文章编号:1004-0609(2013)10-2833-07
磁场对厚板Ti-6Al-4V合金窄间隙TIG焊缝组织的影响
孙清洁1,郭 宁1,胡海峰2,冯吉才1
(1. 哈尔滨工业大学(威海) 山东省特种焊接技术重点实验室,威海 264209;
2. 苏州热工研究院,苏州 215004)
摘 要:对56 mm厚Ti-6Al-4V合金进行窄间隙磁控电弧TIG焊接,通过金相显微镜对接头各区组织进行对比分析。结果表明:在窄间隙的多层单道焊接中,接头各区的组织、结晶形态及生长方向存在很大差异。焊缝区一次结晶组织为表层焊道上表面的柱状粗大组织及熔合线附近、焊道内部的等轴晶组织。熔合线处,电磁作用提高了平面状结晶前沿及后来形成的等轴晶的稳定性,最终随着磁场强度的增加在熔合线附近逐渐由柱状晶转变为等轴晶。焊缝中心处,磁控电弧作用使得生成的等轴晶稳定性提高,随着磁场强度的增加,等轴晶逐渐单方向伸长,在热传导方向上,即焊缝表层垂直方向生成粗大的柱状晶。
关键词:Ti-6Al-4V合金;磁场;窄间隙焊接;焊缝组织
中图分类号:TG442 文献标志码:A
Effect of magnetic field on weld structure of large thickness Ti-6Al-4V alloy with narrow-gap TIG welding method
SUN Qing-jie1, GUO Ning1, HU Hai-feng2, FENG Ji-cai1
(1. Shandong Provincial Laboratory of Special Welding Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology at Weihai, Weihai 264209, China;
2. Suzhou Nuclear Power Research Institute, Suzhou 215004, China)
Abstract: A narrow-gap controlling magnetic field TIG welding experiment was conducted directing at the 56 mm-thickness Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. Afterwards, an analysis was taken to compare each weld joint microstructure by means of metallographic microscope. The results show that, during the multilayer single channel of narrow gap welding, the joint microstructure, the crystal structure and the growth orientation significantly differ from each other. The first crystal structure in the weld zone is an equiaxed grain which shows a columnar coarse grain at the top layer of the weld surface and near the bond line and the internal weld. Since the electromagnetic effect improves the stability of flat crystal and the equiaxed grains appear afterwards, ultimately, there are equiaxed grains translated from coarse columnar grains in the front of bond line with the magnetic field strength increasing. Due to the effect of magnetic controlled arc on improving the stability of equiaxed grains, along with the magnetic field strength increasing, the equiaxed grains gradually extend in a single direction; in the direction of heat conduction, i.e., in the vertical direction of the weld surface, the coarse columnar grains generate.
Key words: Ti-6Al-4V alloy; magnetic field; narrow-gap welding; weld microstructure
钛是继钢、铝及镁之后发展起来的一种金属。钛合金的比强度和比刚度高并具有良好的抗腐蚀性能、高温力学性能、抗疲劳和蠕变性能,是一种很有发展潜力和应用前景的材料[1]。随着国家对深海资源开发的重视,厚板钛合金制耐压壳体受到了更多的关注,目前对于厚板钛合金加工方法多为电子束焊接[2-3],但该方法的成本高,同时受真空室空间及大构件装配精度的约束。
1963年,美国Battelle研究所开发了一种窄间隙焊接方法(Narrow gap welding, NGW),由于坡口间隙很小,厚板焊缝截面积大幅减小,在较小焊接规范下也可以保证较高的焊接生产效率[4]。该技术在保留传统焊接方法优点的同时比较理想地克服了其局限性[5]。由于其线能量较低,可用于高强钢、细晶粒钢的焊接[6],但侧壁熔合不良一直是窄间隙焊接发展的瓶颈[7-8]。
20世纪末,在乌克兰Paton焊接所实现将磁场用于焊接过程中,以此改善电弧相关特性并成功将横向磁场引入到厚板的窄间隙焊接中,解决了窄间隙焊接中的侧壁熔合问题[9]。且BROWN等[10]和TSENG等[11]指出纵向磁场能细化晶粒以提高焊件的力学性能。而对厚板窄间隙焊接过程中磁场对焊后组织的影响报道较少,特别是磁场对Ti-6Al-4V焊后组织的影响分析鲜见报道。
本文作者以56 mm厚的Ti-6Al-4V作为焊接材料,采用双U型坡口的窄间隙磁控电弧TIG多层单道焊,分析接头微观组织变化,重点研究磁场对其影响机理,为厚板钛合金的工业应用提供可靠的理论及实验基础。
1 实验
实验所用母材为厚度56 mm的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金板,采用的焊丝是TA2,直径为3.0 mm。焊前将母材对接端面开双U型坡口,底部圆角半径为5 mm,坡口角度为0°,中心对称钝边2 mm;用细钢丝刷、砂纸除去母材距坡口20 mm以内的表面及坡口端面的油污等,再用丙酮进行擦拭清洗。将填充材料表面用细砂纸打磨,丙酮擦拭清洗。将焊件对接点固,预先设置反变形5°左右。
采用直流TIG焊接电源,加载可控交变磁场,钨极端部距焊道表层距离为4 mm,磁场强度取自垂直焊接方向截面钨极尖端处。为了实现窄间隙中的侧壁熔合,防止焊接缺陷的产生,焊接过程中选取磁场强度为8 mT,频率为10 Hz[12],窄间隙磁控电弧焊接过程如图1所示。
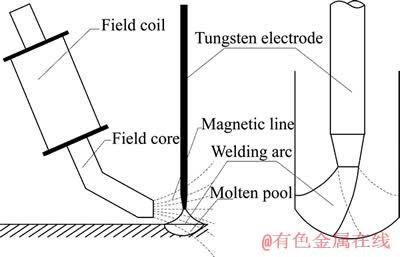
图1 窄间隙磁控电弧焊接方法示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of narrow-gap controlling magnetic field TIG welding
焊后垂直焊缝方向截取金相试样,采用金相砂纸240、500、600和800号顺序打磨,然后用3 μm的金刚石抛光剂抛光,使用HF+HNO3+H2O混合的腐蚀液进行腐蚀3~5 s。采用金相显微镜(OM)观察其显微组织形貌。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 焊接接头的横截面宏观形貌
采用如表1所列的工艺参数(表1中v为焊丝的送进速度,v′为焊接速度)获得钛合金窄间隙接头横截面如图2所示。由图2可以看出,接头明显地分为焊缝区(WZ)、熔合区(FZ)、热影响区(HAZ)和母材区(BM)。层间熔合线较为明显,整体焊接接头的上层焊缝区的最大宽度为11 mm,下层焊缝区的最大宽度为12.5 mm,焊缝宽度都明显大于初始坡口宽度,侧壁熔合良好,接头无明显缺陷。
2.2 钛合金母材区的组织形貌
厚板Ti-6Al-4V合金母材显微组织如图3所示。
表1 焊接参数
Table 1 Welding parameters
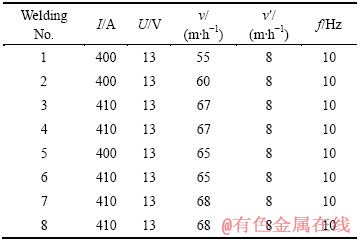
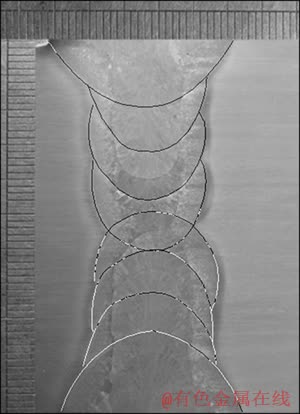
图2 焊接接头的宏观形貌
Fig. 2 Macrostructure of welded joint
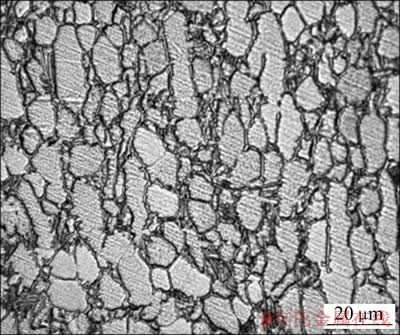
图3 Ti-6Al-4V钛合金的显微组织形貌
Fig. 3 Microstructure of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy
由图3可知,组织细小且均匀,图中亮白色相为初生α相,它在高温β晶粒内部析出,组织呈等轴结构,β相分布在等轴的α相之间。
2.3 焊缝区的组织形貌
在窄间隙的多层单道焊接中,焊缝金属快速冷却,原始β相来不及通过扩散变成平衡的α相,而是通过原子集体有规律近程迁移来实现切变相变,从而获得针状马氏体组织[13]。除针状马氏体α′相外,还存在极少量的残余β相。焊接时,部分β相从高温快速冷却过程中来不及转变而残留在针状马氏体的晶界处[14]。焊缝呈现典型的篮网状组织,先焊焊道及焊道交界处的热量散失大、冷却速度快,造成组织的迅速转变,形成了细小杂乱的马氏体组织(图4(a))。而处于表层焊道、内部焊道中心的组织为平行、粗大的马氏体组织(图4(b)),马氏体针几乎穿过整个原始凝固的β晶粒,这是焊接热量的传输慢,晶粒不断长大而造成的。
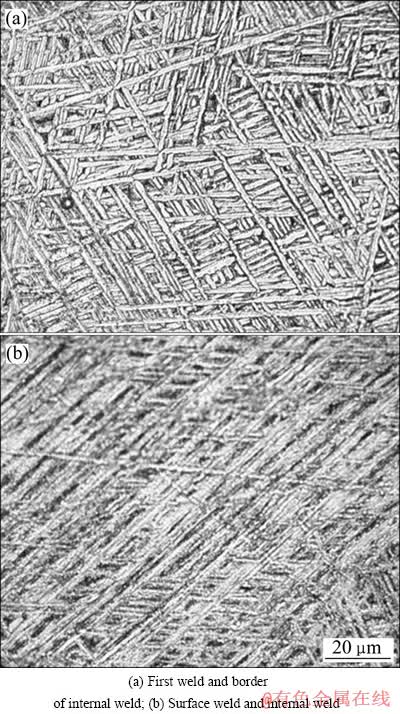
图4 焊缝区的显微组织
Fig. 4 Microstructure of weld zone
焊缝中心处沿厚度方向的组织如图5所示。图5(a)所示为交界处上方1 mm处的组织;图5(b)所示为两道焊道交界处的组织;图5(c)所示为交界处下方1 mm处的组织。
从图5(b)可以看出,在表层焊道交界线上仅存在少量尺寸较大的α′相,其余组织均匀细小,其间残留着大量未转化的β相。图5(a)所示的焊道交界线以上的组织中β相分布均匀并明显多于图5(c)所示的焊道交界线以下的组织。对于焊道交界线下的组织,焊接热循环促使β相的转变,而对于界线上的组织,由于焊接过程中较大的过冷度无法实现β相的及时转变,导致其被大量残留。
2.4 磁场作用下焊缝组织的对比分析
许多相关研究[15-19]表明,外加磁场形成的电磁作用对液态熔池进行搅拌,造成了焊缝金属凝固中的树枝晶晶臂机械断裂,断裂后的晶臂成为新的形核核心,提高了形核率;电磁搅拌引起强烈混合对流,抑制了晶粒的非均匀化生长,晶粒的漂移作用增大了非均匀形核率,从而能细化晶粒。
为了更好地探究外加磁场对钛合金焊缝组织的影响,对比分析磁场对组织的影响。图6所示为强度为8 mT、频率为10 Hz的磁场作用时焊缝组织。在焊缝的表层,组织呈柱状,与普通焊接焊缝中的柱状组织相似,但其生长方向是从表层向内部生长(图6(d)),从焊缝表层向母材过渡,其组织为明显的等轴状晶,只是晶粒的大小在不断减小,直到熔合线附近。
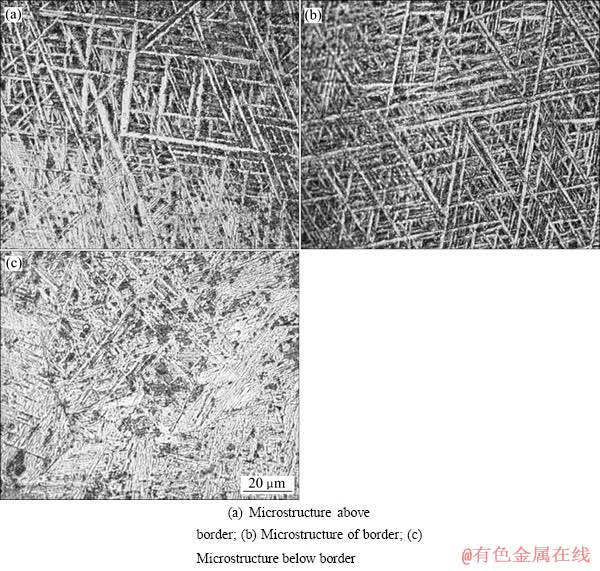
图5 表层焊道交界处显微组织
Fig. 5 Microstructures at border of surface weld
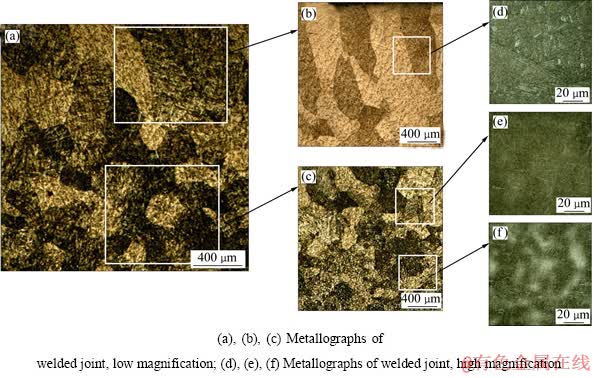
图6 8 mT、10 Hz磁场作用时的焊缝组织
Fig. 6 Microstructures of weld seam at magnetic field strength of 8 mT and frequency of 10 Hz
图7所示为无磁场作用时的焊缝组织。焊缝表层组织为等轴晶(图7(e)),向母材过渡时发现少量的柱状晶(图7(f))。焊缝表层组织从不加磁场时的等轴晶单方向伸长而逐渐转变为柱状组织,且随着磁场强度的加大逐渐变得粗大,其生长方向为热量传导方向,即晶粒从表层向内部生长。从表层向熔合线附近过渡的过程中发现,随着磁场强度的增加,柱状晶逐渐模糊消失,变为明显的等轴晶,晶粒的大小随着向HAZ延伸在不断减小,直到熔合线附近。通常情况下,Ti-6Al-4V焊缝的熔合区及熔合线附近为粗大的柱状晶组织,如图7(f)所示。当熔池受到纵向磁场作用时,搅拌的熔池不仅导致液态金属的浓度梯度大大降低,而且熔池的温度场得到重新分布并趋于稳定和均匀[20],磁场的施加抑制了普通焊接情况下的由熔合线向熔池中心生长方式,抑制了在熔合线内侧形成大量的柱状晶,如图6(e)所示。实验过程中发现在特定位置加载磁场后,出现了由柱状晶(图7(f))向等轴晶(图6(e))转变的现象,并有细化趋势。
在磁场作用下,熔池除了受等离子气流、表面张力及本身焊接电流中的电磁力作用外,磁场的引入增强了电磁力在熔池中的作用,使得熔池中液态金属的运动具有复杂的循环和涡旋的特点。正是由于这种复杂的液态搅拌,当扩散聚集层的杂质被“冲洗”引起液相线温度的变化已超过了由于加热斑点扩大和液态金属搅拌引起温度的提高时,熔池中心附近成分过冷得到提高,成分过冷诱导形核结晶。在电弧的周期摆动下,结晶晶核以等轴晶的形式稳定生长,而受焊接热输入能量的供给,等轴晶不断长大并且不断地将周围的小晶粒吞噬,所以最终形成的焊缝组织,尤其是焊缝的中心表层的组织为粗大组织。
虽然钛合金的导热性较差,但是相对于表层金属一侧的空气来说还是较强的,所以这使得表层金属具有了择向生长的特点,最终在其焊缝的中心表层生成粗大的柱状晶,生长方向垂直于焊道表面,如图6(b)所示。
2.5 焊缝一次组织形成过程
为形象地描述界面层形成过程,建立了磁控作用下钛合金焊缝金属界面层结构及凝固过程示意图,如图8所示。
熔池受电磁作用在结晶前沿以平面晶的形式结晶,在熔池内部,尤其是焊缝中心受成分过冷而产生等轴晶晶核(图8(b))。平面晶在结晶过程中释放结晶潜热,在结晶前沿产生负温度梯度以及杂质在运动的平面状结晶前沿之前聚集促成成分过冷,导致平面晶“凸起”,熔池内部的等轴晶也可生长出枝晶来,但是受到周期摆动的电弧作用,“凸起”及晶臂熔断形成新的晶核,同时原有等轴晶不断长大。由于钛的热传导性能差,热量促使晶粒长大,并且过程中大晶粒不断吞噬周围的小晶粒(图8(c)),最终形成在焊缝表层为柱状晶粒,向母材逐渐过渡为等轴晶粒,最后在熔合线附近为平面状晶(图8(d))。
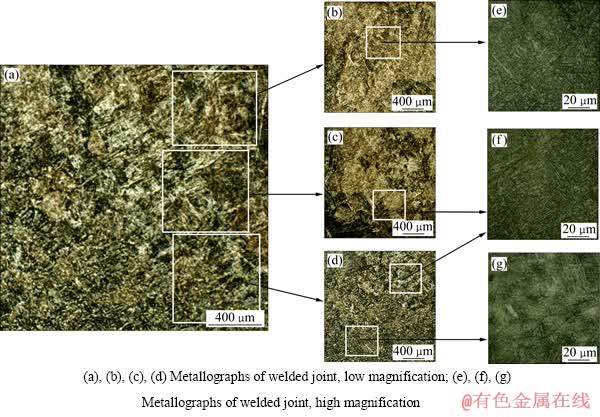

图7 无磁场作用时的焊缝组织
Fig. 7 Microstructures of weld without magnetic field
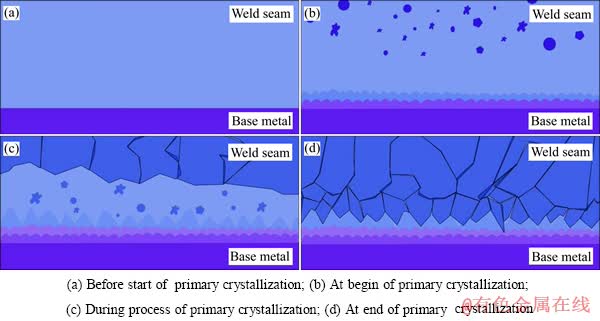
图8 磁场作用下钛合金焊缝金属一次结晶过程示意图
Fig. 8 Schematic diagram of primary crystallization process of titanium alloys weld metal under magnetic field
3 结论
1) 在厚板钛合金窄间隙多层焊接过程中,焊缝金属为针状马氏体α′相与少量残余的β相,出现典型的篮网状组织。且焊接热循序的诱因使得单层焊道的内部组织也不均匀。
2) 在强度为8 mT、频率为10 Hz的外加磁场作用下,窄间隙Ti-6Al-4V焊缝组织在熔合线向内生长的位置出现由柱状晶向等轴晶转变的过渡现象,且晶粒有一定细化趋势。但在焊缝中心处为粗大的柱状晶,生长方向垂直于焊道表面。
REFERENCES
[1] WANG Q, SUN D L, HAN X L, WANG W G. Hot deformation behavior of a near alpha titanium alloy with/without thermal hydrogen processing[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 23(2): 106-112.
[2] 付鹏飞, 黄 锐, 刘方军, 左从进. TA12钛合金电子束焊接组织性能及残余应力分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2007, 28(2): 82-84.
FU Peng-fei, HUANG Rui, LIU Fang-jun, ZUO Cong-jin. Microstructure and residual stress of TA12 titanium alloy with electron beam welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2007, 28(2): 82-84.
[3] 张秉刚, 王 廷, 陈国庆, 冯吉才, 李 东. TC21 钛合金电子束焊缝精细组织及其对硬度的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): s829-s832.
ZHANG Bing-gang, WANG Ting, CHEN Guo-qing, FENG Ji-cai, LI Dong. Fine microstructure and its effect on hardness of electron beam welding joint of TC21 Ti alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): s829-s832.
[4] BUTLER C A, MEISTER R P, RANDALL M D. Narrow gap welding a process for all positions[J]. Welding Journal, 1969, 48(2): 102-108.
[5] ZHANG Fu-ju, XU Wei-gang, WANG Yu-tao, WANG Yan, ZHANG Xue-gang, LIAO Yong-ping. Effect of welding heat input on HAZ character in ultra-fine grain steel welding[J]. China Welding, 2003, 12(2): 122-127.
[6] BISWASA P, MANDALA N R, VASUB P, PADASALAGB S B. Analysis of welding distortion due to narrow-gap welding of upper port plug[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2010, 85(5): 780-788.
[7] HORI K, HANEDA M. Narrow gap arc welding[J]. Journal of the Japan Welding Society, 1999, 68(3): 179-200.
[8] STARLING C M D, MARQUES P V, MODENESI P J. Statistical modeling of narrow-gap GTA welding with magnetic arc oscillation[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1995, 51: 37-49.
[9] PATON B E, ZAMKOV V N, PRILUTSKY V P. Narrow-groove welding proves its worth on thick titanium[J]. Welding Journal, 1996, 75(5): 37-41.
[10] BROWN D C, CROSSLEY F A, RUDY J F, SCHWARTZBART H. The effect of electromagnetic stirring and mechanical vibration on arc welds[J]. Welding Journal, 1962, 41(6): 241-250.
[11] TSENG C F, SAVAGE W F. The effect of arc oscillation[J]. Welding Journal, 1971, 50(12): 777-785.
[12] BELOUS V Y, AKHONIN S V. Influence of controlling magnetic field parameters on weld formation in narrow-gap argon-arc welding of titanium alloys[J]. Paton Welding Journal, 2007, 4: 2-5
[13] BALASUBRAMANIAN M, JAYABALAN V, BALASUBRAMANIAN V. Effect of microstructure on impact toughness of pulsed current GTA welded α-β titanium alloy[J]. Materials Letters, 2008, 62(6/7): 1102-1106.
[14] 张 翥, 王群骄, 莫 畏. 钛的金属学和热处理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2009: 5-29.
ZHANG Zhu, WANG Qun-jiao, MO Wei. Physical metallurgy and heat treatment of titanium alloy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009: 5-29.
[15] GARABEDIAN H, STRICKLAND R F. Collision breeding of ice crystals[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1974, 22(3): 188-192.
[16] 张 奎, 刘国钧, 张永忠, 徐 骏, 吕晋宁, 樊建中, 张少明, 石力开. 半固态金属制备原理与应用[J]. 稀有金属, 1998, 22(6): 447-449.
ZHANG Kui, LIU Guo-jun, ZHANG Yong-zhong, XU Jun,  Jin-ning, FAN Jian-zhong, ZHANG Shao-ming, SHI Li-kai. Mechanism and application of semisolid metal forming[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 1998, 22(6): 447-449.
Jin-ning, FAN Jian-zhong, ZHANG Shao-ming, SHI Li-kai. Mechanism and application of semisolid metal forming[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 1998, 22(6): 447-449.
[17] 张景新, 张 奎, 刘国均, 徐 骏, 石力开. 电磁搅拌制备半固态材料非枝晶组织的形成机制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2000, 10(4): 511-516.
ZHANG Jing-xin, ZHANG Kui, LIU Guo-jun, XU Jun, SHI Li-kai. Formation mechanism of non-dendritic structure in semi-solid metals produced by ES process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2000, 10(4): 511-516.
[18] FAN Z, FANG X, JI S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of rheo-diecast (RDC) aluminium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 412(1/2): 298-306.
[19] LI X, REN Z M, GAGNOUD A, BUDEBKOVA O, FAUTRELLE Y. Effects of thermoelectric magnetic convection on the solidification structure during directional solidification under lower transverse magnetic field[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011, 42(11): 3459-3471.
[20] 张伟强. 金属电磁凝固原理及技术[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2004: 17-42.
ZHANG Wei-qiang. Metal electromagnetic solidification principle and technology[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2004: 17-42.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(2013CB035500);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51105109);国家高技术研究发展计划项目(2008AA092901)
收稿日期:2012-09-20;修订日期:2013-08-07
通信作者:孙清洁,讲师,博士;电话:0631-5677156;E-mail: sunqingjie@gmail.com