文章编号:1004-0609(2013)S1-s0024-05
基板厚度对激光直接成形Ti6Al4V合金显微组织和温度历史的影响
韩远飞1, 2,吴鑫华2,梅俊发2,T. JARVIS2,J. SHURVINTON2,吕维洁1
(1. 上海交通大学 金属基复合材料国家重点实验室,上海 200040;
2. ARC Centre of Excellence for Design in Light Metals, Monash University, Melbourne, 3168, Australia)
摘 要:在金属直接激光快速成形过程中,冷却速率是决定相应材料熔融后显微组织状态的关键之一。通过合理控制基板厚度可改变加热时间和冷却时间,从而影响冷却速率以改变凝固后的显微组织。分别采用脉冲波和连续波集中研究了基板厚度对沉积过程温度场和显微组织的影响规律。结果发现,随着基板厚度的增加,Ti-6Al-4V合金薄壁试样中心部位柱状晶变短变细,且体积分数降低,金相组织由大量等轴晶粒组成;与激光脉冲波沉积试样相比,采用激光连续波可获得几乎100%细小的等轴晶粒;且厚基板在沉积初始阶段可获得较小的温度峰值,但可获得较大的冷却速率,从而改变合金的显微组织状态。
关键词:直接激光制造;Ti6Al4V;等轴晶粒;柱状晶;热分析;显微组织
中图分类号:TG 146.2 文献标志码:A
Effect of substrate thickness on microstructure and temperature history of direct laser fabricated Ti-6Al-4V alloy
HAN Yuan-fei1, 2, WU Xin-hua2, MEI Jun-fa2, T. JARVIS2, J. SHURVINTON2, Lü Wei-jie1
(1. State Key Laboratory of Metal Matrix Composites, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai 200040, China;
2. ARC Centre of Excellence for Design in Light Metals, Monash University, Melbourne, 3168, Australia)
Abstract: Cooling rate is one of the most important factors in determining the resultant microstructure of the material during the direct laser fabrication process (DLF). A gradual heating or prolonged cooling effects are obtained and it is possible to dictate the cooling rates and affect the solidification microstructure through reasonable controlling the thickness of substrate. Pulse wave and continuous wave laser were used to study the effect of various thickness of substrate on the microstructure of the specimens, respectively. It is found that a few volume fractions of columnar grains located in the center of the samples turn to coarser and shorter, and the sample is composed of a large number of equiaxed grains with the increasing of the substrate thickness. Compared with the pulse laser, nearly 100% fine equiaxed grain could be obtained through using continuous wave laser. Thick substrate can get a smaller peak temperature but higher cooling rate to change the microstructure in the initial stage.
Key words: direct laser fabrication; Ti-6Al-4V; equiaxed grain; columnar grain; thermal analysis; microstructure
直接激光快速成形制造技术(Direct laser fabrication)是激光快速凝固和快速原型制造技术相结合的一种先进的材料加工成形技术[1-10]。通过将高能束的激光能量聚焦在加工平面上形成稳定的金属熔池来融化基材和喷射而来的粉末,然后层层累积得到整个三维金属零件,该技术在航空、航天等领域的应用前景非常广阔[3-5]。然而,在金属零件快速成形过程中涉及的变量众多,激光能量产生的高温度梯度的温度场和在基板上堆积凝固成形的方式,将导致沉积零件的显微组织状态(晶粒形态、尺寸等)发生巨大的变化[4]。近几年,很多研究者都曾开展了激光加工工艺对沉积件显微组织的影响[1-5]。WU等[2]就曾对Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2C阻燃钛合金和Ti-6Al-4V钛合金激光快速成形工艺做了深入的研究,指出激光沉积工艺参数(激光功率,扫描速度和送粉率等因素)对金属沉积零件形状和其显微组特征都有着非常重要的影响。然而,针对沉积过程中基板厚度因素是否对沉积件显微组织有影响还较少引起研究者的关注。
因此,本文作者以快速成形Ti-6Al-4V合金薄壁件为研究对象,分别采用脉冲波和连续波集中研究了基板厚度对Ti-6Al-4V合金沉积过程显微组织和温度历史的影响规律。
1 实验
直接激光快速成形实验是在莫纳什大学轻金属研究中心制备的Trumpf激光系统上进行。扫描过程中 由送进系统通过与激光束成45°角的三轴向喷嘴将合金粉末喷入激光熔池熔化沉积,进而堆积成形尺寸为40 mm×4 mm×20 mm的薄壁试样。分别采用连续波和脉冲波形在不同厚度的基板上沉积Ti-6AL-4V合金薄壁试样,基板厚度分别为5、10和60 mm。高能激光束脉冲功率最大值为923 W,平均功率为600 W,扫描速率为800 mm/min,单个脉冲时间为1.3 ms,激光照射在基板上的光斑直径为4 mm,频率为500 Hz,基板距离激光聚焦点距离为16 mm。喷嘴沿Z轴方向以每层0.27 mm的距离移动,经过不间断循环往复的堆积,在堆积至第74层时沉积过程停止,整个沉积过程都在惰性气体环境中完成,氧含量低于2×10-5。沉积中使用的Ti-6AL-4V合金粉末尺寸为100~200 μm。
在本研究中,定义激光点搭接率为60%以保证试样具有相同的形状(图1(a)),分别采用脉冲方波和连续波形在不同厚度的基板上沉积试样以观察显微组织的变化(图1(b)和图1(c))。在沉积试样之前,将3个K型热电偶(TC1、TC2和TC3)焊接在基板的不同位置上以实时记录沉积过程温度变化情况,焊点位置由编写入系统中的机器语言确定以保证位置的准确性(见图2),避免了手工操作所出现的较大误差。
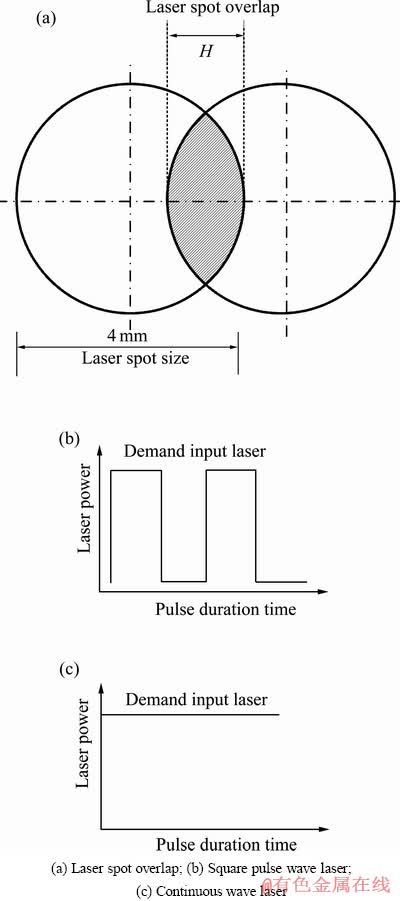
图1 激光点重叠率以及不同波形的激光束
Fig. 1 Laser spot overlap and pulse shape using in laser deposition
2 结果与讨论
2.1 基板厚度对激光沉积Ti-6Al-4V合金薄壁件宏观组织的影响
给定激光平均功率600 W,采用激光快速成形系统直接在5 mm、10 mm和60 mm厚的Ti-6Al-4V合金基板上分别沉积长40 mm、高20 mm、厚4 mm的合金薄壁试样。规定对于沉积的试样,平行于激光熔化沉积层的方向为水平X方向,平行于激光束垂直移动的方向为Z向。图3所示为采用脉冲波激光沉积薄壁试样纵向垂直于扫描方向的剖面组织。剖面宏观组织可以清晰地观察到沉积层宏观形貌特征,其主要由大量的等轴晶粒和巨大的柱状晶组织组成。图3(a)所示为在10 mm厚基板上沉积的试样的宏观组织,主要由含量约为80%的细小的等轴晶粒和含量约为20%的大柱状晶粒组成。图3(b)所示为在60 mm厚基板上沉积的试样的宏观组织,可以发现,试样中心部位柱状晶粒尺寸明显减小,含量降低,主要由90%以上的细小等轴晶粒和10%以下的柱状晶组成。相比较而言,在60 mm基板上沉积的试样中心部位宏观柱状晶较细小,其平均长度约为5 mm。这可能是由于基板厚度的增加,热传导较快,熔池较浅,界面温度梯度较大,同时凝固速度较快,从而导致柱状晶明显细化。
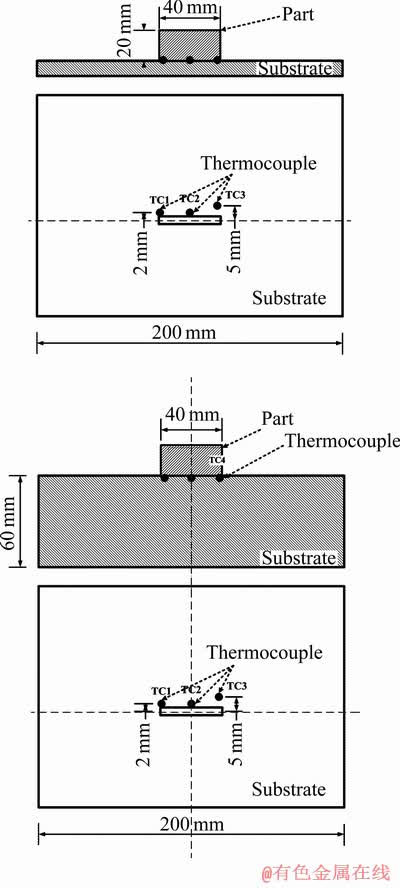
图2 基板上热电偶焊接位置和薄壁试样示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic illustration showing locations of thermocouples on substrate and thin wall specimens
保持激光平均功率以及其他沉积工艺参数不变,改变激光输入形式,图4所示为采用连续波激光快速沉积薄壁Ti-6Al-4V合金试样的宏观组织特征。可以看出,不同厚度基板上沉积的试样的宏观组织都呈现大量细小的等轴晶粒,柱状晶基本消失,仅在薄基板沉积试样中间出现少量的长宽比较小的柱状晶。这说明,采用连续波在厚基板激光沉积的试样,其显微组织更加稳定,更加均匀。

图3 采用脉冲波形在不同厚度基板沉积Ti-6Al-4V合金的宏观组织
Fig. 3 Macrostructures of pulsed laser-deposited Ti-6Al-4V alloy by using different thickness substrate

图4 采用连续波形在不同厚度基板沉积Ti-6Al-4V合金宏观组织
Fig. 4 Macrostructures of continuous wave laser-deposited Ti-6Al-4V alloy by using different thickness substrate
2.2 基板厚度对激光沉积Ti-6Al-4V合金薄壁件温度历史的影响
图5所示为采用脉冲波与连续波在不同厚度基板上激光沉积Ti-6Al-4V合金温度历史情况。可以看出,脉冲波形与连续波形基板温度历史呈现出类似的趋势。在沉积开始阶段,基板温度急剧升高,熔池冷却主要依靠基板中热传导,熔池的冷却速率取决于热量在基板中的传导速率。随着时间的增加,基板温度继续升高,基板中的热传导速率仍是熔池冷却速率的主要影响因素,但是影响程度逐渐减弱。当基板的激光热量小于基板的散失热量时,基板的温度呈现快速下降的趋势,这时基板和已沉积层和周围环境之间的换热过程成为影响熔池冷却速率的主要因素,基板的传热对熔池冷却速率的影响逐渐减弱。
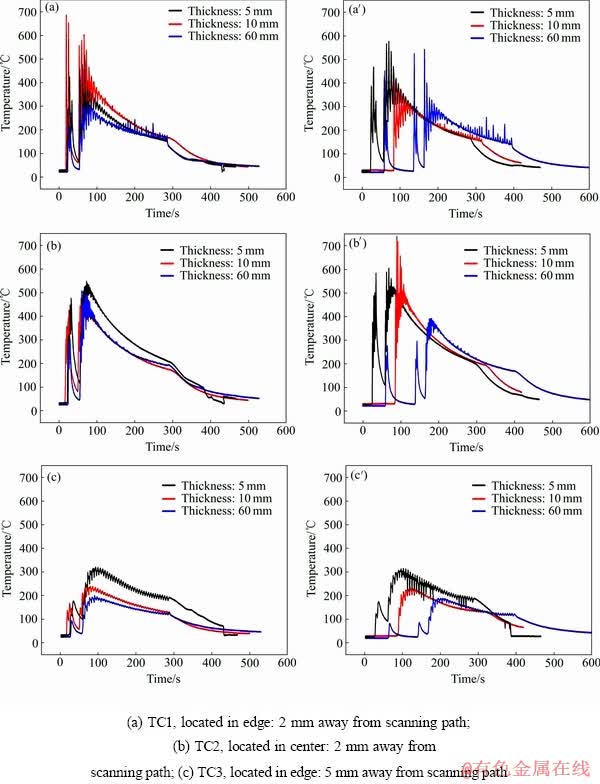
图5 采用脉冲波与连续波在不同厚度基板上激光沉积温度变化情况
Fig. 5 Comparison of measured temperatures of different thickness substrate by using pulse laser ((a), (b), (c)) and continuous wave laser ((a′), (b′), (c′))
采用热电偶实时测量基板不同部位的温度历史发现,在沉积件边缘距离扫描路径2 mm处,其最高温度为600 ℃,而在沉积件边缘距离扫描路径5 mm处,其最高温度仅为300 ℃。说明沉积过程中基板温度历史对基板不同部位的热电偶非常敏感,即使是几毫米的距离,其最高温度都会发生剧烈的变化。因此,可以推测基板厚度的变化也将大幅度地影响沉积过程的温度历史,从而改变熔池的冷却速率。
从图5(a),5(b)和5(c)分别可以看出,随着基板厚度的增加,厚基板(60 mm)同一位置的温度明显低于薄基板(5 mm)的温度。例如图5(c)中,薄基板同一位置的最高温度为370 ℃,而厚基板则仅为200 ℃。这说明基板厚度的变化将直接影响沉积过程的温度历史,而温度历史又是沉积工艺的首要影响因素[3, 11]。增厚基板相当于增加了基板中的热传导速率,增强了基板对熔池冷却速率的影响。因此,基板厚度的改变,对于激光沉积初始阶段具有很大的影响。由于初始阶段是沉积工艺的关键,所以控制基板厚度在沉积工艺中具有十分重要的作用。研究结果显示,在基板相同部位,沉积初始阶段厚基板的冷却速率最大,约为110 ℃/s。
3 结论
1) 随着基板厚度的增加,Ti-6Al-4V合金薄壁试样中心部位柱状晶变短变细,体积分数降低,金相组织主要由大量等轴晶粒组成,因此,使用厚基板可获得大量等轴晶粒,组织更均匀。
2) 与激光脉冲波沉积Ti-6Al-4V合金薄壁试样相比,采用激光连续波可获得更好的显微组织形貌,试样显微组织更加均匀,为几乎100%的细小等轴晶粒。
3) 基板厚度的变化会大程度地影响沉积过程的温度历史,厚基板在沉积初始阶段可获得较小的温度峰值,但却可以获得较大的冷却速率,从而改变试样的显微组织。
REFERENCES
[1] QIAN L, MEI J, LIANG J, WU X. Influence of position and laser power on thermal history and microstructure of direct laser fabricated Ti-6Al-4V samples[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2005, 21: 1-9.
[2] WU X, SHARMAN R, MEI J, VOICE W. Microstructure and properties of a laser fabricated burn-resistant Ti alloy[J]. Materials and Design, 2004, 25: 103-109.
[3] 石力开, 高士友, 席明哲,纪宏志, 张永忠, 杜宝亮. 金属直壁件激光直接沉积过程的有限元模拟—沉积过程中温度场的模拟[J]. 金属学报, 2006, 42(5): 449-453.
SHI Li-kai, GAO Shi-you, XI Ming-zhe, JI Hong-zhi, ZHANG Yong-zhong, DU Bao-liang. Finite element simulation for laser direct depositing process of metallic vertical thin wall parts—The simulation for temperature field during depositing process[J]. Acta Metallurcica Sinica, 2006, 42(5): 449-453.
[4] 张霜银, 林 鑫, 陈 静, 张凤英, 黄卫东. 工艺参数对激光快速成形TC4钛合金组织及成形质量的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(10): 1839-1843.
ZHANG Shuang-yin, LIN Xin, CHEN Jing, ZHANG Feng-ying, HUANG Wei-dong. Influence of processing parameters on microstructure and forming characterizations of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy after laser rapid forming processing[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2007, 36(10): 1839-1843.
[5] 贺瑞军, 王华明. 激光熔化沉积Ti-6Al-2Zr-Mo-V钛合金组织特征研究[J]. 航空材料学报, 2009, 29(6): 18-25.
HE Rui-jun, WANG Hua-ming. Microstructure features of laser deposited Ti-6Al-2Zr-Mo-V alloy[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2009, 29(6): 18-25.
[6] 苏海军, 尉凯晨, 郭 伟, 马菱薇, 于瑞龙, 张 冰, 张 军, 刘 林, 傅恒志. 激光快速成形技术新进展及其在高性能材料加工中的应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(6): 1567-1574.
SU Hai jun, WEI Kai chen, GUO Wei, MA Ling wei, YU Rui long, ZHANG Bing, ZHANG Jun, LIU Lin, FU Heng zhi. New development of laser rapid forming and its application in high performance materials processing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(6): 1567-1574.
[7] 杨永强, 张翠红. 激光熔覆-激光氮化复合法制取TiNi TiN梯度材料[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(2): 213-218.
YANG Yong qiang, ZHANG Cui hong. Synthesis of TiNi TiN gradient coating by hybrid method of laser cladding and laser nitriding[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(2): 213-218.
[8] TAN Hua, CHEN Jing, ZHANG Feng ying, LIN Xin, HUANG Wei dong. Process analysis for laser solid forming ofthin wall structure[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2010, 50: 1-8.
[9] MAZUMDER J, DUTTA D, KIKUCHI N, GHOSH A. Closed loop direct metal deposition: Art to part[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2000, 34: 397-414.
[10] 张冬云, 王瑞泽, 赵建哲, 左铁钏. 激光直接制造金属零件技术的最新进展[J]. 中国激光, 2010, 37: 18-25.
ZHANG Dong yun, WANG Rui ze, ZHAO Jian zhe, ZUO Tie chuan. Latest advance of laser direct manufacturing of metallic parts[J]. Chinese Journal of Laser, 2010, 37: 18-25.
[11] 席明哲, 张永忠, 石力开, 高士友. 激光快速成形金属薄壁零件的三维瞬态温度场数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(4): 887-892.
XI Ming-zhe, ZHANG Yong-zhong, SHI Li-kai, GAO Shi-you. Numerical simulation of 3D transient temperature field in thin-wall metal parts fabricated by laser direct deposition[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(4): 887-892.
(编辑 杨 兵)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2012CB619600)
收稿日期:2013-07-28;修订日期:2013-10-10
通信作者:韩远飞,博士;电话:15026663706;E-mail: hyuf1.npu@gmail.com