降雨入渗对粗粒土路堤变形与稳定性的影响
陈晓斌1, 2,徐望国1,刘小平3
(1. 中南大学 土木建筑学院,湖南 长沙,410075;
2. 广州市建筑科学研究院,广东 广州,510440;
3. 湖南大学 土木工程学院,湖南 长沙,410082)
摘要:针对土石混填粗粒土路堤,分析其降雨入渗机理,得到固定颗粒粒径时的总吸力随饱和度衰减规律,对比降雨入渗深度计算公式。根据饱和土强度折减规律,采用强度折减简要模拟降雨入渗效果,并结合工程实践建立数值模型,对降雨入渗作用下粗粒土路堤变形及稳定性进行计算分析。工程实例计算结果表明:降雨入渗对路堤变形影响明显,随着入渗深度增加,路堤附加沉降增大,当单次入渗深度为2 m时,附加沉降可达1.30 cm;降雨入渗对粗粒土路堤稳定性也有明显影响,入渗作用扩大路堤塑性区范围,降低路堤稳定性。
关键词:降雨入渗;入渗深度;附加变形;路堤稳定性;粗粒土
中图分类号:TU471.8 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)03-0765-07
Effect of rainfall infiltration on additional settlement and stability debasement of granular soil fillings embankment
CHEN Xiao-bin1, 2, XU Wang-guo1, LIU Xiao-ping3
(1. School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Central South University, Changsha 410075, China;
2. Guangzhou Institute of Building Science, Guangzhou 510440, China;
3. College of Civil Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China)
Abstract: The rainfall infiltration mechanism analysis for the granular soil embankment was executed, and the metric suction and shearing strength was generalized when the grain diameter were fixed. The law for granular soil’s metric suction and shearing strength attenuation was obtained and the rainfall infiltration depth calculation formulas were discussed. According to unsaturated soil’s strength attenuation law, the strength discount method was used for the rainfall infiltration effects simulation, and the embankment additional settlement and stability debasement resulting from rainfall infiltration was stimulated by the embankment numerical computation model. The computation results show that rainfall infiltration has effect on the embankment additional settlement, and the additional settlement increases with the increase of the infiltration depth incensement. While the first time infiltration depth reaches 2 m, the additional settlement can reach 1.30 cm. The embankment stability is obviously affected by rainfall infiltration, which expands the plastic zones in the embankment numerical model and thus reduces the stability coefficient.
Key words: rainfall infiltration; infiltration depth; additional embankment deformation; embankment stability; granular soil
土石混填路堤是最典型的粗粒土路堤,在公路建设中应用非常广泛;降雨入渗是粗粒土路堤变形及稳定性降低的自然因素之一。降雨入渗造成的路堤沉降及变形容易导致路面结构应力集中和过早破损。不少学者对土石混填粗粒土填料的工程性质进行了研究,这些研究主要集中在压实度和剪切性能方面[1-3]。但是,对于降雨入渗造成的路堤附加变形及稳定性降低问题,没有引起足够重视。降雨入渗造成的路堤变形及稳定问题核心在于非饱和土水分作用,对于非饱和土中水分迁移问题,许多学者进行了深入研究[4-6]。对于毛细水迁移问题,董加瑞等[7]通过毛细作用下土壤水分扩散特性试验推导出适用于计算土壤水分扩散系数的差分方法。翁通[8]通过试验研究了毛细水在不同时期的上升速度及不同含盐量水的毛细作用强度问题。李锐等[9]应用GEO-SLOPE 软件模拟立于水中的圆柱形土柱,得到了毛细水的上升高度及上升规律。针对降雨水分迁移,陈善雄等[10]用有限差分方法模拟了降雨条件下土体中水分运动情况;朱伟等[11]通过大型降雨渗透试验实测了土堤内入渗线变化和水分移动规律。Pradel等[12]以Green&Ampts模型为基础,考虑降雨强度、降雨持续时间和水的体积分数与土壤的基质吸力关系相互影响等因素,得出了入渗到一定深度所需要时间的计算公式。李焯芬等[13]也提出了入渗深度计算公式。在分析降雨入渗造成的稳定性方面,Fourie等[14]对降雨入渗边坡稳定的影响进行了分析;朱文彬等[15]对降雨条件下土体滑坡进行了有限元数值分析;黄润秋等[16]对滑坡基质吸力进行了观测研究和分析;李兆平等[17]将降雨诱发边坡失稳的原因之一归为降雨使土体含水量增加,黏聚力、内摩擦角及基质吸力降低,从而在整体上降低了土体的抗剪强度;张士宇等[18]对降雨对高填土路堤的入渗深度的进行了测试,同时进行了有限元分析;王瑞钢等[19]对降雨作用下高填土质路堤边坡渗流稳定进行了分析。经调查发现:对于降雨边坡稳定分析问题研究较多,而对降雨入渗造成的路堤尤其是土石混填粗粒土路堤变形及稳定性研究较少。为此,本文作者针对土石混填粗粒土路堤,通过对降雨入渗机理的分析,结合张桑公路工程实践,计算路堤降雨入渗深度,并采用土体强度折减模拟降雨入渗对路堤变形及稳定性的影响,对张桑公路K34+970~35+070段高填路堤在不同降雨入渗深度作用下的变形和稳定性进行分析。
1 非饱和土强度变化
路基土体在正常条件下的水气介质处于平衡状态。图1所示为颗粒间水-气-固相界平衡。由于存在基质吸力,它直接影响土体强度。基质吸力与土体饱和度关系密切,非饱和土中的含水量与基质吸力关系一般用土水特征曲线表达。Rodell[20]只考虑纯水下的吸力,不考虑溶质吸力,非饱和土总基质吸力ψ为:

图1 颗粒间水-气-固相界平衡
Fig.1 Force balance on water-air-grain interface

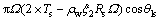 (1)
(1)
式中:ψ为非饱和土总基质吸力;ψ1为非饱和土部分基质吸力;pa和pw分别为孔隙气压力和孔隙水压力;r1为反弯液面曲率半径;Rs为土颗粒的半径;Ts为液面表面张力;ρw为水的密度;ξ2为水膜厚度; 为水膜液面接触角。
为水膜液面接触角。
式(1)中,r1难于直接求解,用土的饱和度参数表示。假设空间正四面体排列下r1可表示为[4]:
 (2)
(2)
式中:Sr为土体饱和度。
式(1)中水膜厚度ξ2也可以用土的饱和度参数表示为:
 (3)
(3)
式(1)中 表示为:
表示为:
 (4)
(4)
据文献[4]可知:在20 ℃时,液面表面张力Ts可取72.7 mN/m,将式(2),(3)和(4)代入式(1),整理得:

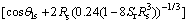 (5)
(5)
由式(5)可知:总基质吸力ψ与饱和度Sr、土颗粒半径Rs、水膜的密度及接触角θls有关。宏观上看,非饱和土强度随着这些参数变化而变化。
假设水的密度为1×103 kg/m3,接触角θls设为 0?,设饱和度0.01≤Sr≤0.50,得到了固定土颗粒半径下的非饱和土总吸力( )随饱和度(Sr)衰减规律曲 线,见图2。
)随饱和度(Sr)衰减规律曲 线,见图2。

图2 基质吸力与饱和度的关系
Fig.2 Relationship between matric suction and saturate degree
2 降雨入渗深度计算
2.1 降雨入渗过程
降雨入渗是水分在路堤填土非饱气带中运动过程,入渗量取决于土体初始含水量、降雨强度、持续时间以及表面径流量,填土路堤降雨入渗形象化过程见图3。
非饱和土中水迁移理论是降雨入渗研究的基本理论。对于饱和-非饱和垂直迁移一维系统,地下水迁移运动偏微分方程为[4]:
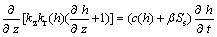 (6)
(6)
式中:kz为竖向渗透系数;kr为径向渗透系数;h为渗透深度;t为迁移时间;z为深度方向坐标;c和β为方程参数。
根据Darcy定律,t时刻其上部边界垂直向下的最大入渗能力R(t)为:
 (7)
(7)
式中:R(t)为最大入渗能力解析解。
基于土中水迁移理论,Green等[21]提出了一维入渗深度Green-Ampt模型。

图3 路堤填土入渗过程
Fig.3 Rainfall infiltration procedure of embankment fillings
2.2 入渗深度计算方法
降雨入渗深度可用的计算方法有Pradel & Raad法和李焯芬公式。早期,通过扩展Green & Ampt入渗模型,Pradel等[12]提出了降雨饱和入渗到深度zw所需时间为:
 (8)
(8)
式中:Tw为入渗所需时间; 和
和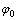 分别为土体的饱和水的体积分数和实测水的体积分数;k为土体湿润区的渗透系数;s为土体入渗峰面的毛细吸力。
分别为土体的饱和水的体积分数和实测水的体积分数;k为土体湿润区的渗透系数;s为土体入渗峰面的毛细吸力。
李焯芬等[13]提出了降雨浸湿深度计算公式:
 (9)
(9)
式中:k为饱和渗透系数;S0为初始饱和度;n为孔隙率;t为降雨持续时间。
2.3 工程实例分析
以张家界市的张桑公路K35+005路堤截面为例,依据土工实验,降雨入渗深度计算参数见表1。依据气象资料,该地区年平均降雨量约为1 464 mm,暴雨衰减系数n=0.75,多年平均的年最大24 h暴雨量 =144 mm。分别采用Pradel & Raad法和李焯芬公式计算降雨入渗深度。
=144 mm。分别采用Pradel & Raad法和李焯芬公式计算降雨入渗深度。
表1 入渗深度计算模型参数
Table 1 Rainfall infiltration depth computation model parameters

把表1中参数代入式(8)和(9)计算不同降雨持续时间的入渗深度。由式(8)得入渗深度为0.96 m时的入渗率为25.5 mm/h,由式(9)计算得入渗率为74 mm/h。实测结果显示[19]:单次暴雨最大入渗深度可达2.0 m。按李焯芬公式,如果路堤入渗2.0 m所需一次降雨时间大于年降雨时间,这与实际情况有出入。Pradel & Raad方法计算的入渗深度则与实际入渗深度比较吻合。工程应用实例表明:对于土石混填的路堤,计算降雨入渗深度时,可以参考采用Pradel & Raad方法。
3 降雨入渗分析模型
张桑公路K34+970~35+070段路堤高度约19.0 m,高填路堤中使用典型的土石混填粗粒土填料,为灰黄色强风化泥质页岩碎石料,岩块几何性状极不规则,呈棱角状。路堤剖面如图4所示。
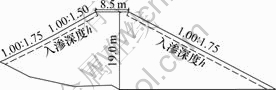
图4 K35+005路堤剖面图
Fig.4 Embankment profile of K35+005 embankment
3.1 计算模型及参数
计算模型长度方向取K34+900 m~K35+150 m,宽度方向上以公路轴线为中心向两边各延伸60 m,高度方向自200 m高程取至地表,地面高程范围为344~406 m。取大地坐标系北偏西27°方向为X轴正向,南偏西63°为Y轴正向,铅直向上为Z轴正向。建立分析模型局部坐标系,取路面中心线上桩号为K35+150点对应X=0,Y=0,计算范围为:X=-250~0 m,Y=-70~ +70 m。取高程0 m处Z=0,Z的计算范围为+200 m高程到地表。所建立的计算模型中地层岩性及路堤分层见图5。

图5 计算模型及地层组成
Fig.5 Numerical computation model and stratus composition
根据地质资料,自上而下考虑了碎石土、强分化页岩、弱风化和微风化页岩。建模时将弱风化页岩和微风化页岩合为一种地层,碎石土厚度取4~7 m,强风化页岩厚度取17~22 m,各岩土体厚度沟谷位置取高值,在坡面位置取低值。按照四面体单元对模型进行网格划分,整个计算区域共离散为192 323个节点、36 150个四面体单元,三维计算网格划分整体模型及细部模型见图6。
在分析时,基层岩土体被视为弹塑性材料,参数见表2。路堤填料按照邓肯-张模型计算,依据路堤填料大型三轴试验确定模型参数,见表3。

图6 数值计算模型网格划分图
Fig.6 Grid of numerical computation model
表2 基层岩土体参数
Table 2 Mechanical parameters for soil and rock layers in model

表3 路堤填土邓肯-张模型参数
Table 3 Ducan-Chang model parameters for embankment fillings

3.2 降雨入渗模拟
图2显示:随着路堤土体饱和度的增加,总基质吸力呈现递减规律,土体强度减小。降雨入渗后的路堤土体增加了浸润区含水量,从而增大了土体的饱和度,降低了基质吸力,降低了土体强度,最终导致路堤附加变形及稳定性降低。
采用土体强度参数折减思路简要模拟路堤降雨入渗效果。在分析中,降雨入渗浸润区粗粒土填土强度参数按照图2所示递减规律进行折减。由于问题的复杂性,此处把浸润区不同饱和度的土体参数均折减63%。依据土工实验及图2所示规律,浸润区填土摩擦角折减为21.6°,黏聚力折减为28.4 kPa,密度则变为1.95 kg/m3。计算时首先将路堤填料重力场作用下的位移清零,然后计算降雨入渗导致的路堤附加变形及稳定性情况。分别计算了路堤两侧坡面降雨入渗为1.0和2 m 2种工况,路面结构以下部位没有考虑入渗的影响。
4 计算结果分析
4.1 沉降特征分析
对计算模型进行数值模拟计算,图7所示为路堤填料在考虑降雨入渗深度为1和2 m时路堤入渗附加变形分布。
从图7可见:降雨入渗造成的路堤附加沉降明显;随着降雨入渗深度的增加,路堤入渗沉降增大;当首次入渗深度为1 m时(图7(a)),最大沉降量为1.00 cm;当入渗深度为2 m时(图7(b)),最大沉降量达到1.30 cm。计算结果说明路堤侧向入渗变形较小,当首次入渗深度为1 m时,最大侧向变形量为0.31 cm;当首次入渗深度为2 m时,最大侧向变形量增大到0.37 cm。
降雨入渗造成的路堤沉降及变形,实际情况往往是不均匀沉降,造成已运营公路路面结构的应力重新分配,路堤入渗变形改变了路面板的支撑条件,容易导致路面结构应力集中和过早破损。
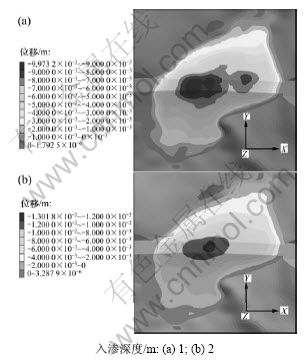
图7 入渗沉降位移云图
Fig.7 Rainfall infiltration settlement contour at embankment
4.2 稳定性分析
路堤稳定性采用塑性区分布情况来表示。不考虑入渗影响的路堤塑性区分布和考虑降雨入渗影响下路堤塑性区分布域如图8所示。
从图8可见:降雨入渗对路堤稳定性有明显影响;当没有降雨入渗时(图8(a)),塑性区分布范围较小,仅仅分布在路堤的边脚地带;当路堤入渗深度为1 m时(图8(b)),路堤塑性区分布范围明显增大,路堤边脚塑性区面积迅速增大,逐渐向路堤顶扩展,路堤稳定性降低;当路堤入渗深度为2 m时(图8(c)),塑性区分布面积缓慢增大,路堤稳定性进一步降低。这表明降雨入渗对路堤稳定影响显著,在路堤建设及养护中应该注意到此问题。

图8 降雨入渗塑性区分布
Fig.8 Plastic zones distributions for rainfall infiltration
5 结论
(1) 降雨入渗增加了路堤粗粒土填料含水量,降低了土体基质吸力和强度,是造成路堤附加变形及稳定性降低的原因。在简要的数值模拟中,依据饱和土强度折减规律,可用强度折减模拟降雨入渗效果。
(2) 降雨入渗对路堤附加变形影响明显,随着降雨入渗深度的增加,路堤入渗沉降增大;当首次入渗深度为2 m时,入渗沉降可达1.30 cm。降雨入渗造成的路堤沉降及变形,容易造成路面结构的应力重分配,容易导致路面结构应力集中和过早破损,应该引起足够重视。
(3) 降雨入渗对路堤稳定性也具有明显影响,入渗作用扩大了路堤塑性区范围,降低了路堤稳定性,在路堤设计施工中应该注意降雨入渗可能造成的路堤失稳问题。
参考文献:
[1] 刘丽萍, 哲学森. 土石混合料压实特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(1): 206-210.
LIU Li-ping, ZHE Xue-seng. Study on compaction property of earth-rock mixture[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(1): 206-210.
[2] 油新华. 土石混合体野外水平推剪试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2002, 75(10): 1637-1640.
YOU Xin-hua. Research on horizontal push-shear in-situ test of soil and rock-mixture[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2002, 75(10): 1637-1640.
[3] 张嘎. 土与结构接触面弹塑性损伤模型用于单桩与地基相互作用分析[J]. 工程力学, 2006, 23(2): 72-78
ZHANG Ga. Elastoplastic damage model of soil-structure interface in single pile-soil interaction analysis[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2006, 23(2): 72-78.
[4] Fredlund D G, Rahardjo H. Soil mechanics for unsaturated soils[M]. New York: Wiley Press, 1993: 63-65.
[5] Paul H, Enrest K. Measurement and estimation of pore shrinkage and pore distribution in clay till during soil-water characteristic cuvre tests[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2001, 38(6): 741-754.
[6] Charles W W N, Pang Y W. Experimental investigations of the soil-water characteristics of volcanic soil[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2000, 37(4): 1252-1264.
[7] 董加瑞, 王昂生. 毛细作用下土壤水分扩散特性研究及试验[J]. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 1998, 34(1): 50-57.
DONG Jia-rui, WANG Ang-sheng. Property of soil water capillary conductivity and some tests[J]. Journal of Peking University: Science Edition, 1998, 34(1): 50-57.
[8] 翁通. 盐渍土毛细水作用及击实特性研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学公路学院, 2006: 12-15.
WEN Tong. Research on the capillary and compaction properties in the salt soil[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University. Highway School, 2006: 12-15.
[9] 李锐, 赵文光, 陈善雄. 基于GEO-SLOPE 的膨胀土路基毛细水上升分析[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 城市科学版, 2006, 23(S1): 36-39.
LI Rui, ZHAO Wen-guang, CHEN Shan-xiong. Capillary water upward movement analysis of expansive soil roadbed based on GEO-SLOPE[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Urban Science Edition, 2006, 23(S1): 36-39.
[10] 陈善雄, 陈守义. 考虑降雨的非饱和土边坡稳定性分析方法[J]. 岩土力学, 2001, 22(4): 44-45.
CHEN Shan-xiong, CHEN Shou-yi. Analysis of stability of unsaturated soil slope due to permeation of rainwater[J]. Soil and Rock Mechanic, 2001, 22(4): 44-45.
[11] 朱伟, 山村和野. 雨水、洪水渗透时河堤的稳定性[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1999, 21(4): 414-419.
ZHU Wei, Kazuya Y. Stability of river embankment under the seepage of rain or flood[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1999, 21(4): 414-419.
[12] Pradel D, Raad G. Effect of permeability on surficial stability of homogeneous slopes[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1993, 119(2): 315-332.
[13] 李焯芬, 汪敏. 港渝两地滑坡灾害的对比研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2000, 19(3): 493-497.
Lee C F, WANG Min. Comparison of land slide hazard between Hong Kong and Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 19(3): 493-497.
[14] Fourie A B, Rowe D, Blight G E. The effect of infiltration on the stability of the slopes of a dry ash dump[J]. Geotechnique, 1998, 17(5): 78-91.
[15] 朱文彬, 刘宝深. 降雨条件下土体滑坡的有限元数值分析[J]. 岩土力学与工程学报, 2002, 21(4): 509-512.
ZHU Wen-bin, LIU Bao-chen. Forming and development process of soil landslide during rainfall[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2002, 21(4): 509-512.
[16] 黄润秋, 戚国庆. 滑坡基质吸力观测研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2004, 26(2): 216-219.
HUANG Run-qiu, QI Guo-qing. Observation of suction in a landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2004, 26(2): 216-219.
[17] 李兆平, 张弥. 考虑降雨入渗影响的非饱和土边坡瞬态安全系数研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2001, 34(5): 57-61.
LI Zhao-ping, ZHANG Mi. Effects of rain infiltration on transient safety of unsaturated soil slope[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2001, 34(5): 57-61.
[18] 张士宇, 王瑞钢. 降雨对高填土路堤的入渗深度的确定及有限元稳定分析[J]. 路基工程, 2004(5): 17-21.
ZHANG Shi-yu, WANG Rui-gang. Infiltration depth computation and FEM analysis of highway embankment[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2004(5): 17-21.
[19] 王瑞钢, 闫澍旺, 邓卫东. 降雨作用下高填土质路堤边坡的渗流稳定分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2004, 17(4): 25-30.
WANG Rui-gang, YAN Shu-wang, DENG Wei-dong. Analysis of seepage stability of high-filled embankment slope due to rainfall infiltration[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2004, 17(4): 25-30.
[20] Rodell A A. 土壤水[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1964: 72-75.
Rodell A A. Water in the soil[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1964: 72-75.
[21] Green W H, Ampt C A. Studies on soil physics: Flow of air and water through soils[J]. Journal of Agriculture Science, 1911(4): 1-24.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2009-05-14;修回日期:2010-07-20
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50908233);中国博士后科学基金资助项目(20080440996)
通信作者:陈晓斌(1978-),男,江西赣州人,博士,从事岩土工程研究;电话:0731-82656563;E-mail: cxb528@163.com