文章编号:1004-0609(2012)04-1068-07
冷轧Cu-15Cr原位复合材料性能及Cr纤维相高温稳定性
毕莉明,刘 平,陈小红,刘新宽,李 伟,马凤仓
(上海理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,上海 200093)
摘 要:采用冷轧变形结合中间退火得到形变Cu-15Cr原位纤维增强复合材料。利用扫描电镜、电子拉力试验机及数字微欧计研究退火温度对材料的Cr纤维形貌、抗拉强度及导电性能的影响。结果表明:Cr纤维的高温不稳定性是边缘球化和晶界开裂的结果;随退火温度升高,Cr纤维的高温失稳过程为Cr纤维发生边缘球化、球化向Cr纤维中心扩展、Cr纤维晶界开裂(三叉晶界处)、Cr纤维断裂。随退火温度升高,Cu-15Cr原位复合材料抗拉强度逐渐降低,导电率先逐渐升高,在550 ℃达到峰值84.4%IACS后迅速下降;经450 ℃退火,能得到具有较好综合性能的冷轧Cu-15Cr原位复合材料,其抗拉强度达到656 MPa,导电率达到82%IACS。
关键词:Cr纤维相;高温稳定性;边缘球化;晶界开裂;抗拉强度;导电率
中图分类号:TB331; TG113.2 文献标志码:A
Properties of cold rolling Cu-15Cr in-situ composites and high temperature stability of Cr filamentary
BI Li-ming, LIU Ping, CHEN Xiao-hong, LIU Xin-kuan, LI Wei, MA Feng-cang
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology,
Shanghai 200093, China)
Abstract: Cu-15Cr in-situ filament-reinforced composites sheets were prepared by cold-rolling and annealing heat treatment. The effects of annealing temperature on Cr filamentary morphology, mechanical and electrical properties of Cu-15Cr in-situ composites were investigated by scanning electronic microscopy (SEM), tensile test and conductivity measurement using micro- ohmmeter. The results show that the reason of high-temperature instability of Cr filament is edge spheroidizing and grain boundary cracking, the failure process of Cr filaments at elevated-temperature is as follows: edge spheroidizing, edge spheroidizing extends to center of Cr filament, grain boundary cracking (trigeminal-phase), fibrous fracture. The tensile strength of Cu-15Cr in-situ composite reduces gradually with increasing annealing temperature, but the electrical conductivity increases gradually first and reaches a maximum 84.4%IACS and then decreases rapidly. After annealing treatment at 450 ℃, the Cu-15Cr in-situ composites show an excellent combination of the tensile strength of 656 MPa and electrical conductivity of 82%IACS.
Key words: Cr filamentary; high temperature stability; grain boundary cracking; edge spheroidizing; tensile strength; electrical conductivity
随着集成电路向大规模和超大规模发展,引线框架铜带要求材料抗拉强度超过600 MPa,导电率大于80%IACS;高速铁路交通要求电气机车接触线常温抗拉强度达到600~700 MPa,导电率达到80%~95%IACS,高温抗拉强度下降率10%;电阻焊电极焊接区温度达到500~650 ℃,要求材料有较高的高温稳定性[1-5]。可见高强高导材料的高温稳定性对其使用性能有极大的影响,因此,对复合材料高温稳定性能的研究是十分有必要的。已有文献[6-8]报道了对Cu-Nb、Cu-Ag和Cu-Ag-Cr等形变原位复合材料在加热时组织和性能变化的研究。结果指出:在退火过程中,复合材料中的Cu基体发生回复、再结晶,纤维发生粗化、球化、柱状化和断开等现象。GE[9]对Cu-Fe形变原位复合材料不同退火温度及不同退火时间的纤维稳定性进行了测试,发现Fe纤维经历了直接边缘球化、晶界分裂、直接柱状化3个过程。陈小红等[10]就Cu-Cr原位复合材料的热稳定性能的研究中发现,随退火温度升高,抗拉强度逐渐下降,并测定了Cr纤维的断开直径,来验证微观组织与宏观力学性能之间的关系。
虽然上述文献对形变铜基原位复合材料的高温稳定性能已有一定的研究,但研究对象均为通过冷拉拔变形制备的线材,强化相是弯曲扭折的纤维,本研究对象是通过冷轧变形制备的带材,强化相是较规则的平直的纤维,其综合性能及纤维的高温失稳过程与线材都有很大不同。二者相比,虽然带材的综合性能(抗拉强度/导电率)不如线材优越,但带材的制备过程简单,更容易实现工业生产。然而带材在高温下更容易失稳,生产和应用中不能以线材的高温性能指标作为带材的参考标准。因此,本研究通过冷轧结合中间退火,制备出变形量为97.5%的薄片状Cu-15Cr形变原位复合材料,研究退火温度对Cr纤维形态、抗拉强度及导电率的影响规律,确定大变形条件下横截面平直的片状增强纤维对复合材料高温组织性能的影响,为提高冷轧形变铜基原位复合材料高温性能的设计提供试验和理论依据。
1 实验
Cu-15Cr合金采用纯度大于99.9%的阴极电解铜、纯度大于99.9%的Cr,在真空中频感应炉中熔炼而成。将铸锭在900 ℃下热锻至20 mm厚,经1 000 ℃固溶处理1 h,随后在室温下冷轧变形+中间热处理,制备成厚度为0.5 mm的原位纤维增强复合材料。将制备好的试样分别在400、450、500、550、600、700、800、900 ℃退火1 h,然后在空气中冷却。考虑到Cr的熔点很高,为了研究Cr相纤维的高温稳定性能,所以将最高退火温度提高到900 ℃。中间退火和最终退火在N2保护气氛中进行。轧制变形量ε定义为:ε= (h0-h)/h0×100%,其中:h0是试样冷变形前的原始厚度;h为变形后的厚度。用ZWICK公司生产的Z50型精密万能试验机测试抗拉强度。用ZY9987数字式微欧计测试电阻然后换算成导电率。用FEI QANTA450型场发射扫描电镜(SEM)观察Cr纤维形貌的变化过程,腐蚀剂采用浓度为63%的HNO3溶液,腐蚀后用酒精在超声波中进行清洗。
2 实验结果
2.1 Cr纤维组织
图1所示为冷轧变形Cu-15Cr原位纤维增强复合材料在变形量ε为97.5%,经不同温度退火1 h后,Cr纤维相平行于轧制方向的SEM像。从图1(a)和(b)中可以看出,经过550 ℃退火,Cu-15Cr复合材料中Cr纤维没有发生明显变化,仍保持冷轧变形后表面光滑的形貌;图1(b)中A处的纤维直接横向撕裂,认为是应力释放的结果。从图1(c)中可以看出,经过600 ℃退火,较薄的Cr纤维边缘区域已有球化现象发生,但纤维较厚区域仍然比较光滑,未发生球化。从图1(d)中可以看出,经过700 ℃退火,纤维球化程度加剧,且从边缘向中心较厚区域扩展。从图1(e)中可以看出,经过800 ℃退火,有一个典型的特征变化,即在三叉晶界处,发生了晶界分离现象,如图1(e)中的A、B和C处所示。从图1(f)中可以看出,经过900 ℃退火,大部分纤维发生球化和断裂,此时的Cr纤维组织已经基本上失去纤维的原有形貌。
图2所示为与图1相对应的Cr纤维相横截面的SEM像,展示Cr纤维随退火温度升高的形态演变过程。从图2(a)~(c)中可以看出,退火温度低于600 ℃时,纤维保持大变形后的形貌,而且看不到Cr纤维中晶粒的情况;退火温度升高到700 ℃时,Cr纤维的横截面观察到了Cr纤维的晶界,如图2(d)所示;当温度升至800 ℃和900 ℃时,Cr纤维已经完全发展为等轴晶,且球化、断裂现象十分明显,如图2(e)和(f)所示。
2.2 导电率与抗拉强度
图3所示为冷轧Cu-15Cr形变原位复合材料不同温度退火1 h的电导率和抗拉强度随退火温度变化的测试结果。从图3中可以看出,抗拉强度随退火温度升高而逐渐降低,导电率随退火温度升高,先缓慢上升而后迅速下降。
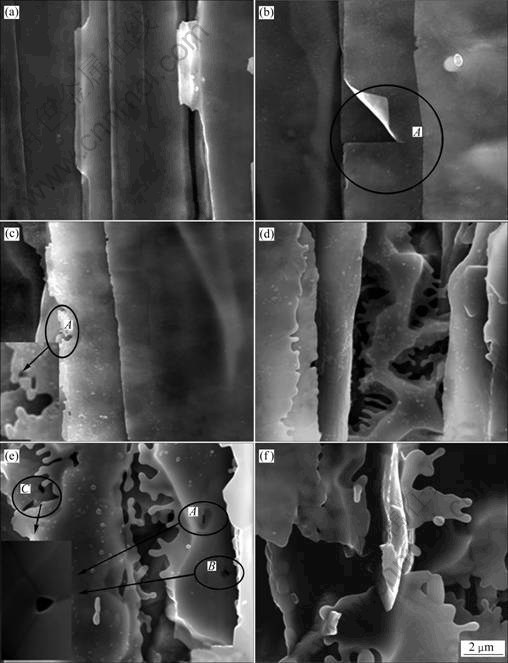
图1 Cu-15Cr原位复合材料ε=97.5%时在不同温度退火1 h后Cr纤维轧制面的SEM像
Fig. 1 SEM images of rolling sections of Cu-15Cr cold rolling at ε=97.5% under various temperature conditions for 1 h: (a) Unannealed; (b) 550 ℃; (c) 600 ℃; (d) 700 ℃; (e) 800 ℃; (f) 900 ℃
未退火时,材料的导电率为78%IACS;当退火温度低于550 ℃时,导电率随温度升高逐渐升高;550 ℃时,达到峰值导电率84.4%IACS;退火温度高于550 ℃时,电导率开始下降;当退火温度达到700 ℃时,导电率呈迅速下降趋势;经900 ℃退火后,下降到46.9%IACS,与退火前相比,下降了39.9%,与峰值导电率相比,下降了44.4%。从两条曲线的对比中可以看出,抗拉强度与电导率之间呈现出不同的变化关系,抗拉强度随退火温度升高逐渐下降,没有出现导电率的峰值现象。低于450 ℃退火,Cu-15Cr原位复合材料的抗拉强度变化不大,从退火前的700 MPa降低到656 MPa;经500 ℃退火后,抗拉强度下降显著,从450 ℃退火的536 MPa降低到了446 MPa,下降了16.8%;经900 ℃退火,合金的抗拉强度降低到了335 MPa,这与图1(f)纤维形貌有很好的吻合。根据材料抗软化温度的定义,即抗拉强度下降15%时的退火温度作为材料的抗软化温度,计算得出冷轧Cu-15Cr形变原位复合材料的抗软化温度为450 ℃。
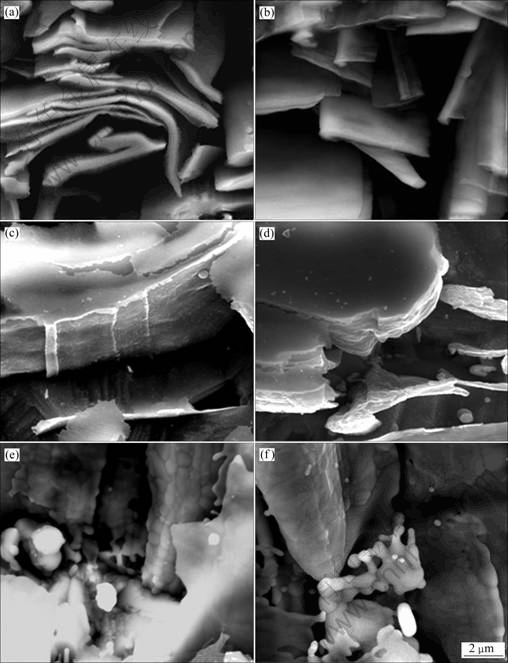

图2 Cu-15Cr原位复合材料ε=97.5%时经不同温度退火1 h后Cr纤维横截面的SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM images of cross sections of Cu-15Cr cold rolling at ε=97.5% under various temperature conditions for 1 h: (a) Unannealed; (b) 550 ℃; (c) 600 ℃; (d) 700 ℃; (e) 800 ℃; (f) 900 ℃
3 分析与讨论
3.1 退火温度对纤维形貌的影响
已有研究表明,Cr纤维的不稳定性可能有边缘球化、晶界分裂、柱状化和Rayleigh扰动4种机制。SHARMA等[11]发现,上述4种纤维高温失稳机制并不是严格按顺序出现,而是受纤维尺寸分布、扩散区重叠及晶粒粗化等因素的影响,不同阶段可能在同一个试样的不同地方同时出现,也可能只出现某一种现象。从本研究结果中分析得出,Cu-15Cr中Cr纤维相的高温失稳过程,并未完全体现上述4种机制,而是边缘球化和晶界开裂共同作用的结果。图4和5所示为片状纤维结构边缘球化及晶界开裂示意图。
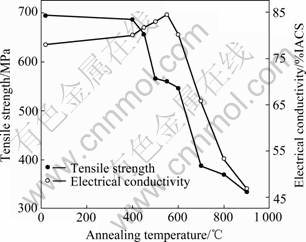
图3 Cu-15Cr原位复合材料抗拉强度及电导率与退火温度曲线
Fig. 3 Electrical conductivity and tensile strength depends on annealing temperatures of Cu-15Cr alloys
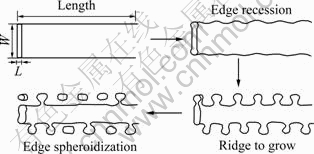
图4 边缘球化示意图
Fig. 4 Illustration of shape instability mechanisms for plate
KAMPE等[12]指出纤维形貌的变化遵循曲率诱导表面扩散机制,纤维宽厚比(w/l)、界面能与表面能之比(γi/γs)对纤维形貌的变化有重要影响。根据原始Cr纤维相形态宽厚比(w/l)可以推断,退火过程中,Cr纤维形态的变化可能的两种情形:1) w/l比较小,由于纤维边缘和相邻平面之间的曲率差,原子从边缘向平滑面移动,在平滑面隆起,最后形成圆柱体[12]。如果体扩散控制其过程,大圆柱体将通过消耗小的圆柱体发生Ostwald粗化;如果是界面扩散控制,圆柱体将通过Rayleigh不稳定过程而分解成一系列球状体。2)有限长并具有大的宽厚比,即(γi/γs)以及(w/l)较大时发生边缘球化,这是片状组织不稳定的主要形式[13]。本文作者在研究形变Cu-15Cr原位复合材料热稳定性时发现边缘球化现象,高温时,由于扩散在亚晶界形成表面张力和界面的表面张力之间局部平衡,而因曲率不同形成的化学势梯度将促使原子离开热蚀沟底部,扩散后打破原来的平衡,需要消耗亚晶界重新建立平衡,结果使热蚀沟加深。对低角度晶界,分裂的驱动力很小,更容易发生边缘球化[7-8]。
图5所示为薄片状纤维晶界开裂示意图。发生晶界开裂现象是因为存在较厚的亚晶界长大的结果,这种亚晶界通过变形片状结构再结晶或相扩散过程而长大[13]。高温下,扩散沿亚晶界表面张力(γb)和相间界面表面张力(γs)的三叉点局部平衡交叉线上形成热蚀沟。由于界面处的曲率不同而形成的化学式梯度,促进质量传递远离热蚀沟,依次打破了局部平衡。平衡的重新建立要通过不断消除亚晶界来实现,因此加深了热蚀沟。如果三叉点(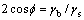 )上的二面角(
)上的二面角(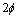 )小于π,出现晶界开裂,这与图1(e)和(f)所示的结果保持一致。
)小于π,出现晶界开裂,这与图1(e)和(f)所示的结果保持一致。
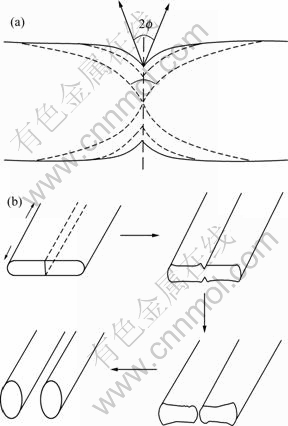
图5 晶界开裂示意图
Fig. 5 Illustration of boundary splitting process: (a) Surface tension balance of interphase interface at triple point junction; (b) Plate splitting caused by presence of internal boundaries within plate
3.2 退火温度对导电率的影响
Cu-15Cr原位复合材料在不同温度退火时,其导电率的变化受Cu基体和Cr纤维的微观组织结构变化的控制。
退火温度对形变Cu-15Cr原位复合材料导电率的影响表现在4个方面:1) 退火温度较低时,Cr纤维没有明显变化,Cr纤维对复合材料导电率的影响不大,但Cu基体处于回复再结晶阶段,晶体缺陷密度下降,复合材料导电率升高;2) 升高退火温度,固溶Cr原子析出,基体中Cr原子含量降低,杂质散射电阻减小,导电率上升;3) 退火温度较高时,Cu基体中Cr的平衡固溶度明显增大,析出的Cr重新溶解到Cu基体中,同时,纤维球化,复合材料导电率降低;4) 退火温度达到800 ℃时,Cr纤维球化,晶界分裂,纤维断裂,此时,Cr纤维微观结构的改变导致界面散射电阻迅速增大,合金导电率大幅降低。
3.3 退火温度对抗拉强度的影响
对于形变原位纤维增强Cu-15Cr复合材料,一般存在加工硬化及纤维相强化两种强化机制。HONG 等[14-15]提出了形变原位纤维增强复合材料抗拉强度的叠加原理强度计算公式:
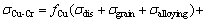
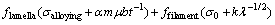
式中:fCu代表基体相体积分数,flamella代表变形组织中较厚片状Cr相体积分数,ffilament代表Cr纤维体积分数,σdis为冷变形引起的位错亚结构强化效应,σgrain为Cu晶粒细化引起的强化效应,σalloying为固溶和沉淀强化效应,σ0为Cr纤维本征断裂应力,k和α为比例常数,m为Taylor常数,μ为切变模量,b为Burges矢量,t为Cr纤维平均厚度,λ为Cr纤维间距。Cu-15Cr复合材料变形后由于加工硬化效应和Cr相的纤维化,σdis和σgrain值较高,t和λ较小,从而在加工硬化和纤维强化的综合作用下导致σCu-Cr有较高的值。
低于400 ℃退火,温度较低,显微组织无明显变化,σgrain、t和λ等值基本保持不变,对强度不造成影响;经450 ℃退火时,Cu基体处于高温回复阶段,位错密度略有下降,σdis值减小,抗拉强度降低;当退火温度升高到500 ℃,Cu基体发生再结晶,位错密度迅速减小,Cu晶粒长大,σdis和σgrain同时降低;进一步升高退火温度到550~700 ℃时,位错密度的进一步减少及Cu基体晶粒的进一步粗化,导致σdis和σgrain持续降低;继续升高退火温度,Cr纤维粗化、边缘球化及球化向中心区域扩展,Cr纤维间距逐渐增大并逐步演变为等轴晶粒,使得t和λ持续增大就,纤维强化效应剧烈消减,复合材料强度持续下降。
4 结论
1) 研究不同温度下退火1 h的大变形Cu-15Cr原位复合材料中Cr纤维的高温失稳过程,其特点是较薄的Cr纤维发生边缘球化→球化从Cr纤维边缘向中心扩展→Cr纤维晶界分离→Cr纤维断裂;大应变条件下,冷轧Cu-15Cr原位复合材料中Cr纤维相的不稳定性受边缘球化和晶界开裂两种机制控制。
2) 随退火温度升高,Cu-15Cr原位复合材料抗拉强度逐渐降低,导电率在550 ℃后达到峰值(84.4%IACS)后逐渐下降;计算得出材料的抗软化温度为450 ℃,其较好的综合性能匹配为抗拉强度、导电率分别为694 MPa、78%IACS(未退火)和656 MPa、82%IACS (450 ℃)。
REFERENCES
[1] 刘 平. 超高强度铜基原位复合材料研究进展[J]. 金属热处理, 2008, 33(1): 72-77.
LIU Ping. Research progress on super-strength copper-based in-situ composites[J]. Heat Treatment of Matels, 2008, 33(1): 72-77.
[2] VIDAL V, THILLY L, VAN P S, STUHR U, LECOUTURIER F, RENAULT P O, SWYGENHOVEN H V. Plasticity of nanostructured Cu-Nb-based wires: Strengthening mechanisms revealed by in situ deformation under neutrons[J]. Scrpta Materialia, 2009, 60(3): 171-174.
[3] VIDAL V, THILLY L, LECOUTURIER F, RENAULT P O. Cu nanowhiskers embedded in Nb nanotubes inside a multiscale Cu matrix: The way to reach extreme mechanical properties in high strength conductors[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57(3): 245-248.
[4] 毕莉明, 刘 平, 贾淑果, 田保红, 任 伟. 形变铜基原位复合材料的研究现状及展望[J]. 热加工工艺, 2009, 38(10): 98-101.
BI Li-ming, LIU Ping, JIA Shu-guo, TIAN Bao-hong, REN Wei. Research situation and developmental tendency of deformation processed copper based in-situ composite[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2009, 38(10): 98-101.
[5] 葛继平, 姚再起. 高强度高导电的形变Cu-Fe原位复合材料[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(4): 568-573.
GE Ji-ping, YAO Zai-qi. High strength and high electrical conductivity deformation-processed Cu-Fe in situ composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(4): 568-573.
[6] HONG S I, HILL M A. Microstructural stability and mechanical response of Cu Ag microcomposite wires[J]. Acta Metall. Mater, 1998, 46: 4111-4122.
[7] HONG S I, HILL M A. Microstructure and conductivity of Cu-Nb microcomposites fabricated by the bundling and drawing process[J]. Scripta Materalia, 2001, 44: 2509-2515.
[8] COURTNEY T H, MALZAHN J C, KAMPE. Shape instabilities of plate-like structuresⅡ analysis[J]. Acta Metall, 1989, 37: 1747-1758.
[9] GE Ji-ping. Modelling of the breakup of Cr filaments in wire-drawn Cu-based in situ composite[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 1999, 9(2): 223-229.
[10] 陈小红, 刘 平, 田保红, 张 毅, 贾淑果, 任凤章, 井晓天. 形变Cu-Cr原位复合材料中纤维相的热稳定性[J].中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(2): 328-333.
CHEN Xiao-hong, LIU Ping, TIAN Bao-hong, ZHANG Yi, JIA Shu-guo, REN Feng-zhang, JING Xiao-tian. Thermal stability of Cr filaments in Cu-Cr in-situ composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(2): 328-333.
[11] SHARMA G, RAMANUJAN R V, TIWARI G P. Instability mechanisms in lamellar microstructures[J]. Acta Metall, 2000, 2000, 48: 875-889.
[12] KAMPE J C M, COURTNEY T H, LENG Y. Shape instabilities of plate-like structure (Ⅰ): Experimental observations in heavily cold worked in situ composites[J]. Acta Metall, 1989, 37: 1735-1745.
[13] MAIZAHN K J C, COURTNEY T H. Elevated temperature microstructural stability of heavily cole-worked in-situ composites[J]. Scripte Materialia, 1986, 20: 285-289.
[14] HONG S I, HILL M A. Microstructural stability of Cu Nb microcomposite wires fabricated by the bundling and drawing process[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 281: 189-197.
[15] HONG S I, HILL M A, KIM H S. Strength and ductility of heavily drawn bundled Cu-Nb filamentary micro composite wires with various Nb contents[J]. Metall Mater Trans, 2000, 31A: 2457-2462.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:上海市教委创新项目( 11YZ112 );上海市科委基础研究重点项目( 10JC1411800 );上海市教育委员会重点学科建设项目( J50503 );上海市研究生创新基金项目(JWCXSL1101)
收稿日期:2011-03-08;修订日期:2011-08-03
通信作者:刘 平,教授,博士;电话:021-55271692;E-mail: lmbi0106@163.com