite ceramics[J]. Scripta Mater, 2001, 44(8/9): 2065-2068.
[8] Liao S C, Mayo W E, Pae K D. Theory of high pressure/low temperature sintering of bulk nanocrystalline TiO2[J]. Acta Mater, 1997, 45(10): 4027-4040.
[9] Kim H G, Kim K T. Densification behavior of nanocrystalline titania powder compact under high temperature[J]. Acta Mater, 1999, 47(13): 3561-3570.
[10] Angerer P, Yu L G, Khor K A, et al. Spark-plasma-sintering (SPS) of nanostructured and submicron titanium oxide powders[J]. Mater Sci Eng, 2004, A381(1): 16-19.
[11] Hahn H, Logas J, Averback R S. Sintering characteristics of nanocrystalline TiO2 [J]. J Mater Res, 1990, 5(3): 609-614.
[12] Liao S C, Pae K D, Mayo W E. Retention of nanoscale grain size in bulk sintered materials via a pressure-induced phase transformation[J]. Nanostruct Mater, 1997, 8(6): 645-656.
[13] Liao S C, Chen Y J, Mayo W E, et al. Transformation-assisted consolidation of bulk nanocrystalline TiO2 [J]. Nanostruct Mater, 1999, 11(4): 553-557.
[14] Shannon R D, Pask J A. Kinetics of the anatase-rutile transformation[J]. J Am Ceram Soc, 1965, 48(7): 391-398.
[15] Kumar K N P, Keizer K, Burggraaf A J, et al. Densification of nanostructured titania assisted by a phase transformation[J]. Nature, 1992, 358(6381): 48-51.
[16] Skandan G, Hahn H, Roddy M, et al. Ultrafine-grained dense monoclinic and tetragonal zirconia[J]. J Am Ceram Soc, 1994, 77(7): 1706-1710.
[17] Bollman W. Triple-line disclinations representations, continuity and reactions[J]. Philos Mag, 1988, A57(4): 637-649.
收稿日期:2007-10-13;修回日期:2007-12-26
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50575217);国家创新群体基金资助项目(50421502)
通信作者:冶银平(1967-),男,甘肃陇南人,博士,研究员,从事纳米材料和材料摩擦磨损性能研究;电话:0931-4968150;E-mail: yeyinping585@sina.com