文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-08-1649-10
稀土La对Zn-Cu-Ti合金显微组织和力学性能的影响
冀盛亚1, 2, 3,梁淑华1,宋克兴2,王 青1
(1. 西安理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,西安 710048;
2. 河南科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,洛阳 471023;
3. 河南工学院 材料工程系,新乡 453003)
摘 要:研究稀土La对Zn-Cu-Ti合金显微组织和力学性能的影响。结果表明:适量添加La有利于固液界面前沿成分过冷区的形成,促进形核,细化晶粒,阻滞枝晶的进一步生长;大部分La与Cu生成高熔点、高稳定的LaCu6和LaCu4;随着La添加量的增加,硬脆、粗大的初晶相εp转变为更加细小弥撒的εⅡ相,且共晶组织TiZn16相层片间距更加细小,推迟裂纹的萌生和发展,提高合金的塑性,合金的断裂机制由脆性向韧性过渡;当添加0.1%La及 0.5%La(质量分数)后,合金的平均晶粒尺寸分别降低70%和72.3%,而塑性则分别增加7%和33.33%;Zn-Cu-Ti合金中第二相的强化效果远大于细晶的强化效果,这也是合金强度先降低而后升高的原因。
关键词:Zn-Cu-Ti 合金;稀土 La;显微组织;第二相;力学性能
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
Zn-Cu-Ti合金的研究始于20世纪30年代的德国,目的是找到铜及其合金的替代品。随着熔炼提纯技术(Pb、Cd、Fe等杂质元素对锌合金的性能影响较大)和加工工艺的进步,20世纪60年代,德国和美国研制出了Zn-Cu-Ti合金的板带[1]。凭借其长寿命、免维护、自修复的优点及优良的成型性能,Zn-Cu-Ti合金为欧美建筑师情有独钟。自20世纪70年代以来,Zn-Cu-Ti合金广泛使用在机场、展览馆、俱乐部、教堂等建筑物的屋顶和外墙装饰[2-3]。目前,欧美各科研机构结合产业需求,一方面,进一步提升合金的综合性能(塑性、硬度、强度和耐腐蚀性)[4];另一方面,不断优化加工工艺[5-8],并对合金的变形机理进行深入研究[9]。
国内对Zn-Cu-Ti合金的研究主要集中于广东冶金研究所、中南大学、河南科技大学等院所。研究基于两条主线:一是探讨合金元素对材料性能的作用及影响机理。资料显示:在一定含量范围内,Cu 元素含量与合金的强度和硬度成正比,Ti元素含量与合金的塑性和韧性成正比[1, 10];Mg元素可以提高合金在3.5%NaCl溶液中的耐腐蚀性能[3];Cr、Mg元素可以提高合金的抗拉强度和蠕变性[2, 11-13]。二是研究加工过程中的组织演变规律。研究发现:挤压过程中第二相的破碎会阻碍再结晶晶粒的长大[14-15],合金的组织随着应变速率和应变量的增大得以细化[16]。
我国铜矿资源匮乏,国内铜需求量的70%来自进口,且不断增加[17]。以国家重点科技支撑计划项目“铜合金替代材料—环保高性能变形锌合金关键技术研究与产业化开发”[18]为导向,开发高性能变形锌合金,推动其产业化生产及规模化应用,不但可以缩小与欧美等发达国家在锌合金生产加工方面的技术差距,而且可以发挥我国的锌资源优势,实现“以锌代铜”,降低国内日益明显的铜资源供需矛盾,具有显著的经济、社会和生态效益。
有“工业味精”美誉的稀土由于其独特的原子结构、优异的活化性能被广泛地作为微量元素使用在镁、铝、铜、锌、镍等有色合金中,来提高合金的综合力学性能[19-20]。本文作者以工业应用的Zn-Cu-Ti合金为基础,研究添加微量La对合金显微组织和力学性能的影响,为该合金的大批量工业应用提供实验基础和理论支持。
1 实验
制备Zn-Cu-Ti合金采用纯度为(质量分数):99.995%Zn、 99.995%La、99.7%海绵Ti、99.95 %Mg及H62黄铜(Cu-Zn中间合金)。在高纯氩气保护下,用高纯石墨坩埚在ZGJL001-40-4型真空中频感应炉中熔炼,以防止合金元素在空气中氧化烧损。熔炼温度580~600 ℃,待合金完全熔化后,在500~520 ℃浇入d 80 mm×210 mm铸铁模具中,并在氩气流保护下冷却到室温。合金的化学成分如表1所列。铸锭经锯切缩口、车皮、线切割成10 mm×10 mm×10 mm金相试样,经机械抛光,用铬酐硫酸钠溶液(100 g CrO3,75 g Na2SO4,500 mL H2O)腐蚀液擦拭试样表面, 而后对其进行微区成分、点成分(美国EDAX公司生产)及SEM(JSM-5610LV型扫描电子显微镜) 分析。采用德国布鲁克生产的D8 ADVANCE型X射线衍射仪和JEM-2100型透射电子显微镜进行显微组织观察及物相分析。
表1 Zn-Cu-Ti-xLa合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of Zn-Cu-Ti-xLa alloys
2 结果与讨论
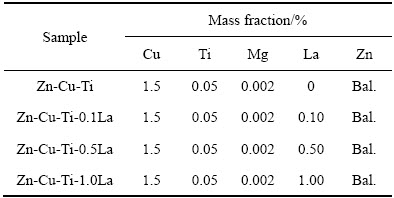
2.1 Zn-Cu-Ti-xLa合金的物相分析
图1所示为Zn-Cu-Ti-xLa合金的XRD谱。由图1(a)可知,未添加La的Zn-Cu-Ti合金主要由η相(Zn)、γ相(Cu5Zn8)、TiZn16相、ε相(CuZn5)和Mg2Zn11相这5种物相组成。稀土La的添加在未改变原有物相的基础上使合金生成了LaCu6相与LaCu4相。
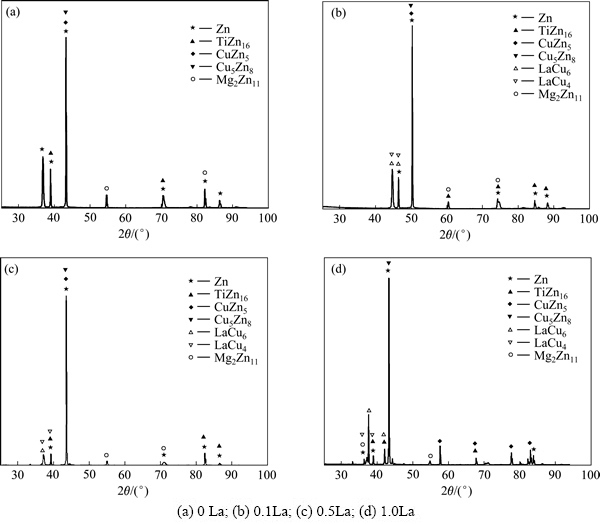
图1 Zn-Cu-Ti-xLa合金的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Zn-Cu-Ti-xLa alloy
影响元素之间形成化合物的一个重要因素就是元素的电负性,各元素间电负性差值越大,则元素间成键化合的可能性就越强,越易形成化合物[21]。Zn、Cu、Ti、Mg、La的电负性分别是1.65、1.90、1.54、1.31和1.1,Cu与La两种元素电负性的差值为0.8,远大于Zn与La的差值(0.55),从热动力学理论判断La将与Cu元素优先结合生成化合物。
2.2 La对Zn-Cu-Ti合金铸态显微组织形貌的影响
图2所示为不同La 含量的Zn-Cu-Ti合金的SEM像。由图2(a)和表2可知,Zn-Cu-Ti合金由黑色的η相(Zn)基体、粗大骨骼状ε相(CuZn5)、少量γ相(Cu5Zn8)、纤维状或针片状TiZn16共晶组织组成。未添加La时,合金的表面布满粗大的枝晶,二次枝晶发达,枝晶臂间距大。
根据Cu-Zn二元相图[22],虽然γ相可以产生在一个较宽的温度范围内,但形成γ相的成分范围中Cu的摩尔分数达到30%~45%,由于整个合金中Cu的比例只有1.5%,γ相不可能大量存在,所以B1点所示粗大骨骼状枝晶为富铜ε相及少量γ相。共晶组织TiZn16相属于金属和金属型共晶,形成共晶的两相与液相的界面均为粗糙界面,两相都是以单原子迁移来完成向液体中的生长[23]。合金中Ti含量稀少(0.05%), 过薄的共晶层片收缩成纤维状或针状。
对比图2(a)可知,当添加0.1% La时(见图2(b)和表3),原本粗大连续的骨骼状ε相和γ相的混合相逐渐断开并破碎成不连续的花瓣状;原来为纤维状、针片状的TiZn16共晶组织逐渐转变为线状。由此可见,微量La能明显细化铸态合金的微观组织,使粗大的合金相逐渐变得更加细小弥散。由于Zn-Cu-Ti-0.1La合金中的稀土合金相数量较少,所以能谱不能检测出LaCu6和LaCu4两种物相。
当添加0.5% La时,粗大骨骼状ε相和γ相的混合相及细线状的TiZn16共晶组织完全消弥(见图2(c))。参考Zn-Cu-Ti-0.5La合金的XRD谱(见图1(c)),ε相、γ相、TiZn16相依然存在,这说明合金相随La含量的增加被进一步细化。同时由表4可知,基体中开始出现近六边形或花状LaCu6、LaCu4及TiZn16的混合相。
Zn-Cu-Ti-1.0La合金主要由富锌η相、ε相(CuZn5)及存在于晶界处的LaCu6、LaCu4相组成(见图2(d)和表5)。稀土相的形状由六边形或花状向四边形和三角形演变,且其数量明显多于另外3种合金数量。合金表面布满凹坑和孔洞。凹坑处(见表5特征点B4)Zn的摩尔分数达到94.74%,近似于纯Zn的,这是由于LaCu6相、LaCu4相的增多导致基体η(富锌)相中Cu元素含量的下降。同时,基体η(富锌)相被优先腐烛、脱落。这些凹坑和孔洞是金相试样制备时腐蚀液腐蚀所致。当使用相同的腐蚀液时,Zn-Cu-Ti-1.0La合金腐蚀时间更短,少于25 s,另外3种合金的腐蚀时间为50 s左右,Zn-Cu-Ti-1.0La合金的腐蚀程度更严重。这主要是因为硬脆的稀土相机械地混合在基体组织中,与基体并无很好的共格关系,具有较高的界面能,导致合金更易腐蚀。
图2 不同La 含量的Zn-Cu-Ti合金的SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM images of Zn-Cu-Ti-xLa alloy
表2 Zn-Cu-Ti合金中铸态组织不同位置的能谱分析
Table 2 Energy spectrum analysis of cast microstructure of Zn-Cu-Ti alloy in different locations shown in Fig. 2(a)
表3 Zn-Cu-Ti-0.1La合金中铸态组织不同位置的能谱分析
Table 3 Energy spectrum analysis of cast microstructure of Zn-Cu-Ti -0.1La alloy in different locations shown in Fig. 2(b)
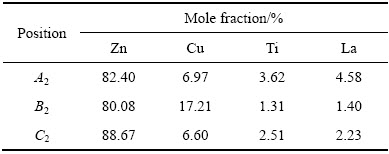
表4 Zn-Cu-Ti-0.5La合金铸态组织不同位置的能谱分析
Table 4 Energy spectrum analysis of cast microstructure of Zn-Cu-Ti -0.5La alloy in different locations shown in Fig. 2(c)
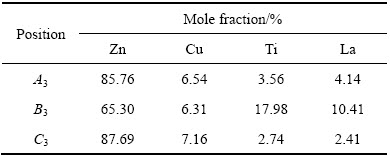
表5 Zn-Cu-Ti-1.0La合金铸态组织不同位置的能谱分析
Table 5 Energy spectrum analysis of cast microstructure of Zn-Cu-Ti -1.0La alloy in different locations shown in Fig. 2(d)
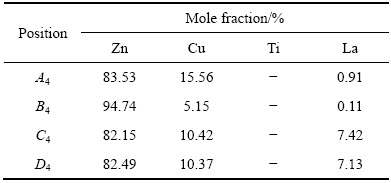
2.3 La含量对Zn-Cu-Ti合金晶粒细化的效果
为了进一步定量研究La含量对Zn-Cu-Ti合金平均晶粒尺寸的影响,借助于合金显微组织的TEM(透射电镜)照片,使用Image J软件测量了不同La含量的4种Zn-Cu-Ti合金铸态组织的平均晶粒尺寸,结果如表6所列。
表6 不同La含量对Zn-Cu-Ti合金晶粒细化效果
Table 6 Effects of La content on grain refinement of Zn-Cu-Ti alloy
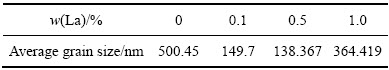
由表6可知,随着La含量的增加,Zn-Cu-Ti合金基体组织的平均晶粒尺寸先急剧减小后逐渐增大。未添加La的Zn-Cu-Ti合金平均晶粒尺寸为500.45;当添加0.1%和0.5%La 后,合金平均晶粒尺寸分别为149.7及138.367 nm,降低70%和72.3%。 因此,稀土La对Zn-Cu-Ti合金基体的细化作用是非常显著的。然而,添加1.0%La 后,合金平均晶粒尺寸上升到364.419 nm,这表明过量添加La对合金基体组织的晶粒细化效果会明显减弱。
2.4 La含量对合金铸态组织形态的影响机理
合金在浇铸到铸模后,由于铸模的激冷作用,铸锭的凝固通常是由表层向中心推进,固液界面前沿的形核条件决定了晶粒的最终形貌(等轴或柱状)。过冷度ΔT与形核功ΔG呈反比,过冷度越大形核功越小,越易形核。合金形成等轴晶的关键因素在于凝固过程中在固液界面前沿产生一定的过冷度[24]。
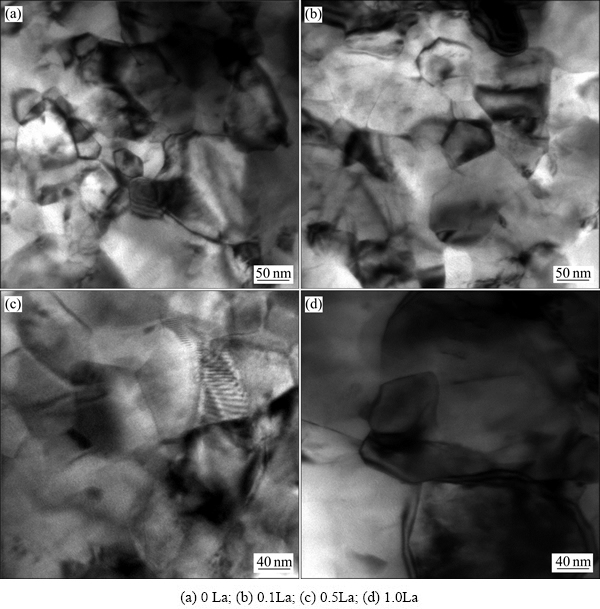
图3 不同La含量的Zn-Cu-Ti合金的TEM像
Fig. 3 TEM images of Zn-Cu-Ti-xLa alloy
众所周知,当合金凝固时,产生成分过冷的必要条件即为[23]
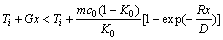 (1)
(1)
式中:Ti为固液界面温度;m为液相线温度斜率;c0为合金成分;D为扩散系数;K0为溶质的平衡分配系数;R为凝固速度;x为凝固距离。对液体而言,D较大,Rx/D较小,则 ,即可得成分过冷的临界条件:
,即可得成分过冷的临界条件:
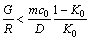 (2)
(2)
由式(2)可知,液相线陡峭以及液相线和固相线之间的距离大,有利于产生成分过冷。参考《常用有色金属二元合金相图集》中的Cu与La及Zn与La二元相图[22], 可知,La在Zn-Cu-Ti合金熔体中极易产生成分过冷。
EASTON等[25]和陈曦[26]进一步验证了枝晶生长的液-固界面前沿由于溶质的偏析导致出现了成分过冷区域,成分过冷区域不但为熔体激活形核提供了必要驱动力,而且阻滞了枝晶的进一步生长。由此可见,溶质良好的偏析能力和有效的形核质点是基体晶粒细化过程必不可少的两个因素。
一系列合金系资料显示,只有当溶质原子与溶剂原子直径的相对差值小于14%~15%时,它们之间才能形成大的固溶度,甚至形成无限固溶体,否则,溶解度是非常有限的[27]。La的原子半径是2.74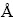 ,Cu、Zn、Ti、Mg的原子半径分别是1.57、1.53、2和1.72
,Cu、Zn、Ti、Mg的原子半径分别是1.57、1.53、2和1.72 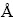 。 La的原子半径远大于另外4种金属原子的半径。一方面,造成La在4种金属中的溶解度非常小,很难形成固溶体。另一方面,La也不满足基体η相异质核心的“尺寸结构匹配”原则,因此稀土相很难成为Zn-Cu-Ti合金的非均匀形核核心,导致凝固过程中La在固液界面前沿富集,固液界面前沿液体的实际温度就低于同成分合金的液相线温度,成分过冷区形成在固液界面的结晶前沿。随着凝固过程的进一步发展,La的富集程度更加明显;当成分过冷度增大到一定程度时,新晶核带就会形成在固液界面前沿的成分过冷区。合金在结晶的过程中,成分过冷的区域越多,形成的新晶核带就会越多,形成细等轴晶区域也就越多。
。 La的原子半径远大于另外4种金属原子的半径。一方面,造成La在4种金属中的溶解度非常小,很难形成固溶体。另一方面,La也不满足基体η相异质核心的“尺寸结构匹配”原则,因此稀土相很难成为Zn-Cu-Ti合金的非均匀形核核心,导致凝固过程中La在固液界面前沿富集,固液界面前沿液体的实际温度就低于同成分合金的液相线温度,成分过冷区形成在固液界面的结晶前沿。随着凝固过程的进一步发展,La的富集程度更加明显;当成分过冷度增大到一定程度时,新晶核带就会形成在固液界面前沿的成分过冷区。合金在结晶的过程中,成分过冷的区域越多,形成的新晶核带就会越多,形成细等轴晶区域也就越多。
稀土元素还能提高锌合金流动性[28]。流动的熔体能够对铸模的模壁和固液界面产生冲刷作用,导致枝晶脱落和游离,也促使枝晶分枝细化。熔断并游离的小枝晶自动成为各初生相非自发形核核心,增加了初生相的晶核数目,细化了初生相晶粒尺寸(见图4)。
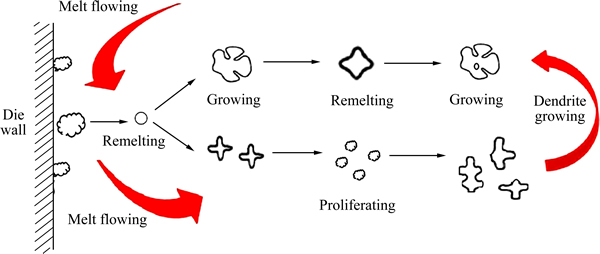
图4 熔体的流动造成枝晶熔断及晶核增殖示意图
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of dendrite fusing and crystal nucleus proliferation caused by melt flow
对比各相的析出温度,如LaCu6(920 ℃)、LaCu4(743 ℃)、ε相(CuZn5)(597 ℃)、TiZn16(约418 ℃)[22],可知在合金的凝固结晶过程中,优先析出稀土相。这些细小的稀土相以结晶固体的形式存在于合金熔体中,阻挡TiZn16共晶组织的上浮及ε相、少量γ相的下沉,阻滞了枝晶的进一步发展,加剧了枝晶熔断,降低了合金的凝固过程中成分偏析现象,也阻止合金基体组织的进一步长大。
另外,在室温下,Cu在Zn中的固溶度仅为0.3%;425 ℃时,Cu在Zn中的固溶度上升为2.7%。Zn与Cu二元合金平衡结晶状态主要的反应过程如下[11, 22, 29]:
1) 当2.75%<w(Cu)<11.7%时,
结晶过程如下:L→εp(597 ℃)→L+εp(425 ℃)→η+εp→ (εp+η+εⅡ+ηⅡ)。
室温下Zn-Cu-Ti合金组织为εp+η+εⅡ+ηⅡ。
2) 当1.7%<w(Cu)<2.75%时,
结晶过程如下:L→εp→L+εp (425 ℃)→(包晶反应L+ε→η)η+L→η+εⅡ。
室温下Zn-Cu-Ti合金组织为η+εⅡ;
3) 当w(Cu)<1.7%时,
结晶过程如下:L→η→η+εⅡ。
室温下Zn-Cu-Ti合金组织为η+εⅡ。
当未添加La时,熔体中游动原子团簇之间存在着成分差异,这种由原子热运动导致的浓度起伏(熔体中局域成分不均匀现象)使局部熔体Cu含量大于2.75%,进而由液相直接析出粗大的骨骼状枝晶εp相(597 ℃,L→εp)。随着La含量的增大,稀土相LaCu6与LaCu4的生成消耗一部分Cu元素。同时,合金的流动性进一步增强,使各元素在熔体中均质分布,熔体中各处Cu含量均小于2.75%,导致合金中的εp相(一次析出相)转变为εⅡ相。相对于集中、粗大的εp相,εⅡ相更加细小弥散。此外,基体组织越细小,εⅡ相也越细小。因此,Zn-Cu-Ti合金铸态组织中的固溶体ε相随着La添加量的增大逐渐变少、变细(见图2)。
共晶组织TiZn16层片间的距离取决于凝固时的过冷度,过冷度越大,层片间距越小[23, 30]。TiZn16相随着La添加量的增大逐渐消弥(见图2),实际是熔体成分过冷增大导致共晶层片更加细小弥散的一种表象。
然而,当在合金中添加1.0%La 后(见图3(d)),合金基体晶粒呈明显长大趋势,这是因为LaCu6和LaCu4结晶的同时释放了大量的结晶潜热,固液界面前沿的成分过冷程度被大幅度降低,进而使形核率降低,造成合金基体组织的晶粒细化程度明显减弱。
2.5 La对Zn-Cu-Ti合金室温拉伸性能的影响
表7所列为La含量对Zn-Cu-Ti合金拉伸性能的影响。由表7可知,添加0.1%La、0.5%La、1.0%La后,塑性分别增加7.8%、33.33%和31.3%,且La添加到0.5%时塑性达到最高,这是因为Zn-Cu-Ti合金是多相合金,合金的塑性变形主要发生在塑性η(富Zn)相的晶粒内部,晶界处的硬脆的ε(CuZn5)相并不参加塑性变形,对变形起阻碍作用。随着变形程度的增大,应力集中易产生在塑性η(富Zn)相及硬脆的ε(CuZn5)相的相界处, 导致裂纹的早期产生,降低合金的塑性。随着La含量的增加,LaCu6相与LaCu4相的生成降低了合金中Cu的比例,εp相(一次析出相)转变为更加细小弥散的εⅡ相(见图2),推迟了裂纹的萌生和发展,使合金可发生较大的塑性变形。
表7 La含量对Zn-Cu-Ti合金拉伸性能的影响
Table 7 Effects of La content on tensile properties of Zn-Cu-Ti alloy
另外,La细化了合金基体组织的晶粒尺寸(见表6)。一方面,在变形量一定的前提下,单位体积内晶粒数目越多,晶粒越细小,在每个晶粒内部变形量的分配就越分散,整个合金的变形就越均匀,这样可以减少应力集中,降低裂纹形成比率。另一方面,晶粒尺寸越小,推动硬位向晶粒转动所需要的剪切力越小,使变形平均分散在合金的各处,进而提高了合金的塑性。
合金的屈服强度及抗拉强度随La含量的增加呈先降低而后增加的趋势,且加入La后,合金的屈服强度及抗拉强度几乎均小于未添加La 的Zn-Cu-Ti合金(见表7)。
根据两相合金的等应变理论,合金产生一定应变的平均流变应力[31]:
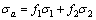 (3)
(3)
式中:σ1和σ2为两相在此应变时的流变应力;f1和f2
为两相的体积分数,f1+f2=1。
由式(3)可以看出,只有当第二相强度较高时,合金强度才可能增大。随着La含量的增加,硬脆的εp相逐渐转变为更加细小弥散的εⅡ相,TiZn16相的消弥,高熔点的LaCu6相与LaCu4相逐步生成,消弥进程与生成进程的不同步是合金强度先降低而后升高的主要原因。
虽然La对Zn-Cu-Ti合金的晶粒细化效果非常明显,但第二相的破碎、消弥导致合金屈服强度与抗拉强度的急剧降低,甚至抵消了细晶强化的成效。由此可见,Zn-Cu-Ti合金中第二相强化远大于细晶强化的效果。
2.6 La含量对Zn-Cu-Ti合金拉伸断口形貌的影响
图5所示为铸态Zn-Cu-Ti-xLa合金室温拉伸断口形貌。由图5(a)可知,Zn-Cu-Ti合金的断口是由一系列小裂面组成,高度不同的两个平行小裂面之间形成明显的台阶,整个断面可以看到一系列的 “河流花样”、“舌状裂面”,这是明显的解理断裂形貌,撕裂棱较少,属于穿晶脆性断裂。
由图5(b)可知,Zn-Cu-Ti-0.1La合金的拉伸断口仍是由一系列的“河流花样”小裂面、解理台阶构成,仍属于穿晶脆性断裂。但解理面及解理台阶明显细化,“舌状裂面”明显减少。Zn-Cu-Ti合金中加入0.5%La后(见图5(c)),合金的拉伸断口除了有“河流花样”小裂面、解理台阶,撕裂棱取向的一致性已不那么明显。断口开始出现细小的凹凸(韧窝),表现出一定的韧性断口形态。由图5(d)可知,Zn-Cu-Ti-1.0La合金的拉伸断口主要由一些大小不等的圆形、椭圆形的窝坑构成,表现出以韧性为主,夹杂少量脆性解理为辅的混合断口相貌。对比4种合金拉伸断口的SEM像(见图5),随着La添加量的增加,合金的断裂机制由脆性向韧性过渡。
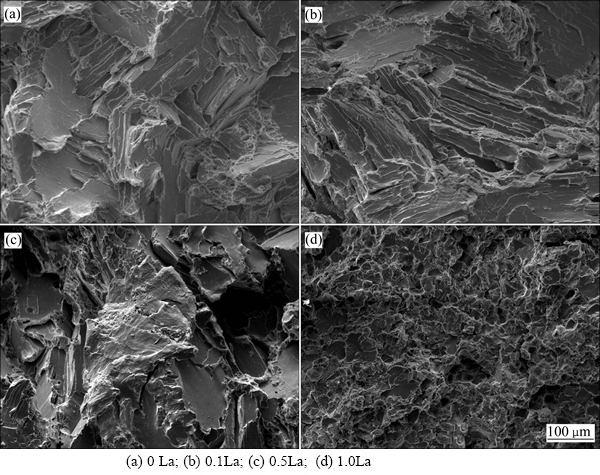
图5 铸态Zn-Cu-Ti-xLa合金室温拉伸断口形貌
Fig. 5 SEM images of tensile fracture morphology of cast Zn-Cu-Ti-xLa alloy at room temperature
3 结论
1) 适量添加La有利于固液界面前沿成分过冷区的形成,这促进形核,细化晶粒,阻滞枝晶的进一步生长。随着La添加量的增加,硬脆、粗大的εp相(一次析出相)转变为更加细小弥散的εⅡ相,且共晶组织TiZn16相层片间距更加细小,推迟裂纹的萌生和发展,提高合金的塑性。当添加0.1%La及 0.5%La后,合金的平均晶粒尺寸分别降低70%和72.3%,而塑性则分别增加7%和33.33%。
2) 大部分La与Cu结合生成高熔点、高稳定性的LaCu6相和LaCu4相,且随着La含量的增加,εp相与TiZn16相的消弥,LaCu6相与LaCu4相的逐步生成,消弥进程与生成进程的不同步导致合金强度先降低,后升高。
3) La对Zn-Cu-Ti合金的晶粒细化效果非常明显,但第二相的破碎、消弥导致合金屈服强度与抗拉强度的急剧降低,甚至抵消了细晶强化的成效,这表明Zn-Cu-Ti合金中第二相强化远大于细晶强化的效果。
4) 合金的断裂机制随着La添加量的增加由脆性断裂向韧性断裂过渡。
REFERENCES
[1] 邓 猛. Zn-Cu-Ti合金组织性能及热变形行为的研究[D]. 洛阳: 河南科技大学, 2014: 12, 25.
DENG Meng. Structure properties and hot deformation behaviors of zinc-copper-titanium alloy[D]. Luoyang: Henan University of Science and Technology, 2014: 12, 25.
[2] 肖来荣, 张喜民, 王 艳, 曾德露, 张宏岭, 李 威. Zn-1.0Cu-0.2Ti合金的静态再结晶行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(11): 2775-2779.
XIAO Lai-rong, ZHANG Xi-min, WANG yan, ZENG De-lu, ZHNAG Hong-ling, LI Wei. Static recrystallization behavior of Zn-1.0Cu-0.2Ti alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(11): 2775-2779.
[3] 王彦红, 肖来荣, 耿占吉, 饶 博, 康思清. 应变速率及环境介质对Zn-Cu-Ti合金应力腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2013, 34(5): 410-412.
WANG Yan-hong, XIAO Lai-rong, GENG Zhan-ji, RAO Bo, KANG Si-qing. Effects of strain rate and environment medium on stress corrosion cracking of Zn-Cu-Ti alloy[J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2013, 34(5): 410-412.
[4] ARENAS M A, DAMBORENA J D. Protection of Zn-Ti-Cu alloy by cerium trichloride as corrosion inhibitor[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2005, 200(7): 2085-2091.
[5] FAUR M, GHIBAN B. Effects of hot and cold rolling on the microstructure of low alloy Zn-Cu and Zn-Cu-Ti zinc alloy with improved corrosion resistance[J]. Metallurgic International, 2009, 14(3): 23-26.
[6] YU Li-na, HUANG Wei-qing. Microstructure and fitting analysis of Zn-Cu-Ti alloy during deformation[J]. Foundry Technology, 2015(8): 1914-1916.
[7] BOCZKAL G, MIKULOWSKI B. The brittleness of Zn-Cu-Ti sheet alloys[J]. Archives of Metallurgy & Materials, 2015, 60(3): 2355-2360.
[8] VHLKE T, ALKORA J, GARCIA-ROSALES C, DOMINGUEZ I, GIL SEVILLANO J. Structure and texture of twin roll cast strips of Zn-Cu-Ti zinc alloy[J]. Materials Science & Technology, 2014, 30(1): 91-95.
[9] BOCZKAL G. Second phase morphology in the Zn-Ti0.1-Cu0.1 single crystals obtained at different growth rates[J]. Archives of Metallurgy & Materials, 2012, 57(2): 479-484.
[10] 陈 行, 杨 灯, 田明杰, 龙雪梅, 黎安聪. 形变热处理对Zn-Cu-Ti合金组织与性能的影响[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2015, 35(6): 669-672.
CHEN Hang, YANG Deng, TIAN Ming-jie, LONG Xue-mei, LI An-cong. Effect of thermomechanical treatment on the structure and properties of Zn-Cu-Ti alloy[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2015, 35(6): 669-672.
[11] 张喜民. 变形锌铜钛合金蠕变行为及其组织与性能研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010: 31, 36.
ZHANG Xi-min. Study on creep behavior, microstructure and properties of deformed zinc copper titanium alloy[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010: 31, 36.
[12] 耿占吉. 合金化与热处理对锌铜钛合金应力腐蚀性能和蠕变性能的影响研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012: 26.
GENG Zhan-ji. Effect of alloying and heat treatment on the stress corrosion behavior and creep properties of zinc copper Titanium alloy[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012: 26.
[13] 王 艳, 肖来荣, 万 磊, 张宏岭, 曾德露, 刘 峤. 两种变形Zn-Cu-Ti锌合金的组织与性能[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2013, 32(11): 1054-1058.
WANG Yan, XIAO Lai-rong, WAN Lei, ZHANG Hong-ling, ZENG De-lu, LIU Qiao. Microstructure and properties of two kinds of wrought Zn-Cu-Ti alloy[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2012, 32(11): 1054-1058.
[14] 谭 颖, 林向飞, 张世道, 王洪洋, 林高用. Zn-Cu-Ti变形锌合金异常力学行为[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2015, 6(6): 57-64.
TAN Ying, LIN Xiang-fei, ZHANG Shi-dao, WANG Hong-yang, LIN Gao-yong. Abnormal mechanical behaviors of deformed Zn-Cu-Ti alloy[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science & Engineering, 2015, 6(6): 57-64.
[15] 张喜民, 肖来荣, 温燕宁, 耿占吉, 张宏岭, 孙泉胜. 挤压Zn-Cu-Ti合金的组织及其力学性能[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2010, 28(4): 576-581.
ZHANG Xi-min, XIAO Lai-rong, WEN Yan-ning, GENG Zhan-ji, ZHANG Hong-ling, SUN Quan-sheng. Microstructure and mechanical properties of extruded Zn-Cu-Ti alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Engineering, 2010, 28(4): 576-581.
[16] XU Xiao-qing, LI De-fu, GUO Sheng-li, WU Xiao-ping. Microstructure evolution of Zn-8Cu-0.3Ti alloy during hot deformation[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(7): 1606-1612.
[17] 周 平. 新常态下中国铜资源供需前景分析与预测[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2015: 18.
ZHOU Ping. An analysis and forecast of China copper supply and demand prospects under the new normal economy[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2015: 18.
[18] 中华人民共和国科学技术部. http://www.most.gov.cn/kjbgz/ 200904/t20090427_68866.htm[EB/OL]. 2009.
Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. http://www.most.gov.cn/kjbgz/200904/t20090427_ 68866. htm[EB/OL]. 2009.
[19] 肖 旋, 徐 乐, 秦学智, 侯介山, 王常帅, 郭建亭, 周兰章. 稀土元素Y和Ce对定向凝固镍基高温合金高温氧化行为的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(11): 2769-2776.
XIAO Xuan, XU Le, QIN Xue-zhi, HOU Jie-shan, WANG Chang-shuai, GUO Jian-ting. ZHOU Lan-zhang. Effect of elements Y and Ce on high temperature oxidation behavior of directionally-solidified Ni-based superalloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(11): 2769-2776.
[20] 李德君, 任凤章, 刘 平, 赵士阳, 田保红, 马战红. 稀土Nd对AZ31变形镁合金组织与性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(10): 1876-1882.
LI De-jun, REN Feng-zhang, LIU Ping, ZHAO Shi-yang, TIAN Bao-hong, MA Zhan-hong. Effect of rare earth Nd on microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31B wrought magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(10): 1876-1882.
[21] 中山大学金属系. 稀土物理化学常数[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1978: 98.
Department of Metal, Zhongshan University. Rare earth physical and chemical constants[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1978: 98.
[22] 郭青蔚, 王桂生, 郭庚辰. 常用有色金属二元合金相图集[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009: 70, 58, 101, 110.
GUO Qin-wei, WANG Gui-sheng, GUO Geng-chen. Two element alloy phase atlas of common non-ferrous metals[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009: 70, 58, 101, 110.
[23] 石德珂. 材料科学基础[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2003: 199, 201.
SHI De-ke. Fundamentals of material science[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2003: 199, 201.
[24] 周尧和, 胡壮麒, 介万奇. 凝固技术[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1998: 79-80.
ZHOU Yao-he, HU Zhuang-lin, JIE Wan-qi. Solidification technology[M]. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press,1998: 79-80.
[25] EASTON M, STJOHN D. Grain refinement of aluminum alloys: Part II. Confirmation of, and a mechanism for, the solute paradigm[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A, 1999, 30(6): 1625-1633.
[26] 陈 曦. 纯镍的晶粒细化及其机理研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2013: 30.
CHEN Xi. The research on grain refinement and mechanism of pure nickel[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2013: 30.
[27] 高 仑. 锌与锌合金及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2011: 18.
GAO Lun. Zinc and zinc alloy and its application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2011: 18.
[28] 宋 丹. 热浸镀锌基合金液态性能的研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2010: 45.
SONG Dan. Research on liquid properties of zinc-based alloys in hot-dip galvanizing[D]. Kunming: Kunming Science and Engineering College, 2010: 45.
[29] FERGUS J W, MISHRA B, ANDERSON D, SARVER E A, NEELAMEGGHAM N R. Twins evolution during the recrystallization induced by electric current pulses in a Cu-Zn alloy[M]. Engineering Solutions for Sustainability: Materials and Resources II. John Wiley & Sons., Inc., 2015: 103-111.
[30] IVANOV M A, NAUMUK A Y. Kinetics of eutectic solidification[J]. Physics of Metals & Metallography, 2014, 115(5): 471-480.
[31] 胡赓祥. 材料科学基础[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2010: 177-178.
HU Geng-xiang. Material science foundation[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, 2010: 177-178.
Effect of La on microstructure and mechanical properties of Zn-Cu-Ti alloy
JI Sheng-ya1, 2, 3, LIANG Shu-hua1, SONG Ke-xing2, WANG Qing1
(1. Faculty of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an 710048, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, China;
3. Department of Materials Engineering, Henan Institute of Technology, Xinxiang 453003, China)
Abstract: The effects of La on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Zn-Cu-Ti alloy were investigated. The results show that composition supercooling forms on the solid-liquid interface by adding La, promoting nucleation, refining grain and preventing dendrite growth. La and Cu generate LaCu6 and LaCu4 with high melting point and stability; with the increase of the La content, brittle and coarse εp phase turns into thinner and dispersed εⅡ phase; meanwhile, the layer of eutectic organization TiZn16 becomes thinner. Both of them block the initiation and development of cracks, increase the plasticity of alloy. The fracture mechanism of alloy transits from brittleness to ductility; when the La content is 0.1% and 0.5% (mass fraction), the average grain size of alloy decreases by 70% and 72.3% respectively, while its plasticity increases by 7% and 33.33% accordingly. The strengthening effect of second phase is more obvious than that of the refined grain.
Key words: Zn-Cu-Ti alloy; rare earth La; microstructure; second phase; mechanical property
Foundation item: Project(U1502274) supported by the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(C20150014) supported by Innovation Scientists and Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Henan Province, China; Project(14IRTSTHN007) supported by Program for Innovation Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Henan Province, China; Project (16A430004) supported by Key Scientific Program of Henan Province, China
Received date: 2015-11-01; Accepted date: 2016-03-24
Corresponding author: SONG Ke-xing; Tel: +86-379-64252673; E-mail: kxsong@haust.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金重点项目(U1502274);河南省创新型科技团队资助项目(C20150014);河南省高校科技创新团队支持计划资助项目(14IRTSTHN007);河南省高等学校重点科研项目(16A430004)
收稿日期:2015-11-01;修订日期:2016-03-24
通信作者:宋克兴,教授,博士;电话:0379-64252673;E-mail: kxsong@haust.edu.cn