文章编号:1004-0609(2015)04-1072-08
基于区位氧势硫势梯度变化下铜富氧底吹熔池熔炼非稳态多相平衡过程
郭学益,王亲猛,田庆华,张永柱
(中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:结合富氧底吹熔池熔炼机理模型和Cu-Fe-S-O-SiO2系氧势-硫势热力学优势图,研究底吹熔炼过程中的多相平衡状态及炉内不同空间位点的氧势-硫势分布规律。结果表明:铜富氧底吹熔池熔炼是烟气-炉渣-铜锍三相共存体系,随着连续加料、连续鼓氧及放渣和放锍操作的进行,体系远未达到平衡,而是处于动态的非稳态近似多相平衡状态,炉内不同空间位点的氧势-硫势不同,存在着梯度变化。反应区、分离过渡区及液相澄清区由下到上氧势逐渐降低,而硫势逐渐升高,其中反应区的氧势-硫势差梯度较大,氧和硫的传质较快。通过调节熔炼过程工艺参数,使炉内不同空间位点的氧势-硫势控制在更为合理的范围,可提高底吹熔炼能力。
关键词:铜冶炼;富氧底吹;熔炼机理;氧势;硫势;非稳态多相平衡
中图分类号:TF811 文献标志码:A
Non-steady multiphase equilibrium process of copper oxygen-enriched bottom blowing bath smelting with gradual change of oxygen and sulfur potential of different positions in furance
GUO Xue-yi, WANG Qin-meng, TIAN Qing-hua, ZHANG Yong-zhu
(School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The multiphase equilibrium state and oxygen-sulfur potential distribution rule of oxygen-enriched bottom blowing smelting (BBS) process were investigated by mechanism model of BBS and oxygen-sulfur potential diagram for Cu-Fe-S-O-SiO2 system. The results show that BBS is at the state of dynamic non-steady approximate multiphase equilibrium of gas-slag-matte three phases coexistence system which is far from equilibrium with continuous feeding, injecting oxygen, slagoff and ejecting matte. And the value of oxygen and sulfur potential changes gradually in different locations of furnace. Oxygen potential decreases and sulfur potential increases gradually from bottom to up in reaction region, separation transition region and liquid phase clarification region, and oxygen and sulfur transfers faster in reaction region with larger oxygen-sulfur potential gradient. The capacity of BBS can be improved by reasonably regulating process parameters to control the value in different layers and regions.
Key words: copper smelting; oxygen-enriched bottom blowing; smelting mechanism; oxygen potential; sulfur potential; non-steady multiphase equilibrium
铜富氧底吹熔池熔炼技术具有完全的中国自主知识产权,是继奥托昆普法、诺兰达法、特尼恩特法、澳斯麦特-艾萨法、三菱法及白银法等之后的一种新型铜冶炼方法[1-2],因其更加清洁高效,被誉为“世界第四代新型炼铜法”[3]。国家工信部发布的《有色金属工业“十二五”发展规划》[4]及《铜冶炼行业规范条件》[5]中,明确指出把氧气底吹连续炼铜技术列为我国有色金属工业重点开发技术,并将氧气底吹炼铜技术列为铜冶金技术改造的重点,加强其推广和应用。目前该技术已先后成功应用于山东方圆有色金属公司、山东恒邦冶炼股份有限公司、内蒙古华鼎冶炼厂、中条山有色金属有限公司及河南豫光金铅集团等冶炼企业[6],表现出高效、节能及环境友好等优势,因此,该技术成为了重要的应用理论研究对象。
底吹熔炼过程中,富氧空气从炉体底部鼓入,与矿料快速进行化学反应,并对熔体进行强烈的搅拌,同时多相多组元快速进行传质作用,导致在动态生产中炉内不同的空间位点的氧势-硫势不断变化,形成氧势-硫势梯度分布状态,使熔炼过程处于非稳态多相平衡状态。为了进一步优化氧气底吹熔炼过程,提高其熔炼能力,有必要对熔炼过程中的非稳态多相平衡及炉内氧势-硫势的梯度分布状态进行深入分析。
根据文献[7-11]可知,对铜冶炼过程中多相平衡热力学过程已经进行了相关研究,但这些已有研究都是针对理想状态的稳态过程,并未涉及动态生产过程中炉内不同空间位点的非稳态多相平衡过程。张振扬等[12-13]对氧气底吹熔炼过程中气液两相流动情况进行了水模实验和数值模拟研究,但其研究并未涉及熔炼过程中的相变及氧势-硫势梯度分布状态。本文作者首次结合底吹炉内氧势-硫势梯度分布特性进行熔炼过程中非稳态多相平衡状态的研究,从而为底吹炼铜技术提供理论指导。
1 铜富氧底吹熔池熔炼技术特性
1.1 工艺概况
铜富氧底吹熔池熔炼工艺概况[14]:不同成分的高硫铜精矿、低硫铜精矿、高含贵金属精矿及返料,按照不同配料比例进行配料,获得混合铜精矿,不经过磨细、干燥或制粒,直接搭配一定量的石英砂熔剂,经传送皮带连续地从炉顶3个加料口加入到炉内;矿料自由落体坠入的高温熔体中,迅速被卷入搅拌的熔体中,形成良好的传热和传质条件,使氧化反应和造渣反应激烈地进行,释放出大量的热能,使炉料很快熔化;氧气和空气通过炉体底部氧枪连续送入炉内的铜锍层, 富氧浓度达到73%以上。氧枪分为两层,内层输送制氧站制造的纯度为99.6%的氧气,外层输送空气,外层的空气对氧枪有降温保护作用,同时氧枪周围形成“蘑菇头”,主要成分为Fe3O4,可有效防止熔体对氧枪的侵蚀作用[15]。
1.2 炉体结构及特点
富氧底吹熔池熔炼是一种高效的铜冶金熔炼方法。该方法通过一座可以转动的卧式圆筒炉来实现熔炼目的,生产过程中炉膛下部是熔体,其前段为反应区,后段为沉淀区。在反应区的下边有氧气喷枪将氧气吹入熔池,使熔池处于强烈的搅拌状态,如图1所示。
该方法最大的特点是:气流是以许多微细的小气流从熔体底部吹入,最先进入铜锍层,气液相接触面积大、历程长,气体在熔体内停留时间长,有较好的反应动力学条件,因此有较大的熔炼潜能;生成的熔锍能高效捕集矿物中的金银等多种贵金属,实现了“造锍捕金”目的[16]。
2 氧气底吹熔炼过程非稳态多相平衡
造锍熔炼是一个氧化脱硫过程,目的是将炉料中的铜富集到由FeS和Cu2S组成的铜锍中,并使部分铁通过氧化造渣去除。推动熔炼过程进行的动力是各相间(气相、渣相及锍相)硫浓度差和氧浓度差(即硫势差和氧势差)[17]。在实际熔炼过程中,经常是烟气-炉渣-铜锍共存的三相体系或者四相体系,反应的进行难于达到真正的平衡状态,而是处于动态的近似多相平衡状态。
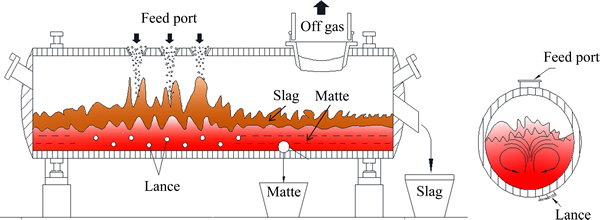
图1 氧气底吹熔炼炉示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of BBS furnace
2.1 铜富氧底吹熔池熔炼机理
通过深入分析底吹炉内流体动力学特性,并结合熔炼反应过程,构建了底吹熔炼机理模型,如图2所示。在该模型中,揭示了底吹炉的沿横向分区情况,主要为反应区、分离过渡区、液相澄清区3个区域。
反应区横截面由上到下、由外到内分为4个主级层,分别为烟气层、矿料分解过渡层、渣层及冰铜层。同时渣层又细分为传质渣层和造渣过渡层,冰铜层细分造锍过渡层、弱氧化层和强氧化层,总计细化为7个次级层。
模型中各层/区分别承担不同的功能,构成一个有机整体,共同完成底吹熔炼过程;体系中多相多组元如CuFeS2、FeS2、Cu2S、FeS 、2FeO·SiO2、Cu2O、FeO、Fe3O4、Fe2O3、SO2、H2O、N2、S2等由于各自的物化性质差异,在熔体流场作用下穿过层/区间的界面进行传质行为。
2.2 铜富氧底吹熔炼过程热力学
对铜冶金过程热力学来说,用氧势-硫势(lg pO2-lg pS2)作为反应体系状态的独立变量,可清晰地阐明硫、氧传递及熔炼过程变化的基本规律[18]。图3所示为1573 K时Cu-Fe-S-O-SiO2系氧势-硫势热力学优势图,可清晰地确定在不同氧势-硫势下的相平衡状态,其中封闭圈内部为烟气-炉渣-铜锍三相共存的稳定区域。
由于富氧底吹炼铜的平均温度在1473 K左右,图4所示为该温度下的Cu-Fe-S-O-SiO2系氧势-硫势关系,同时结合底吹熔炼机理模型(见图2),可对铜富氧底吹熔池熔炼过程多相平衡进行深入分析。
底吹炉内整体上处于烟气-炉渣-铜锍三相共存状态;强氧化区内发生剧烈的氧化反应,经弱氧化层传质过来的的FeS被氧化脱硫生成FeO,甚至少量FeO会进一步被氧化为Fe3O4及Fe2O3,部分Cu2S也被氧化为Cu2O,生成的Cu2O、FeO、Fe3O4及Fe2O3随着流场作用分别进入其他功能层/区参与反应,该区主要把部分O2转化为氧化物MexOy,并以O2和MexOy形式及向其他功能层/区传递O元素,该区的氧势较高,硫势较低;由于熔体温度高达1473 K,矿料落到炉渣熔体上面后,促使其中的部分高价硫化矿分解为低价硫化物和单质硫气体,烟气层及矿料分解过渡层的硫势较高,氧势降低。根据YAZAWA等[19]对1473 K温度下该体系热力学平衡过程的研究方法及结果[19],本文作者分析了底吹熔炼的氧势-硫势,并在图4中标出了底吹熔炼炉内强氧化反应、矿料分解及熔炼平衡相对应的氧势-硫势。
2.3 底吹熔炼非稳态多相平衡过程中氧势-硫势梯度变化分析
图5所示为底吹炉内各空间点位置,主要对反应区、分离过渡区及液相澄清区中的各功能层进行分析,并将各个点连成闭合路径进行比较。

图2 铜富氧底吹熔池熔炼机理模型
Fig. 2 Mechanism model of BBS process
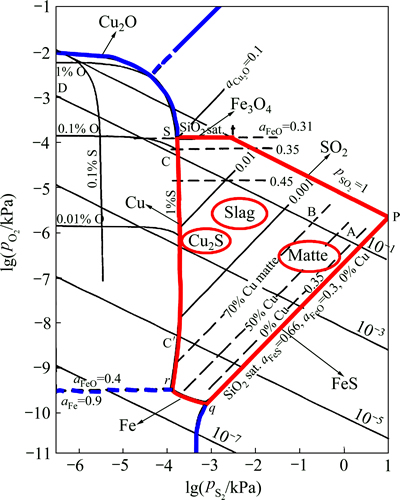
图3 1573 K时Cu-Fe-S-O-SiO2系氧势-硫势热力学优势图
Fig. 3 Sulfur-oxygen potential diagram for Cu-Fe-S-O-SiO2 system at 1573 K
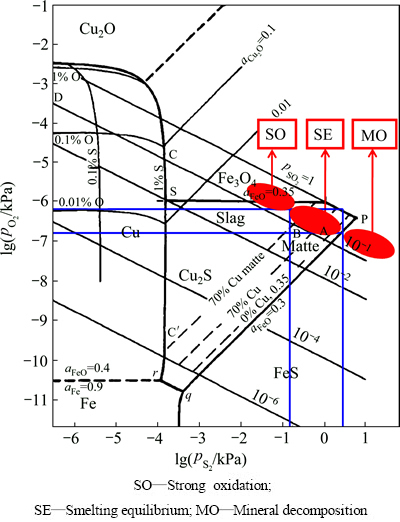
图4 1473 K时铜富氧底吹熔池熔炼Cu-Fe-S-O-SiO2系氧势-硫势热力学优势图
Fig. 4 Sulfur-oxygen potential diagram for Cu-Fe-S-O-SiO2 system of BBS process at 1473 K

图5 底吹炉内各空间位点
Fig. 5 Different space sites in BBS furnace
图6所示为反应区及分离过渡区的氧势-硫势变化趋势。由图6可知,在底吹炉的反应区内,垂直方向上,由下自上炉内的氧势是逐步下降的,而硫势是逐步升高的,反应的核心区即氧枪上部周围区域的氧势最高,鼓入的富氧气体与铜锍快速反应,实现强化熔炼过程,由于氧势过高,部分FeS和Cu2S被氧化为FeO、Fe3O4及Cu2O。反应核心区往上依次进入弱氧化区、造锍过渡层、造渣过渡层、渣层、矿物分解层、烟气层,氧势逐渐降低,矿物分解层内部分硫元素以硫单质气体形式分解出来,并进入气相层。
在底吹炉的分离过渡区内垂直方向,如图6(b)所示,由下自上炉内的氧势也逐步下降,硫势逐步升高,该区内除完成造锍造渣反应外,也进行锍和渣分离,反应产物在各层间进行快速传质过程,该区承担了反应区到液相澄清区的过渡作用。

图6 反应区及分离过渡区的氧势-硫势变化趋势
Fig. 6 Change trends of sulfur-oxygen potential at different regions
图7所示为液相澄清区及炉底的氧势-硫势变化趋势。由图7(a)可知,在底吹炉的液相澄清区内垂直方向,由下自上炉内的氧势也是逐步下降的,硫势逐步升高的,该区的渣层内铜锍微滴汇集、长大、沉降,锍层内的残留渣相逐步上浮进入渣层,且气相层的硫势较高,对渣层有一定得硫化作用,实现渣层锍层液相澄清。
在底吹炉炉底横向路径水平方向上,如图7(b)所示,由点D0到E0、G、F0氧势逐步下降,硫势逐步升高,由强氧化区、弱氧化区过渡到锍相的澄清区域,锍相的Cu2O、FeO及Fe3O4含量逐渐减少。
图8所示为烟气层的氧势-硫势变化趋势。由图8可知,在底吹炉上部烟气层横向路径水平方向,由于气相中组元的传质速度快,基本形成一体的均匀气相,由点D6到E4、F2氧势硫势变化很小,氧势和硫势略微降低。其原因主要是由于矿相分解产生的S2不断与从熔体中溢出的O2反应,气相中O2含量由点D6到E4、F2不断减少,分解产生的S2不断进入气相层,对澄清区的渣层有自还原作用,有利于降低渣中的含铜量。

图7 液相澄清区及炉底的氧势-硫势变化趋势
Fig. 7 Change trends of sulfur-oxygen potential at different regions

图8 烟气层的氧势-硫势变化趋势
Fig. 8 Change trend of sulfur-oxygen potential in gas layer
为了便于分析整个炉内连续空间的氧势-硫势连续变化情况,将反应区、分离过渡区及液相澄清区3个区间的空间点连接起来,如图9所示,通过D6和E4两个点将反应区和分离过渡区连接,通过E0和F0两个点将分离过渡区和液相澄清区连接,组成一个连续的炉内路径,并经过氧枪喷气口、加料口、放锍口及放渣口等重要位点。
图10所示为沿底吹炉内连续路径的氧势-硫势梯度变化情况。由图10可知,在整个路径中氧枪上部强氧化区域的D0点氧势最高,大量的FeS和Cu2S被氧化脱硫生成FeO、Fe3O4、Fe2O3和Cu2O,随着路径延伸,D0→D6氧势先下降,然后E4→E0氧势上升,最后F0→F2氧势又下降,中间D6和E4区间出现一个氧势的平台,主要是由于该区间处于气相层,氧势变化很小;路径中的硫势变化与氧势变化趋势相反,呈先上升,后下降,最后再上升的趋势。中间平台的硫势较高,主要是由于矿料分解过渡层产生大量的单质S2气体进入烟气层。
根据扩散定律,在连续的稳态流条件如式(1)所示:
 (1)
(1)
式中:JO为单位面积单位时间氧的扩散量; 表示在温度T下,在Z1方向变动的二相间氧势差梯度;DO为扩散系数。由图10可知,反应区的氧势差梯度要大于分离过渡区和液相澄清区的氧势差梯度,因此反应区的氧的传递流量JO较其他两区的也更大,同时在流场的搅拌作用下,反应区氧的传质更加迅速,可使连续鼓入的氧气与连续加入的矿料快速作用;同理硫的传质过程遵守相同规律。
表示在温度T下,在Z1方向变动的二相间氧势差梯度;DO为扩散系数。由图10可知,反应区的氧势差梯度要大于分离过渡区和液相澄清区的氧势差梯度,因此反应区的氧的传递流量JO较其他两区的也更大,同时在流场的搅拌作用下,反应区氧的传质更加迅速,可使连续鼓入的氧气与连续加入的矿料快速作用;同理硫的传质过程遵守相同规律。
这种炉内不同空间位点的氧势-硫势梯度变化状态,为熔炼过程非稳态多相平衡提供了热力学条件,保证了连续加料、连续鼓氧、放渣和放锍的动态生产过程正常进行。
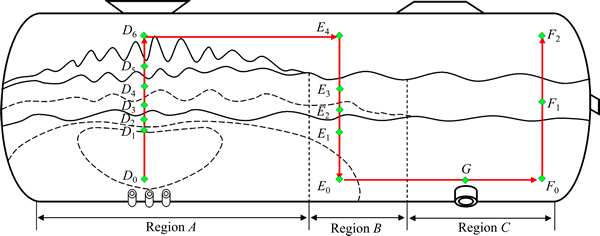
图9 底吹炉内各点连续路径图
Fig. 9 Continuous path diagram in BBS furnace

图10 炉内连续路径的氧势-硫势变化趋势
Fig. 10 Change trends of sulfur-oxygen potential of continuous path in BBS furnace
3 结论
1) 铜富氧底吹熔池熔炼是烟气-炉渣-铜锍三相共存体系,随着连续加料、连续鼓氧及放渣和放锍操作的进行,体系远未达到平衡,而是处于动态的非稳态近似多相平衡状态,炉内不同空间位点的氧势-硫势不同,存在着梯度变化。
2) 熔炼过程中,氧是通过铜锍传递给炉渣,炉内反应区、分离过渡区及液相澄清区由下到上氧势逐渐降低,硫势逐渐升高,其中反应区的氧势-硫势差梯度较大,氧和硫的传质较快。矿料分解产生的单质硫气体和熔体中溢出氧气在烟气层中不断反应,氧势-硫势沿轴向变化很小,从反应区到液相澄清区,烟气层内的氧势-硫势略有降低;炉底铜锍层虽为连续相,但在底吹氧气传质及流场循环作用下,从反应区到液相澄清区,氧势逐渐降低,硫势逐渐升高。
3) 熔炼过程中,通过调节原料成分、加料速度、富氧浓度、氧压、氧气鼓入流量、渣层及锍层厚度等工艺参数,使炉内不同空间位点的氧势-硫势控制在更为合理的范围,可进一步提高底吹炉的熔炼能力。
REFERENCES
[1] 陈淑萍, 伍赠玲, 蓝碧波, 郭其章. 火法炼铜技术综述[J]. 铜业工程, 2010(4): 44-49.
CHEN Shu-pin, WU Zeng-ling, LAN Bi-bo, GUO Qi-zhan. Summarize on the technology of copper pyrometallurgy[J]. Copper Engineering, 2010(4): 44-49.
[2] 崔志祥, 申殿邦, 王 智, 李维群, 边瑞民. 高富氧底吹熔池炼铜新工艺[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2010(3): 17-20.
CUI Zhi-xiang, SHEN Dian-bang, WANG Zhi, LI Wei-qun, BIAN Rui-min. New process of copper smelting with oxygen enriched bottom blowing technology[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2010(3): 17-20.
[3] 申殿邦. 氧气底吹炼铜新工艺[EB/OL]. [2012-01-31]. http://www.cmra.cn/a/33333/2012/0131/228221.html.
SHEN Dian-bang. New process of copper smelting with oxygen enriched bottom blowing technology[EB/OL]. [2012-01-31]. http://www.cmra.cn/a/33333/2012/0131/228221.html.
[4] 中华人民共和国工业和信息化部. 关于印发《有色金属工业“十二五”发展规划》的通知[EB/OL]. [2012-01-30]. http://www.miit.gov.cn/n11293472/n11293832/n11293907/n11368223/14447635.html.
Ministry of industry and information technology of the people’s republic of China. Announcement on the issuance of “non-ferrous metals industry twelfth five-year development plan”[EB/OL]. [2012-01-30]. http://www.miit.gov.cn/n11293472/ n11293832/n11293907/n11368223/14447635.html.
[5] 中华人民共和国工业和信息化部. 铜冶炼行业规范条件[EB/OL]. [2014-04-28]. http://www.miit.gov.cn/n11293472/ n11293832/n12845605/n13916898/15976630.html.
Ministry of industry and information technology of the people’s republic of China. Copper smelting industry norms conditions [EB/OL]. [2014-04-28]. http://www.miit.gov.cn/n11293472/ n11293832/n12845605/n13916898/15976630.html.
[6] 陈知若. 底吹炼铜技术的应用[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2009(5): 16-22.
CHEN Zhi-ruo. The application of oxygen bottom-blown bath smelting of copper[J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2009(5): 16-22.
[7] YAZAWA A. Thermodynamic considerations of copper smelting[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 1974, 13(3): 443-453.
[8] SERGEI A D, ARTHUR D P. A thermodynamic database for copper smelting and converting [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1999, 30(4): 661-669.
[9] SRIDHAR R, TOGURI J M, SIMEONOV S. Copper losses and thermodynamic considerations in copper smelting[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1997, 28(2): 191-200.
[10] NAGAMORI M, MACKEY P J. Thermodynamics of copper matte converting: Part 1. Fundamentals of the Noranda process[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1978, 9(3): 255-265.
[11] MACKEY P J. The physical chemistry of copper smelting slags—A review[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 1982, 21(3): 221-260.
[12] 张振扬, 陈 卓, 闫红杰, 刘方侃, 刘 柳, 崔志祥, 申殿邦. 富氧底吹熔炼炉内气液两相流动的数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(6): 1826-1834.
ZHANG Zhen-yang, CHEN Zhu, YAN Hong-jie, LIU Fang-kan, LIU Liu, CUI Zhi-xian, SHEN Dian-ban. Numerical simulation of gas-liquid multi-phase flows in oxygen enriched bottom-blown furnace[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(6): 1826-1834.
[13] 张振扬, 闫红杰, 刘方侃, 王计敏. 富氧底吹熔炼炉内氧枪结构参数的优化分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(5): 1471-1477.
ZHANG Zhen-yang, YAN Hong-jie, LIU Fang-kan, WANG Ji-min. Optimization analysis of lance structure parameters in oxygen enriched bottom-blown furnace[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(5): 1471-1477.
[14] 崔志祥, 申殿邦, 王 智, 边瑞民. 低碳经济与氧气底吹熔池炼铜新工艺[J]. 工艺节能, 2011(1): 17-20.
CUI Zhi-xiang, SHEN Dian-bang, WANG Zhi, BIAN Rui-min. Low-carbon economy and new process of copper smelting with oxygen enriched bottom blowing technology[J]. Energy Saving on Technique, 2011(1): 17-20.
[15] 刘 柳, 闫红杰, 周孑民, 高 强, 张振杨, 刘方侃, 崔志祥. 氧气底吹铜熔池熔炼过程的机理及产物的微观分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(7): 2116-2124.
ZHANG Zhen-yang, YAN Hong-jie, LIU Fang-kan, WANG Ji-min. Mechanism of copper smelting process by oxygen bottom blowing and microanalysis of smelting products[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(7): 2116-2124.
[16] 曲胜利, 董准勤, 陈 涛. 富氧底吹造锍捕金工艺研究[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2013(6): 40-42.
QU Sheng-li, DONG Zhun-qin, CHEN Tao. Study on gold collection in matte with oxygen enriched bottom blowing smelting process[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2013(6): 40-42.
[17] 刘纯鹏. 铜冶金物理化学[M]. 上海: 科学技术出版社, 1990: 363-371.
LIU Chun-peng. Physical chemistry of copper metallurgy[M]. Shanghai: Science and Technology Press, 1990: 363-371.
[18] 朱祖泽, 贺家齐. 现代铜冶金学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 320-322.
ZHU Zu-ze, HE Jia-qi. Current copper metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003: 320-322.
[19] YAZAWA A. Thermodynamic evaluations of extractive metallurgical processes[J]. Metallurgical Transaction B, 1979, 10: 307-321.
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:湖南有色研究基金重点资助项目(YSZN2013YJ01)
收稿日期:2014-08-15;修订日期:2015-01-07
通信作者:郭学益,教授,博士;电话:0731-88877863;E-mail: xyguo@csu.edu.cn