文章编号: 1004-0609(2005)02-0210-07
Ca对镁合金组织、 力学性能和腐蚀性能的影响
樊 昱, 吴国华, 高洪涛, 翟春泉, 朱燕萍
(上海交通大学 材料科学与工程学院, 上海 200030)
摘 要: 研究了Ca对AZ91D镁合金显微组织、 力学性能和腐蚀性能的影响。 当AZ91D中加入的Ca含量大于1.0%时, β相(Mg17Al12)减少, 并且在晶界上形成了网状分布的Al2Ca相。 拉伸测试表明, 当加入Ca含量小于1%时, 可以提高合金的常温抗拉强度和延伸率, 继续增大Ca含量时合金的力学性能明显下降。 当AZ91D中加入的Ca含量达到1.0%时, 常温抗拉强度和延伸率较AZ91D分别提高了8.2%和29.3%, 并且腐蚀速率下降为AZ91D的17.2%。 其原因主要是由于形成了网状分布的Al2Ca相, 使镁合金的自腐蚀电位升高, 腐蚀电流密度降低, 从而阻碍了镁合金的腐蚀。
关键词: 镁合金; 钙; 显微组织; 力学性能; 腐蚀; 极化曲线 中图分类号: TG146.2
文献标识码: A
Effect of calcium on microstructure, mechanical properties and
corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy
FAN Yu, WU Guo-hua, GAO Hong-tao, ZHAI Chun-quan, ZHU Yan-ping
(School of Materials Science and Engineering,
Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai 200030, China)
Abstract: The effect of calcium on microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy was studied. When the addition of Ca is more than 1%, the β phase decreases and some reticular Al2Ca phases form on grain boundaries. The tensile tests indicate that when the Ca addition is less than 1%, the ultimate strength and elongation of AZ91D alloy increase, but when the Ca addition is more than 1%, the strength and elongation of AZ91D alloy decrease. The ultimate strength and elongation of AZ91D alloy with the addition of 1% Ca respectively increase by 8.2% and 29.3%, and the corrosion rate decreases to 17.2%. This is mainly caused by the formation of reticular Al2Ca phase, which acts as an effective barrier against corrosion and makes the corrosion potential increasing and the corrosion current density decreasing.
Key words: magnesium alloy; calcium; microstructure; mechanical properties; corrosion; polarization curves
在铸造镁合金中, AZ91是应用最为广泛的一种, 它具有良好的铸造性能和较高的屈服强度, 可用于多种形式的机械部件[1, 2]。 但其力学性能随环境温度升高而迅速下降和它在各种介质中的耐腐蚀性能较差严重制约了它的进一步应用。 AZ91在酸性、 中性和弱碱性环境中都不耐腐蚀, 在pH=11的碱性溶液中, 由于生成稳定钝化膜, 因而具有较好的耐蚀性[3, 4]。 但当碱性溶液中存在Cl-时, 镁合金的表面钝态被破坏, 合金也会受到腐蚀。
Ca是提高镁合金性能的重要合金元素[5]。 在耐热镁合金中, 用Ca进行合金化是提高镁合金高温性能的主要措施之一[6, 7]。 在AZ91镁合金中, 添加一定量的Ca也可以提高其高温下的力学性能[8], 从而使AZ91合金的应用范围更为广泛。 有关 AZ91镁合金腐蚀性研究的报导不少[9-11], 但关于Ca合金化对AZ91镁合金耐腐蚀性影响的报导甚少。 本文作者研究了Ca合金化对AZ91D镁合金耐蚀性能的影响及其作用机理, 这对扩大Ca在镁合金中的应用, 提高镁合金的性能有着重要的现实意义。
1 实验
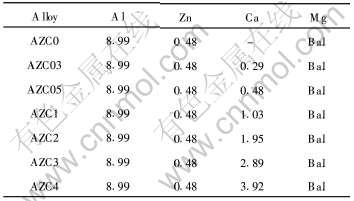
实验合金系为AZ91D+xCa(x的取值为0, 0.3, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4)。 采用工业用AZ91D和纯Ca(实收率约80%), 在电阻坩埚炉中熔炼, 以空气+SF6+CO2混合气体作为保护气体。 合金编号命名为AZC, 其中C代表Ca, 其化学成分见表1。
表1 合金的化学成分(质量分数, %)
Table 1 Compositions of studied alloys (mass fraction, %)
采用线切割把铸锭加工成符合国标GB228-87的板状比例拉伸试样, 试样标距为25mm, 厚度为2mm, 宽度为10mm, 在Zwick Roell材料实验机上进行常温拉伸测试。 金相样品从铸锭上切取, 经金刚石研磨膏粗抛光后用MgO粉精抛, 并用4%的硝酸酒精溶液浸蚀, 然后采用光学显微镜、 SEM、 XRD等手段进行合金组织及相分析。
腐蚀试样尺寸为d35mm 4mm, 实验前经1000#金相砂纸打磨处理, 然后用丙酮、 酒精清除表面油污, 再称量试样的初始质量。 平行实验的试样数量为3片, 取平均值作为实验结果。 实验采用5%的NaCl溶液(pH=8.3)作为腐蚀介质, 实验温度为(25±3)℃。 将腐蚀试样悬挂在腐蚀介质中浸泡3d, 之后在沸腾的铬酸溶液(Cr2O3 180mg/mL+1%AgNO3)中清洗5min, 然后再用丙酮、 酒精进行清洗, 之后烘干并在分析天平上称量。 腐蚀后的试样在SEM上进行腐蚀表面形貌观察。
极化测试采用ZF-10电化学测试系统, 以恒电位扫描法测定试样在5%的NaCl溶液(pH=8.3)中的极化曲线, 扫描速率为1mV/s。 实验采用三电极系统, 参比电极为饱和甘汞电极, 辅助电极为不锈钢电极, 工作电极为片状试样, 试样尺寸为10mm 10mm 2mm。 试样先经1000#金相砂纸打磨处理, 然后用丙酮、 酒精清洗, 之后经过蜡封使试样与NaCl溶液接触面积大约为2mm2。
2 结果与分析
2.1 显微组织
图1所示为AZ91D镁合金中加入不同含量Ca时的显微组织。 通常Mg-Al-Zn系镁合金的显微组织由基体固溶体α相、 分布在晶界周围的白色条状β相(Mg17Al12)和少量的共晶组织组成。 从图1(a)、 (b)中可以看出, 当加入的Ca含量不超过0.5%时, 其显微组织仍为α相和β相, β相得到了一定的细化, 并且出现了一些粒状的β相。 同时XRD分析也并未发现新相。 这说明少量的Ca加入到AZ91合金中, 主要是以固溶原子形式存在的, 没有形成新相。 而闵学刚等[12]在研究中也指出少量的Ca加入到AZ91中并不形成新相。
从图1(c)中可以明显看出, 当Ca含量达到1%时, 在晶界上除了白色的β相外, 还出现了一些层片状的黑色组织。 从图1(d)可以看出, 当Ca含量达到2%时, 晶界上的β相Mg17Al12明显减少, 出现了大量的黑色层片状组织。 图2(a)为其XRD分析结果, 表明合金中除了α相和β相以外, 还出现了新相Al2Ca, 说明黑色层片状组织为Al2Ca相。 当加入的Ca含量达到3%时, 黑色层片状的Al2Ca相更加粗化, 层与层之间的片间距也增大, 基本上看不到白色的β相Mg17Al12, 说明β相已经大大减少。
当加入的Ca含量达到4%时, 由图1(f)可以看出, 黑色的Al2Ca相进一步粗化。 图3为AZC4的SEM照片。 从图3(a)可以看出, 白色的Al2Ca相及少量的Mg2Ca相成连续的网状和鱼骨状分布; 从图3(b)可以看出, 白色的Al2Ca在晶界上呈相互平行的层片状析出。 AZC4的XRD分析表明(图2(b)), 此时合金组织为基体α相、 Al2Ca和Mg2Ca, β相Mg17Al12已经完全消失, 晶界强化相变成Al2Ca。 这主要是由于Al2Ca的熔点(1079℃)远高于Mg17Al12的熔点(437℃), 并且Al2Ca比Mg17Al12更稳定, 因此随着Ca含量的增加, Al容易与Ca结合生成Al2Ca相, 而多余的Al则固溶于基体中, 从而使Mg17Al12相逐渐减少直至消失。
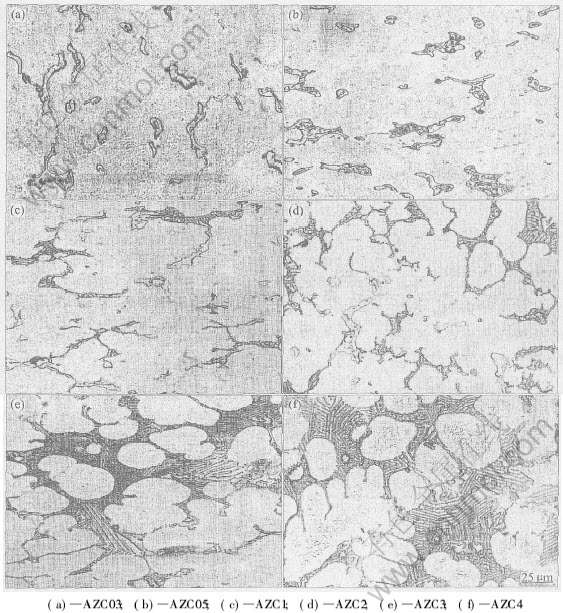
图1 铸态AZC系列合金的显微组织
Fig.1 Optical microstructures of as-cast AZC alloys
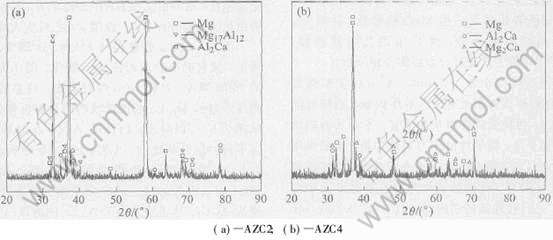
图2 铸态AZC系列合金的X射线衍射谱
Fig.2 XRD patterns of AZC alloys
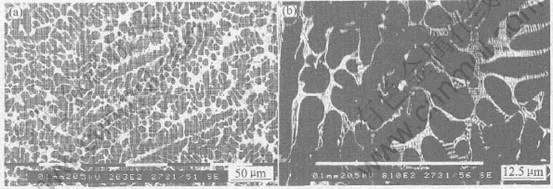
图3 铸态AZC4合金扫描电镜照片
Fig.3 SEM photos of as-cast AZC4 alloy
2.2 力学性能
图4所示为AZC系列合金的常温拉伸实验结果。 当Ca含量为1.0%时, AZ91合金具有较高的抗拉强度和延伸率, 分别比AZC0提高了8.2%和29.3%, 而对屈服强度影响不大, 当加入Ca为0.3%时屈服强度略有增加。 这说明在镁合金中添加少量的Ca, 可以提高其常温力学性能。 结合显微组织分析, Ca的存在使合金组织得到了细化, 并且少量Ca还具有一定的固溶强化作用。 根据Mg-Al和Al-Ca二元相图可知[13, 14], Al2Ca和Mg17Al12的熔点分别为1079℃和437℃, 因此在合金凝固过程中, Al2Ca优先于Mg17Al12并在凝固早期开始形成, 首先形成的Al2Ca相能够阻止凝固和冷却后期晶粒的长大, 使合金组织细化。
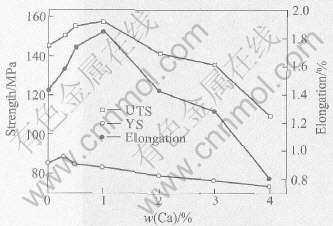
图4 AZC系列合金常温拉伸力学性能
Fig.4 Tensile properties of AZC alloys at room temperature
但是如果进一步加大Ca含量, AZ91D合金的抗拉强度和延伸率明显下降, 屈服强度也呈缓慢下降的趋势。 这是由于Ca在镁中的固溶度很低(最大为0.82%[15]), 多余的Ca在晶界上形成Al2Ca相和少量的Mg2Ca相, 并呈连续的网状分布, 从而割裂了基体组织, 使合金的强度和塑性大大降低。 另外, 脆性相Al2Ca呈层片状析出, 增加了合金的脆性, 因而过量的Ca会导致合金脆性增强, 常温抗拉强度和延伸率下降。
2.3 腐蚀性能
2.3.1 腐蚀失重实验结果
图5所示为在AZ91D合金中加入Ca时, 腐蚀试样在5%的NaCl溶液(pH=8.3, 温度为(25±3)℃中所测得的腐蚀速率结果。 从图5可以看出, 随着Ca含量的增加, AZC系列合金的腐蚀速率明显降低, 尤其当Ca含量达到1%以上时, 其腐蚀速率均在0.1mg/(cm·d)以下, 相当于原AZ91D腐蚀速率的20%左右。 当Ca含量达到2%时, AZC系列合金的腐蚀速率下降到原AZ91D腐蚀速率的十分之一以下; 如果Ca含量继续增大, AZC系列合金的腐蚀速率又缓慢增大。
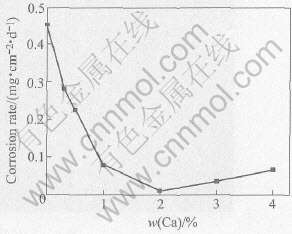
图5 AZC系列合金的腐蚀速率
Fig.5 Corrosion rate of AZC alloys (pH 8.3, 25℃)
2.3.2 腐蚀表面形貌
从图6(a)和(b)可以看出, AZC0的腐蚀形貌主要有两大特征, 一是表面腐蚀膜受到破坏后, 发生大面积的脱落(如图6(a)所示), 腐蚀膜脱落后合金表面又发生了局部腐蚀; 二是某些局部区域发生了较为严重的腐蚀, 出现了较深的腐蚀深坑(如图6(b)所示), 其中白色的为腐蚀产物, 黑色的为较深的蚀坑。 图6(c)为AZC1合金的腐蚀表面SEM形貌, 从中可以看出在AZ91D中加入1%Ca后, 其腐蚀膜脱落减少, 并且局部腐蚀坑的数量与AZC0相比也大大减少, 腐蚀坑的深度也变浅, 表明合金的耐蚀性增强。 当AZ91D中的Ca含量达到2%时(如图6(d)所示), 其腐蚀膜基本上完好无损地覆盖在合金表面, 对合金起到了很好的保护作用。
2.3.3 极化曲线
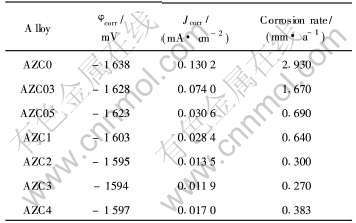
AZC系列合金的极化曲线如图7所示。 从图中可以看出, Ca的加入改变了合金的阴极极化曲线, 其极化曲线的电化学处理结果见表2。 从表2可以看出, 在AZ91D中加入Ca后, 合金的腐蚀电位明显增加, 当Ca含量达到1%时, 合金的腐蚀电位比AZ91D的腐蚀电位大约高40mV; 继续增大Ca含量, 合金的腐蚀电位基本上保持不变。 另外, 从表2中的腐蚀电流密度来看, Ca含量的增大使其腐蚀电流密度降低, 并且依据法拉第电化学当量的换算, 得到合金的腐蚀速度, 此腐蚀速度的变化规律与失重法测得的腐蚀速率基本上吻合。
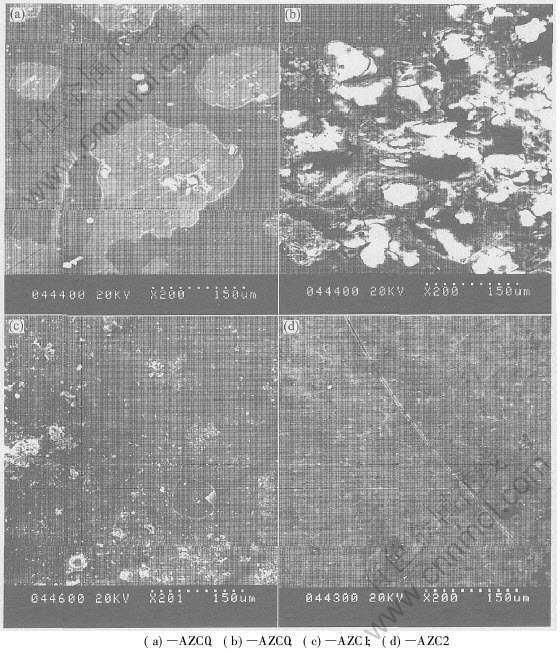
图6 AZC系列合金腐蚀后的SEM形貌
Fig.6 SEM morphologies of corrosion surfaces of AZC alloys
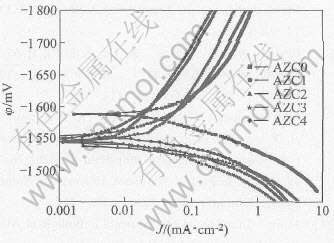
图7 AZC系列合金的极化曲线
Fig.7 Polarization curves of AZC alloys
表2 AZC系列合金电化学腐蚀数据
Table 2 Electrochemical corrosion data of AZC alloys
3 讨论
Song等[16]在研究中发现, AZ91D合金表面β相(Mg17Al12)的体积分数大且呈网状连续分布, 起到阻碍腐蚀的作用, 大大提高了合金的耐蚀性。 另外, Ko等[17]在研究Mg17Al12相析出对AZ91D镁合金腐蚀性能的影响时发现, 网状分布的Mg17Al12相可以有效地阻碍腐蚀。
在AZ91D中加入Ca时, 其耐蚀性明显提高。 结合AZC系列合金的显微组织分析, 当Ca含量达到1%时, 晶界上已经形成网状分布的Al2Ca相和β相, 这种网状分布的Al2Ca相和β相, 大大阻碍了镁合金的腐蚀, 从而提高其耐蚀性。 由于网状分布的Al2Ca相的形成及不断增多, 镁合金的腐蚀电位升高, 腐蚀试样的坑蚀深度减小, 试样的腐蚀速率降低。 这充分表明Ca的加入能够提高AZ91的耐蚀性。 但当加入Ca达到4%时, 由于网状Al2Ca相的明显粗化, 使合金的腐蚀电流密度从AZC2的0.0135mA/cm2增大到0.0170mA/cm2, 从而导致合金的腐蚀速率略有增大。
当AZ91中Ca含量达到1%时, 其腐蚀速率下降到AZ91D的20%左右; 当Ca含量达到2%时, 腐蚀速率最小, 说明其耐蚀性最佳。 但当Ca含量超过1%时, 过多的脆性相Al2Ca使合金的力学性能显著降低。 因此, 结合力学性能和耐腐蚀性能二方面因素, 以加入1%Ca时效果最好。
4 结论
1) 当AZ91D中加入0.5%Ca时, 其显微组织仍为基体α相和β相(Mg17Al12), 与AZ91D相同; 当加入的Ca含量达到1%时, 其晶界上形成了网状分布的Al2Ca相和β相; 当Ca含量增大到4%时, β相已完全消失, 并且出现了新相Mg2Ca。
2) 在AZ91D中添加少量的Ca, 可以提高其常温力学性能。 当Ca含量为1.0%时, 合金具有较高的抗拉强度和延伸率, 分别比AZ91D提高了8.2%和29.3%, 而对屈服强度影响不明显。 但是如果进一步加大Ca含量, 其抗拉强度和延伸率明显下降。
3) 当在AZ91D中加入1.0%Ca时, 其腐蚀速率下降为AZ91D的17.2%。 这主要是由于Ca的加入形成了网状分布的Al2Ca相, 阻碍了镁合金的腐蚀, 使镁合金的腐蚀电位升高, 腐蚀试样的坑蚀深度减小, 试样的腐蚀速率降低, 从而大大提高了镁合金的耐蚀性。
REFERENCES
[1]WU Guo-hua, XIE Min, ZHAI Chun-quan, et al. Purification technology of AZ91 magnesium alloy wastes[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2003, 13(6): 1260-1264.
[2]王业双, 王渠东, 马春江, 等. Zn和RE对Mg-9Al合金热裂倾向性的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(1): 40-45.
WANG Ye-shuang, WANG Qu-dong, MA Chun-jiang, et al. Hot-tearing susceptibility of Mg-9Al-xZn-yRE alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(1): 40-45.
[3]Mathieu S, Rapin C, Steinmetz J, et al. A corrosion study of the main constituent phases of AZ91 magnesium alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2003, 45: 2741-2755.
[4]Ambat R, Aung N, Zhou W. Evaluation of microstructural effects on corrosion behaviour of AZ91D magnesium alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2000, 42: 1433-1455.
[5]刘生发, 范晓明, 王仲范. 钙在铸造镁合金中的作用[J]. 铸造, 2003, 52(4): 246-248.
LIU Sheng-fa, FAN Xiao-ming, WANG Zhong-fan. The role of calcium in cast magnesium and magnesium alloys[J]. Foundry, 2003, 52(4): 246-248.
[6]Ninomiya R, Ojtro T, Kubpta K. Improved heat resistance of Mg-Al alloys by the Ca addition[J]. Acta Metall Master, 1995, 43(2): 669-683.
[7]Mihriban O, Eric B. Creep resistant magnesium diecasting alloys based on alkaline earth elements[J]. Mater Trans JIM, 2001, 42(7): 1258-1293.
[8]曾小勤, 王渠东, 吕宜振, 等. Mg-9Al-0.5Zn-0.1Be-xCa合金的组织和力学性能研究[J]. 机械工程材料, 2001, 25(5): 104-107.
ZENG Xiao-qin, WANG Qu-dong, L Yi-zhen, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-9Al-0.5Zn-0.1Be-xCa alloys[J]. Materials for Mechnical Engineering, 2001, 25(5): 104-107.
[9]Mathieu S, Rapin C, Hazan J, et al. Corrosion behavior of high pressure die-cast and semi-solid cast AZ91D alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2002, 44: 2737-2756.
[10]Mathieu S, Rapin C, Steinmetz J. A corrosion study of the main constituent phases of AZ91 magnesium alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2003, 45: 2741-2755.
[11]Song G, Bowles A L, Stjohn O H. Corrosion resistance of aged die cast magnesium alloy AZ91D[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 366(1): 74-86.
[12]闵学刚, 孙扬善, 杜温文, 等. Ca, Si和RE对AZ91合金的组织和性能的影响[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 32(3): 409-414.
MIN Xue-gang, SUN Yang-shan, DU Wen-wen, et al. Effects of Ca, Si and RE additions on the microstructures and mechanical properties of AZ91 based alloys[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2002, 32(3): 409-414.
[13]Murray J L. The Al-Mg system[J]. Bulletin of Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1982, 3(1): 60-64.
[14]Itkin V P, Alcock C B, Van P J, et al. The Al-Ca system[J]. Bulletin of Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1988, 9(6): 652-657.
[15]Nayeb Hashemi A A, Clark J B. The Mg-Ca system[J]. Bulletin of Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1987, 8(1): 58-65.
[16]Song G, Atrens A, Dargusch M. Influence of microstructure on the corrosion of diecast AZ91D[J]. Corrosion Science, 1999, 41: 249-273.
[17]Ko Y J, Yim C K, Lim J D, et al. Effect of Mg17Al12 precipitate on corrosion behavior of AZ91D magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2003, 419(1): 851-856.
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金资助项目(50474005)
收稿日期: 2004-08-10; 修订日期: 2004-10-14
作者简介: 樊 昱(1979-), 男, 博士研究生.
通讯作者: 樊 昱, 博士研究生; 电话: 021-62932549; 传真: 021-62932113; E-mail: fyspy@sjtu.edu.cn
(编辑袁赛前)