氧气底吹铜熔炼过程多相平衡模拟
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2017年第11期
论文作者:王亲猛 郭学益 王松松 廖立乐 田庆华
文章页码:2503 - 2511
关键词:多相平衡模拟;氧气底吹铜熔炼;SKS工艺;元素分配
Key words:multiphase equilibrium modeling; oxygen bottom-blown copper smelting; SKS process; element distribution
摘 要:基于氧气底吹工艺特性和最小吉布斯自由能原理,构建了氧气底吹铜熔炼热力学计算模型。模拟结果表明:在给定的稳定生产条件下,铜锍中Cu、Fe和S含量分别是71.08%、7.15%和17.51%,渣中Fe、SiO2和Cu含量分别是42.17%、25.05%和3.16%。微量元素在底吹熔炼过程中气相、渣相和铜锍相三相间的模拟分配比例为:砷82.69%、11.22%和6.09%;锑16.57%、70.63%和12.80%;铋68.93%、11.30%和19.77%;铅19.70%、24.75%和55.55%;锌17.94%、64.28%和17.79%。将模拟结果和实际生产数据进行验证,结果一致,表明了该多相平衡热力学计算模型具有可靠性,可以指导氧气底吹铜熔炼生产实践,优化工艺操作参数。
Abstract: A computational thermodynamics model for the oxygen bottom-blown copper smelting process (Shuikoushan, SKS process) was established, based on the SKS smelting characteristics and theory of Gibbs free energy minimization. The calculated results of the model show that, under the given stable production condition, the contents of Cu, Fe and S in matte are 71.08%, 7.15% and 17.51%, and the contents of Fe, SiO2 and Cu in slag are 42.17%, 25.05% and 3.16%. The calculated fractional distributions of minor elements among gas, slag and matte phases are As 82.69%,11.22%, 6.09%, Sb 16.57%, 70.63%, 12.80%, Bi 68.93%, 11.30%, 19.77%, Pb 19.70%, 24.75%, 55.55% and Zn 17.94%, 64.28%, 17.79%, respectively. The calculated results of the multiphase equilibrium model agree well with the actual industrial production data, indicating that the credibility of the model is validated. Therefore, the model could be used to monitor and optimize the industrial operations of SKS process.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 2503-2511
Qin-meng WANG1, Xue-yi GUO2, Song-song WANG2, Li-le LIAO2, Qing-hua TIAN2
1. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 27 July 2016; accepted 21 June 2017
Abstract: A computational thermodynamics model for the oxygen bottom-blown copper smelting process (Shuikoushan, SKS process) was established, based on the SKS smelting characteristics and theory of Gibbs free energy minimization. The calculated results of the model show that, under the given stable production condition, the contents of Cu, Fe and S in matte are 71.08%, 7.15% and 17.51%, and the contents of Fe, SiO2 and Cu in slag are 42.17%, 25.05% and 3.16%. The calculated fractional distributions of minor elements among gas, slag and matte phases are As 82.69%,11.22%, 6.09%, Sb 16.57%, 70.63%, 12.80%, Bi 68.93%, 11.30%, 19.77%, Pb 19.70%, 24.75%, 55.55% and Zn 17.94%, 64.28%, 17.79%, respectively. The calculated results of the multiphase equilibrium model agree well with the actual industrial production data, indicating that the credibility of the model is validated. Therefore, the model could be used to monitor and optimize the industrial operations of SKS process.
Key words: multiphase equilibrium modeling; oxygen bottom-blown copper smelting; SKS process; element distribution
1 Introduction
The oxygen bottom-blown copper smelting process is a newly developed technology for copper smelting, which is originally from the Shuikoushan (SKS) copper smelting method, and the intellectual property belongs to China. Recently, this copper smelting technology is widely adopted by copper companies due to its significant advantages over other copper smelting technology [1,2], such as higher oxygen enrichment, lower slag copper content, stronger adaptability of raw materials, higher efficiency of pyretic smelting and easily controlled matte grade. The main equipment of the SKS process is a d4.4 m × 16.5 m horizontal cylindrical airtight reactor as shown in Fig. 1, similar to the Noranda and Teniente furnace [3].
Because the copper concentrates are becoming lower grade and more complex, which contain multifarious impurity elements such as arsenic, lead and zinc. Interest in the deportment of those elements between phases is growing. Investigation on the process multiphase equilibrium is essential to make it clear, and the concern now is mainly focused on two aspects. One is the existing form and behavior of both minor and major elements as well as intensification of the elements distribution for further poly-metallic extraction or disposal during the smelting process. The other is the efficient and reliable algorithm for solving the complex multiphase equilibrium model. In the copper metallurgical area, GOTO et al [4-6] developed a basic copper multiphase equilibrium model and then improved it. TAN et al [7] solved the model using a modified form of the Newton-Raphson technique and applied it to the various copper pyro-metallurgy processes to simulate the distribution behaviors of Ni, Zn, As, Sb, Bi, etc. The model [8] for the Isasmet process is based on the concept that there were two independent reaction sites in a slag bath: one for fast oxidation and the other for slow reduction. In this model the oxidizing and reducing reactions were assumed to proceed under a separate set of equilibrium conditions. TONG et al [9] simplified the model development to some extent and deduced element- potential-based copper flash smelting multiphase equilibrium to calculate equations using the element potential concept coupled with the Gibbs function principle, and solved it with RAND algorithm. But the correctness of the results was closely determined by the algorithm’s initial values. WEI et al [10] used modified τ-method, LIN et al [11] used genetic algorithm and XU et al [12] used one-step algorithm for the chemical multiphase equilibrium calculation, but all the algorithms used were only allowed to handle the variable numbers below ten as it was quite time consuming.
Up to date, no work on the computational thermodynamics model considering the characteristics of SKS process has been reported. In this work, we developed a multiphase equilibrium model based on the thermodynamic principle of Gibbs energy minimization and the characteristics of SKS process, which could be used to optimize the industrial operations of SKS process.
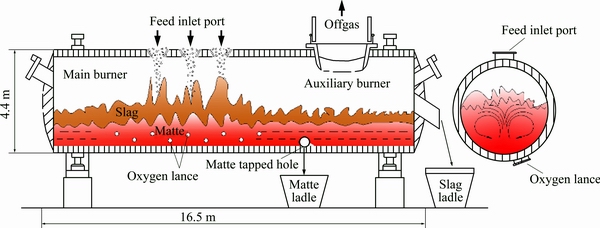
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of SKS furnace
2 Establishment of SKS thermodynamic model
2.1 Thermodynamic theory for model establishment
The SKS process is a typical multiphase and multicomponent system coupling with various chemical reactions. According to the second law of thermodynamics, spontaneous reaction always conducts towards the direction that the total Gibbs free energy decreases. An isothermal and isobaric chemical system is at equilibrium when the total Gibbs free energy is minimized [13]. It is assumed that the SKS process is under the isothermal and isobaric condition and reaches its thermodynamic equilibrium, so the total Gibbs free energy of the SKS system attains its minimization.
The total Gibbs free energy function [14] for a multiphase and multicomponent system can be expressed as
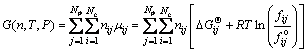 (1)
(1)
where Np and Nc are the number of phases and component in phases, respectively; nij is the mole number of component i in phase j; μij is the partial molar Gibbs free energy, i.e., chemical potential of component i in phase j in the system conditions, which is composed of two parts to modify its non-ideality, one part is 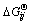 , the standard Gibbs free energy of formation of component i in phase j under the system temperature and standard pressure. This modifies the impact of temperature on the standard Gibbs free energy [13] and can be calculated by
, the standard Gibbs free energy of formation of component i in phase j under the system temperature and standard pressure. This modifies the impact of temperature on the standard Gibbs free energy [13] and can be calculated by
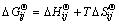 (2)
(2)
The other part is RTln(fij/f o ij), which modifies the influence of pressure or concentration under non-ideal condition on the standard Gibbs free energy; R is mole gas constant; T is the thermodynamic temperature in Kelvin; fij is the partial fugacity of component i in the phase j; f o ijis the fugacity of component i in the phase j at reference state. The value of fugacity is depended on the system temperature and pressure. In the SKS process, the gas phase is treated to be ideal. The high temperature melts are non-ideal liquid solutions, therefore, activity coefficient is introduced to substitute fugacity to modify the chemical potential of constituents in real solution against the in-adaptation of the ideal solution. So, the fugacity of components in molten phase and gas phase can be expressed by [14,15]
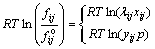 (3)
(3)
where λij and xij are respectively the activity coefficient and mole fraction of component i in the phase j. yij is the partial pressure of component i in the gas phase and p is the total pressure of the gas phase.
At the same time, according to the element conservation law principle, the inputs of elements to the system should be equal to the outputs and the mole number of each component should be above zero. So, the multiphase equilibrium thermodynamic model is established and the component content at equilibrium can be obtained by finding the minimum value of the total Gibbs free energy under the specific operation conditions with the input and output constraints of elements.
2.2 Mathematic modeling in SKS process
2.2.1 Model assumption
In the SKS process, the elements of Cu, Fe, S, O, N, H, Si, As, Sb, Bi, Pb, Zn, Mg, Ca and Al are taken into consideration for multiphase equilibrium calculation in account of the actual plant production. When the system is close to equilibrium, three independent stable phases include matte, slag and gas phase. The assumptions made are listed below and incorporated the consideration of practical situations [7].
1) The SKS system is approximately under the isothermal and isobaric airtight conditions.
2) The smelting temperature is around 1473 K (1200 °C).
3) The components were taken into consideration in the matte phase including Cu2S, Cu, FeS, FeO, Fe3O4, Pb, PbS, ZnS, As, Sb and Bi.
4) The components were take into consideration in the slag phase including FeO, Cu2S, Cu2O, Fe3O4, FeS, PbO, ZnO, As2O3, Sb2O3, Bi2O3, SiO2, CaO, MgO and Al2O3.
5) The components were taken into consideration in the gas phase including SO3, SO2, S2, O2, N2, H2O, PbO, PbS, Zn, ZnS, As2, AsO, AsS, SbO, SbS and Bi2O3.
6) The components of H2O and SiO2 are all in the gas and slag phase, respectively.
2.2.2 Consideration for behavior of S2
In the SKS process, the copper sulfide concentrates and flux are fed into the top of furnace, and the concentrates decompose into Cu2S, FeS, S2, etc [16]. The Cu2S and FeS sink to form the matte layer, and S2 decomposes directly into the gas phase. Because of the special route, the oxygen is blown into the furnace, the decomposed S2 can hardly get full contact and react with the oxygen, and a large portion of S2 passes into the flue directly. Theoretically, the chemical multiphase equilibrium calculation is based on the assumption that the substances are fully in contact. However, the real truth is that quite quantities of S2 is too late to react with the oxygen and directly passes into the flue in the SKS process. So, it should be taken into consideration in the copper multiphase equilibrium calculation to achieve more precise and reliable results.
2.2.3 Consideration for mechanical entrainment
During the period of copper concentrates smelting and further copper matte converting, they produce slag containing copper in dissolved forms as well as mechanically entrained forms. But most times, the copper in dissolved forms is much less than the mechanically entrained inclusions. It is worth mentioning that the mechanically entrained inclusions are influenced by many factors, such as the operation specification, the specific gravity and viscosity of the melts, the clarification time. Due to the multiphase equilibrium model not depicting the mechanically entrained inclusions parts, we draw lessons from NAGAMORI and MACKEY [17] and establish a copper mechanical entrainment model that suits the SKS process as follows, Eq. (4) for slag entrainment in matte phase and Eq. (5) for matte entrainment in slag phase:
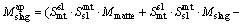
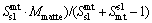 (4)
(4)
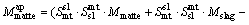
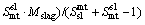 (5)
(5)
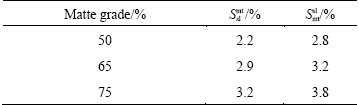
where Mslag and Mmatte are respectively the calculated mass of slag and matte phase at equilibrium; M ap slag and M ap matte are the calculated apparent slag mass to the matte phase and matte mass to the slag phase, respectively; Smt sl and Ssl mt are respectively the entrainment coefficient for the slag to matte phase and the matte to slag phase, which are derived based on the actual plant production data and experience. The entrainment coefficients for the slag to matte phase and the matte to slag phase are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Phase entrainment coefficient in SKS process
2.3 Data for SKS multiphase equilibrium calculation
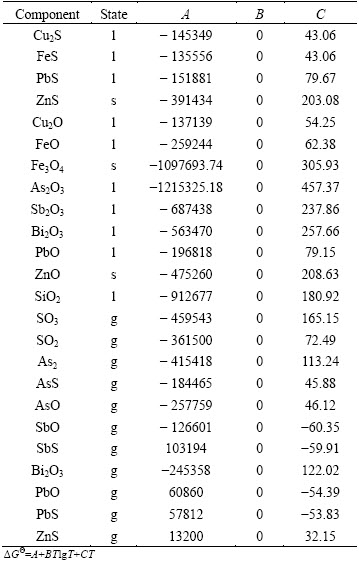
The activity coefficients of each component in the specified phase selected from Refs. [5,7,8,18-20] are listed in Table 2, which are crucial in the SKS process multiphase equilibrium calculation. wCu refers to matte grade and NCu2S, NCu2O, NFeO, NFe3O4, NSiO2 refer to mole fraction of Cu2S, Cu2O, FeO, Fe3O4 and SiO2, respectively. The standard Gibbs free energies of formation of each component are listed in Table 3, which are chosen from the database of HSC chemistry software for Windows.
Table 2 Activity coefficient of component in SKS process

3 Design of HLPSO algorithm for SKS model
The SKS process multiphase equilibrium model developed in Section 2 is a classical single objective optimization problem with linear constraints. But the problem is intricate somehow with hyper-high dimensional variables and its objective function is complex and non-convex, which can be summarized by
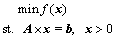 (6)
(6)
where A is the coefficient matrix of the linear equality constrains, b is a constant vector and f(x) is the objective function. The search space is x>0, each point x in the search space that satisfies the linear equality constraints is called a feasible point. Here in the SKS multiphase equilibrium model, the objective function f(x) is equal to the total Gibbs free energy of the system. The matrix A is composed of the components’ stoichiometric numbers and b is composed of total input element mole numbers. The x is composed of the current mole numbers of component that should be non-negative at equilibrium. Owing to the problem to be handled is multivariable and non-convex and has multiple local minima, and it is believed that the stochastic global optimization method will be more reliable and desirable for this kind of problem [21]. So, in this section, an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm for the hyper-high dimensional variable and linear constrains (HLPSO) problem is developed, which will be discussed in detail as follows. The standard particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm is not related here and can be acquired from Ref. [22].
Table 3 Standard Gibbs free energy of formation of each component
3.1 Constraint handling mechanism
The most common method of constraint handling is using penalty function [23] by adding a penalty to the objective function to decrease the quality of infeasible solutions, and hence the constrained problem can be transformed to an unconstrained one. But due to the designated type of mathematic model developed in Section 2 that only contains a set of equality linear constraints by the form Ax=b, here, we devised a strategy firstly by initializing the swarm particles within the constrained hyper-plane [23-25]. Then, by the velocity update mechanism, all particles are kept only flying within this constrained hyper-plane at each iteration. This kind of strategy is especially effective for hyper-high dimensional problems, because the swarm detect the solution only confined in the feasible space rather than the whole search space.
3.1.1 Initializing of swarm
Owing to the given conditions that A≥0 and b≥0, the variable x must be confined that within the upper limit to guarantee all members in x are above zero. Hence, the upper limit of member j in x can be calculated by
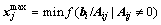 (7)
(7)
Supposing that the matrix A is a m×n matrix and the rank of matrix A is m, so we choose m linearly independent columns from matrix A to form the square matrix B, and the rest n-m columns to form the matrix C. Similarly, vector variable x is split into [xB; xC], where xB and xC are called as basic and non-basic variables, respectively. Hence, the linear constraints A·x=b can be transformed into Eq. (8). The non-basic variable xC is randomly assigned within the confined interval 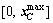 , and then the xB can be attained by Eq. (9):
, and then the xB can be attained by Eq. (9):
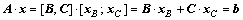 (8)
(8)
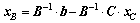 (9)
(9)
Examining if all members in xB are above zero, if not, repeating the process by randomly assigning the non-basic variable xC and calculating xB until all members in x are above zero. After the above steps, the x will be a feasible position that lies in the hyper-plane defined by the linear equality constraints.
The next step is the initialization of velocity (v) and because the velocity is the solution to the homogeneous equations A·x=0, the velocity can be calculated by
v=x(t+1)-x(t) (10)
To avoid particle flying beyond the feasible region at the next particle position update, a restriction (called update step length) should be added to the velocity. The update step length λ can be acquired by
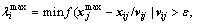
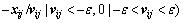 (11)
(11)
where ε is the calculation precision to avoid the divisor to be zero. If all particle updates follow the  , the local exploitation ability of the swarm will be slowly reduced during the iteration. So, a part of particles will be chosen to set the update step length as one when the
, the local exploitation ability of the swarm will be slowly reduced during the iteration. So, a part of particles will be chosen to set the update step length as one when the  >1. Then, the position update will follow Eq. (12):
>1. Then, the position update will follow Eq. (12):
xi(t+1)=xi(t)+λi·vi(t+1) (12)
When the member number of variable x is over 15, the initialization will take a long time to get the right x that satisfies the condition A·x=b and x>0. But most of the time, the matrix A always contains a number of element zero with low coupling relationship, so the matrix A can sometimes be decomposed into many vectors or small matrices. Hence, the initialization of swarm can be done by those vectors or small matrices.
3.1.2 Velocity update mechanism for the particles
Since the standard particle swarm optimization algorithm is only suited for unconstrained optimization, the velocity update follows the rules in Eq. (13). Each dimension of the particle’s velocity is updated by individually different uniform random numbers r1 and r2 between zero and one. In Eq. (13), w is called as inertia weight, vij(t+1) is the jth velocity dimension of particle i at the (t+1) times iteration, p(t) and g(t) are, respectively, so far the best position of particle and the best position of swarm:
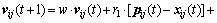
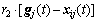 (13)
(13)
But in the HLPSO algorithm, to maintain that A·v=0 after the velocity update, the particle’s velocities of all dimensions are updated with a same random constant. It is somehow a simplification of the standard PSO and can be expressed by
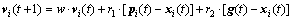 (14)
(14)
where vi(t+1) is the velocity of particle i at the (t+1) times iteration and the flight of the particles is defined by standard linear operations on vectors. It is supposed that after the t times iteration, the vi(t) satisfies A·vi(t)=0, and xi(t) is a feasible position. Since pi(t) and g(t) are chosen from the x(t), the [pi(t)-xi(t)] and the [g(t)-xi(t)] are the solution to the homogeneous equation Ax=0. As a result, the vi(t+1) is also the solution of the Ax=0 that still meets A·vi(t+1)=0.
From the above analyses, it can be concluded that if the swarm is initialized to a set of feasible solutions at first, all solutions are stipulated to be feasible when the swarm begins to search in the space.
3.2 Local best neighbor topology
Topology is important for the PSO performance, and profoundly affects the convergence and search capacity of the swarm. A better topology can improve the swarm’s ability of overall exploration to fight against premature convergence at early search stage, and ability of local exploitation to detect a more precise solution at the last search stage. The ring neighborhood structure [26] is commonly used by the PSO implementations and the neighbor of each particle is elaborately selected. The most common way of choosing the neighbor is that for each particle k, and a neighborhood of size n is composed by the next n/2 linked particles and n/2 previous particles. But this way of neighbor choosing is easily inclined to add the premature of the swarm. So, a topology called singly-linked ring neighborhood structure is preferred. For each particle k in the swarm, a neighborhood of size n is composed by the particles k+1, k-2, k+3, k-4, …, k+n-1 and k-n. The particle in between cancels the mutual attraction, and in consequence reduces the convergence of the swarm. A typical neighborhood of size 2 swarm is graphically presented as shown in Fig. 2.
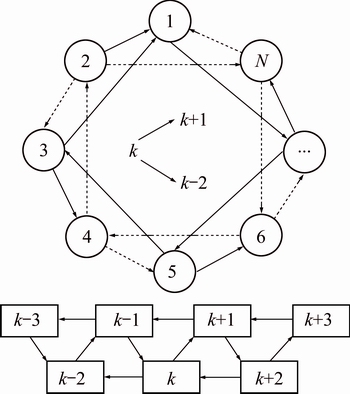
Fig. 2 Singly-linked ring neighborhood structure
From the strategy implementation above, the best neighbor for each particle i denoted as li can be obtained. So in the HLPSO, the update of the particle’s velocity can also use the information of the local best position. And it is revealed as Eq. (15):
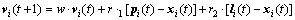 (15)
(15)
3.3 Perturbation to position and velocity
Perturbation to the optimal solution of the swarm denoted as p will keep the diversity of the swarm and guide the swarm towards good spots without destroying its original organization structure. Thus, only the historical best position of particles, i.e., p may be altered by the perturbation operators.
3.3.1 Perturbation to the best position
The perturbation to the current particle’s best position is implemented by linear combination of three particle’s position vectors to yield a set of temporal particle positions as shown in Eq. (16). Two of the particle’s positions are randomly selected from the current particle best position pool [27,28], and r is a random number between zero and one. The ptemp still meets A·ptemp=b after the perturbation, which is compared with its corresponding father pi next. If ptemp has a better adaptive value, then the pi gets updated using the value of ptemp:
ptemp=pi+r·(prand1-prand2) (16)
3.3.2 Perturbation to velocity
Perturbation to the current particle’s velocity[29] is implemented using a multi-dimension matrix named velocity stat matrix to yield a temporal velocity according to Eq. (17):
vtemp=vi·v/||v|| (17)
The matrix v is a m×m square matrix, m is the dimension of the swarm. The row of the matrix v is composed by m particle’s velocity vectors randomly selected from the current particle velocity pool. The current velocity is transformed into a new temporal velocity, and this transformation helps the particle to move to an arbitrary orientation around the current position, therefore strengthening the local exploitation ability of the particle. Meanwhile, the vtemp still meets A·vtemp=0, determining the update step length following the Eq. (11), and updating the ptemp as Eq. (18). Finally, by comparing the adaptive value with its corresponding father pi, if it wins, the ptemp is used to update the value of pi:
ptemp=pi+λ·vtemp (18)
3.4 Balance of overall exploration and local exploitation
To balance the particles’ ability of overall exploration and local exploitation, the inertia weight influence and velocity update strategy are carefully investigated. In general, the swarm needs higher overall exploration ability at early search stage, and higher local exploitation ability at the late search stage [30]. A higher inertia weight means a rapid movement of particles in the search space, so the inertia weight should be kept at a high level at the early stage and then slowly decrease to zero with the number of iteration times increase. The inertia weight w is calculated by
w=exp[-30(k/M)10] (19)
where M is the total number of the iteration times, and k is the current number of iteration times. The velocity is sectionalized and updated. During the first 90% of the iteration times, the velocity update follows Eq. (15) to gain a large swarm diversity, and during the last 10% of the iteration times, the velocity update follows Eq. (14) to quickly converge to the optimal solution. Thus, the particles are diverse and not prone to become premature at the early search stage, and can rapidly achieve convergence at the later search stage.
4 Results predication and model validation
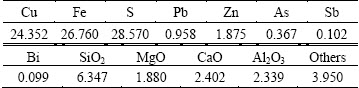
Initial conditions and operation parameters are adopted from a copper oxygen bottom blowing plant in China, which are crucial for the model calculation. The compositions of the mixed concentrates into the furnace are listed in Table 4, and the operation parameters in 2014 are listed in Table 5.
Table 4 Compositions of mixed concentrates into furnace (mass fraction, %)
The smelter mentioned above produced a high grade matte of above 70% and achieved autogenously smelting, resulting in less coal consumption. The multiphase equilibrium of the SKS process calculation is based on the above initial conditions and operation parameters. A set of the SKS plant monthly statistic industrial data under stable operation conditions in 2014 are chosen to compare with the predicted data, and the results are listed in Tables 6 and 7. Moreover, the mechanical entrainment coefficients in the model are obtained by the matte and slag analysis results in stable operation specifications, which is believed to be approximately to the current condition.
Table 5 Operation parameters for SKS process from a plant in China in 2014
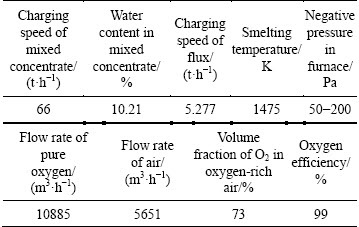
Tables 6 and 7 are comparisons of the predicted data with the actual plant data in the SKS process in 2014. From Table 6, most of the data between predicted and industrial values show a good agreement. The predicted and industrial matte grades are respectively 71.08% and 70.83%. The mass fractions of Fe in predicted and industrial matte are 7.15% and 7.31%, and in the slag are separately 42.17% and 42.58%. The results show that the predicted data of the matte and slag content are in good accordance with the actual industrial plant data, even including the minor elements, such as Pb, Zn, As, Sb and Bi.
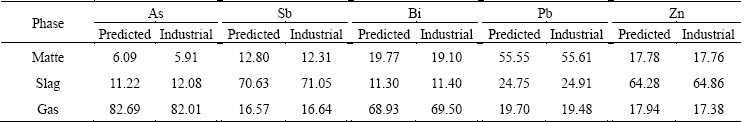
From Table 7, a good agreement of minor element distribution is among the matte, slag and gas phases between the predicted and actual industrial plant data. The tri-phase predicted distribution coefficients of arsenic are 6.09%, 11.22%, 82.69%, antimony 12.80%, 70.63%, 16.57%, bismuth 19.77%, 11.30%, 68.93%, lead 55.55%, 24.75%, 19.70% and zinc 17.78%, 64.28%, 17.94%, respectively, in matte, slag and gas phase, from which the minor element trends in the matte, slag and gas can be clearly seen.
Table 6 Comparison of predicted data with actual plant data of matte and slag content in SKS process in 2014 (mass fraction, %)
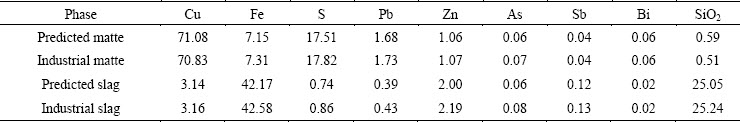
Table 7 Comparison of prediction data with actual plant data of minor element distribution in SKS process in 2014 (mass fraction, %)
From the above comparison, the agreement between the multiphase equilibrium model predictions data and the industrial data is excellent. Consequently, the reliability of the present multiphase equilibrium model is validated and it can be further used for the prediction of element distribution, optimizing practical operation parameter of the SKS process, or as a metallurgical calculation model synthesizing with the DCS or PLC control system.
5 Conclusions
Based on the theory of Gibbs energy minimization, a multiphase equilibrium model for the SKS process was established. Meanwhile, the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm was developed for a special kind of mathematical model in the SKS process. It is found that the matte grade may reach 71.08% under the condition of oxygen blowing speed 10885 m3/h, air blowing speed 5651 m3/h and mixed copper concentrates input speed 66 t/h. The tri-phase (matte, slag and gas phase) distribution coefficients of arsenic are 6.09%, 11.22%, 82.69%, antimony 12.80%, 70.63%, 16.57%, bismuth 19.77%, 11.30%, 68.93%, lead 55.55%, 24.75%, 19.70% and zinc 17.78%, 64.28%, 17.94%. A good agreement was obtained between the predicted data and the actual plant data that validated the reliability of the developed model and solution algorithms. This is attributed to deepening the understanding of the SKS process and great significance for further regulating the production in factories. Furthermore, the model and its solution algorithm could be used to optimize the operation parameters of the SKS process.
References
[1] CUI Zhi-xiang, YAN Hong-jie, SHEN Dian-bang, CUI Zhi-qiang, YU Peng-fei. The research of metallurgical reaction engineering in oxygen bottom blowing copper smelting [C]//Proceedings of 5th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2014: 547-554.
[2] CUI Zhi-xiang, SHEN Dian-bang, WANG Zhi, LI Wei-qun, BIAN Rui-ming. The theory and practice of copper smelting with oxygen enriched bottom blowing [J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2010(6): 21-26. (in Chinese)
[3] ZHAO Bao-jun, CUI Zhi-xiang, WANG Zhi. A new copper smelting technology—Bottom blown oxygen furnace developed at Dongying Fangyuan nonferrous metals [C]//Processing of 4th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2013: 3-10.
[4] GOTO S. Equilibrium calculations between matte, slag and gaseous phases in copper smelting [J]. London: IMM, 1975: 23-34.
[5] SHIMPO R, WATANABE Y, GOTO S, OGAWA O. An application of equilibrium calculations to the copper smelting operation[J]. Advances in Sulfide Smelting, 1983,1: 295-316.
[6] SHIMPO R, GOTO S, OGAWA O, ASAKURA I. A study on the equilibrium between copper matte and slag [J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 1986, 25(2): 113-121.
[7] TAN Peng-fu, ZHANG Chuan-fu. Computer model of copper smelting process and distribution behaviors of accessory elements [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 1997, 4(1): 36-41. (in Chinese)
[8] NAGAMORI M, ERRINGTON W J, MACKEY P J, POGGI D. Thermodynamic simulation model of the Isasmelt process for copper matte [J]. Metall Mater Trans B, 1994, 25(6): 839-853.
[9] TONG Chang-ren, WU Wei-guo, ZHOU Xiao-xue. Establishment and application of multiphase equilibrium mathematical model for copper flash smelting process [J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering & Research, 2006,27(6): 6-9. (in Chinese)
[10] WEI Qin-sheng, HU Yang-dong, AN Wei-zhong, WU Lian-ying, LIU Jing-jing. Equilibrium calculation of multiphase and multicomponent system by using modified τ-method [J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2007, 35(12): 38-41. (in Chinese)
[11] LIN Jin-qing, LI Hao-ran, HAN Shi-jun. Computation algorithm for simutaneous chemical and phase equilibrium by using genetic algorithm [J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2002, 53(6): 616-620. (in Chinese)
[12] XU Hui-lin, CHEN Jian, TANG Hong-qing. One-step algorithm for multiphase equilibrium calculation using state equations [J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2003, 31(5): 66-69. (in Chinese)
[13] LIDE D. CRC handbook of chemistry and physics [M]. 85th ed. Boca Raton: CRC press Inc, 2004.
[14]  A, LANTAGNE G, MARCOS B. Computation of complex and constrained equilibria by minimization of the Gibbs free energy [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2012, 82: 260-271.
A, LANTAGNE G, MARCOS B. Computation of complex and constrained equilibria by minimization of the Gibbs free energy [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2012, 82: 260-271.
[15] ROSSI C, CARDOZO-FILHO L, GUIRARDELLO R. Gibbs free energy minimization for the calculation of chemical and phase equilibrium using linear programming [J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2009, 278(1): 117-128.
[16] GUO Xue-yi, WANG Qin-meng, LIAO Li-le, TIAN Qing-hua, ZHANG Yong-zhu. Mechanism and multiphase interface behavior of copper sulfide concentrates melting in oxygen-enriched bottom blowing furnace [J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2014, 5(5): 28-34. (in Chinese)
[17] NAGAMORI M, MACKEY P J. Thermodynamics of copper matte converting: Part I. Fundamentals of the noranda process [J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1978, 9(2): 255-265.
[18] SEO K W, SOHN H Y. Mathematical modeling of sulfide flash smelting process. Part III: Volatilization of minor elements [J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1991, 22(6): 791-799.
[19] TAKEDA Y, ISHIWATA S, YAZAWA A. Distribution equilibria of minor elements between liquid copper and calcium ferrite slag [J]. Transactions of the Japan Institute of Metals, 1983, 24(7): 518-528.
[20] CHAUBAL P C, SOHN H Y, GEORGE D B, BAILEY L K. Mathematical modeling of minor-element behavior in flash smelting of copper concentrates and flash converting of copper mattes [J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1989, 20(1): 39-51.
[21] ENGELBRECHT A. Fundamentals of computational swarm intelligence [M]. 1st ed. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2006.
[22] KENNEDY J, EBERHART R. Particle swarm optimization [C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Service Center, 1995: 1942-1948.
[23] YENIAY O. Penalty function methods for constrained optimization with genetic algorithms [J]. Mathematical and Computational Applications, 2005,10(1): 45-56.
[24] PAQUET U, ENGELBRECHT A. Particle swarms for linearly constrained optimization [J]. Fundamenta Informaticae, 2007, 76(1-2): 147-170.
[25] CHENG Biao, CHEN De-zhao. Complex phase equilibrium computation based on hybrid particle swarm optimization [J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2008, 22(2): 320-324.
[26] AGUIRRE A, ZAVALA A, DIHARCE E, RIONDA S. COPSO: Constrained optimization via PSO algorithm [J]. Center for Research in Mathematics (CIMAT). Technical report No. I-07-04/22-02-2007, 2007: 1-30.
[27] VOGLIS C, PARSOPOULOS K, PAPAGEORGIOU D, LAGARIS I, VRAHATIS M. Mempsode: A global optimization software based on hybridization of population-based algorithms and local searches [J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2012, 183(5): 1139-1154.
[28] VOGLIS C, PIPERAGKAS G, PARSOPOULOS K, PAPAGEORGIOU D, LAGARIS I. Mempsode: comparing particle swarm optimization and differential evolution within a hybrid memetic global optimization framework [C]//Proceedings of the 14th annual conference companion on Genetic and evolutionary computation. New York, NY, USA: ACM, 2012: 253-260.
[29] ZHOU Xiao-jun, YANG Chun-hua, GUI Wei-hua. State transition algorithm [J]. Journal of Industrial and Management Optimization, 2012,8(4): 1039-1056. (in Chinese)
[30] SCHUTTE J, GROENWOLD A. A study of global optimization using particle swarms [J]. Journal of Global Optimization, 2005, 31(1): 93-108.
王亲猛1,郭学益2,王松松2,廖立乐2,田庆华2
1. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院 长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:基于氧气底吹工艺特性和最小吉布斯自由能原理,构建了氧气底吹铜熔炼热力学计算模型。模拟结果表明:在给定的稳定生产条件下,铜锍中Cu、Fe和S含量分别是71.08%、7.15%和17.51%,渣中Fe、SiO2和Cu含量分别是42.17%、25.05%和3.16%。微量元素在底吹熔炼过程中气相、渣相和铜锍相三相间的模拟分配比例为:砷82.69%、11.22%和6.09%;锑16.57%、70.63%和12.80%;铋68.93%、11.30%和19.77%;铅19.70%、24.75%和55.55%;锌17.94%、64.28%和17.79%。将模拟结果和实际生产数据进行验证,结果一致,表明了该多相平衡热力学计算模型具有可靠性,可以指导氧气底吹铜熔炼生产实践,优化工艺操作参数。
关键词:多相平衡模拟;氧气底吹铜熔炼;SKS工艺;元素分配
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (51620105013) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Xue-yi GUO; Tel: +86-731-88876255; E-mail: xyguo@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60277-2

