文章编号:1004-0609(2014)01-0174-05
纤维结构钼铜复合材料的制备及组织性能
王婕丽,林文松,姜自旺,杨国良,段丽慧
(上海工程技术大学 材料工程学院,上海 201620)
摘 要:在真空环境下,将铜熔渗到钼纤维预制体中,制得纤维结构的致密的钼铜复合材料。通过控制钼纤维预制体的表观密度,可以方便地改变钼铜复合材料的成分组成。采用扫描电镜和金相显微镜观察材料的微观组织形貌,研究工艺参数对钼铜复合材料的成分、密度、硬度和电导率的影响。结果表明:采用无纺技术结合模压成形获得的钼纤维预制体可形成较宽范围的孔隙度,从而得到钼含量不同的钼铜复合材料;熔渗工艺制得的钼铜复合材料具有致密均匀、特征明显的纤维结构组织;所得钼铜复合材料的致密度均达到99%以上。当钼质量分数为84.77%时,得到的材料致密度达到最大值99.43%,其硬度为226.7HV,电导率为16.5 MS/m。
关键词:纤维结构;钼铜复合材料;钼纤维;熔渗
中图分类号:TG 146.4 文献标志码:A
Fabrication and structure properties of fiber-structured Mo-Cu composites
WANG Jie-li, LIN Wen-song, JIANG Zi-wang, YANG Guo-liang, DUAN Li-hui
(School of Materials Engineering, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai 201620, China)
Abstract: In vacuum environment, the dense fiber-structured molybdenum-copper (Mo-Cu) composites were fabricated by infiltrating liquid copper into molybdenum fibrous preform. By controlling the relative density of molybdenum fibrous preform, the composition of Mo-Cu composites could be easily changed. The microstructure and morphologies of Mo-Cu composites were observed by scanning electron microscopy and optical microscopy, and the effects of process parameters on the composition, physical and mechanical properties were investigated. The results indicate that molybdenum fibrous preform obtained by non-woven technology with mould pressing formation has wider range of porosity, Mo-Cu composite with different molybdenum contents are obtained. The Mo-Cu composites have dense and homogeneous structure with obvious fibrous character by infiltration. The relative density of the composites is above 99%. When the mass fraction of molybdenum is 84.77%, the maximum relative density reaches 99.43% for fiber-structured Mo-Cu composites. Meanwhile, their hardness and electrical conductivity are 226.7HV and 16.5 MS/m, respectively.
Key words: fibrous structure; molybdenum-copper composites; molybdenum fiber; infiltration
钼铜复合材料是由钼、铜两种单体均匀混合而成的特殊功能材料。它综合了钼与铜的本征物理性能,具备良好的抗熔焊、耐烧损和耐高温强度、高导电导热等性能,因而,广泛应用于电子、电力、军事等行业[1-5]。与电触头常用元素钨相比,钼的电子逸出功较小、截流值较小,更利于提高材料的抗电弧烧蚀性,同时,钼的导电率较钨高、加工性较钨好,因而,钼铜复合材料在电触头领域发展是极有潜力的。但在真空开关接触材料领域不仅要求钼铜材料具有合适的硬度、优良的导电性和耐损蚀性,还要求其全致密(98%以上)[6]。然而钼、铜(钼:10.22 g/cm3,铜:8.93 g/cm3)的密度相差较小,故常规粉末冶金方法制备的高钼含量的钼铜材料存在成形性不好、孔隙分布不均、难以完全致密等问题,这极大地限制了生产和实际应用[7-9]。当前,钼铜复合材料的制备难点在于如何保持高钼含量的同时仍能保持其高致密度,其关键在于控制材料的组织均匀性。针对以上问题,国内外学者进行了大量探索,引入了许多新构思,其研究工作主要集中在钼铜纳米复合粉末的制备和钼铜梯度功能材料的制备等方面[10-14],但有关纤维结构钼铜复合材料的制备的报道还较少。
金属纤维继承了金属本身固有的特性。且在同一孔隙度下,液态金属在纤维预制体中的渗透系数比在粉末预烧结坯的渗透系数大[15]。同时,纤维结构的材料从理论上分析,其孔隙率变化范围大,且易于调节。据此,本文作者首先制备了三维钼纤维预制体,并作为钼铜复合材料的基体相,将铜熔渗其中,成功地制备了一种纤维基体相结构的钼铜功能材料,并对其显微结构和基本性能等进行研究分析。
1 实验
实验原料为钼纤维(纯度≥99.9%),丝径为0.2 μm。铜为T2紫铜。图1所示为钼纤维的SEM像。将钼纤维通过无纺铺制、叠配,经高温烧结制成极度蓬松的纤维毡,纤维毡中孔隙的体积比最大达90%。再将纤维毡通过模压压制成尺寸为d12.5 mm×5 mm的柱状纤维预制体,压制压力控制在20~80 MPa范围 内。将T2紫铜和钼纤维预制体一起放置于ZrO2烧结舟中,铜放置于钼纤维预制体上面,在真空度为1 MPa的真空环境下进行熔渗烧结,烧结温度为1 240 ℃,保温时间为1.5 h,最终获得纤维结构的钼铜复合材料。

图1 钼纤维的SEM像
Fig. 1 SEM image of molybdenum fiber
采用排水法利用阿基米德原理测量钼纤维预制体和钼铜复合材料的密度,采用Mettler Toledo AL204分析天平称量,精度为0.1 mg。
用Keyence VHX-600K超景深金相显微镜观测金相组织;用Hitachi 3400-N型扫描电子显微镜对钼纤维及钼铜复合材料的微观形貌进行观察;采用7501型涡流电导仪(厦门第二电子仪器厂生产)测量电导率;采用HXD-1000TMSC/LCD显微硬度计(上海泰明光学仪器有限公司生产)测定硬度。
2 结果与分析
2.1 钼纤维预制体的压制特性
图2所示为钼纤维预制体的致密度与压制压力的关系。由图2可知,在模压过程中,随着压制压力的增大,钼纤维预制体的致密度逐渐升高,最高可达84.25%,并且两者近似呈线性关系。本研究中采用的无纺编织技术得到的钼纤维毡极为蓬松,但纤维之间彼此连接构成连通孔的网络骨架,并且骨架中的孔空间被气体所填充。当纤维毡受到一定压制压力时,孔空间内部的气体含量减小,使纤维预制体的孔隙度不断减小,其致密度不断增大。随着压制压力的增大,纤维相互间接触面积增大,同时纤维受压弯曲,并逐步产生塑性变形,且塑性变形较小,弹性后效小,纤维预制体的孔隙度与其受到的压力近似呈线性关系,也即说明纤维预制体的致密度得到较好的控制,由此可方便地改变钼铜复合材料的成分组成。
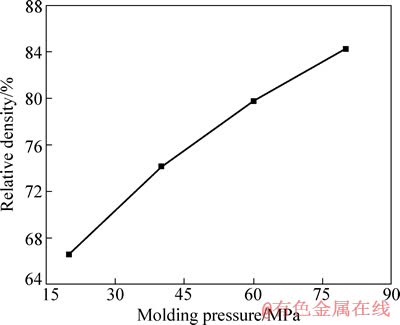
图2 压制压力与钼纤维预制体致密度的关系
Fig. 2 Relationship between molding pressure and relative density of molybdenum fibrous preform
2.2 纤维结构Mo-Cu复合材料的组织与形貌

图3 不同钼质量分数钼铜复合材料的金相组织
Fig. 3 Metallographs of fiber-structured Mo-Cu composites with different mass fractions of molybdenum
图3所示为不同钼质量分数下钼铜复合材料的金相结构。其中灰色区域为钼纤维,黄色区域为金属铜。由图3可知,钼铜复合材料具有致密均匀、特征明显的纤维结构组织。尽管钼纤维预制体经过高温烧结,但其仍保持无纺编织的形态,且其间隙分布均匀。在1 240 ℃的熔渗温度下,铜较好地浸渗到钼纤维预制体的孔隙中,并保持原来的金属光泽。随钼质量分数的增加,钼纤维预制体的孔隙度由33.46%减小到15.75%,其组织结构趋于紧密排列。李君强等[16]报道了钨纤维增强W-Cu复合材料的制备,其中钨纤维被缠绕在不锈钢棒上,形成螺旋状,并通过压制制得钨纤维预制体。但随着钨纤维预制体孔隙度的增大,纤维骨架经熔渗出现移位、松散甚至部分解旋的现象。而无纺技术编制的钼纤维毡,经压制后在熔渗的过程中不会出现此类现象。由此可以断定,通过无纺技术,经压制获得的钼纤维预制体可形成较宽范围的孔隙度,同时,高温烧结后能保持一定的孔隙度和孔径形状,从而可得到钼含量不同的钼铜复合材料。
界面结构是复合材料发挥优良性能的关键因素。图4所示在钼质量分数为84.77%钼铜复合材料中钼铜两相界面形貌。由图4可知,钼纤维与铜相间界面结合紧密、平整,不存在异质相,其组织形貌保持明显的纤维毡结构特征。由于3D纤维预制体在空间中形成网络骨架,骨架内通道彼此连通,利于铜相充分浸渗,从而形成两相结合稳定的界面结构,其有利于材料性能的提高。
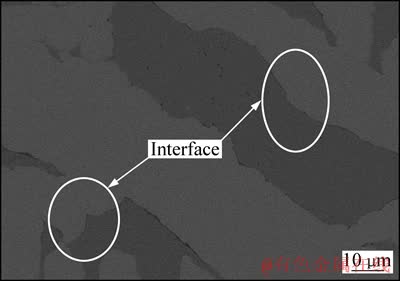
图4 钼含量为84.77%时钼铜复合材料的界面形貌
Fig. 4 Interface morphology of Mo-Cu composites with molybdenum content of 84.77%
2.3 纤维结构Mo-Cu复合材料的性能
图5所示为压制压力对纤维结构钼铜复合材料密度与致密度的影响。该复合材料在压制压力为20~80MPa范围变化下,其钼质量分数对应为67.42%~84.77%。由图5可知,钼铜复合材料的致密度均大于99%;且随着压制压力的增大,复合材料的密度及致密度均呈上升趋势,在钼质量分数为84.77%时得到的材料的致密度达到最大值99.43%。当纤维预制多孔体的孔隙度大于10%时,全部为贯通孔[15]。本研究中,随钼质量分数的增加,钼纤维预制体的孔隙度范围为15.75%~33.46%,因而,预制体的孔空间形成贯通孔。在真空高温烧结气氛下,铜相流动性增加,同时,钼纤维预制体中连通孔空间无气体占据,有利于铜相的充分渗透,材料的致密化程度较高。
与此同时,液相铜在纤维中的熔渗过程实质是铜在钼纤维表面的润湿过程,即外部液相铜对钼纤维预制体产生毛细浸渗的作用,使液相铜沿着预制体内孔隙流动,至孔隙被完全填充为止。而纤维内部通常不存在孔洞,故只需考虑钼纤维间孔隙被液相铜填充的情况。液相的铜在钼纤维预制体的孔隙中所形成的毛细管力,可以根据Laplace方程[17]进行估算:
 (1)
(1)
式中:p为毛细管作用力,MPa;σ为熔液的表面张力,N/m;θ为润湿角;r为钼纤维预制体的孔半径。
当θ> 时,毛细孔力为负数,此时,铜将无法渗入预制体中。由夏扬等[18]指出,熔渗温度为1 200~ 1 260 ℃时,铜在钼表面的润湿角为20°~14°,远小于上述不能润湿的限值,也即说明本实验满足润湿条件。随着压制压力的增大,钼纤维预制体结构的致密程度提高,预制体内孔径r减小,故毛细管作用力p增大,液相铜对钼纤维预制体的浸渗能力加强,复合材料趋于致密化,因此,当压制压力越大,材料的致密度越大。
时,毛细孔力为负数,此时,铜将无法渗入预制体中。由夏扬等[18]指出,熔渗温度为1 200~ 1 260 ℃时,铜在钼表面的润湿角为20°~14°,远小于上述不能润湿的限值,也即说明本实验满足润湿条件。随着压制压力的增大,钼纤维预制体结构的致密程度提高,预制体内孔径r减小,故毛细管作用力p增大,液相铜对钼纤维预制体的浸渗能力加强,复合材料趋于致密化,因此,当压制压力越大,材料的致密度越大。
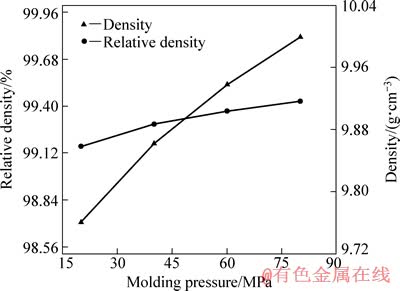
图5 压制压力对钼铜复合材料的密度与致密度随的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of molding pressure on density and relative density of Mo-Cu composites
图6所示为钼质量分数与钼铜复合材料的硬度及电导率的关系。由图6可知,随着钼质量分数增加,钼铜复合材料的硬度相应增加,其电导率逐渐下降。在钼质量分数为84.77%,材料的硬度可达最高226.7HV,相应电导率为16.5 MS/m;而在钼质量分数为67.42%,材料的电导率达到最大值,为21 MS/m,其硬度为193.7HV。由于钼铜两元素的溶解度极小,基本可以忽略,这决定了钼铜材料只能形成假合金,在组织结构上钼铜复合材料即由该两种金属相组成(见图3所示),因此,其硬度和电导率均可视为两相的加和。由于钼的硬度比铜高,可认为其在复合材料中是硬质相,故随钼质量分数的增加,钼在复合材料中的比例逐渐增加,材料整体的硬度也随之增加。相应地,复合材料中铜比例下降,致使钼铜材料的导电能力下降,即其电导率降低,反之亦然。

图6 钼质量分数与钼铜复合材料的硬度及电导率的关系
Fig. 6 Relationships among mass fraction of molybdenum and hardness and electrical conductivity of Mo-Cu composites
3 结论
1) 采用无纺技术结合模压成形获得的钼纤维预制体,在20~80 MPa的压制压力下,可形成较宽范围的孔隙度,孔隙度范围为15.75%~33.46%,同时,钼纤维预制体的致密度与其压制压力近似呈线性关系。
2) 钼纤维预制体于1 240 ℃烧结1.5 h后,能保持一定的孔隙度和孔径形状,制得的纤维结构钼铜复合材料具有致密均匀、特征明显的纤维结构组织,其界面结合紧密、平整。
3) 纤维结构钼铜复合材料的致密度可达到99%以上。在钼质量分数为84.77%时,所得材料的致密度达到最大值99.43%,其硬度为226.7 HV,电导率为16.5 MS/m。
REFERENCES
[1] GUO Shi-bo, KANG Qi-ping, CAI Chun-bo, QU Xuan-hui. Mechanical properties and expansion coefficient of Mo-Cu composites with different Ni contents[J]. Rare Metals, 2012, 31(4): 368-371.
[2] LI Zai-yuan, ZHAI Yu-chun. Preparation of Mo60Cu40 composite nano-powder by hydrogen reaction[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(1): 6-9.
[3] SUN Ao-kui, WANG De-zhi, WU Zhuang-zhi, CHENG Qi-jun. Mechanochemical synthesis of Mo-Cu nanocomposite powders[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509: L74-L77.
[4] AGUILAR C, CASTRO F,  D, CUEVAS F, LOZADA L, VIELMA N. Structural study of nanocrystalline solid solution of Cu-Mo obtained by mechanical alloying[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 548: 189-194.
D, CUEVAS F, LOZADA L, VIELMA N. Structural study of nanocrystalline solid solution of Cu-Mo obtained by mechanical alloying[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 548: 189-194.
[5] 陈玉柏, 范景莲, 刘 涛, 成会朝, 田家敏. 细晶钼铜合金的制备[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(6): 1039-1044.
CHEN Yu-bai, FAN Jing-lian, LIU Tao, CHENG Hui-chao, TIAN Jia-min. Fabrication of fine-grained Mo-Cu alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(6): 1039-1044.
[6] 李晓燕. 触头材料用铜合金电击穿性能研究[D]. 洛阳: 河南科技大学, 2008: 29-41.
LI Xiao-yan. Research on electrical breakdown property of Cu alloy for contact materials[D]. Luoyang: Henan University of Science, 2008: 29-41.
[7] 周贤良, 叶志国, 华小珍, 张建云. 熔渗和液相法烧结Mo-Cu合金的组织和性能[J]. 有色金属, 2006, 58(2): 1-4.
ZHOU Xian-liang, YE Zhi-guo, HUA Xiao-zhen, ZHANG Jian-yun. Tissues and properties of Mo-Cu alloy prepared by infiltration and liquid-phase sintering[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 58(2): 1-4.
[8] 韩胜利, 蔡一湘, 宋月清, 崔 舜. 制备工艺对Mo-Cu合金组织性能的影响[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2010, 4(2): 100-105.
HAN Sheng-li, CAI Yi-xiang, SONG Yue-qing, CUI Shun. Microstructure and properties of Mo-Cu alloys prepared by different techniques[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2010, 4(2): 100-105.
[9] 张青花. Mo-Cu复合材料的最新研究进展[J]. 河西学院学报, 2009, 25(2): 51-55.
ZHANG Qing-hua. The new development of Mo-Cu composites[J]. Journal of HeXi University, 2009, 25(2): 51-55.
[10] FAN Jing-lian, CHEN Yu-bo, LIU Tao, TIAN Jia-min. Sintering behavior of nanocrystalline Mo-Cu composite powders[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(10): 1693-1697.
[11] 程继贵, 弓艳飞, 宋 鹏, 李 洁. 凝胶-共还原法制备超细Mo-Cu粉末及其烧结性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(3): 422-427.
CHENG Ji-gui, GONG Yan-fei, SONG Peng, LI Jie. Characterization and sintering behavior of ultra-fine Mo-Cu powder prepared by gelatinization-coreduction method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(3): 422-427.
[12] 田家敏, 范景莲, 陈玉柏, 刘 涛. 细晶Mo-40%Cu合金的烧结性能[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 41(5): 1736-1742.
TIAN Jia-min, FAN Jing-lian, CHEN Yu-bo, LIU Tao. Sintering characteristics of fine grained Mo-40Cu alloy[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2010, 41(5): 1736-1742.
[13] SUN Ao-kui, DONG Xiao-jia, WANG Xiao-ying, DUAN Bo-hua, WANG De-zhi. Synthesis of novel core-shell Cu-Mo nanoparticles with good sinterability[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 555: 6-9.
[14] 王鹏飞, 沈卫平, 张 强, 张 珂, 蒋志明, 陈鹏万. 自蔓延预热爆炸固结Mo/Cu功能梯度材料的研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(4): 652-655.
WANG Peng-fei, SHEN Wei-ping, ZHANG Qiang, ZHANG Ke, JIANG Zhi-ming, CHEN Peng-wan. Self-propagating combustion preheating and explosive consolidation of Mo/Cu functionally gradient material[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2007, 36(4): 652-655.
[15] 奚正平, 汤慧萍. 烧结金属多孔材料[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2009: 2-95.
XI Zheng-ping, TANG Hui-ping. Porous materials of sintered metals[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009: 2-95.
[16] 李君强, 陈文革, 陶文俊, 丁秉钧. W纤维增强高Cu含量W-Cu复合材料的研究[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 2012, 30(2): 125-129.
LI Jun-qiang, CHEN Wen-ge, TAO Wen-jun, DING Bing-jun. Research on the tungsten fiber reinforced W/Cu composite materials with high-copper content[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2012, 30(2): 125-129.
[17] CHO H S, KIM H Y, KANG J Y, KIM T S. How the capillary burst microvalve works[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2007, 306: 379-385.
[18] 夏 扬, 宋月清, 崔 舜, 林晨光, 韩胜利. Mo-Cu和W-Cu合金的制备及性能特点[J]. 稀有金属, 2008, 32(2): 240-244.
XIA Yang, SONG Yue-qing, CUI Shun, LIN Chen-guang, HAN Sheng-li. Preparation and properties of Mo-Cu and W-Cu alloys[J]. Rare Metals, 2008, 32(2): 240-244.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:上海市教委基金重点项目(13zz133);上海工程技术大学研究生科研创新资助项目(2012yjs14)
收稿日期:2013-04-10;修订日期:2013-09-01
通信作者:林文松,教授,博士;电话:021-67791198;E-mail:linwensong@yahoo.cn