Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 444-450
High temperature mechanical behavior of alumina dispersion strengthened copper alloy with high content of alumina
Zi-qi XIANG1, Zhou LI1,2, Qian LEI1, Zhu XIAO1, Yong PANG1
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 31 March 2014; accepted 25 July 2014
Abstract: The microstructure and its effects on the high temperature mechanical behavior of Cu-2.7%Al2O3 (volume fraction) dispersion strengthened copper (ADSC) alloy were investigated. The results indicate that fine alumina particles are uniformly distributed in the copper matrix, while a few coarse ones are distributed on the grain boundaries. Tensile tests results show that Hall-Petch mechanism is the main contribution to the yield strength of ADSC alloy at room temperature. Its high temperature strength is attributed to the strong pinning effects of alumina particles on the grain and sub-grain boundaries with dislocations. The ultimate tensile strength can reach 237 MPa and the corresponding yield strength reaches 226 MPa at 700 °C. Tensile fracture morphology indicates that the ADSC alloy shows brittleness at elevated temperatures. Creep tests results demonstrate that the steady state creep rates at 400 °C are lower than those at 700 °C. The stress exponents at 400 °C and 700 °C are 7 and 5, respectively, and the creep strain rates of the ADSC alloy are controlled by dislocation core diffusion and lattice diffusion.
Key words: copper alloys; alumina dispersion strengthened alloy; high temperature mechanical behavior; creep behavior; fracture; strengthening mechanism
1 Introduction
Alumina dispersion strengthened copper (ADSC) alloys have attached wide attention due to their high strength and excellent creep properties at elevated temperatures. Reinforced alumina particles are finely dispersed in the copper matrix. They do not dissolve or coarsen even when the temperature is up to the melting point of copper. This can effectively hinder the motion of dislocations and sliding of grain boundary and extend the using temperature range of the copper alloy [1]. Therefore, ADSC alloys have been widely used in many fields such as contacts, lead wires, vacuum technique parts and electrical conductors employed at high temperatures [2,3]. Many investigations have been done to characterize ADSC alloys, which were mainly concentrated on the preparation methods and recrystallization behaviors [4-6]. However, the microstructure and its effects on the mechanical properties of ADSC alloy are still not clear. SONG et al [7] studied the influence of annealing treatment on properties and structures, They found that both high cold work deformation degree and high alumina content lead to high hardness of ADSC alloy under annealing treatment. TIAN et al [8] investigated the high- temperature tensile properties and fracture of Cu- 0.5%Al2O3 composite. The results showed that Al2O3 particles could limit the nuclei formation of recrystallization process at elevated temperature. But the effect of fine-grain strengthening was not taken into consideration. GUO et al [9,10] studied the cold rolling effects on properties, microstructures, tensile fracture and found that the mechanical properties of the material were related to its anisotropy. The high temperature tensile properties and creep behaviors of ADSC alloy are very important in many application areas. Nonetheless, few researches have been performed on it so far.  et al [11] discussed the creep behaviors of Cu-1.5%Al2O3 alloy in two distinctly different temperature intervals, and the results showed that creep mechanism was sensitive to the temperature. Nevertheless, the effect of microstructure on creep properties was ignored in that situation. The nano- indentation creep of ultrafine-grained Al2O3 particle reinforced copper composites was also investigated by SONG et al [12], and the stress exponent determined by nano-indentation creep was much larger than that determined by traditional uniaxial tensile or compressive creep.
et al [11] discussed the creep behaviors of Cu-1.5%Al2O3 alloy in two distinctly different temperature intervals, and the results showed that creep mechanism was sensitive to the temperature. Nevertheless, the effect of microstructure on creep properties was ignored in that situation. The nano- indentation creep of ultrafine-grained Al2O3 particle reinforced copper composites was also investigated by SONG et al [12], and the stress exponent determined by nano-indentation creep was much larger than that determined by traditional uniaxial tensile or compressive creep.
In order to broaden the temperature range of applications, both tensile and creep properties of ADSC with high content of nano-scale alumina at elevated temperatures were investigated in this work. In situ X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was performed to determine the structure transformation of alumina during heating. Steady state creep behaviors were studied at 400 °C and 700 °C to figure out the creep mechanism. Tensile fracture and distribution of alumina particles in the matrix were examined.
2 Experimental
The experimental ADSC alloy was produced by internal oxidation, and the fabrication procedure was as follows: Cu-0.6%Al (mass fraction) alloy induction melting → nitrogen atomization → mixing of Cu-Al alloy and oxidant → internal oxidation at 1000 °C for 1 h → hydrogen reduction at 900 °C for 1 h → vacuum hot-pressing (950 °C for 3 h, under a pressure of 27 MPa and vacuum of 1.33×10-2 Pa) → packaging the billet with pure copper → hot-extrusion at 930 °C into bars (extrusion ratio 20:1). The extruded bars were annealed at 900 °C for 1 h in the argon atmosphere to eliminate internal stress and homogenize the microstructure.
The specimens with the size of 5 mm in diameter and 25 mm in length were machined from the annealed bars for tensile and creep experiments. Tensile and creep tests were conducted on a computer-controlled universal WSM-200kN testing machine. The temperature fluctuations were controlled within ±0.5 °C. The loading direction was parallel to the extrusion direction. After chemical etching in solution containing 5 g FeCl3, 25 mL HCl and 200 mL C2H5OH, metallographic observation was operated using a Leica EC3 optical microscope. Microstructures observation was carried out on a JEM-2100F transmission electron microscope (TEM) with operation voltage of 200 kV. In situ XRD experiments were carried out on a Rigaku D/max diffractometer using Cu Kα radiation by heating the sample successively from 25 to 800, 900, 1000 and 1100 °C respectively. The scanning speed was 2 (°)/min with a range of 20°-80°. Tensile fracture morphology observations were performed on a Sirion 200 scanning electron microscope (SEM).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure
Figure 1 shows the microstructures of the annealed ADSC alloy. Perpendicular to the extrusion direction of the sample, the microstructure exhibits fine grains (Fig. 1(a)). Grains are elongated along with the extrusion direction and fiber-like tissues are formed (Fig. 1(b)).
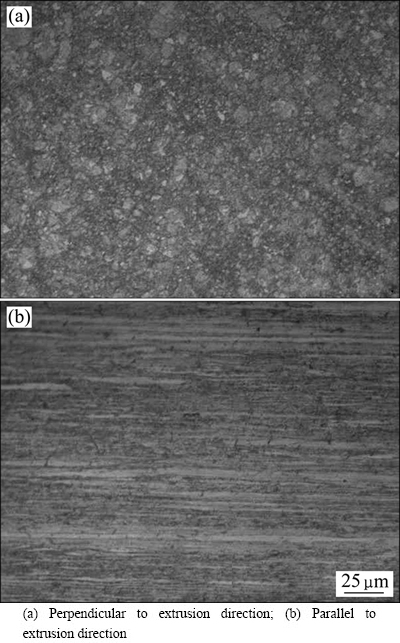
Fig. 1 Optical micrographs of annealed ADSC alloy
Figure 2 shows the TEM images of the annealed ADSC alloy. Alumina particles with size of about 25 nm are distributed in the matrix grain evenly (Fig. 2(a)). A few coarse alumina particles with size of about 80 nm are presented on the grain boundaries (Fig. 2(c)). The indexation of selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of fine alumina particles indicates that they are γ-Al2O3 phase (Fig. 2(b)). The grain size of the fine grains varies from 0.2 to 0.5 μm (Fig. 2(d)).
3.2 XRD analysis
In order to investigate phase transition temperature of Al2O3 particles, the Al2O3 particles were extracted by dissolving ADSC specimen in 30% (volume fraction) HNO3 solution. XRD patterns of the extracted alumina particles from annealed ADSC alloy at different temperatures are shown in Fig. 3. When the testing temperature is below 1000 °C, the structures of alumina are α, γ and θ, and no transformation among the different kinds of alumina phase occurs. While γ- and θ-Al2O3 phases are transformed into α-Al2O3 as the temperature is high than 1000 °C. When heated up to 1200 °C, there is only α-Al2O3 phase.
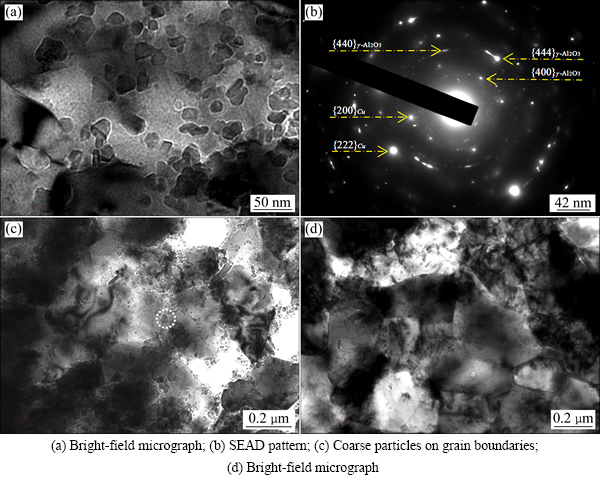
Fig. 2 TEM images of annealed ADSC alloy
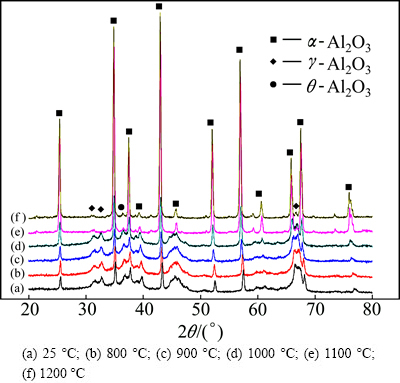
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of extracted alumina particles from ADSC alloy after being heated at different testing temperatures for 1 h
3.3 Mechanical properties
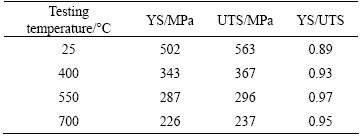
Figure 4 shows the tensile test results of ADSC alloy at different temperatures, the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and yield strength (YS) of ADSC alloy are listed in Table 1. The ultimate tensile strength decreases with the increase of testing temperature. The tensile strength tested at 700 °C is 237 MPa, while that tested at 25 °C is 563 MPa.
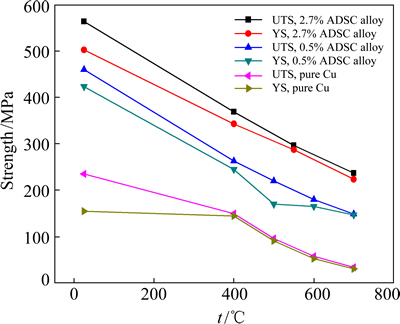
Fig. 4 UTS and YS of ADSC alloy tested at different testing temperatures (UTS and YS of copper and Cu-0.5%Al2O3 are from Ref. [8])
As shown in Fig. 4, the UTS and YS of ADSC alloy decrease with the increase of temperature, while the ratio of YS to UTS increases with the temperature increasing (Table 1). This might be related to the effect of alumina particles. As pointed out by TIAN et al [8], the main contributions of alumina particles to the elevated temperature strength are the strong pinning effects on the grain boundaries and sub-grain boundaries with high density dislocations.
Table 1 Ultimate tensile strength and yield strength of ADSC alloy tested at different testing temperatures
3.4 Creep behaviors
Creep curves of ADSC alloy the annealed at 400 °C and 700 °C under different stresses are shown in Fig. 5. It takes longer time to approach the steady state creep stage as tested at 400 °C with given applied stresses compared with these tested at 700 °C. At the same time, the steady state creep rates at 400 °C are also slower than those at 700 °C. Because dislocation movement occurs more easily by thermal activation at elevated temperature. ADSC alloy possesses better creep resistance at 400 °C. All the creep data under different testing conditions are summarized in Table 2.
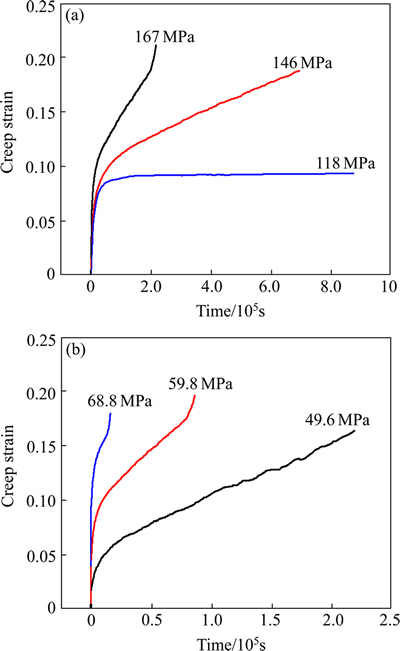
Fig. 5 Creep curves of ADSC alloy tested at 400 °C (a) and 700 °C (b) with different stresses
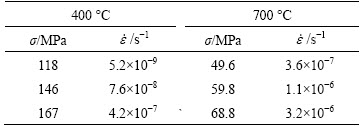
Table 2 Steady state creep rates  of ADSC alloy measured at different temperatures and applied stresses σ
of ADSC alloy measured at different temperatures and applied stresses σ
The power-law relationship for above creep curves is as follows [13]:
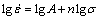 (1)
(1)
where  is the steady state creep rate, n is the stress exponent, σ is the applied stress and A is a constant. According to Eq. (1), the steady state creep rates and the applied stresses are depicted with a double-logarithmic relationship (Fig. 6). The steady state creep rates in ADSC alloy at both temperatures are much lower than those in pure copper. The creep strain rate is controlled by dislocation core diffusion in ADSC copper and the stress exponent n is close to 7 as tested at 400 °C; while the creep strain rate is controlled by lattice diffusion and the corresponding stress exponent is about 5 when tested at 700 °C. The results are similar with those reported by
is the steady state creep rate, n is the stress exponent, σ is the applied stress and A is a constant. According to Eq. (1), the steady state creep rates and the applied stresses are depicted with a double-logarithmic relationship (Fig. 6). The steady state creep rates in ADSC alloy at both temperatures are much lower than those in pure copper. The creep strain rate is controlled by dislocation core diffusion in ADSC copper and the stress exponent n is close to 7 as tested at 400 °C; while the creep strain rate is controlled by lattice diffusion and the corresponding stress exponent is about 5 when tested at 700 °C. The results are similar with those reported by  et al [11].
et al [11].
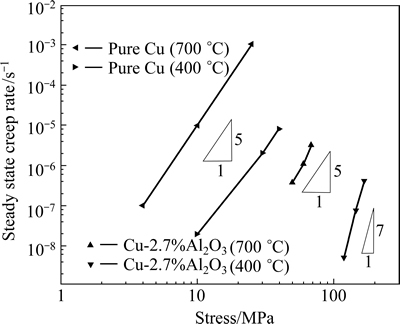
Fig. 6 Relationship between steady state creep rates  and applied stresses σ for ADSC alloy tested at 400 °C and 700 °C compared with that of pure copper [14]
and applied stresses σ for ADSC alloy tested at 400 °C and 700 °C compared with that of pure copper [14]
3.5 Tensile fracture
The tensile fracture mode of ADSC alloy at room temperature is observed and shown in Fig. 7. The dimples are predominant with a few transcrystalline fracture. A few particles with size of about 80 nm situated in the dimples (marked by arrow), which are the internal oxidized alumina particles and result in the nucleation of micro-crack due to incoherence plastic deformation.
Tensile fractures of ADSC alloy at different temperatures are shown in Fig. 8. In the tensile fractograph of the alloy tested at 25 °C, the undeveloped dimples on the fracture surface can be observed, which indicates that stress concentration presents here and eventually results in the fracture of material (Fig. 8(a)). The morphology at 400 °C is flatter than that at 25 °C (Fig. 8(b)), and more developed dimples appear on the fracture surface. For the synergistic deformation between the alumina particles and the matrix, more heavy stress concentration presents before the final fracture. Meanwhile, thermal activation results in stress relaxation around the interfaces between alumina and copper. The reinforced alumina particles become the source of cracks and final fracture occurs there. When the alloy is tested at 550 °C, the binding strength between alumina particles and the matrix copper decreases rapidly with the increasing temperature before the failure of the alloy, and the proportion of transcrystalline fracture increases (Fig. 8(c)). The proportion of transcrystalline fraction further increases when tested at 700 °C (Fig. 8(d)), and inhomogeneous plastic deformation occurs in the whole composite matrix.
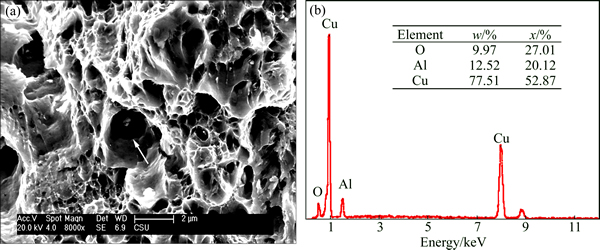
Fig. 7 Tensile fracture morphology of ADSC alloy tested at 25 °C (a) and EDS spectrum of particle marked by arrow in Fig. 7 (b)
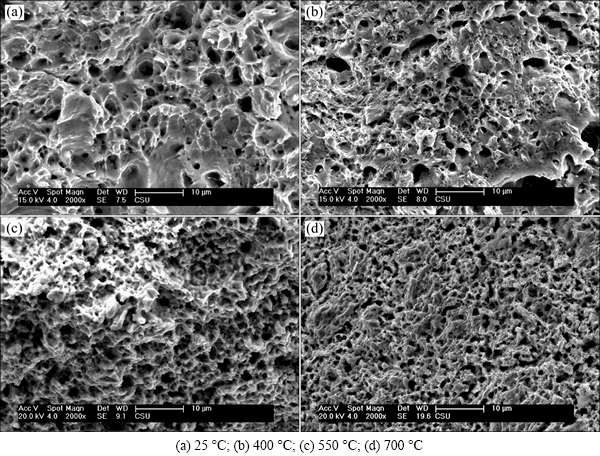
Fig. 8 Tensile fractograhs of ADSC alloy tested at different temperatures
3.6 Strengthening mechanism
The high strength of ADSC alloy is due to grain boundary strengthening and the interaction of moving dislocation and dispersively distributed alumina particles when tested at low temperatures (<400 °C). However, both grain refining strengthening and grain boundary strengthening would decrease with increasing the testing temperature. Diffusion can easily take place through the grain boundaries for the irregular arrangement of atoms on them. Thus, the grain boundary strengthening decreases rapidly and the sliding of grain boundary occurs. Meanwhile, inhomogeneous deformation occurs between the alumina particles and the matrix copper, which would cause stress concentration. At room temperature, the strengthening effects of dispersion strengthened alloys are mainly related to the alumina particles and the grain size. According to HOLZWARTH and STAMM [15], the increment of critical resolved shear stress (Δτ0) produced by the interaction of moving dislocation and dispersion distributed alumina particles is as follows:
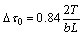 (2)
(2)
where T is the line tension of the dislocation line. For the residual concentration of aluminum solid solution atoms is very low, the line tension values are those of pure copper. The values are different for edge and screw dislocations with 1.0×10-9 N and 2.5×10-9 N, respectively [16]. b is the modulus of its Burgers vector, and L is the mean interparticle spacing of dispersion distributed alumina particles decided by the volume fraction f and average radius r. So, Δτ0 could be expressed as [8]
 (3)
(3)
The average radius of alumina particles r is 12.5 nm (Fig. 2(a)), the volume fraction f is 2.7% and b is 2.56×10-10 m for unit dislocation in copper matrix [17]. The increments of the critical resolved shear stress of Δτ0=60 MPa for edge dislocations and 150 MPa for screw dislocations are obtained, which are about 12% and 30% of the composite’s yield strength. In other words, the alumina particles maintain the strength of ADSC alloy to some extent. Dislocations require greater stress to overcome obstacles and move forward. So, the strength of ADSC is higher than that of pure copper. Furthermore, according to the Hall-Petch equation:
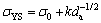 (4)
(4)
where σ0=40 MPa is the total resistance of the dislocation motion in single crystals of copper, and k=0.19 MPa·m1/2 [18], da is the average grain size of the composite. The grains are usually grown abnormally at elevated temperatures for ADSC alloy, but the results show that fine grains are stable at high temperatures due to the grain boundary pinning effect of alumina particles [19]. According to ZHAO et al [20], da could be calculated by the following equation:
 (5)
(5)
where df=0.3 μm is the average grain size of the fine grained region from the typical image shown in Fig. 2, dc=4 μm is the average grain size of the coarse grained region and fc=0.5 is the area fraction of the coarse grained region (from Fig. 1(a)). The contribution of grain boundary strengthening to the yield strength σYS is calculated to be 294 MPa according to Eqs. (4) and (5), which is more than half of the composite’s yield strength. In sum, the overall strengthening effect of the interaction of moving dislocation and dispersively distributed alumina particles and Hall-Petch mechanism can reach 354 MPa (edge dislocations) and 444 MPa (screw dislocations), which are about 70% and 88% of the composite’s yield strength. It can be concluded that the above two mechanisms are the main contributions to the yield strength of ADSC alloy at room temperature. Moreover, the screw dislocations in ADSC alloy should be dominated, because the calculated yield strength using screw dislocation mode is more close to the experimental results. The rest might be attributed to some coarse alumina particles and other strengthening mechanisms such as strengthening effect of enhanced dislocation density due to the residual plastic strain caused by thermal expansion mismatch between the matrix and reinforcement particles and between processing and testing temperatures [21].
4 Conclusions
1) Fine alumina particles distribute homogeneously within the matrix grain. A few coarse alumina particles are merely presented on the boundaries. α, γ and θ alumina particles coexist in ADSC alloy as the temperature is lower than 1000 °C. Phase transition among these alumina particles only occurs above 1000 °C.
2) Tensile cracks generate around the alumina particles because of the inconsistency between alumina particles and matrix during deformation. Furthermore, the plasticity of ADSC alloy decreases at elevated temperatures.
3) Due to the existence of alumina particles, the effect of strengthening of ADSC alloy is rather dramatic compared with the pure copper. By analyzing the steady state creep, the stress exponent is close to 5 at 700 °C and is close to 7 at 400 °C for the ADSC alloy.
References
[1] LIANG Shu-hua, FAN Zhi-kang, XU Lei, FANG Liang. Kinetic analysis on Al2O3/Cu composite prepared by mechanical activation and internal oxidation [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2004, 35(12): 1441-1446.
[2] MOTTA M S, JENA P K, BROCHI E A,  L G. Characterization of Cu-Al2O3 nano-scale composites synthesized by in situ reduction [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2001, 15(1-2): 175-177.
L G. Characterization of Cu-Al2O3 nano-scale composites synthesized by in situ reduction [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2001, 15(1-2): 175-177.
[3] LEE J S, KIM Y C, LEE S, KIM N J, AHN S. Correlation of the microstructure and mechanical properties of oxide-dispersion- strengthened coppers fabricated by internal oxidation [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2004, 35(2): 493-502.
[4] MANDAL D, BAKER I. On the effect of fine second-phase particles on primary recrystallization as a function of strain [J]. Acta Materialia, 1997, 45(2): 453-461.
[5] KIM S H, LEE D N. Annealing behavior of alumina dispersion-strengthened copper strips rolled under different conditions [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, 33(6): 1605-1616.
[6] BAKER I, LIU L, LEE L. The effect of internal oxidation on the stored energy and recrystallization of copper single crystals [J]. Scripta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1994, 30(9): 1167-1170.
[7] SONG Ke-xing, XING Jian-dong, TIAN Bao-hong, LIU Ping, DONG Qi-ming. Influence of annealing treatment on properties and microstructures of alumina dispersion strengthened copper alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2005, 15(1): 139-143.
[8] TIAN B H, LIU P, SONG K X, LIU Y, REN F Z, SU J H. Microstructure and properties at elevated temperature of a nano-Al2O3 particles dispersion-strengthened copper base composite [J]. Material Science and Engineering A, 2006, 435-436: 705-710.
[9] GUO M X, WANG M P, SHEN K, CAO L F, TAN W. Tensile fracture behavior characterization of dispersion strengthened copper alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 469(1-2): 488-498.
[10] GUO Ming-xing, WANG Ming-pu, SHEN Kun, CAO Ling-fei, LEI Ruo-shan, LI Shu-mei. Effect of cold rolling on properties and microstructures of dispersion strengthened copper alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18: 333-339.
[11]  Creep in copper dispersion strengthened with alumina particles (ODS copper) [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 348(1-2): 170-179.
Creep in copper dispersion strengthened with alumina particles (ODS copper) [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 348(1-2): 170-179.
[12] SONG M, LIU Y, HE X Y, BEI H B, HU W P, LIU F, LI Z. Nanoindentation creep of ultrafine-grained Al2O3 particle reinforced copper composites [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 560: 80-85.
[13] SCHNEIBEL J H, LIU C T, MILLER M K, MILLS M J, SAROSI P, HEILMAIER M, STURM D. Ultrafine-grained nanocluster- strengthened alloys with unusually high creep strength [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2009, 61(8): 793-796.
[14] RAJ S V, LANGDON T G. Creep behavior of copper at intermediate temperatures-I. Mechanical characteristics [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1989, 37(3): 843-852.
[15] HOLZWARTH U, STAMM H. The precipitation behaviour of ITER-grade Cu–Cr–Zr alloy after simulating the thermal cycle of hot isostatic pressing [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2000, 279(1): 31-45.
[16] MUGHRABI H, BRULIN I O, HSIEH R K T. Continuum models of discrete systems [M]. Amsterdam North-Holland, 1981: 241.
[17] COULOMB P. Comment on graphs relating some property to stacking fault energy [J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1981, 15(7): 769-770.
[18] AFSHAR A, SIMCHI A. Flow stress dependence on the grain size in alumina dispersion-strengthened copper with a bimodal grain size distribution [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 518(1-2): 41- 46.
[19] AFSHAR A, SIMCHI A. Abnormal grain growth in alumina dispersion-strengthened copper produced by an internal oxidation process [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 58(11): 966-969.
[20] ZHAO M C, YIN F X, HANAMURA T, NAGAI K, ATRENS A. Relationship between yield strength and grain size for a bimodal structural ultrafine-grained ferrite/cementite steel [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57(9): 857-860.
[21] ZHANG Z, CHEN D L. Consideration of Orowan strengthening effect in particulate-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites: A model for predicting their yield strength [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 54(7): 1321-1326.
高浓度氧化铝弥散强化铜合金的高温力学行为
向紫琪1,李 周1, 2,雷 前1,肖 柱1,庞 咏1
1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:研究Cu-2.7%Al2O3弥散强化铜合金的微观组织及其高温力学行为。结果表明:细小的Al2O3粒子均匀分布在铜基体当中,部分粗大的Al2O3粒子分布在晶界上。拉伸试验表明Hall-Petch机制是影响氧化铝弥散强化铜合金室温屈服强度的主要因素,其高温强度主要由于Al2O3粒子对晶界和亚晶界与位错的强烈钉扎作用。合金在700 °C下的抗拉强度和屈服强度分别达到237 MPa和226 MPa。拉伸断口表明弥散强化铜合金显示出高温脆性。蠕变测试表明400 °C下的稳态蠕变速率比700 °C下的稳态蠕变速率小很多,其400 °C和700 °C的蠕变应力指数分别为7和5,蠕变机制为位错核心扩散型和晶格扩散型蠕变。
关键词:铜合金;氧化铝弥散强化合金;高温力学行为;蠕变行为;断口;强化机制
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (51271203) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; the PPP project between the CSC (China Scholarship Council) and the DAAD (German Academic Exchange Service), Project (11JJ2025) supported by Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (YSZN2013CL06) supported by the Nonferrous Metals Science Foundation of HNG-CSU Project supported by the Aid program for Science Technology Innovative Research Team in Higher Educational Institutions of Hunan Province, China
Corresponding author: Zhou LI; Tel: +86-731-88830264; Fax: +86-731-88876692; E-mail: lizhou6931@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63622-6