文章编号: 1004-0609(2005)01-0084-05
氨络合物体系中Ti基IrO2涂层阳极的析氮过程
郑国渠, 郑利峰, 曹华珍, 张九渊
(浙江工业大学 材料科学与工程研究所, 杭州 310014)
摘 要: 采用线性扫描技术研究了氯盐氨络合物体系中Ti基IrO2涂层阳极的析氮过程, 对3种含有不同氧化物涂层电极的析氮电催化性能进行了比较, 并结合扫描电镜(SEM)及能谱(EDX)探讨了不同析氮电催化活性的原因。 研究结果表明: 当电极电位低于1.1V(vs SCE)时, Ti基IrO2涂层阳极析气反应主要为析氮反应, 氮气的产生主要是由于氨水在电极上发生电化学氧化引起的; Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极具有最佳的析氮电催化活性, 其可能原因是金属元素PdRuTi的存在导致该电极表面特征裂纹最宽且最深, 氧化物涂层总析氮面积增多, 电催化活性增加。
关键词: 氨络合物体系; Ti基IrO2阳极; 析氮; 电催化活性 中图分类号: TF813
文献标识码: A
Nitrogen evolution of Ti based IrO2 anodes in leaching solution containing ammonia and chloride
ZHENG Guo-qu, ZHENG Li-feng, CAO Hua-zhen, ZHANG Jiu-yuan
(Institute of Materials Science and Engineering,
Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310014, China)
Abstract: Nitrogen evolution on Ti based IrO2 anodes in leaching solution containing ammonia and chloride was investigated by means of linear sweep voltammetric technique. The electrocatalytic activities of three different kinds of Ti based IrO2 containing different oxides species were compared with each other. The reasons of different electrocatalytic activities corresponding to different anodes were examined in terms of SEM and EDX. The results show that the main reaction on Ti based IrO2 anodes is nitrogen evolution, which is ascribed to the electrochemical oxidation of ammonia at electrode potential lower than 1.1V or so. The Ti based IrO2 anode containing Pd, Ru, Ti elements displays better electrocatalytic activity. It is probably due to the existence of elements, such as Pd, Ru, Ti, which results in a wide and deep, typical morphology of cracks. The typical morphology of cracks contributes to the existence of electrochemically active surface area and an improvement of electrocatalytic active for nitrogen evolution.
Key words: ammonia coordinate system; Ti based IrO2 anode; nitrogen evolution; electrocatalytic activity
氨络合物体系电积金属过程中阳极析出氮气已为众多学者所证实。 国内学者[1-3]在氨络合物体系电积金属锌时认为阳极析出氮气, 本文作者[4, 5]采用气相色谱法对氯盐氨络合物体系中RuO2/Ti阳极上产生的气体进行了表征, 证实阳极气体主要成分为氮气。 但是对氮气产生的过程认识不一致[6-11],有研究者[6]认为NH+4和NH3·H2O很难直接氧化分解生成氮气, 只有在新生成Cl2的催化作用下才可分解成氮气。 王鹏等[7]以SnO2/Ti作为阳极对垃圾渗沥液电化学氧化去除氨氮的研究, 认为阳极先电解析出氯气, 进而生成次氯酸, 并作为氧化剂氧化去除氨氮产生氮气。 Vooys等[8]采用循环伏安技术及在线质谱分析对含氨的碱溶液体系阳极析氮行为进行研究, 认为氨电化学氧化生成氮气。 Bradley等[9]认为氨电化学氧化过程中NH3不断脱氢生成NH2、 NH, 最终反应生成N原子, 两个N原子复合成N2。 因此, 在氯盐氨络合物体系中同时存在NH3、 NH+4以及Cl-的情况下, 对阳极析氮的过程有必要进行深入研究。 本文作者采用线性扫描技术对Ti基IrO2涂层阳极在氯盐氨络合物体系中的析氮过程进行了研究, 并对3种含不同氧化物组分的Ti基IrO2涂层电极的表面形貌及析氮电催化性能进行了比较。
1 实验
1.1 电极制备及形貌检测
将表面喷砂的尺寸为100mm×10mm×1mm的TA2型纯钛板经碱洗除油及水洗后, 再在沸腾的草酸溶液中酸刻蚀3h, 用去离子水冲洗干净并经过热风吹干。 采用传统的热分解法制备氧化物涂层。 以水合三氯化钌、 氯铱酸、 钛酸四丁脂、 二氯化钯、 五氯化钽等试剂制备含PdRuTi、 RuTi、 Ta 3种混合氧化物IrO2涂层钛阳极。 各种试剂按金属元素一定的比例, 如IrTa为0.6∶0.4(摩尔比), 溶于正丁醇或正丁醇乙醇混合溶液中。 Ir涂敷量为8~40g·m-2。 用毛刷将涂液涂敷于钛基体上, 在100~200℃下烘干后, 于箱式加热炉中400~550℃下热氧化10min, 最后烧结1h。 上述工艺过程反复进行, 直至涂液涂敷完毕。 热分解过程中, 各种金属盐类相应转化为各自的氧化物, 最后获得金属氧化物电极。 采用 HITACHIS-4700场发射型扫描电镜(SEM)观察涂层表面形貌, 用Thermo Noran Vantage-EST 能谱仪测定涂层表面金属元素的含量。
1.2 电化学测试
实验中以CHI650电化学工作站测定线性扫描曲线, 采用传统的三电极体系, 工作电极为3种含有不同氧化物组分的Ti基涂层电极(IrO2占主要部分), 面积为1cm2, 非工作面积用环氧树脂进行涂封, 辅助电极为大面积的铂电极, 参比电极为饱和甘汞电极, 工作电极在每次测试之后, 先在Na2SO3溶液中浸泡1min, 然后在稀HCl溶液中浸泡1min, 反复几次后先用蒸馏水清洗残留在电极表面的Na2SO3和HCl, 再用无水乙醇除油, 最后用二次蒸馏水清洗。
用于电化学测量的氯盐电解液采用二次蒸馏水、 分析纯氯化镍、 氯化铵及浓氨水配置, 配好后电解液贮存于密闭容器中待用。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 Ti基IrO2涂层阳极析氮过程
3种含有不同氧化物组分的Ti基IrO2涂层阳极有着类似的析氮过程, 本文中仅探讨Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极的析氮过程。 图1所示是Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极在不同溶液体系的析气极化曲线。 实线为该阳极在NiCl2·6H2O+NaCl体系中的析氯析氧极化曲线。 从实线可知此阳极上析氯析氧电位在1.1V(vs SCE)左右。 虚线为Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极在NiCl2·6H2O+NH4Cl+NH3·H2O体系中的极化曲线。 从虚线可知, 当电极电位大于0.95V时阳极电流迅速增大, 出现明显的析气现象。 该实验现象表明, 当电极电位低于1.1V时Ti基IrO2涂层阳极上出现了一个新的不同于析氯析氧的电化学反应, 即析氮反应。
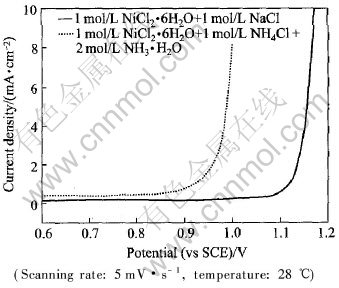
图1 IrO2/Ti阳极在不同溶液中的析气极化曲线
Fig.1 LSV plots of gas evolution on IrO2/Ti anode at various solution systems
为进一步探讨氮气产生的原因, 分别考察了NH+4浓度及NH3·H2O浓度对Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极上阳极极化曲线的影响。 图2所示是Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极在不同NH+4浓度体系的析气极化曲线。 从图2可知, 随着NH+4浓度的增加, 气体析出电位仍保持在1.1V左右, 与析氯析氧电位相吻合, 表明不同NH+4浓度下的析气反应仍为析氯析氧反应, 氮气的产生与NH+4无关。 图3所示是Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极在不同NH3·H2O浓度下的极化曲线。 当NiCl2·6H2O+NH4Cl体系中加入1mol·L-1 NH3·H2O后, 1.0V电位下的析气反应电流密度为1.5mA·cm-2, 明显高于NiCl2·6H2O+NH4Cl体系中同电位下的反应电流密度(无电化学反应产生, 反应电流密度基本为0), 表明氨水加入后, 电极表面发生析氮反应, 并且随着氨水浓度的增加, 析氮反应加剧, 在极化曲线上表现为析氮反应电流密度明显增加。 由此可知, 氯原子或氧原子在Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极表面未析出之前, 氮气的析出主要是由于氨水在Ti基IrO2涂层阳极表面的电化学氧化引起的。
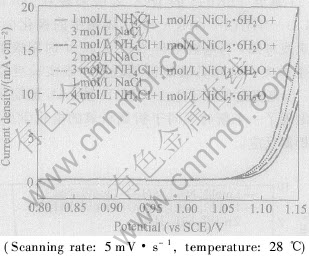
图2 IrO2/Ti阳极上不同NH+4浓度的析气极化曲线
Fig.2 LSV plots of gas evolution on IrO2/Ti anode at various ammonium
chloride concentrations
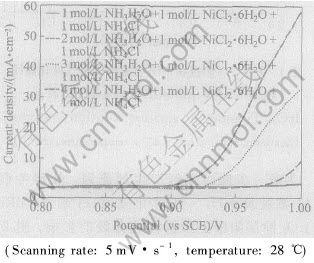
图3 IrO2/Ti阳极上不同NH3H2O浓度下的极化曲线
Fig.3 LSV plots of gas evolution on IrO2/Ti anode at various ammonium concentrations
2.2 不同氧化物组分Ti基IrO2涂层阳极的表面形貌及金属元素含量
3种不同氧化物组分的Ti基IrO2涂层阳极的表面形貌如图4~6所示。 从图可见, Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极表面出现的特征裂纹最宽且最深, Ti基含RuTi的IrO2涂层阳极表面析出细小的疏松的粒状晶粒簇, Ti基含Ta的IrO2涂层阳极表面析出的粒状簇粗大且致密。 表1列出了3种含有不同氧化物组分的Ti基IrO2涂层阳极的金属元素含量。 由此认为, 3种含有不同氧化物组分的Ti基IrO2涂层阳极的形貌可能与涂敷液中添加入不同试剂及不同试剂间的摩尔比有关。
2.3 不同氧化物组分Ti基IrO2涂层阳极的析氮电催化活性
图7所示为3种不同氧化物组分Ti基IrO2涂层阳极在氯盐氨络合物体系中析氮反应的Tafel曲线。 从该图可知, 3种电极的Tafel关系曲线均呈现两个直线部分, 第一直线部分的斜率为0.032~0.035V·dec-1, 第二直线部分的斜率为0.085~0.099V·dec-1, 表明不同电极电位范围内, 析氮的反应机理发生了改变。 从3条曲线来看, 在该实验温度(33℃)下Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极的电流值最大, 表明该电极具有最佳的析氮电催化活性, 其余两种电极的析氮电催化活性相近。 另外实验中发现, 当实验温度为47℃时, Ti基含RuTi的IrO2涂层阳极的析氮电流密度明显大于Ti基含Ta的IrO2涂层阳极, 与Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极相近。 表2列出了3种不同氧化物组分Ti基IrO2涂层阳极在33℃时的析氮动力学参数。 从表2可知, Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极析氮反应具有最小的塔菲尔斜率及最低的析氮过电位, 表现出良好的析氮电催化活性。 从Ti基IrO2涂层阳极的微观形貌来看, Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极电极表面特征裂纹最宽且最深, 氧化物涂层总析氮面积增多, 电催化活性增加。 Ti基含RuTi的IrO2涂层阳极表面表面析出细小的疏松的粒状晶粒簇, 微观粗糙度上升, 电极活性点增多, 当实验温度升高时, 电极表现出较高的析氮电催化活性。 Ti基含Ta的IrO2涂层阳极表面析出的粒状晶粒簇较为粗大且致密, 其电催化性并不高, 可见裂纹及晶粒簇的大小在很大程度上增加了电极的总反应活性点[12]。

图4 Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极的表面形貌
Fig.4 Surface morphology of Ti based IrO2 anode containing PdRuTi

图5 Ti基含RuTi的IrO2涂层阳极的表面形貌
Fig.5 Surface morphology of Ti based IrO2 anode containing RuTi

图6 Ti基含Ta的IrO2涂层阳极的表面形貌
Fig.6 Surface morphology of Ti based IrO2 anode containing Ta
表1 3种含有不同氧化物组分的Ti基IrO2涂层阳极的金属元素含量
Table 1 Metal element amount of three kinds of Ti based IrO2 anodes containing different oxides
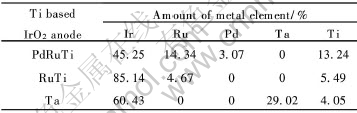
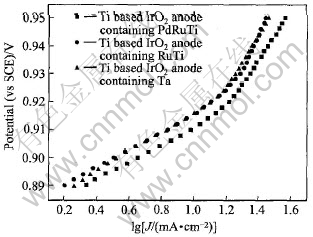
图7 3种Ti基IrO2涂层阳极析氮反应的Tafel关系曲线
Fig.7 Tafel plots of nitrogen evolution on three kinds of Ti based IrO2 anodes
表2 3种含有不同氧化物组分Ti基IrO2涂层阳极的析氮动力学参数
Table 2 Kinetics parameters of nitrogen evolution on three kinds of Ti based IrO2 anodes containing different oxides
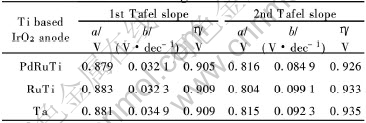
图8所示为0.94V(vs SCE)电位下3种Ti基IrO2涂层阳极析氮电流密度与温度的关系图。 经线性拟合得出各电极析氮的表观活化能, 各电极电位下3种Ti基IrO2涂层阳极的析氮表观活化能示于图9。 从图9可知, 在0.92~0.96V(vs SCE)电位范围内Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极的析氮表观活化能最低, 表现出较高的析氮电催化活性。 Ti基含Ta的IrO2涂层阳极由于其较为致密及粗大的晶粒簇而表现出较高的析氮表观活化能, 催化活性较低。
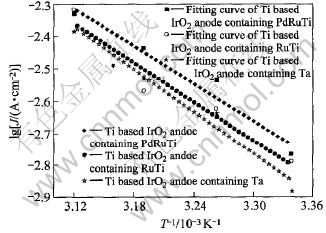
图8 3种电极析氮电流密度与温度的关系
Fig.8 Influence of temperature on current density of three kinds of Ti based IrO2 anodes
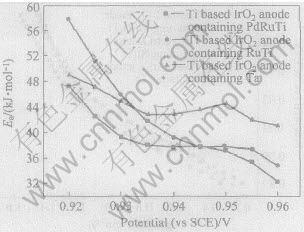
图9 3种Ti基IrO2涂层阳极在不同电极电位下的析氮表观活化能
Fig.9 Apparent activation energy of nitrogen evolution on Ti based IrO2 anodes containing different oxides at different electrode potentials
3 结论
电极电位低于1.1V时, Ti基IrO2涂层阳极上发生的析气反应主要为析氮反应, 氮气的产生主要是由于氨水在电极上发生电化学氧化引起的。 Ti基含PdRuTi的IrO2涂层阳极析氮反应具有最小的塔菲尔斜率及最低的析氮过电位, 析氮反应的表观活化能最低, 表现出良好的析氮电催化性能, 其可能原因是金属元素PdRuTi的存在导致该电极表面特征裂纹最宽且最深, 氧化物涂层总析氮面积增多, 电催化活性增加。
REFERENCES
[1]唐谟堂, 杨声海. Zn(II)-NH3-NH4Cl-H2O体系电积锌工艺及反应机理[J].中南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 1999, 30(2): 153-156.
TANG Mo-tang, YANG Sheng-hai. Electrowinning Zinc in the system of Zn(Ⅱ)-NH3-NH4Cl-H2O and mechanism of anodic reaction[J]. J Cent South Univ Technol, 1999, 30(2): 153-156.
[2]张保平, 唐谟堂, 杨声海. 氨法处理氧化锌矿制取电锌[J]. 中南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 34(6): 619-623.
ZHANG Bao-ping, TANG Mo-tang, YANG Sheng-hai. Treating zinc oxide ores using ammonia-ammonium chloride to produce electrolysis zinc[J]. J Cent South Univ Technol, 2003, 34(6): 619-623.
[3]张保平, 唐谟堂, 杨声海. 锌氨配合物体系电积锌研究[J]. 湿法冶金, 2001, 20(4): 175-178.
ZHANG Bao-ping, TANG Mo-tang, YANG Sheng-hai. Study on electrowinning zinc in Zn(Ⅱ)-NH3-NH4Cl-H2O system[J]. Hydrometallurgy of China, 2001, 20(4): 175-178.
[4]ZHENG Guo-qu, ZHENG Li-feng, CAO Hua-zhen, et al. Nickel electrodeposition from leaching solution containing ammonia and chloride[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2003, 13(1): 217-220.
[5]郑国渠, 高志峰, 曹华珍, 等. 氨络合物体系电积镍的阳极过程研究[J]. 有色金属, 2003, 55(2): 31-32.
ZHENG Guo-qu, GAO Zhi-feng, CAO Hua-zhen, et al. Anodic process of nickel electrowinning from leaching solution containing ammonia and chloride[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 55(2): 31-32.
[6]Zoppi G. Process for Heavy Metal Electrowinning[P]. US 5468354, 1995.
[7]王鹏, 刘伟藻, 方汉平. 垃圾渗沥液中氨氮的电化学氧化[J].中国环境科学, 2000, 20(4): 289-291.
WANG Peng, LIU Wei-cao, FANG Han-ping. Electrochemical oxidation of ammonium inlandfill leachate[J]. China Environmental Scince, 2000, 20(4): 289-291.
[8]de Vooys A C A, Koper M T M, van Santen R A, et al. The role of adsorbates in the electrochemical oxidation of ammonia on noble and transition metal electrodes[J]. J Electroanal Chem, 2001, 506: 127-137.
[9]Bradley J M, Hopkinson A, King D A. Control of a biphasic surface reaction by oxygen coverage: the catalytic oxidation of ammonia over Pt{100}[J]. J Phys Chem, 1995, 99: 17032-17042.
[10]Gootzen J F E, Wonders A H, Visscher W, et al. A DEMS and cyclic voltammetry study of NH3 oxidation on platinized platinum[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1998, 43: 1851-1861.
[11]de Mishima B A Lopez, Lescano D, Molina Holgado T, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of ammonia in alkaline solutions: its application to an amperometric sensor[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1998, 43: 395-404.
[12]胡吉明, 孟惠民, 张鉴清, 等. 制备条件对钛基IrO2+Ta2O5涂层阳极性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2002, 38(1): 69-73.
HU Ji-ming, MENG Hui-min, ZHANG Jian-qing, et al. Effect of preparation conditions on the properties of Ti based IrO2+Ta2O5 anodes[J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2002, 38(1): 69-73.
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金资助项目(50004005)
收稿日期: 2004-06-15; 修订日期: 2004-10-09
作者简介: 郑国渠(1965-), 男, 博士, 副教授.
通讯作者: 郑国渠, 副教授; 电话: 0571-88320238; E-mail: zgq003047@163.com
(编辑龙怀中)