Article ID: 1003-6326(2005)06-1219-07
Electrode degradation mechanism during
resistance spot welding of zinc coated steel using
Cu-TiB2 electrodes
DONG Shi-jie(董仕节)1, ZHOU Norman2, CHENG Chang-kun(程长坤)1,
SHI Yao-wu(史耀武)3, CHANG Bao-hua(常保华)4
(1. Department of Material Engineering, Hubei Automobile Industrial Institute,
Shiyan 442002, China;
2. Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Waterloo,
Waterloo, Ontario, N2L 3G1, Canada;
3. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Polytechnic University,
Beijing 100022, China;
4. School of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China)
Abstract: The TiB2 dispersion-reinforced copper-matrix composite used as electrode material in resistance spot welding of zinc coated steels was studied. The service life of the composite electrode reaches 7700 welds, which is 4 times that of the conventional Cu-Cr-Zr electrode. Little gross deformation is observed on the composite electrodes because of the higher thermal strength; therefore, it is believed that wear is the only mechanism for the composite electrode deterioration. However, both wear and plastic deformation are responsible for the large increase in the tip diameter of the Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes. Moreover, the large deformation of the Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes may contribute to the increased wear rate of the tips.
Key words: Cu-TiB2 electrodes; electrode materials; resistance spot welding; TiB2 dispersion-reinforced copper-matrix composite; zinc coated steels; degradation mechanism CLC
number: TG431 Document code: A
1 INTRODUCTION
Resistance spot welding(RSW) is the most commonly used method for joining steel sheets in the automotive industry. In RSW, a weld is formed between two workpieces through melting and coalescence of a small volume of the material at the faying surfaces due to the resistance heat caused by the passage of electric current when the workpieces are held together under a large electrode force[1, 2]. Over the past decade, the requirement of improved corrosion resistance in automobile body panels because of the use of lighter gauges of steels sheets has dramatically increased the application of zinc coated steels. As a result, accelerated degradation of electrodes by the zinc coating becomes one of the major problems. To improve the electrode life, considerable work has been done to study the effects of processing conditions (welding parameters, electrode geometry and materials, coating thickness, etc) on the electrode deterioration and to understand the degradation mechanism[3-5].
Electrodes degrade during welding because of their interactions with workpieces under the influences of high-temperature thermal cycling and repeated high-pressure mechanical impact. A number of factors have been proposed to be responsible for the degradation: softening, pitting, cavitation, erosion, alloying with the zinc coating, recovery and recrystallization, thermal fatigue, etc[6, 7]. However, almost all of these factors contribute, through two major mechanisms—plastic deformation and electrode tip wear, to an increase in the tip diameter, which leads to a decrease in current density and, eventually electrode failure because of undersized welds produced.
Plastic deformation(or “mushrooming”) of the electrode tips due to the combined effect of high temperature and electrode force results in an increased tip diameter. Recovery and recrystallization of cold-worked electrode materials affect the plastic deformation[6], and alloying with the zinc coating contributes to the deformation through forming a lower-yield-strength microstructure[8].
Electrode wear can increase the tip diameter due to the loss of material from the tip surface. Localized bonding (by soldering or brazing) would form at the tip and steel faying surfaces because of the low melting point of zinc and zinc alloys formed by the interalloying/interdiffusion[6]. It is thought that these localized adhesions may also be formed by forge welding(seizing) at the contacting surfaces under high pressure although there is no direct experimental evidence[9]. These local bridges (which can be in either molten or solid/solidified state) fracture during electrode retraction after each welding cycle, which removes material away from the tip surface and results in tip surface erosion (pits, and more severely, cavity/crater formation).
As for the electrode materials, they must possess high electrical conductivity to minimize electrode heat, and high thermal conductivity to dissipate heat from the tip and steel faying surfaces; at the same time, they should also exhibit high resistance to softening and to alloying[6]. The precipitation strengthened Cu-Cr, Cu-Cr-Zr and Cu-Zr alloys were most commonly used electrode materials for resistance spot welding of coated steels. There has been, however, a continuous effort to develop different types of electrode material to increase electrode tip life.
[BJ(,,,][BJ)] Vol.15 №.6 Electrode degradation mechanism during resistance spot welding Aluminum-oxide dispersion-reinforced copper alloys(Al2O3/Cu) have been shown to have much higher thermal strength than precipitation strengthened alloys. However, there were conflicting experimental results on whether the higher thermal strength could be transited into an increased tip life[9, 10]. These contradicting results may be a consequence of the fact that softening of the tip surface is likely to be affected by a range of processing variables[6]. For example, under normal welding conditions, electrode hardness reduction is predominately caused by alloying and recovery rather than recrystallization. The softening characteristics of the precipitation and dispersion strengthened materials are similar under such conditions. A molybdenum alloy, TZM (0.5%Ti, 0.08%Zr, balance Mo) capping material brazed onto a copper shank has superior resistance to deformation compared with the copper alloy electrodes[10]. However, heat cracking of the molybdenum alloy surface is one of the most serious drawbacks of the material[11]. A recent invention claims that the TiC coating on electrode tips can increase the tip life by 2-5 times compared with a conventional copper electrode[12, 13] .
This work reports a preliminary study of a new electrode material—TiB2 reinforced copper matrix composite. Electrode degradation mechanisms during RSW of coated steels using the composite electrodes TiB2/Cu are investigated using optical microscope, scanning electron microscope(SEM) and electron microprobe analyzer(EMPA). A Cu-Cr-Zr electrode material is also used for comparison.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
The electrode geometry used in this study is shown in Fig.1. The TiB2 reinforced copper matrix composite is 1.5%TiB2/Cu (mass fraction), and the Cu-Cr-Zr material contains 0.65%Cr, 0.25%Zr, 0.1%Nb, 0.04%Mg, 0.03%Re and balance Cu (mass fraction). The TiB2/Cu composite was made by mechanical alloying followed by sintering under pressure[14]. The electrodes made of the TiB2/Cu were also subjected to the same amount of cold drawing(10%) as the Cu-Cr-Zr electrode for comparison. The steel sheet used is 1.0mm-thick electro-galvanized steel of Fe-0.08%C-0.05%Mn-0.004%Si-0.0054%Al-0.009%P-0.008%S(mass fraction) with a coating of Zn-5.5%Al(mass fraction). RSW was performed on a press type (DN3-300) 50kVA welder under the welding conditions of 2400N electrode force, 11kA welding current, 10 cycle (at 60Hz) welding time, 4L/min cooling water and 30 weld per minute welding rate. Welding was interrupted after 100 welds interval to determine joint strength using a peel test and to measure the tip diameter by a carbon imprint test[15]. Welding tests were terminated when the peel strength fell below 80% of the initial value that was determined at the beginning of the tip life test. The tested electrodes after welding are analyzed using optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy(SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy(EDX).
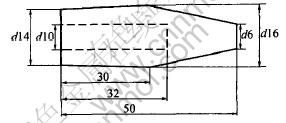
Fig.1 Electrode geometry
3 RESULTS
The average electrode life of TiB2/Cu is 7700 welds, which is over 4 times that of the Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes (1800 welds). Fig.2 shows the variations in electrode tip diameter as a function of the number of welds. The electrode tip surfaces of the final Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes appear very roughly and have many pits and cavities, and large plastic deformation (such as tip “mushrooming” and buildup of overlayers around the tip peripheries) is obvious on the Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes. Otherwise, the tip surfaces of the final TiB2/Cu electrodes appear relatively cleanly and have only a few small pits; no gross deformation is seen on the tips. In fact, it is observed during welding that the Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes start to show pickups and “mushrooming” after 50 welds, and surface pitting after 100 welds; while the TiB2/Cu electrodes only experience some minor pickups and pits after 2000 welds.
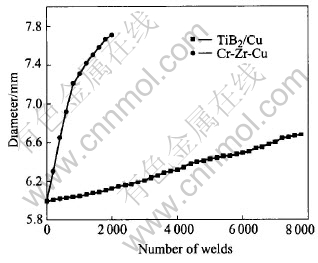
Fig.2 Variations of tip diameter as function of number of welds
SEM photographs of the final electrodes of the TiB2/Cu and Cu-Cr-Zr are shown in Fig.3 with a large cavity pointed out on the Cu-Cr-Zr tip surface. The EDX analysis of the same electrode tip surfaces shows(Table 1) that the TiB2/Cu electrode has much higher Zn content on the tip surface ( Fig.4(a)), indicating that the tip is mainly covered by the pickups from the zinc coating. On the contrary, the Cu-Cr-Zr electrode has much lower Zn but higher Cu contents, which indicates a higher percentage of the coating material of the zinc coated steel on the TiB2/Cu electrode tip surface. The area mapping of Zn, Al, Fe and Cu (Fig.4) indicates that this phenomanon is due to the higher Cu and lower Zn contents seen on the pit and cavity regions (e.g., on a large cavity A in Fig.3(b)).
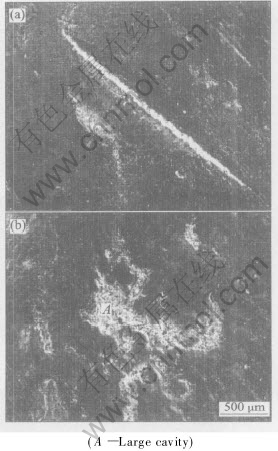
Fig.3 SEM photographs of tip surfaces of TiB2/Cu electrodes (after 7800 welds)(a) and Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes (after 1800 welds)(b)
Table 1 Average chemical compositions on tip surface (mass fraction, %)
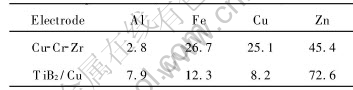
Fig.5 shows the microphotographs of the tip cross sections of the final electrodes of TiB2/Cu and Cu-Cr-Zr. There is an alloying zone on the TiB2/Cu tip and a recrystallization zone between the alloying layer and the elongated grains of the cold-worked microstructure (Fig.5(a)). The alloying zone is very thin on the Cu-Cr-Zr tip (Fig.5(b)), and the recrystallization zone is much wider so that the elongated grains of the cold-worked microstructure are not shown in Fig.5(b). It is also interesting to note a narrow fine-grained region between the alloying layer and the recrystallization zone in Fig.5(b), which is thought to be the result of repeated hot-working during resistance spot welding. The difference in softening temperature between TiB2/Cu (about 900℃[14, 16]) and Cu-Cr-Zr (about 500℃[15]) can explain the observed difference in recrystallization between the two materials. The lower thermal strength of the Cu-Cr-Zr materials compared with the TiB2/Cu material also contributes to the large “mushrooming” of the Cu-Cr-Zr electrode.
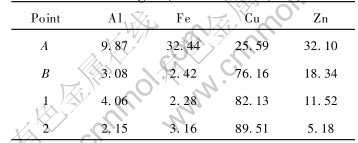
The alloying zone on the TiB2/Cu tip in Fig.5(a) consists actually of two layers (Fig.6(a)). Table 2 lists the contents of Al, Fe, Cu, Zn of point A, B in Fig.6(a) and point 1, 2 in Fig.6(b). It is indicated that the outer layer has much higher contents of Zn, Al and Fe compared with the inner layer. Fig.7(a) also shows that the outer layer contains much higher contents of Zn, Al and Fe compared with the inner layer. However, the alloying zone on the Cu-Cr-Zr electrode tip in Fig.5(b) consists only one thin layer (Fig.6(b)). Table 2 lists that the contents of Zn, Al, and Fe of alloying layer of Cu-Cr-Zr tip are lower than those of composite tip. In an investigation of the heat treat- ment of Cu-Cr and Cu-Zr electrode alloys in a
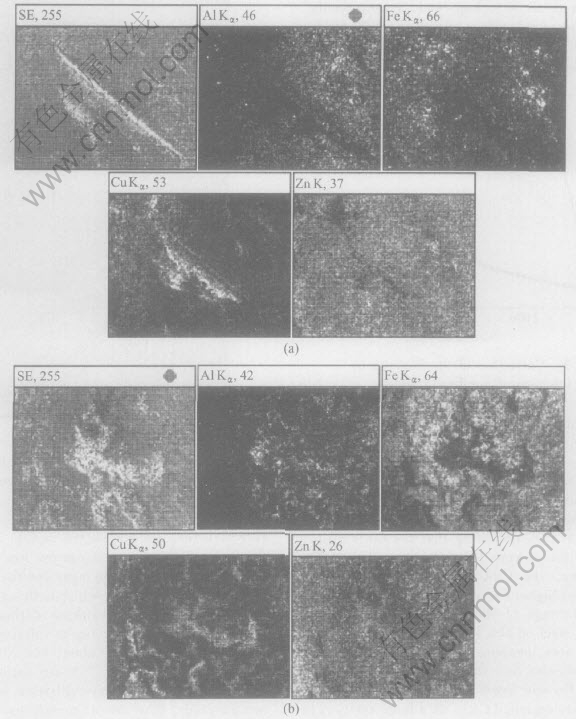
Fig.4 EDX area mappings of Zn, Al, Fe, Cu on tip surfaces of TiB2/Cu electrode(a) and Cu-Cr-Zr electrode(b) in Fig.3
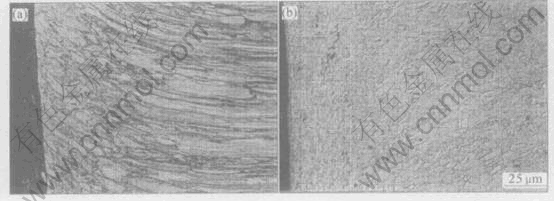
Fig.5 Microphotographs of tip cross-sections of TiB2/Cu electrodes (after 7800 welds)(a) and Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes (after 1800 welds)(b)
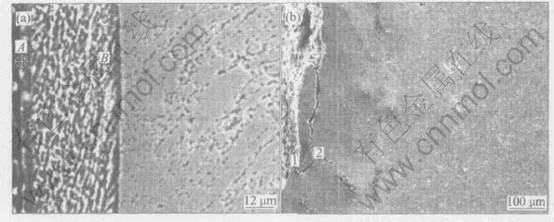
Fig.6 SEM microphotographs of tip cross-sections of TiB2/Cu electrode(a) and Cu-Cr-Zr electrode(b) in Fig.5
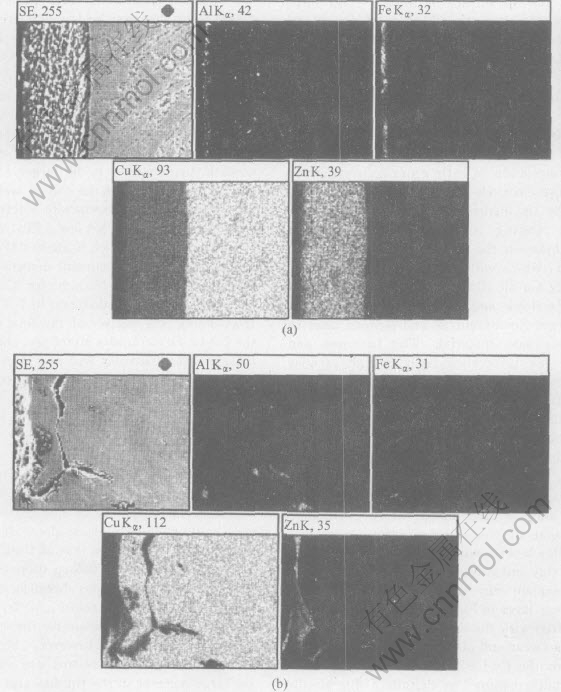
Fig.7 Elemental distributions of Zn, Al, Fe and Cu on tip cross-sections of TiB2/Cu electrode(a) and Cu-Cr-Zr electrode(b) in Fig.6
Table 2 Chemical compositions of zones in Fig.6 (mass fraction, %)
molten zinc bath, Parker et al[6] have also seen a dual-layer alloy formation that consists of an outer γ-brass and an inner layer of α-β brass. The high Zn content in the tip surface of the composite electrode(Table 2) may indicate an outer γ-brass, but the alloying layer of the tip surface of Cu-Cr-Zr electrode may indicate α-brass. Fig.6(b) also shows that the tip surface of the Cu-Cr-Zr electrode is cracked and roughed because of the pit and cavitiy formation(Fig.3); while that of the TiB2/Cu electrode is smooth and crack-free (Fig.6(a)). Cracking of the alloy layers, especially the γ-brass, has been observed in previous works[3].
4 DISCUSSION
The observation on little gross deformation at the composite electrode tips indicates that the increase in the tip diameter is caused by the wear mechanism. During welding, chemical reaction will occur between the electrodes and the molten zinc coating, which will result in a series of products (mainly Cu-Zn alloys). The products would be mainly Zn-rich ε- and γ-brass next to the molten zinc and lower-Zn-content α- and β-brass next to the electrode base material. The hardness and strength of the outer alloy layer is high because TiB2 reinforces not only the parent copper but also the outer alloy layer, so the brittle outer alloy layer is difficult to detach from the tip surface under repeated impact (under pressure up to 85MPa) and thermal cycling (thermal stress and thermal fatigue, etc). The high content Zn, Al, Fe elements of tip surface may diffuse to inner surface then form inner alloying layer under the spot welding. The new outer alloying layer may form when the old outer alloy layer is worn out, but the inner layer tends to stay and grow because it dose not wear. This may explain why the outer layer is thinner than the inner layer in Fig.7(a).
Compared with the composite electrodes, two mechanisms (wear and plastic deformation) are responsible for the Cu-Cr-Zr electrode degradation. The tip “mushrooming” is definitely due to the much lower softening temperature of the Cu-Cr-Zr material (500℃ versus 900℃ for the composition material)[14-16]. Although it is impossible to compare the difference in wear rate between two electrode materials, it is thought that the large deformation in the Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes will greatly speed up the wear rate. Larger tip deformation will promote cracking in the brittle alloying layer on the Cu-Cr-Zr tip surface, which in turn speeds up the tip material loss. This may also explain why there appears only one single layer on the Cu-Cr-Zr tip surface(Fig.7(b)) since the outer alloy products (mainly ε- and γ-brass) continuously detach away and form again, and no time is available for the formation and, more important, growth of a inner layer (α- and β-brass).
It is interesting to note that the final diameter of the composite electrodes is much smaller than that of the Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes(Fig.2). This is believed to be due to the pit and cavity formation on the Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes[17]. It is known that an increase in tip diameter leads to a decrease in current density and, eventually, electrode failure. Since the tip surfaces of the composite electrodes are reasonably smooth, it is assumed that the whole tip surfaces are still able to conduct current even in the end of welding. However, the Cu-Cr-Zr tip surfaces have many pits and cavities that will reduce the effective current carrying area and allow the nominal tip diameter to be larger. For example, the current density in the end of welding is about 321A/mm2 for the composite electrodes (with a welding current of 11kA and a final tip diameter of 6.6mm, Fig.2), which is about 83% of the initial current density. The current density at the end of welding is about 236A/mm2 for Cu-Cr-Zr in appearance(with a final diameter of 7.7mm, Fig.2). If assuming one quarter of the final tip surface of the Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes are of pits and cavities, the actural current density will be 315A/mm2, which is surprisingly close to the failure current density for the composite electrodes.
5 CONCLUSIONS
A new electrode material, TiB2 dispersion-reinforced copper matrix composite, was studied in resistance spot welding of zinc coated steels. The service life of the composite electrode reaches 7700 welds, which is 4 times that of Cu-Cr-Zr electrode material. Little gross deformation is observed on the composite electrodes because of the higher thermal strength; therefore, it is believed that wear is the only mechanism for the composite electrode deterioration. However, both wear and “mushrooming” mechanisms are responsible for the large increase in the tip diameter of the Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes. Moreover, the large deformation of the Cu-Cr-Zr electrodes may contribute to the increased wear rate of the tips.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author wishes to thank Dong Feng Motor Corporation for financial support of this study. The contributions of DUANG Reng-ming, LIU Zhong-hou and ZHAO Yu-mei for their metallographic, microprobe work, shear tension test and resistance spot welding are also greatly appreciated.
REFERENCES
[1]Dong S J, Zhou Y. Effect of TiC composite coating on electrode degradation in microresistance welding on nickel-plated steel [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2003, 34(7): 1501-1511.
[2]Friedman L M, McCauley R B. Influence of metallurgical characteristics on resistance welding of galvanized steel[J]. Welding Journal, 1969, 48(10): 454s-462s.
[3]Filay R, Samandi M, Howes S. PVD coating of resistance spot welding electrode[J]. Australasian Welding Journal, 1997, 42(1): 39-42.
[4]Holliday R J. Mechanisms of electrode growth during spot welding of coated sheet steels[D]. Swansea: University of Wales, 1996.
[5]Howe P, Kelley S C. Coating weight effect on the resistance spot weldability of electrogalvanized sheet steels[J]. Welding Journal, 1988, 67(12):271s-280s.
[6]Parker J D, Williams N T, Holliday R J. Mechanisms of electrode degradation when spot welding coated steels[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 1998, 3(2): 65-74.
[7]Chatterjee K L, Waddel W. Electrode wear during spot welding of coated steels[J]. Welding & Metal Fabrication, 1996(3): 110-114.
[8]Dong P, Li V M, Kimchi M. Finite element analysis of electrode wear mechanisms: face extrusion and pitting effects[J]. Science Technology of Welding and Joining, 1998, 3(2): 59-64.
[9]Gould J E, Kimchi M, Campbell D H. Weldability and electrode wear characteristics of hot-dip galvanized steel with and without a ferrophos containing primer[R]. SAE Technical Paper Series, 1988. 880370.
[10]Freytag N A. A comprehensive study of spot welding galvanized steel[J]. Welding Journal, 1965, 44(4): 145s-1156s.
[11]Key J F, Courtney T M. Refractory metal composite tips for resistance spot welding of galvanized steel[J]. Welding Journal (Supplement), 1974(6): 261-266.
[12]Nadkarni AV, Weber E P. A new dimension in resistance welding electrode materials [J]. Welding Journal, 1977, 56(11): 331s-338s.
[13]DONG Shi-jie, ZHOU Norman. Effect of TiC coating on electrode tip surface on electrode degradation during resistance spot welding zinc coated steel [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(2): 184-191.(in Chinese)
[14]Dong S J, Zhou Y, Shi Y W, et al. Formation of a TiB2-reinforced copper-based composite by mechanical alloying and hot pressing[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, 33(4): 1275-1280.
[15]Holliday R J. Mechanisms of electrode growth during spot welding of coated sheet steels[D]. Swansea: University of Wales,1996.
[16]Biselli C, Morris D G, Randall N. Mechanical alloying of high-strength copper alloys containing TiB2 and Al2O3 dispersoid particles[J]. Scripta Metallurgica et Materials, 1994, 30(10): 1327-1332.
[17]Prabhjit S. Wear mechanism and technology improvement of TiC cap electrode for resistance spot welding[D]. Waterloo: The University of Waterloo, 2002.
(Edited by YANG Bing)
Received date: 2005-05-09; Accepted date: 2005-08-08
Correspondence: DONG Shi-jie, Professor, PhD; Tel: +86-13508683572; E-mail: dongsjsj@sina.com