文章编号:1004-0609(2011)07-1554-08
选区激光熔化制备TiCx/Ti纳米复合材料的
致密化及显微组织
李 闯1, 顾冬冬1, 2, 沈以赴1, 孟广斌1
(1. 南京航空航天大学 材料科学与技术学院,南京 210016;
2. Fraunhofer Institute for Laser Technology ILT, Aachen D-52074, Germany)
摘 要:利用选区激光熔化(SLM)工艺制备TiCx增强Ti基纳米复合材料试件;通过X射线衍射仪和场发射扫描电子显微镜等研究激光线能量密度η(激光功率与扫描速率之比)对选区激光熔化试件的致密化过程、物相及显微组织的影响规律,并讨论激光快速熔凝过程中TiC0.625层片状纳米结构的形成机理。结果表明:当激光线能量密度η为1 100 J/m时,成形试件的致密度可达95.6%;其内部增强体为层片状纳米结构,平均厚度为54 nm,且在Ti基体中分布均匀。增强相TiCx以亚化学计量TiC0.625形式存在,具有立方晶体结构。
关键词:选区激光熔化;线能量密度;致密度;显微组织;TiC0.625
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
Densification and microstructure of
TiCx/Ti nanocomposites prepared by selective laser melting
LI Chuang1, GU Dong-dong1, 2, SHEN Yi-fu1, MENG Guang-bin1
(1. College of Materials Science and Technology,
Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China;
2. Fraunhofer Institute for Laser Technology ILT, Aachen D-52074, Germany)
Abstract: The TiCx reinforced Ti matrix nanocomposites parts were prepared by selective laser melting (SLM). The effects of applied linear laser energy density η (the ratio of laser power to scan speed) on evolutions of the densification behavior, phases, and microstructures of SLM-processed parts were studied using X-ray diffractometer (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM). The formation mechanism of TiC0.625 reinforcing phase with a lamellar nanostructure during the laser-induced rapid melting/solidification process was discussed. The results show that a high densification level of 95.6% is obtained for SLM-processed parts at a laser linear energy density η of 1 100 J/m. The TiCx reinforcing phase disperses uniformly in the Ti matrix, having an ultrafine lamellar nanostructure with an average thickness of 54 nm. The reinforcing phase is present in the form of substoichiometric TiC0.625 with a cubic crystal structure.
Key words: selective laser melting (SLM); linear energy density; densification; microstructure; TiC0.625
Ti基纳米复合材料(Titanium matrix nano- composites, TMNC)是以Ti及其合金为基体,与一种或几种纳米级金属或者陶瓷增强体相结合的复合材 料[1-2]。由于TiC陶瓷与金属Ti的密度、热膨胀系数最为接近(ρTi=4.5 g/cm3, ρTiC=4.9 g/cm3;αTi=9.41×10-6 K-1,αTiC=7.4×10-6 K-1),且泊松比相同(μ=0.3),所以,TiC和Ti具有良好的物理和化学相容性,而TiC的硬度、弹性模量及抗拉强度均远高于Ti的[3]。因此,TiC/Ti纳米复合材料兼具二者的优异性能。
目前,陶瓷增强金属基复合材料制备方法很多,如粉末冶金、铸造法、熔渗法和自蔓延高温合成法 等[3]。但由于陶瓷与金属的成分、晶体结构及物理性质的差异,陶瓷/金属润湿性差、线膨胀系数差异大,传统的制备工艺极易导致成形材料中陶瓷增强体局部团聚以及界面裂纹,从而降低复合材料的综合性能[4]。选区激光熔化(Selective laser melting,SLM),作为一种新型的快速成形(Rapid manufacturing,RM)技术,能根据零件的计算机辅助设计(Computer aided design,CAD)模型,利用高能量激光束逐层熔化处于松散状态的粉体材料,从而堆积成任意形状的三维零部件[5-6]。SLM过程中温度梯度大(7×106 K/s),凝固速率极快,可使成形材料微观组织显著细化[7]。特别是,若金属基体中增强相细化至纳米级,可有效约束基体热膨胀变形,克服界面裂纹,改善SLM成形复合材料试件的综合性能[8]。
尽管如此,SLM形成的非平衡态激光熔池涉及一系列复杂的化学冶金和物理冶金现象,包括热量、质量及动量的多重传递[9]。凝固析出的陶瓷增强体的晶粒形貌、大小和分散状态等,随着激光工艺参数的改变表现出较强敏感性及复杂多变性,导致组织可控性差[10]。另一方面,SLM涉及激光功率P、扫描速度ν、扫描间距l和铺粉厚度d等一系列工艺参数,而工艺参数的选取对SLM试件显微组织及性能亦具有重要影响。从能量输入的角度分析,对于SLM单道激光扫描过程,激光功率P和扫描速度v是决定粉体接受能量大小的主要因素,而其最终作用形式,则是激光线能量密度η(η=P/ν,J/m)[11]。为综合控制能量输入以及SLM成形过程,本文作者在不同激光线能量密度η下进行SLM成形实验,制备TiCx/Ti纳米复合材料试件,分析η值对成形试件的致密化过程、物相及显微组织的影响,探讨高能激光束动态扫描作用下纳米增强相的生长机制。
1 实验
1.1 材料
实验材料如下:纯度为99.9%、粒度为1.5 μm的TiC粉末;纯度为99.9%,粒度为45 μm的Ti粉末。将TiC和Ti粉末按质量比3?7配料,并置于德国Fritsch公司生产的Pulverisette-6单罐行星式高能球磨机中球磨,转速为300 r/min,时间为10 h,球料比为10?1;球磨过程采用球磨20 min,空气冷却10 min,以避免罐内温度升高。经10 h高能球磨,复合粉末显著细化,形成等轴状微细颗粒,平均粒度为6 μm (见图1(a));TiC以纳米级颗粒形态分布在Ti基体中,TiCp/Ti纳米复合粉末内部结构如图1(b)所示。

图1 球磨10 h后TiC/Ti纳米复合粉末的SEM及TEM像
Fig.1 SEM image (a) and TEM image (b) of as-milled TiC/Ti nanocomposites powders at 10 h
1.2 工艺及分析
本实验所使用的SLM成形系统主要包括:高功率Nd?YAG(λ=1.064 μm)激光器、用于成形控制的计算机系统、自动铺粉装置以及保护气氛装置,如图2所示。SLM过程中,铺粉装置将一定厚度的粉末均匀铺放在成形缸基板上,激光束根据计算机设计的CAD模型逐行扫描分层的某一区域,以形成零件在一个水平方向上的二维截面;随后,成形缸活塞下降一定距离,供粉缸活塞上升相同距离,铺粉装置再次铺粉,激光束开始依照零件第2层CAD信息扫描粉末;如此叠加,制备尺寸为9 mm×9 mm×9 mm的块体试件,如图3所示。成形过程采用氩气进行保护,氩气出气压力为3 kPa,成形系统内O2的体积分数低于1×10-5。激光工艺参数如下:光斑直径200 μm,激光功率110~130 W,扫描速率100~400 mm/s,扫描间距140 μm,铺粉厚度50 μm。

图2 SLM成形系统示意图
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of SLM apparatus

图3 SLM 成形试件照片
Fig.3 Photos of SLM-processed samples
利用线切割获得横截面试样,依照规定程序对其打磨及抛光以获得金相分析试样。金相分析利用光学显微镜(OM)观察,试样致密度利用Archimedes定律测算。物相利用BRUKER D8 ADVANCE型X射线衍射仪(XRD)分析(Cu Kα,电压为40 kV,电流为40 mA,扫描速度为4 (°)/min)。腐蚀剂选用含HF(2 mL)、HNO3(6 mL)、H2O(96 mL)的溶液,腐蚀时间为25 s。SLM试样的显微组织利用LEO 1550型场发射扫描电镜(FE-SEM)观察(加速电压为5 kV)。试样的化学元素分布采用EDAX型能量散射谱(EDX)测定。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 致密化过程
图4所示为不同线能量密度η(600~1 300 J/m)下SLM试件截面抛光后的显微组织。图5所示为试件致密度随线能量密度η的变化。由于TiC/Ti纳米复合粉末选区激光熔化主要涉及液相成形机制(纳米复合粉末完全熔化),因此,激光熔池中液相的表面张力、黏度和流变特性等(主要受η影响)将直接影响凝固组织的致密化过程(如孔隙尺寸和形状、组织连续性等)[12]。

图4 不同线能量密度下SLM试件的金相图片
Fig.4 OM images of SLM samples at various η: (a) 600 J/m; (b) 800 J/m; (c) 1 100 J/m; (d) 1 300 J/m
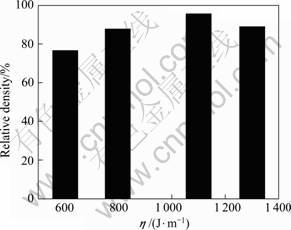
图5 SLM试件致密度随线能量密度η的变化
Fig.5 Variation of relative density of SLM samples with linear energy density (η)
当η为600 J/m时,液相凝固组织的连续性分布较差,成形试件表面孔隙尺寸较大,且形状不均匀,如图4(a)所示。SLM试件密度仅为理论密度的76.6%。其原因在于:线能量密度过低,导致激光熔化的液相量偏少,液相黏度较高,液相不足以铺展开来,很难形成连续的凝固组织,致使尺寸较大的孔隙存在于成形试件中,降低了试件的致密度。
当η增加至800 J/m时,液相凝固组织的连续性得到较大改善,SLM试件密度也提高到理论密度的87.8%。尽管仍存在少数不均匀形状的孔隙,但试件成形性得到较大提高,如图4(b)所示。这是由于随着线能量密度的增大,激光熔池内的作用温度升高,粉层熔化完全,形成的液相量增加,液相黏度降低。当光斑移动到下一扫描区域时,熔化的液相有较充足时间及时铺展并凝固,因此,组织致密度提高[13]。
当η增加至1 100 J/m时,SLM试件中无明显孔隙,凝固组织的连续性及均匀性显著提高,如图4(c)所示。试件密度达理论密度的95.6%,这是由于η足够大,形成液相的黏度更低,更有利于熔池内液相流动速度的增加,熔化的液相可以更好地铺展,形成连续的冶金结合,从而显著提高试件的致密度。
当η继续增大至1 300 J/m,尽管凝固组织仍较为连续致密,但其中分布着一系列尺寸为15~30 μm的微小孔隙,如图4(d)所示。此时,SLM试件的密度也下降,为理论密度的88.9%。这是由于此时线能量密度η过高,激光熔化单道线后,热量相对长时间地停留在某一位置,造成“过烧根瘤”现象[14],从而导致试件致密度降低。综合分析可知,当激光线能量密度η为1 100 J/m时,成形试件的致密度最高(95.6%),且成形显微组织的连续性和均匀性最佳。
2.2 物相分析
图6所示为不同线能量密度η下成形试样的XRD谱。SLM工艺后,试样中主要含Ti(JCPDS 65-9622)和以亚化学计量存在的TiC0.625(JCPDS 79-0971)两种物相。 TiC0.625晶体呈传统TiC所具有的立方晶体结构。根据XRD谱可知,TiC0.625衍射峰宽化现象较为明显,表明SLM成形试样中TiC0.625增强相晶粒尺寸非常细小。

图6 不同线能量密度下SLM试样的XRD谱
Fig.6 XRD patterns of SLM samples prepared at various linear energy densities (η): (a) 600 J/m; (b) 1 100 J/m; (c) 1 300 J/m
2.3 显微组织分析
图7和8所示为在不同线能量密度η下SLM试件断面腐蚀后的显微组织。其中,层片状增强相分布情况如图7所示,而高倍下增强相纳米结构特征如图8所示。EDX点成分扫描结果显示,试样中分散的白色层片状结构主要含C和Ti元素,且C与Ti的摩尔比约为0.6?1,如图8(d)所示。结合XRD分析结果,白色层片状结构为亚化学计量形式TiC0.625;而其周围的灰色基体只含Ti元素。结合XRD谱(见图6)可知,在本SLM工艺条件下成功制备了TiC0.625/Ti纳米复合材料。
当η为600 J/m时,TiC0.625呈团絮状分布于Ti基体中(见图7(a)),增强体尺寸和形状不均匀(见图8(a))。这是由于线能量密度过低,致使粉体接受的激光能量较少,激光熔池中温度较低,形成的液相表面张力大,不利于TiC0.625分布均匀,增强相易于团聚。当η升高至1 100 J/m时,TiC0.625呈层片状形貌,其显微结构明显细化,平均长度为707 nm、宽度为276 nm、厚度为54 nm(见图8(b)),且均匀分布在Ti基体中(见 图7(b))。因TiC0.625增强相在厚度方向上的尺寸小于100 nm,故其具有典型的纳米结构特征。此时,由于线能量密度高,Marangoni流形成的液相毛细管力较大[15],促进TiC0.625均匀排布,避免发生团聚。当η继续增大至1 300 J/m时,TiC0.625层片状结构略显粗化,平均尺寸为长度886 nm、宽度411 nm、厚度78 nm(见图8(c)),其分布亦较为均匀(见图7(c))。此时,TiC0.625增强相仍具有纳米结构特征。

图7 不同线能量密度下SLM试样的低倍显微组织及其对应的高倍显微组织
Fig.7 SEM images of SLM samples under low magnification (a), (b), (c) and high magnification (d), (e), (f) at various linear energy densities (η): (a), (d) 600 J/m; (b), (e) 1 100 J/m; (c), (f) 1 300 J/m

图8 不同线能量密度下SLM试样的显微组织及层片状结构能谱
Fig.8 SEM images of SLM samples at various linear energy densities (η) and EDX analysis of lamellar structure: (a) 600 J/m; (b) 1 100 J/m; (c) 1 300 J/m; (d) EDX
在SLM工艺中,随着激光能量的大量注入,辐照区域内的TiC/Ti纳米复合粉末迅速被加热并完全熔化,形成一定截面形状的熔池。当激光束远离熔池时,由于TiC0.625的熔点(3 160 ℃)高于Ti的(2 730 ℃),TiC0.625首先形核长大析出。因激光能量密度呈Gauss分布,故熔池中心及边缘将形成明显的温度梯度,由此产生液相表面张力梯度,致使熔池中形成Marangoni流。Marangoni流对激光作用下熔池内热量、质量和动量的传输过程起着关键作用,进而形成液相毛细管力[15-16]。TiC0.625在溶解-析出过程中受到毛细管力的影响。ANESTIEV和FROYEN[17]证实,毛细管力大小与液相的表面张力成反比关系,当适当提高线能量密度η时,激光作用的熔池中液相量增加,液相的表面张力降低,促使液相作用于TiC0.625的毛细管力增加,毛细管力可有效提高TiC0.625的重排率,从而有利于TiC0.625在基体Ti中分布均匀,避免团聚。此外,激光作用的熔池中由熔池蒸气压力及表面张力所产生的有效微观应力有利于加速TiCx的局部迁移,进而促使TiCx在基体中分布均匀,如图7所示。因此,适当提高激光线能量密度至1 100 J/m以上,有利于获得纳米结构的TiC0.625增强相,并使其在基体中分散均匀。
2.4 TiC层片状纳米结构的形成机理
图9所示为TiC0.625层片状结构形成机理。满足标准化学计量的TiC晶体结构为NaCl型,属立方晶系,其晶体空间群为Fm3m(255),沿垂直于{111}面的方向观察,Ti和C都处于面心立方晶格的节点处,由 aá1/2,1/2,1/2?相互取代,C原子占据Ti原子所有的八面体间隙[18]。然而,由于TiC晶体结构中C原子节点处C原子的缺失,致使未能形成Ti与C摩 尔比为1?1的TiC,而是以亚化学计量TiCx(TiC0.50~TiC0.97)形式存在[19],根据XRD分析,TiC0.625呈传统TiC所具有的立方晶体结构。
陶瓷相TiCx的熔点高于Ti的,因此,在激光辐照瞬间形成的熔池中,TiC0.625晶粒在高温熔体中首先形核长大,并经过溶解-析出机制形成一定形貌的结构,而其形貌取决于本身的生长习性和生长环境[20]。TiC晶体结构中{110}面不易显露、而{111}面的生长方式为二维形核,易于显露。当{110}面生长速度快、{111}面生长速度慢时,晶体易呈现层片状结构[21]。本研究中,当TiCx核心开始形成时,TiCx的生长就受到了激光熔池中特有的“微观有效应力”抑制,使其难以长大,从而保证TiC0.625的纳米结构。而激光熔池中“微观有效应力”peff 可以表示为peff = pr + pst[22]。式中,pr为熔池蒸气压力,定义如下:
pr =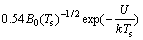 (1)
(1)
式中:B0为蒸发系数;Ts为表面温度;U为每个原子的蒸发潜热;k为麦克斯韦常数;pst为杨氏-拉普拉斯方程,其定义如下:
pst=σ/rm (2)
式中:σ为表面张力;rm为熔体弯曲半径。
本研究中,正是由于受到激光熔池中特有的非平衡微观应力的影响,TiC0.625在其核心形成后受到一系列“短波脉冲”作用,进而导致其晶体中{111}面沿[111]方向生长受到抑制,而{110}沿[110]方向生长状况良好;同时,Ti和C原子不断在{111}晶面上“沉积”,继而形核、长大、堆垛,最终形成以{111}为基面的立方型层片状结构[23]。值得注意的是,SLM工艺涉及非平衡快速熔凝过程,TiC0.625晶体的最终形貌除受其本身晶体结构的影响外,还会受到实际生长动力学条件下溶质传输过程的限制。由于熔池中Marangoni流的作用,TiC0.625晶体凝固前沿处各部位的溶质过饱和度及化学成分梯度不均匀,该条件下凝固形成的晶体形态容易“失稳”[21]。因此,最终形成近立方型的层片状结构,如图9所示。此外,考虑到熔池区域在激光束离开后快速凝固,冷却速度可达106 K/s [24],因此,TiC0.625层片状堆垛时间很短,因而SLM过程中析出的TiC0.625增强相在{111}面厚度方向上很薄,小于 100 nm,具有典型的纳米结构特征。
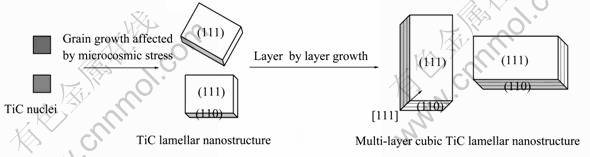
图9 TiC0.625层片状结构成形机理示意图
Fig.9 Schematic diagram of formation mechanisms of TiC0.625 lamellar nanostructure
3 结论
1) 采用选区激光熔化SLM工艺,制备TiC0.625/Ti纳米复合材料试件,亚化学计量TiC0.625晶体结构为立方结构。
2) 当激光线能量密度η为1 100 J/m时,成形试件致密度最高(95.6%),增强体TiC0.625呈细化的层片状纳米结构(平均厚度54 nm),且在Ti基体中分布 均匀。
3) 受激光作用的熔池中特有的“微观应力”及TiC0.625自身晶体结构的影响,Ti0.625在{111}面上形核、长大、 堆垛,形成立方型层片状结构;由于晶体结构“失稳”,最终形成以{111}为基面的层片状结构。
REFERENCES
[1] 龚荣洲, 沈 翔, 张 磊, 张 凌. 金属基纳米复合材料的研究现状和展望[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(5): 1311-1320.
GONG Rong-zhou, SHEN Xiang, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Ling. Status and expectation of research on metal matrix nanocomposites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(5): 1311-1320.
[2] 于翔天, 王华明. 激光熔化沉积(TiB+TiC)/TA15原位钛基复合材料的显微组织与力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2008, 25(4): 113-118.
YU Xiang-tian WANG Hua-ming. Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser melting deposited (TiB+TiC) /TA15 in situ titanium matrix composites [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2008, 25(4): 113-118.
[3] 孔令超, 宋卫东, 宁建国, 毛小南. TiC颗粒增强钛基复合材料的静动态力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(10): 1756-1762.
KONG Ling-chao, SONG Wei-dong, NING Jian-guo, MAO Xiao-nan. Static and dynamic behaviors of TiC particle reinforced titanium matrix composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(10): 1756-1762.
[4] 罗吉祥, 唐 春, 郭 然. 纤维增强复合材料界面脱层和基体裂纹的模拟分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2009, 26(6): 201-209.
LUO Ji-xiang, TANG Chun, GUO Ran. Numerical simulations of interfacial debonding and matrix cracking in fiber reinforced composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2009, 26(6): 201-209.
[5] 尹 华, 白培康, 刘 斌, 李玉新. 金属粉末选区激光熔化技术的研究现状及其发展趋势[J]. 热加工工艺, 2010, 39(1): 139-144.
YIN Hua, BAI Pei-kang, LIU Bin, LI Yu-xin. Present situation and development trend of selective laser melting technology for metal powder[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2010, 39(1): 139-144.
[6] 黄卫东, 李延民, 冯莉萍, 陈 静, 杨海鸥, 林 鑫. 金属材料激光立体成形技术[J]. 材料工程, 2002, 36(3): 40-44.
HUANG Wei-dong, LI Yan-min, FENG Li-ping, CHEN Jing, YANG Hai-ou, LIN Xin. Laser solid forming of metal powder materials[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2002, 36(3): 40-44.
[7] YADROITSEV I, SHISHKOVSKY I, BERTRAND P, SMUROV I. Manufacturing of fine-structured 3D porous filter elements by selective laser melting[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255(10): 5523-5527.
[8] 付立定, 史玉升, 章文献, 刘锦辉, 鲁中良. 316L不锈钢粉末选择性激光熔化快速成形的工艺研究[J]. 应用激光, 2008, 28(2): 108-111.
FU Ding-li, SHI Yu-sheng, ZANG Wen-xian, LIU Jin-hui, LU Zhong-liang. The process of 316L stainless steel in selective laser melting[J]. Applied Laser, 2008, 28(2): 108-111.
[9] 钟敏霖, 刘文今. 国际激光材料加工研究的主导领域与热点[J]. 中国激光, 2008, 35(11): 1653-1659.
ZHONG Min-lin, LIU Wen-jin. Leading areas and hot topics on global laser materials processing research[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2008, 35(11): 1653-1659.
[10] THIJS L, VERHAEGHE F, CRAEGHS T, HUMBEECK J V, KRUTH J P. A study of the microstructural evolution during selective laser melting of Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58(9): 3303-3312.
[11] GU D D, SHEN Y F. Effects of processing parameters on consolidation and microstructure of W-Cu components by DMLS[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 473(1/2): 107-115.
[12] 顾冬冬, 沈以赴, 杨家林, 王 洋. 多组分铜基金属粉末选区激光烧结致密化机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(4): 596-602.
GU Dong-dong, SHEN Yi-fu, YANG Jia-lin, WANG Yang. Densification mechanism of multi-component Cu-based metal powder in selective laser sintering process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(4): 596-602.
[13] 陈 瑶, 王华明. 激光熔覆TiC/FeAl复合材料涂层显微组织及初生TiC生长机制研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2003, 32(7): 569-572.
CHEN Yao, WANG Hua-ming. Microstructure of laser clad TiC/FeAl composite coating and growth mechanism of primary TiC carbide[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2003, 32(7): 569-572.
[14] 王 迪, 杨永强, 吴伟辉. 光纤激光选区熔化316L不锈钢工艺优化[J]. 中国激光, 2009, 36(12): 3233-3239.
WANG Di, YANG Yong-qiang, WU Wei-hui. Process optimization for 316L stainless steel by fiber laser selective melting[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2009, 36(12): 3233-3239.
[15] WANG Z Y, SHEN Y F, GU D D. Development of porous 316L stainless steel with novel structures by selective laser melting[J]. Powder Metallurgy, 2011, 15(3): 225-230.
[16] 欧阳鸿武, 余文焘, 陈 欣, 何世文, 黄劲松. 利用“球化效应”激光扫描制备球形Ti粉的研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(9): 1608-1612.
OUYANG Hong-wu, YU Wen-tao, CHEN Xin, HE Shi-wen, HUANG Jin-song. Spherical Ti powder fabricated with laser scanning by balling effect[J]. Rare Metal Materials Engineering, 2007, 36(9): 1608-1612.
[17] ANESTIEV L A, FROYEN L. Model of primary the rearrangement processes at liquid phase sintering and selective laser sintering due to biparticle interactions[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1999, 86(7): 4008-4017.
[18] YANG Y F, WANG H Y, WANG J G, JIANG Q C. Lattice parameter and stoichiometry of TiCx produced in alloyed Ti-C systems by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(11): 3813-3816.
[19] HUGOSSON H W, JANSON U, JOHANSSON B, ERIKSSON O. Phase stability diagrams of transition metal carbides: A theoretical study[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2001, 333(6): 444-450.
[20] LIU G H, CHEN K X, ZHOU H P, GUO J M, REN K G. Layered growth of Ti2AlC and Ti3AlC2 in combustion synthesis[J]. Materials Letters, 2007, 61(3): 779-784.
[21] 金云学, 张 虎, 曾松岩, 张二林, 李庆芬. 自生TiCp/Ti复合材料中TiC的生长习性[J]. 金属学报, 2002, 38(11): 1223-1227.
JIN Yun-xue, ZHANG Hu, ZENG Song-yan, ZHANG Er-lin, LI Qing-fen. Study of growth habit of tic in TiCp/Ti composites[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2002, 38(11): 1223-1227.
[22] SEMAK V V, KNOROVSKY G A, MACCALLUM D O, ROACH R A. Effect of surface tension on melt pool dynamics during laser pulse interaction[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2006, 39(3): 590-595.
[23] LI S B, XIANG W H, ZHAI H X, ZHOU Y. Formation of TiC hexagonal platelets and their growth mechanism[J]. Powder Technology, 2008, 185(1): 49-53.
[24] SIMCHI A, POHL H. Effects of laser sintering processing parameters on the microstructure and densification of iron powder[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 359(1/2): 119-128.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:德国洪堡基金资助项目;国家自然科学基金资助项目(51054001);江苏省自然科学基金资助项目(BK2009374);航空科学基金资助项目(2010ZE52053);南京航空航天大学基本科研业务费专项科研资助项目(NS2010156)
收稿日期:2010-06-07;修订日期:2010-11-29
通信作者:顾冬冬,教授;电话:025-52112626,E-mail:dongdonggu@nuaa.edu.cn