文章编号:1004-0609(2013)04-1092-07
镀钼石墨纤维/铜复合材料的微观组织和热性能
张昊明,何新波,沈晓宇,刘 骞,曲选辉
(北京科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,北京 100083)
摘 要:以磨碎中间相沥青基石墨纤维和铜粉为原料,采用金属有机化学气相沉积工艺对原料纤维进行镀钼处理,通过真空热压烧结制备镀钼石墨纤维/Cu复合材料,对其微观组织及热性能进行检测和分析。结果表明:纤维在垂直于热压方向的平面上出现择优排布,使得复合材料在二维方向上拥有较高的热导率和较低的热膨胀系数;纤维表面的Mo镀层,烧结过程中部分与纤维反应生成连续的Mo2C层,能有效改善纤维与金属基体的界面结合,进而促进复合材料热性能的改善。当纤维体积分数为35%~55%时,复合材料二维方向的热导率在367~382 W/(m·K)之间,热膨胀系数为4.2×10-6~8.6×10-6 K-1,可以很好地满足大功率电子器件对封装材料的散热及匹配性要求。
关键词:石墨纤维/Cu复合材料;钼镀层;微观组织;热导率;热膨胀
中图分类号:TB333 文献标志码:A
Microstructure and thermal properties of
Mo-coated graphite fiber/Cu composites
ZHANG Hao-ming, HE Xin-bo, SHEN Xiao-yu, LIU Qian, QU Xuan-hui
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China)
Abstract: Mo-coated graphite fiber/Cu composites were fabricated by vacuum hot-press sintering with milled mesophase pitch-based graphite fibers and Cu powder. The molybdenum coatings on the fibers were obtained via metal organic chemical vapor deposition technique. Microstructure and thermal properties of the composites was examined. The results show that the fibers have a preferential orientation in the plane perpendicular to the pressure axis, which leads to the composites possess higher thermal conductivities and lower coefficients of thermal expansion (CTEs) at the 2-D direction. The Mo coating reacts with graphite fiber, and part of which forms a continuous Mo2C layer during densification process, which can improve the interfacial bonding between the fiber and metal matrices effectively, and then improve the thermal properties of the composites. The composites achieve 2-D thermal conductivities between 367-382 W/(m·K) and CTEs of 4.2×10-6-8.6×10-6 K-1 with the fiber content ranging 35%-55% (volume fraction). They can commendably meet the heat dispersion and matching requirements of power electronic devices to the packaging materials.
Key words: graphite fiber/Cu composites; molybdenum coating; microstructure; thermal conductivity; thermal expansion
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助(51274040);中央高校基本科研业务费专项基金资助(FRF-TP-10-003B)
收稿日期:2012-07-16;修订日期:2012-10-20
通信作者:何新波,教授;电话:010-823772896;E-mail: xb_he@163.com
电子封装材料的开发与设计一直以来是电子设备热管理中的重要环节。随着电子器件和装置中元器件复杂性和密集性的日益提高,现代热管理要求封装材料具有尽可能高的热导率,与半导体材料GaAs、Si和绝缘陶瓷基板材料Al2O3、AlN等相匹配的热膨胀系数(CTE, 4×10-6~9×10-6 K-1),良好的加工性能以及合理的价格成本[1-2]。单一金属或陶瓷材料很难同时兼顾对上述性能的要求,而金属基复合材料可将金属基体优良的导热性能和陶瓷材料低热膨胀的特性结合起来,获得既具有良好导热性又可与芯片和基板材料的热膨胀系数相匹配的复合材料,已经成为高性能电子封装材料的研发方向[3-4]。
以中间相沥青为先驱体制备的高性能碳纤维,通常被称为中间相沥青基石墨纤维,其轴向热导率接近1 100 W/(m·K),热膨系数可达-1.5×10-6 K-1[5]。随着石墨纤维技术的不断进步,该种石墨纤维的非连续形式(磨碎或短切形式)已具备了较低的价格(为连续长纤维的1/10),因此,非常适合作为电子封装用金属基复合的增强相材料。若将其与高导热的金属Cu复合,则有望获得导热性良好、线膨胀系数可调、加工性优良、价格成本合理的电子封装用铜基复合材料。然而,目前将非连续形式的该种石墨纤维与Cu复合应用于热管理领域及对其热性能的研究却十分有限[2, 6]。
本文作者拟通过真空热压烧结将磨碎中间相沥青基石墨纤维与铜粉进行复合。然而,对于C/Cu复合材料体系,因高温下C和Cu不润湿、不反应,其界面是仅依靠微弱范德华力的机械结合,会严重影响材料力学性能及热物理性能的发挥,必须对其界面结合进行改善[7]。对C/Cu导热系复合材料界面及热性能的研究结果表明,通过在Cu基体中添加或在C增强体表面镀覆碳化物形成元素,如Ti、Cr或Mo等,C-Cu间的界面能通过这些元素与碳反应生成碳化物形成冶金结合而得到改善,进而提升复合材料的热物理性 能[8-13]。考虑到Cu的热导率对Ti、Cr元素的加入十分敏感,有研究表明[8-9],在Cu中分别加入1%(质量分数)的Ti或Cr,Cu的热导率从394 W/(m·K)分别降低到175和290 W/(m·K)。而金属Mo的热导率要比Ti、Cr的高得多,在Cu基体中的扩散极少,且Mo/Cu材料本身就是很好的电子封装材料。因此,本文作者从增强体表面金属化改性的角度出发,在烧结前采用金属化学气相沉积工艺(Metal organic chemical vapor deposition, MOCVD)对石墨纤维表面进行镀钼金属化处理,用以改善石墨纤维与Cu之间结合力差的状况。对所制备镀钼石墨纤维/Cu复合材料的微观组织及界面特性进行表征,并初步探讨纤维的排布、钼金属化改性以及体积含量对其热导率和热膨胀的影响。
1 实验
1.1 实验原料
实验采用日本石墨纤维公司(Nippon Graphite Fiber Corp., Japan)提供的XN100型磨碎中间相沥青基石墨纤维,其基本参数与热性能列于表1。图1所示为该石墨纤维原料的SEM像。所用铜粉为北京有色金属研究总院提供的无氧铜粉,其纯度超过99.9%,平均粒度为20 μm。
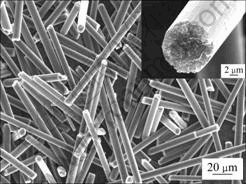
图1 石墨纤维原料的SEM像
Fig. 1 SEM images of as-received graphite fibers
1.2 制备过程
采用MOCVD法在石墨纤维表面镀覆钼层。镀覆时以羰基钼(Mo(CO)6)络合物为前驱体、高纯H2为载带气体,具体工艺过程如下:1) 将石墨纤维放入MOCVD沉积室内,并将晶体Mo(CO)6(s)放入镀覆系统的油浴锅设备中;2) 对固态Mo(CO)6(s)进行油浴加热升华,油浴温度为80 ℃可将固态Mo(CO)6(s)转变为气态Mo(CO)6(g);3) 将载带H2通入油浴锅设备,并载带气态Mo(CO)6(g)进入MOCVD气相沉积室;4) 气态Mo(CO)6(g)接触到沉积室内已被加热的石墨纤维表面,发生吸热分解释放出金属Mo原子和CO气体,这些活性Mo原子沉积到石墨纤维表面,形成镀层。其中镀覆温度(即纤维加热温度)为550 ℃,镀覆时间为80 min,载带H2的流量控制在300 mL/min。
表1 磨碎中间相沥青基石墨纤维的参数及热性能
Table 1 Parameters and thermal properties of milled mesophase pitch-based graphite fibers

图2所示为镀钼后石墨纤维的SEM像。从图2可以看出,纤维表面镀钼层连续均匀并且结构致密,无漏镀现象。将镀覆后的石墨纤维与环氧树脂混合并镶样,通过扫描电镜测量钼镀层的厚度在250~400 nm之间,平均厚度约300 nm。

图2 镀钼石墨纤维的SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM images of Mo-coated graphite fibers
镀钼石墨纤维与铜粉的混合在V型混料桶中进行,混料桶转速为150 r/min,混合时间为24 h。混合后的粉末在真空热压烧结炉的石墨模具中进行烧结。系统的真空度为10-3 Pa,升温速率约10 ℃/min。烧结体在温度为950 ℃,烧结压力为40 MPa的条件下保温40 min,随炉冷却至200 ℃左右时取出。分别制备石墨纤维在复合材料中体积含量为35%、40%、45%、50%、55%的试样,其尺寸约为d 20 mm×15 mm。
1.3 检测方法
用排水法测定复合材料的致密度;采用LEO-1450扫描电镜(SEM)观察复合材料的组织及断口形貌;用Siemens D5000X射线衍射(XRD)仪(Cu靶)对复合材料进行物相分析;通过LEO JSM-7001F场发射扫描电镜(FE-SEM)和JEM-2100透射电镜(TEM)对复合材料的界面区域进行观察和分析。
复合材料的室温热扩散率α在NETZSCH LFA 427激光热导仪上测量,并根据关系式λ=αρc计算热导率。其中λ为热导率,W·m-1·K-1;α为热扩散率,m2·s-1;ρ为样品密度,kg·m-3;c为样品比热容,J·kg-1·K-1,采用差分扫描量热法于NETZSCH DSC 404F1 Pegasus差示扫描量热仪上测定。复合材料热膨胀系数的测试在NETZSCH DIL 402C热膨胀仪上进行,测试温度范围为25~200℃,升温速率3 ℃/min,氮气为保护气氛。在本实验中,复合材料的热膨胀系数为50~100 ℃温度范围的平均热膨胀值。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 微观组织与界面特性
经排水法测定,制备的不同石墨纤维体积含量试样的致密度均在97%以上。图3(a)和(b)所示为典型的镀钼石墨纤维/Cu复合材料的SEM像,其中石墨纤维体积分数为50%。可以看出,纤维在Cu基体中分布相对均匀且无明显损伤,没有发现界面脱粘现象和孔洞的存在。值得注意的是,在热压烧结过程中,具有一定长径比的石墨纤维受到剪切应力的作用以及模具几何形状的限制,在Cu基体中的排列出现了明显的择优取向。如图3(c)所示,若定义压力方向为Z方向,垂直于压力方向为X-Y方向,则纤维择优排布在X-Y方向的二维平面上。显然,纤维的这种排布方式会导致复合材料的热性能呈现各向异性。

图3 复合材料在垂直和平行于热压压力方向的典型SEM形貌以及纤维取向示意图
Fig. 3 Typical SEM morphologies of composite in vertical(a) and parallel(b) to hot-pressed direction and schematic diagram of fiber orientation(c)
图4所示为镀钼石墨纤维体积含量50%时复合材料的XRD谱。从图4可以看出,复合材料中不仅存在Cu、石墨和Mo相,还检测到了Mo2C相。由此可以判断,在热压烧结过程中,部分石墨纤维表面的Mo镀层与纤维发生合成反应生成了Mo2C。

图4 镀钼石墨纤维/Cu复合材料的XRD谱
Fig. 4 XRD pattern of Mo-coated graphite fiber/Cu composite
图5(a)所示为复合材料界面区域的FE-SEM像。从低倍的二次电子像中可以清晰地看到在石墨纤维和基体铜之间的Mo层,且该层在复合材料制备中,保

图5 复合材料界面区域的FE-SEM像和反应层与石墨纤维界面处的TEM像及反应层区域的电子衍射花样
Fig. 5 FE-SEM images of interface area of composite(a) and TEM image of carbide/graphite fiber interface and corresponding electron diffraction pattern from interfacial carbide (Mo2C)(b)
持了均匀连续的形貌,与纤维和Cu基体之间的连接良好。由于Mo和Cu之间的扩散极少,该层的厚度较之前纤维表面Mo镀层的厚度(300 nm左右)无太大变化。而从图5(a)中插入的高倍FE-SEM背散射像中可以看到,在Mo层(亮白衬度)与石墨纤维(亮黑衬度)之间,存在不同于Mo和石墨纤维衬度的暗灰衬度层。由XRD的检测结果可初步判断该层为Mo2C反应层。经观察,该反应层连续但不均匀,厚度约在50~100 nm间。图5(b)所示该反应层与石墨纤维界面处的TEM像以及反应层区域的电子衍射花样,由此进一步确认该反应层由Mo2C组成,而且这种碳化物层与石墨纤维的界面结合处平直,呈现出紧密的结合状态。
2.2 纤维排布对热性能的影响
由于实验所用的沥青基石墨纤维在其径向和轴向的热性能差异很大(见表1),尤其是纤维的热导率在径向和轴向相差接近一个数量级,因此,纤维在基体中的排布方式对复合材料热性能有很大影响。从对复合材料的组织观察中可以看出(见图3),纤维择优在垂直于热压压力的二维平面上随机地排列,因此,可以近似地认为该复合材料的热性能在二维方向上各向同性。以镀钼石墨纤维体积含量为50%的复合材料为例,对其X-Y方向和Z方向热导率和热膨胀系数(CTE)的测量结果列于表2。从表2可以看出,其X-Y方向上的热导率比Z方向上的高约75%,而热膨胀系数低60%左右。显然,纤维的这种排布方式使其轴向的高热导和低热膨胀在X-Y方向要比在Z方向上得以利用的程度高得多。
表2 镀钼石墨纤维/Cu复合材料X-Y和Z方向的热性能
Table 2 Thermal properties of Mo-coated graphite fiber/Cu composite measured along X-Y and Z directions
2.3 纤维钼金属化对热性能的影响
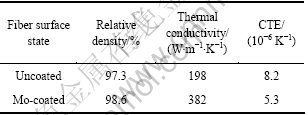
为考察石墨纤维钼金属化改性对复合材料热性能带来的影响,实验采用相同的混粉和热压工艺制备了无镀层石墨纤维/Cu复合材料。表3对比了用不同表面状态石墨纤维制备的复合材料的致密度和热性能,二者中纤维的体积含量均为50%,热性能测量方向为X-Y向。
表3 不同表面状态石墨纤维/Cu复合材料的性能
Table 3 Properties of composites with uncoated and Mo-coated graphite fiber

从表3可以看出,虽然二者致密度相差不到1.5%,但后者的热导率却是前者的近2倍。对于超高模量的中间相沥青基碳纤维来说,由于纤维内部六边形结构的石墨微晶基面大都沿着平行于纤维轴向排列,其结构致密,无定形C原子少,表面能极低[5, 14]。因此,在与Cu复合时,二者间的机械结合性更差。如图6所示,在对无镀层石墨纤维/Cu复合材料的TEM观察中,经常会发现在其界面连接处存在纳米尺度的狭缝,充分表明这种石墨纤维和基体Cu之间依赖机械互锁结合的界面,结合性极差且不稳定,因此严重降低了复合材料整体的导热性能。而通过对石墨纤维表面镀覆碳化物形成元素Mo,石墨纤维与金属之间能通过Mo镀层与纤维表面发生反应生成的连续碳化物(Mo2C)形成良好的结合,促进了复合材料热导率的提高。但需要指出的是,尽管Mo层是高导热的金属镀层,但Mo及Mo2C的热导率(分别为135和80 W/(m·K))还是远低于石墨纤维和Cu的热导率,因此,本文作者认为膜层太厚时会对复合材料的导热产生不利影响,而对于有效或最佳的镀覆层厚度范围还有待进一步 研究。
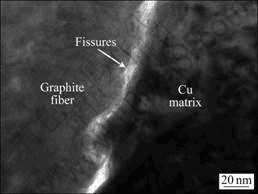
图6 无镀层石墨纤维/Cu复合材料界面的TEM像
Fig. 6 TEM image of interface of uncoated graphite fiber/Cu composite
从表3中还可以看出,镀钼石墨纤维复合材料的热膨胀系数要比无镀层的低约55%。大量对复合材料热膨胀行为的研究表明,复合材料的热膨胀系数不仅与基体和增强相本身的热膨胀有关,还取决于增强相通过界面对基体热膨胀的约束[15-18]。对比图7给出的二者的断口形貌(断裂面沿Z向)可以看出,无镀层的石墨纤维大都保持其完整的形貌从铜基体中拔出或剥离,而镀覆的复合材料中,大多数纤维则呈现断裂、弯曲或破碎的形貌。显然,镀钼纤维复合材料的界面结合强度远高于无镀层复合材料的,因此,纤维通过界面对金属基体热膨胀的约束作用强,从而呈现出了较低的热膨胀系数。由此看来,对石墨纤维表面进行钼金属化改性是提高该石墨纤维/Cu复合材料的热导率、降低其热膨胀系数的有效方法。

图7 无镀层和镀钼石墨纤维/Cu复合材料的断口形貌
Fig. 7 Fractographies of composites with uncoated(a) and Mo-coated(b) graphite fiber
2.4 纤维含量对热性能的影响
图8所示为镀钼石墨纤维体积含量分别为35%、40%、45%、50%和55%的复合材料在X-Y方向上的热导率和热膨胀系数。实验中,采用制备复合材料所用的金属铜粉以及相同的热压工艺参数制备了纯铜烧结体,用于和复合材料的热导率进行对比,测得其热导率为327 W/(m·K)。
从图8看出,随着纤维体积含量的增加,复合材料的热导率呈先升高后降低的趋势,当纤维体积分数为50%时,热导率达到最高。且在该体积变化范围内,复合材料的热导率均高于相同条件下得到的纯铜烧结体的热导率。一方面,石墨纤维在轴向的热传导能力远高于基体Cu的热传导能力,所以石墨纤维含量的增加可提升复合材料在X-Y方向的导热性能;另一方面,随纤维含量的增加,纤维间金属Cu粘结相的含量相对减小,给复合材料的致密化带来困难(不同纤维含量复合材料的致密度分别为99.7%、99.5%、99.1%、98.6%和97.1%),因此,材料内部的缺陷和孔洞逐渐增多,在一定程度会削弱复合材料的有效导热能力。这些因素综合作用的结果,使得纤维体积含量小于50%时,复合材料的热导率随纤维体积含量增加而上升,但上升的趋势逐渐减小,而当体积含量超过50%时,缺陷和孔洞的影响更大,热导率已开始呈现随纤维含量增加而下降的趋势。需要说明的是,在该实验条件下,当纤维体积含量超过55%以后,采用热压烧结法已经很难获得高致密度、纤维均匀分布的复合材料。从图8中还可以看出,与热导率的变化趋势不同,复合材料的热膨胀系数对纤维体积含量的变化十分敏感,随纤维体积含量的增加,几乎呈线性趋势迅速下降。

图8 纤维含量对复合材料热导率和热膨胀系数的影响
Fig. 8 Effect of fiber content on thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal expansion of composites
整体来看,纤维体积分数在35%~55%之间时,复合材料二维方向的热导率在367~378 W/(m·K)之间,略低于纯铜的理论热导率(394 W/(m·K)),远高于现有封装材料如W/Cu(160~210 W/(m·K)),SiC/Al(170~ 220 W/(m·K))的热导率[3, 14]。其二维方向的热膨胀系数在4.2×10-6~8.6×10-6 K-1之间,可与半导体或陶瓷基板材料如Si(4.1×10-6 K-1)、GaAs(5.8×10-6 K-1)、AlN(4.5×10-6 K-1)及Al2O3(6.7×10-6 K-1)的热膨 胀[1, 14]匹配好。因此,该复合材料能很好地满足大功率电子器件对封装材料的散热及匹配性要求。
3 结论
1) 热压法制备镀钼石墨纤维/Cu复合材料,纤维择优在垂直于热压方向的二维平面上随机排布,复合材料是各向异性材料,在二维方向上拥有较高的热导率和较低的热膨胀系数。
2) 采用金属化学气相沉积法在纤维表面镀覆的Mo层,烧结过程中部分与纤维反应生成了连续的Mo2C层,能有效改善纤维与金属基体间的界面结合,促进复合材料热导率的提高和热膨胀系数的降低。
3) 纤维体积分数在35%~55%之间时,复合材料的热导率先升高后降低,体积分数为50%时达到最大值;热膨胀系数呈线性趋势迅速降低。其二维方向的热导率在367~382 W/(m·K)之间,热膨胀系数可在4.2×10-6~8.6×10-6 K-1间调节。该材料能很好地满足大功率电子器件对封装材料的散热及匹配性要求。
REFERENCES
[1] ZWEBEN C. Thermal materials solve power electronics challenges[J]. Power Electronics Technology, 2006, 32(2): 40-47.
[2] ZWEBEN C. Advances in high-performance thermal management materials: A review[J]. Journal of Advanced Materials 2007, 39(1): 3-10.
[3] QU Xuan-hui, ZHANG Lin, WU Mao, REN Shu-bin. Review of metal matrix composites with high thermal conductivity for thermal management applications[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2011, 21(3): 189-197.
[4] MALLIK S, EKERE N, BEST C, BHATTI R. Investigation of thermal management materials for automotive electronic control units[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2011, 31(2/3): 355-362.
[5] GALLEGO N C, EDIE D D. Structure-property relationships for high thermal conductivity carbon fibers[J]. Composites: Part A, 2001, 32(8): 1038-1043.
[6] CORNIE J A, ZHANG S. Manufacturing and evaluation of thermal expansion behavior of discontinuous pitch graphite fiber reinforced copper alloys for CTE matching heat sink applications[C]// Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, 2003, 5288: 310-315.
[7] MIRACLE D B. Metal matrix composites: From science to technological significance[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2005, 65(15/16): 2526-2540.
[8] LIOYD J C, NEUBAUER E, BARCENA J, CLEGG W J. Effect of titanium on copper–titanium/carbon nanofibre composite materials[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2010, 70(16): 2284-2289.
[9] WEBER L, TAVANGAR R. On the influence of active element content on the thermal conductivity and thermal expansion of Cu-X (X=Cr, B) diamond composites[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57(11): 988-991.
[10] BARCENA J, GARCIA DE CORTAZAR M, SEDDON R, LLOYD J C, TORREGARAY A, COLETO J. Effect of the incorporation of interfacial elements on the thermophysical properties of Cu/VGCNFs composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2010, 70 (16): 2258-2262.
[11] REN Shu-bin, SHEN Xiao-yu, GUO Cai-yu, LIU Nan, ZANG Jian-bing, HE Xin-bo, QU Xuan-hui. Effect of coating on the microstructure and thermal conductivities of diamond-Cu composites prepared by powder metallurgy[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2011, 71(13): 1550-1555.
[12] SHEN Xiao-yu, HE Xin-bo, REN Shu-bin, ZHANG Hao-ming, QU Xuan-hui. Effect of molybdenum as interfacial element on the thermal conductivity of diamond/Cu composites[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 529: 134-139.
[13] SONG J, GUO Q, GAO X, TAO Z, SHI J, LIU L. Mo2C intermediate layers for the wetting and infiltration of graphite foams by liquid copper[J]. Carbon, 2011, 49(10): 3165-3170.
[14] ENDO M, KIM C, KARAKI T, KASAIT T, MATTHEWS M J, BROWN S D M, DRESSENLHAUS M S, TAMAKI T, NISHIMURA Y. Structural characterization of milled mesophase pitch-based carbon fibers[J]. Carbon, 1998, 36(11): 1633-1641.
[15] HUBER T, DEGISCHER H P, LEFRANC G, SCHMITT T. Thermal expansion studies on aluminium-matrix composites with different reinforcement architecture of SiC particles[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2006, 66(13): 2206-2217.
[16] DENG C F, MA Y X, ZHANG P, ZHANG X X, WANG D Z. Thermal expansion behaviors of aluminum composite reinforced with carbon nanotubes[J]. Materials Letters, 2008, 62(15): 2301-2303.
[17] ZHANG L, QU X H, HE X B, DUAN B H, REN S H, QIN M L. Thermo-physical and mechanical properties of high volume fraction SiCp/Cu composites prepared by pressureless infiltration[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 489(1/2): 285-293.
[18] HE Xin-bo, QU Xuan-hui, REN Shu-bin, JIA Cheng-chang. Net-shape forming of composite packages with high thermal conductivity[J]. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 2009, 52 (1): 238-242.
(编辑 龙怀中)