文章编号:1004-0609(2015)06-1678-09
氧气底吹铜熔炼渣中多组元造渣行为及渣型优化
王亲猛1, 2,郭学益1, 2,田庆华1, 2,廖立乐1, 2,张永柱1, 2
(1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 中国有色金属工业清洁冶金工程研究中心,长沙 410083)
摘 要:通过分析氧气底吹铜熔炼过程产生的铁硅型工业铜渣中SiO2、Fe、S、Cu、CaO等组元含量变化趋势,结合冶金过程原理,研究上述各组元造渣行为及组元含量相互间的映射关系,并进行渣型优化。结果表明:SiO2、Fe、S、Cu及CaO等组元的造渣行为具有相互关联性,且各组元与Cu造渣行为的关联性由强到弱的顺序依次为S、m(Fe)/m(SiO2)、SiO2、Fe。同时,SiO2和Fe含量对Cu含量的耦合作用较明显,随SiO2含量升高,Fe含量降低,Cu含量呈降低趋势。通过渣型优化,渣中SiO2含量为26.5%~28%、Fe含量为38.5%~40%(质量分数),该渣型的流动性较好,理论上底吹熔炼渣含Cu可降低到2.5%(质量分数)以下。
关键词:铜冶炼;氧气底吹;铜渣;组元行为;渣型优化
中图分类号:TF811 文献标志码:A
Multicomponent slagging behavior and constitution optimization of slag in copper oxygen bottom blowing bath smelting process
WANG Qin-meng1, 2, GUO Xue-yi1, 2, TIAN Qing-hua1, 2, LIAO Li-le1, 2, ZHANG Yong-zhu1, 2
(1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Cleaner Metallurgical Engineering Research Center, Nonferrous Metal Industry of China,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The multicomponent slagging behavior and mapping relationship of SiO2, Fe, S, Cu and CaO and slag constitution optimization were investigated by analyzing SiO2, Fe, S, CaO and Cu content variation trends of industrial iron silicate slag in copper oxygen bottom blowing bath smelting (BBS) process, combined with metallurgical process principles. The results show that the slagging behaviors of SiO2, Fe, S, Cu and CaO have certain correlation, and the correlation sequence with Cu slagging behavior is S, m(Fe)/m(SiO2), SiO2, Fe. The rule of coupling interaction between SiO2 and Fe to Cu is sensible. Cu content increases with the increase of SiO2 and the decrease of Fe. Through optimizing the slag, SiO2 and Fe contents in slag are 26.5%-28% and 38.5%-40% (mass fraction), respectively. The slag has good fluidity, Cu content of BBS slag is lower than 2.5% in theory.
Key words: copper smelting; oxygen bottom blowing; copper slag; component behavior; slag constitution optimization
氧气底吹炼铜技术具有我国自主知识产权[1-2],因其更加清洁高效[3],国家工信部发文[4-5]明确指出把该技术列为我国有色金属工业重点开发技术,并加强其推广和应用。该技术已先后成功应用于国内外多家铜冶炼企业[6],表现出高效、节能及环境友好等优势,目前,该技术已成为重要的应用理论研究对象。
氧气底吹炼铜技术因其工艺特性,目前主要采用高m(Fe)/m(SiO2)渣型,渣含铜3%左右,为进一步优化底吹炼铜过程和降低渣含铜,有必要了解该工艺的工业炉渣中多组元行为的相互映射关系。YAZAWA[7]、SERGEI等[8]、SRIDHAR等[9]、NAGAMORI等[10]和MACKEY[11]等对铜冶炼过程广义的组元行为、过程热力学及炉渣相图进行了研究;CHEN等[12]和刘柳等[13]分析了氧气底吹铜熔炼渣的微观形貌;GUI等[14]、刘建华等[15]采用基于数据驱动的方法对闪速炼铜及转炉吹炼过程进行了过程优化及在线控制研究,但目前有关针对氧气底吹炼铜工艺中炉渣内多组元行为分析及渣型优化的研究还鲜见报道,因此,以期本文研究成果为底吹炼铜工艺炉渣组元预测、控制及渣型优化提供理论指导。
1 实验
1.1 造锍熔炼
造锍熔炼是在国内某铜厂的氧气底吹炉中进行的,炉体结构如图1所示。
根据配料比例,不同成分的铜精矿混合配料后,
不经过磨细、干燥或制粒,直接搭配一定量的石英砂熔剂,经传送皮带连续地加入到炉内,氧化反应和造渣反应激烈地进行,并通过间歇式放渣、放铜锍,使熔炼过程连续进行。入炉混合料成分如表1所列。
表1 混合矿料的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of mixed ore (mass fraction, %)

氧气和空气通过炉体底部氧枪连续送入炉内的铜锍层,富氧浓度73%以上,氧枪内层输送氧气,外层输送空气对氧枪有降温保护作用,使氧枪周围形成“蘑菇头”[13, 16-17],主要成分为Fe3O4,可有效防止熔体对氧枪的侵蚀作用。
1.2 反应原理
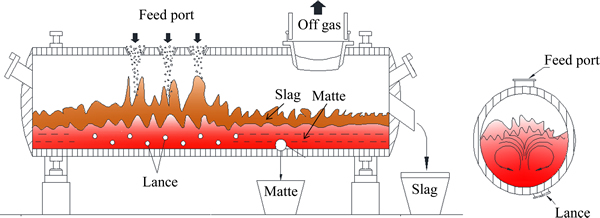
图1 氧气底吹熔炼炉示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of BBS furnace

图2 氧气底吹铜熔炼机理模型
Fig. 2 Mechanism model of BBS process
氧气底吹熔炼机理如图2所示,沿轴向分为反应区、分离过渡区、液相澄清区3个区域。气体在向上喷吹过程中,分化为许多微细的小气流,先进入铜锍层,气液相接触面积大、历程长,气体在熔体内停留时间长,有较好的反应动力学条件,有较大的熔炼潜能。
由于底吹炉内熔体温度高达1200℃,矿料落到炉渣熔体上面后,促使其中的部分高价硫化矿分解为低价硫化物和单质硫气体,硫化物进入熔体内部逐渐被氧化进行造锍和造渣反应,具体反应如式(1)~(7)所示:
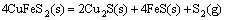 (1)
(1)
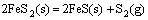 (2)
(2)
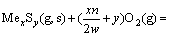
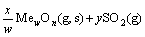 (3)
(3)
 (4)
(4)
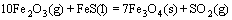 (5)
(5)
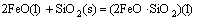 (6)
(6)

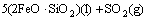 (7)
(7)
1.3 数据分析方法
炉渣经冷却、破碎、细磨、筛分、制样,测定样品成分,渣中SiO2、Fe、S、Cu、CaO等组元的质量分数分别为wSiO2、wFe、wS、wCu、wCaO。连续一个月每天采集上述数据,采用Origin9.0软件分析wSiO2、wFe、wS、wCu、wCaO等数据相互之间的关联性(即映射关系),并通过分析实测数值与拟合公式的预测数值之间的绝对误差与相对误差,评估wSiO2、wFe、wS、wCu、wCaO等数据相互之间关联性的强弱及预测准确性。
2 结果与分析
氧气底吹炼铜属于强氧化熔炼过程,其渣型为FeO-SiO2型,且m(Fe)/m(SiO2)较高,CaO含量较低,铜在渣中的损失物相分布有别于其他工艺,因此,有必要对氧气底吹炼铜工业渣进行深入分析,了解该渣中各组元的内在关联性及对渣含铜的影响,进而对渣型进行优化。
2.1 单组元之间的映射关系
主要分析底吹工业渣中多组元Cu、SiO2、Fe、S、CaO及铁硅比m(Fe)/m(SiO2)之间的映射关系,重点研究其他各主要组元含量对渣含Cu的影响。
2.1.1 渣中Cu含量与SiO2含量之间的映射关系及分析
SiO2是铁橄榄石渣的主要成分之一,它在渣中的含量对炉渣的性质及渣含铜影响极大,因此,首先关注的成分是SiO2。图3所示为渣中Cu含量与SiO2含量之间的映射关系及分析。如图3(a)所示,渣中SiO2含量为21.3%~27.8%(质量分数),Cu含量在2.3%~3.8%(质量分数)之间波动,且有一定的关联性,wCu整体上呈现出随wSiO2的增加而降低的趋势。对wCu和wSiO2进行拟合,式(8)为其拟合函数关系式。
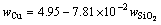
R2=0.11 (8)
这种趋势的主要原因是随着SiO2含量的增大,渣的黏度、渣-锍间界面张力、渣-锍间的密度差发生变化所致。在SiO2含量较小时,如在21.3%~27.8%(质量分数)内时,随着SiO2含量的增大,可以有效降低FeO的活度,从而降低Fe3O4的含量,进而降低炉渣的黏度,改善渣中机械夹带的冰铜滴汇集、生长、沉降的条件,降低渣含铜;但若SiO2含量继续增大,超过一定值后,渣中的硅氧四面体链状结构增多,黏度呈现上升的趋势。
在铜锍品位一定时,随渣中SiO2含量逐渐增大,渣-铜锍间界面张力增大,渣的密度降低,渣-铜锍间的密度差增大,铜锍滴在渣中的沉降速度增加,从而有利于铜锍与渣的分离。球形铜锍液滴在熔渣中沉降速度服从方程(9):
 (9)
(9)
式中:g为重力加速度(m/s2);r为锍滴直径(m);△ρ为铜锍与炉渣的密度差(kg/m3);μ为熔渣黏度(Pa·s)。
因此,当SiO2含量在21.3%~27.8%(质量分数)区间时,Cu含量应随SiO2含量(wSiO2)的增加而降低。图3(a)中的渣中Cu含量有较大的上下波动现象,主要是除了渣中SiO2含量影响Cu含量外,Fe含量、CaO含量及铜锍品位对Cu含量也有较大影响,且样本中的Fe含量、CaO含量及铜锍品位并非完全稳定的值,存在一定的波动。
通过函数关系式(8)对炉渣中Cu含量(wCu)进行分析,如图3(b),得出预测值分布在2.8%~3.3%(质量分数)之内,图3(c)中绝对误差在-0.8%~0.5%(质量分数)之内,因wCu基数较小,图3(d)中最大相对误差为28%,但主体的相对误差<15%,因此,实测数值和预测数值有一定的一致性,在SiO2含量21.3%~ 27.8%(质量分数)区间内,一定程度上可用wSiO2预测wCu。

图3 渣中Cu含量与SiO2含量之间的映射关系及分析
Fig. 3 Mapping relationship and analysis of wCu and wSiO2 in slag ( and
and  are predicted wCu and measured wCu, respectively)
are predicted wCu and measured wCu, respectively)
2.1.2 渣中Cu含量与Fe含量之间的映射关系及分析
FeO与SiO2一样,也是铁橄榄石渣的另一种主要成分,其在渣中的含量对炉渣的性质及渣含铜有较大影响。图4所示为渣中Cu含量及Fe含量之间的映射关系及分析。如图4(a)所示,渣中Fe含量在38%~42.3%(质量分数)范围内,Cu含量与Fe含量也呈一定的相关性,wCu整体上呈现出随wFe的增加而增加的趋势,式(10)为其拟合函数关系式。

R2=2.79×10-2 (10)
这种趋势的主要原因是在Fe含量38%~42.3%(质量分数)范围内,随着Fe含量的增大,FeO的活度增加,从而Fe3O4的含量增加,增大了炉渣的黏度,恶化了渣中机械夹带的冰铜滴汇集、生长、沉降的条件,使渣含铜上升。
通过函数关系式(10)对Cu含量进行分析,如图4(b),得出预测值分布在2.9%~3.2%(质量分数)之内,图4(c)中绝对误差在-0.8%~0.7%之内,图4(d)中最大相对误差为29%,主体的相对误差<18%,因此,wFe单独预测wCu的准确度不及wSiO2的。
2.1.3 渣中Cu含量与铁硅比Fe/SiO2之间的映射关系及分析
单独使用wSiO2和wFe预测wCu,但准确度都不是很理想,由于铁硅比m(Fe)/m(SiO2)是炼铜过程中的重要因素,因此有必要使用m(Fe)/m(SiO2)对渣中Cu含量的影响进行分析。图5所示为渣中Cu含量与m(Fe)/m(SiO2)之间的映射关系及分析。
图5(a)中,m(Fe)/m(SiO2)在1.4~2.0范围内,wCu随m(Fe)/m(SiO2)的增加而增加,且有一定的线性关系,式(11)为其拟合函数关系式。

R2=0.14 (11)
式(11)的相关系数R2值要比式(8)的和式(10)的大,说明m(Fe)/m(SiO2)预测wCu可能比单独使用wSiO2和wFe预测wCu效果要好。
通过函数关系式(11)对炉渣中Cu含量进行预测分析,如图5(b),得出预测值分布在2.7%~3.4%之内,图5(c)中绝对误差在-0.7%~0.5%之内,图5(d)中最大相对误差为20%,主体的相对误差<12%,印证了采用m(Fe)/m(SiO2)预测wCu的效果比单独使用wSiO2或wFe要好。

图4 渣中Cu含量与Fe含量之间的映射关系及分析
Fig. 4 Mapping relationship and analysis of wCu and wFe in slag ( and
and  are predicted wCu and measured wCu, respectively)
are predicted wCu and measured wCu, respectively)

图5 渣中Cu含量与m(Fe)/m(SiO2)之间的映射关系及分析
Fig. 5 Mapping relationship and analysis of wCu and m(Fe)/m(SiO2) in slag ( and
and  are predicted wCu and measured wCu, respectively)
are predicted wCu and measured wCu, respectively)
2.1.4 渣中Cu含量与S含量之间的映射关系及分析
S在渣中以多种形态存在,主要为Cu2S和FeS,而Cu在渣中的主要损失形态为Cu2S和Cu2O,且渣中的S含量对渣的氧势-硫势有一定影响,进而影响Cu2O的含量,因此在渣中S含量对渣中的Cu损失总量应有一定的映射关系。图6所示为渣中Cu含量与S含量之间的映射关系及分析。图6(a)所示,当S含量 0.6%~ 1.5%时,wCu随wS的增加而增加,且呈二次线性关系。对其进行线性拟合,线性相关系数R2为0.36,式(12)为其拟合函数关系式:
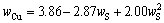
R2=0.36 (12)
渣中不同锍滴中的Cu2S与FeS比例不尽相同,且渣中Cu2O的溶解量还受到铜锍品位等多因素的影响,因此在S含量 0.6%~1.5%范围内,wCu随wS的增加而有一定的上下波动。
通过函数关系式(12)对炉渣中Cu含量进行预测分析,如图6(b)所示,得出预测值分布在2.8%~3.8%之内,图6(c)中绝对误差在-0.8%~0.7%之内,由于样本中个别数据本身的差异,虽然图6(d)中的最大相对误差为25%,但主体的相对误差<10%,因此,相比单独使用wFe、wSiO2或Fe/SiO2预测wCu,使用wS预测wCu的准确度获得进一步提升。
2.1.5 渣中组元含量之间其他次要映射关系
除了上述的多组元因素对渣含Cu的映射关系外,渣中其他组元之间也存在着一定的相关性,具体如图7所示。
图7(a)中wS和wCaO之间的线性关系较为明显,wS整体上呈现出随wCaO的增加而降低的趋势,其主要原因是在CaO含量1.5%~2.3%范围内,wCaO的增加有助于降低炉渣的黏度,减少铜锍的机械夹带,进而可降低渣中S含量,式(13)为其拟合函数关系式:
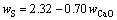
R2=0.39 (13)
由于其他组元之间的映射关系不是很明显,且不是炉渣优化的主要考虑因素,因此,本研究中不做进一步细化分析。
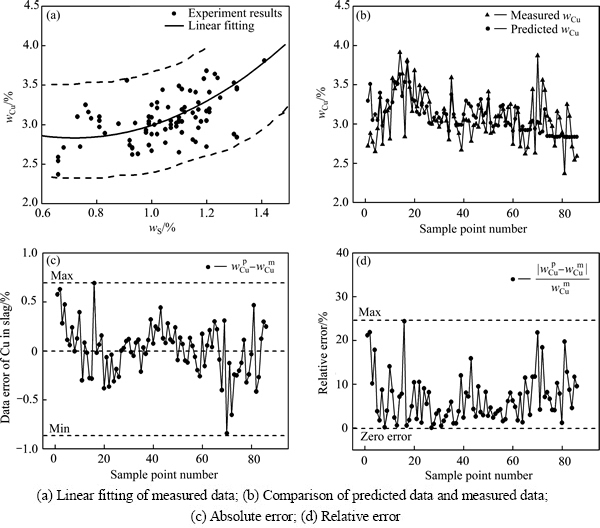
图6 渣中Cu含量与S含量之间的映射关系及分析
Fig. 6 Mapping relationship and analysis of wCu and w S in slag (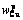 and
and  are predicted wCu and measured wCu, respectively)
are predicted wCu and measured wCu, respectively)
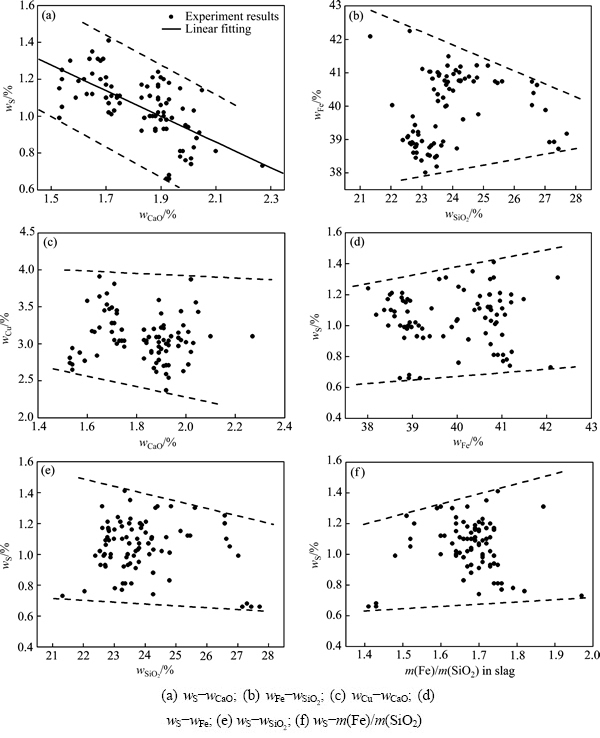
图7 渣中组元含量之间其他次要映射关系
Fig. 7 Other secondary mapping relationship of multicomponent content in slag
2.2 多组元复合映射关系及渣型优化
通过对渣中多组元含量的映射关系分析,发现wSiO2、wFe和wS分别对wCu有较大影响,且呈现出较强规律性。因此,有必要对wSiO2、wFe及wS三者对wCu的复合映射关系进行研究,进行精确分析及渣型优化。
又由于渣中S和Cu类似,都是从铜锍中通过机械夹带或溶解而进入炉渣的,属于渣型结构的因变量,而不是自变量,因此,将复合因素中的wS排除,主要研究wSiO2和wFe二者对wCu的复合映射关系,深入分析其耦合作用。图8所示为渣中SiO2含量和Fe含量对Cu含量的复合映射关系。
图8(a)和(b)展示了wSiO2和wFe对wCu的耦合作用关系。从图中可见,耦合规律较明显,由于渣中SiO2含量与FeO含量之和小于100%,所以,wSiO2+wFe是有最高限度的,函数关系只能出现在图中一定的区域范围内;随wSiO2升高、wFe降低,wCu呈降低趋势;随wSiO2降低、wFe升高,wCu呈升高趋势;随wSiO2、wFe同时降低,渣中的杂相含量会增加,因此,wCu升高。式(14)为其拟合函数关系式:

R2=3.97×10-2 (14)
图9所示为渣型优化分析结果。把wSiO2和wFe对wCu的耦合作用三维关系图进行平面等值化处理后,其关系如图9(a)所示。A和B区域对应的wSiO2和wFe范围内wCu>3.2%,A区域主要是由SiO2和FeO含量变化对炉渣黏度、密度、界面张力等性质产生影响造成的;B区域主要是渣中FeO和SiO2含量太低,杂质多引起的;由于A区与B区的原理不同,因此,两区域是分开的。

图8 渣中SiO2含量和Fe含量对Cu含量的复合映射关系
Fig. 8 Mapping relationship between wSiO2 and wFe and wCu in slag

图9 渣型优化分析结果
Fig. 9 Analysis results of slag constitution optimization
图9(b)中,由点C到点D渣含Cu是逐渐降低的,其中点D附近区域对应的渣含Cu在2.3%~2.5%。
因此,在采用FeO-SiO2渣进行氧气底吹造锍熔炼时,渣型优化为渣含SiO2: 26.5%~28%(质量分数)、Fe: 38.5%~40%(质量分数),理论上渣含Cu可保持在2.5%以下。该渣型的铁硅比m(Fe)/m(SiO2)为1.35~ 1.50,渣率有所上升,但渣流动性较好。
3 结论
1) 氧气底吹铜熔炼过程产生FeO-SiO2型渣中SiO2、Fe、S、Cu及CaO等组元行为之间呈现出一定的相关性,对渣中Cu含量预测分析的准确性由高到低的顺序依次为S、m(Fe)/m(SiO2)、SiO2、Fe。
2) 渣中SiO2含量和Fe含量对Cu含量的耦合作用规律较明显,随SiO2含量升高、Fe含量降低,Cu含量呈降低趋势;随SiO2含量降低、Fe含量升高,Cu含量呈升高趋势;若SiO2含量、Fe含量同时降低,则渣中的杂相含量会增加,Cu含量会升高。
3) 通过渣型优化,底吹熔炼过程采用渣成分为SiO2: 26.5%~28%(质量分数)、Fe: 38.5%~40%(质量分数),理论上渣中Cu含量可降低到2.5%以下,且该渣型的流动性较好。
REFERENCES
[1] 陈淑萍, 伍赠玲, 蓝碧波, 郭其章. 火法炼铜技术综述[J]. 铜业工程, 2010(4): 44-49.
CHEN Shu-ping, WU Zeng-ling, LAN Bi-bo, GUO Qi-zhang. Summarize on the technology of copper pyrometallurgy[J]. Copper Engineering, 2010(4): 44-49.
[2] 崔志祥, 申殿邦, 王 智, 李维群, 边瑞民. 高富氧底吹熔池炼铜新工艺[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2010(3): 17-20.
CUI Zhi-xiang, SHEN Dian-bang, WANG Zhi, LI Wei-qun, BIAN Rui-min. New process of copper smelting with oxygen enriched bottom blowing technology[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2010(3): 17-20.
[3] 申殿邦. 氧气底吹炼铜新工艺[EB/OL]. [2012-01-31]. http://www.cmra.cn/a/33333/2012/0131/228221.html.
SHEN Dian-bang. New process of copper smelting with oxygen enriched bottom blowing technology[EB/OL]. [2012-01-31]. http://www.cmra.cn/a/33333/2012/0131/228221.html.
[4] 中华人民共和国工业和信息化部. 有色金属工业“十二五”发展规划[EB/OL]. [2012-01-30]. http://www.miit.gov.cn/ n11293472/n11293832/n11293907/n11368223/14447635.html.
Ministry of industry and information technology of the people’s republic of China. Non-ferrous metals industry twelfth five-year development plan [EB/OL]. [2012-01-30]. http://www.miit.gov.cn/ n11293472/n11293832/n11293907/n11368223/14447635.html.
[5] 中华人民共和国工业和信息化部. 铜冶炼行业规范条件[EB/OL]. [2014-04-28]. http://www.miit.gov.cn/n11293472/ n11293832/n12845605/n13916898/15976630.html.
Ministry of industry and information technology of the people’s republic of China. Copper smelting industry norms conditions [EB/OL]. [2014-04-28]. http://www.miit.gov.cn/n11293472/ n11293832/n12845605/n13916898/15976630.html.
[6] 陈知若. 底吹炼铜技术的应用[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2009(5): 16-22.
CHEN Zhi-ruo. The application of oxygen bottom-blown bath smelting of copper[J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2009(5): 16-22.
[7] YAZAWA A. Thermodynamic considerations of copper smelting[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 1974, 13(3): 443-453.
[8] SERGEI A D, ARTHUR D P. A thermodynamic database for copper smelting and converting[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1999, 30(4): 661-669.
[9] SRIDHAR R, TOGURI J M, SIMEONOV S. Copper losses and thermodynamic considerations in copper smelting[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1997, 28(2): 191-200.
[10] NAGAMORI M, MACKEY P J. Thermodynamics of copper matte converting: Part 1. Fundamentals of the Noranda process[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1978, 9(3): 255-265.
[11] MACKEY P J. The physical chemistry of copper smelting slags—A review[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 1982, 21(3): 221-260.
[12] CHEN Mao, CUI Zhi-xiang, ZHAO Bao-jun. Slag chemistry of bottom blown copper smelting furnace at Dongying Fangyuan[C]// Orlando, FL, USA: The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 2015: 257-264.
[13] 刘 柳, 闫红杰, 周孑民, 高 强, 张振杨, 刘方侃, 崔志祥. 氧气底吹铜熔池熔炼过程的机理及产物的微观分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(7): 2116-2124.
LIU Liu, YAN Hong-jie, ZHOU Jie-min, GAO Qiang, ZHANG Zhen-yang, LIU Fang-kan, CUI Zhi-xiang. Mechanism of copper smelting process by oxygen bottom blowing and microanalysis of smelting products[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(7): 2116-2124.
[14] GUI Wei-hua, WANG Ling-yun, YANG Chun-hua, XIE Yong-fang, PENG Xiao-bo. Intelligent prediction model of matte grade in copper flash smelting process[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(5): 1075-1081.
[15] 刘建华, 桂卫华, 谢永芳, 王雅琳, 蒋朝辉. 基于投影寻踪回归的铜闪速熔炼过程关键工艺指标预测[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(11): 3255-3260.
LIU Jian-hua, GUI Wei-hua, XIE Yong-fang, WANG Ya-lin, JIANG Zhao-hui. Key process indicators predicting for copper flash smelting process based on projection pursuit regression[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(11): 3255-3260.
[16] 崔志祥, 申殿邦, 王 智, 边瑞民. 低碳经济与氧气底吹熔池炼铜新工艺[J]. 工艺节能, 2011(1): 17-20.
CUI Zhi-xiang, SHEN Dian-bang, WANG Zhi, BIAN Rui-min. Low-carbon economy and new process of copper smelting with oxygen enriched bottom blowing technology[J]. Energy Saving on Technique, 2011(1): 17-20.
[17] 曲胜利, 董准勤, 陈 涛. 富氧底吹造锍捕金工艺研究[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2013(6): 40-42.
QU Sheng-li, DONG Zhun-qin, CHEN Tao. Study on gold collection in matte with oxygen enriched bottom blowing smelting process[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2013(6): 40-42.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:湖南有色研究基金重点项目(YSZN2013YJ01)
收稿日期:2014-10-20;修订日期:2015-04-13
通信作者:郭学益,教授,博士;电话:0731-88877863;传真:0731-88836207;E-mail: xyguo@csu.edu.cn