Y或La对Ca-Si-Al-O-N氧氮玻璃结构与性能的影响
罗志伟,刘学锋,王克强,胡晓林,卢安贤
(中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:在高纯氮气保护气氛下于1 550~1 650 ℃在硅钼电阻炉中熔融2 h制备添加钇或镧的Ca-Si-Al-O-N系氧氮玻璃。采用X线衍射和扫描电镜(SEM)确定玻璃样品的无定形态本质。利用傅里叶变换红外光谱(IR)研究玻璃的基本结构单元。对比La3+平衡浓度比或Y3+平衡浓度比对氧氮玻璃的热膨胀系数(α)、玻璃转变温度(Tg)、析晶温度(Tc)、维氏显微硬度(HV)和抗弯强度(σ)等性能的影响。利用阳离子场强(CFS)讨论玻璃的结构与性能之间的关系。研究结果表明:玻璃的性能分别随La或Y平衡浓度比的变化几乎呈线性变化。Y对玻璃的结构和性能的影响比La更大。
关键词:稀土;氧氮玻璃;红外光谱;热性能;力学性能
中图分类号:TQ171.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)11-4415-08
Effects of yttrium/lanthanum on structure and properties of Ca-Si-Al-O-N oxynitride glasses
LUO Zhiwei, LIU Xuefeng, WANG Keqiang, HU Xiaolin, LU Anxian
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Ca-Si-Al-O-N oxynitride glasses with rare-earth yttrium and lanthanum were prepared by melting batches at 1 550-1 650 ℃ for 2 h under N2 atmosphere in a Si-Mo-heated resistance furnace. The amorphous nature of the samples was verified by an X-ray diffractometer and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The basic structural units in these glasses were studied by Fourier-transform IR spectroscopy. The influences of La3+ or Y3+ on the properties such as thermal expansion coefficients (α), glass transition temperature (Tg), the crystallization temperature (Tc), Vickers hardness (HV) and bending strength (σ) were comparatively studied. The relationship between these properties and the structures of the glasses were discussed by using cationic field strength (CFS). The results show that the physical properties change linearly with the concentration of lanthanum or yttrium content, respectively. In general, the structure and properties of glasses show a larger dependence on the yttrium content than on the content of lanthanum.
Key words: rare-earth; oxynitride glass, IR spectra, thermal properties; mechanical properties
自在氮化硅陶瓷的晶间相发现氧氮玻璃[1-2]以来,许多学者对氧氮玻璃的性能和制备进行了研究。氧氮玻璃作为大块材料具有许多潜在的用途,因此,研究这类玻璃是非常有价值的。在硅酸盐玻璃中引入氮原子后对机械性能如抗弯强度、断裂韧性、弹性模量以及显微硬度有显著的影响,因此,氧氮玻璃引起了学者们的关注[3-5]。通过进一步研究发现,氮对玻璃的热性能也有较大的影响,氧氮玻璃具有更高的玻璃转变温度以及较低的热膨胀系数,热性能的提高对于大块材料的潜在应用十分有利[6]。研究发现:玻璃的性能与氮含量和网络修饰体或掺杂体的离子半径呈线性关系,氮含量和稀土含量对玻璃性能的影响可能是独立和累加的[7]。Drew等[8]发现M-Si-Al-O-N(M=Mg, Ca, Nd, Y)系氧氮玻璃只改变修饰体离子的种类,氧氮玻璃的硬度、黏度和玻璃转变温度从低到高的顺序为Mg,Ca,Nd和Y。Ohashi等[9]对稀土掺杂硅酸盐氧氮玻璃进行了研究,结果表明:保持M,Si,O,N(M=Y, La, Ce, Nd, Gd, Dy)摩尔比不变时,玻璃的弹性模量和玻璃转变温度随阳离子场强(CFS)呈线性变化。为了解释这一实验结果,Ohashi等[9-10]认为高CFS的阳离子通过对N或者O阴离子施加更大的吸引力使玻璃网络的键合更加牢固。有少量的研究[11-12]报道了混合修饰体阳离子(即Si4+和Al3+以外的阳离子)氧氮玻璃,但仅仅研究了氮取代氧对玻璃性能的影响而不是混合阳离子修饰体成分或其比例对氧氮玻璃性能的影响。Weldon等[13]对La-Er共掺Si-Al-O-N玻璃进行了研究,指出氧氮玻璃的摩尔体积、硬度、玻璃转变温度与稀土修饰体阳离子La或 Er阳离子场强有关。高强度的氧氮玻璃作为窗口材料用作透明装甲车的硬质面板材料层是目前一个重要的研究方向[14]。相对氧化铝透明陶瓷、Al-O-N单晶而言,氧氮玻璃的优势在于成形过程较简单,可以制成大尺寸的部件,氧氮玻璃的成形温度比透明陶瓷低,一般低于1 800 ℃,可以采用普通玻璃的成形工艺。而透明晶体装甲材料,如Al2O3陶瓷和Al-O-N晶体的制备需要很困难的烧结程序(或者从熔体得到单晶),本质上都需要非常高的温度[15]。人们对Ca-Si-O-N和Ca-Si-Al-O-N体系氧氮玻璃已有较多研究[16-18],该体系氧氮玻璃的特点是熔化温度相对较低,但机械性能和耐化学腐蚀能力较差,析晶性能较好。而对稀土与Ca混合的Si-Al-O-N氧氮玻璃的研究较少。为此,本文作者用稀土Y或La逐步取代Ca-Si-Al-O-N 氧氮玻璃中的Ca制备RE-Ca-Si- Al-O-N氧氮玻璃,以期在较低熔化温度下制备的氧氮玻璃具有优异的热性能和机械性能。为获得Ca-Si-Al-O-N系玻璃中添加稀土Y或La含量对玻璃的结构、热性能和机械性能的影响,测试玻璃样品的X线衍射图谱、SEM显微照片、热膨胀系数、差热分析曲线、维氏硬度、抗弯强度和红外吸收光谱,并对比Y或La对玻璃结构和性能的影响。
1 实验
1.1 材料制备
本实验采用熔融法制备含稀土Y或La的Ca-Si-Al-O-N系氧氮玻璃,样品的编号及其化学组成(平衡浓度比)如表1所示。选取SiO2,CaCO3和Al2O3 (分析纯,质量分数为99.9%,上海国药集团生产)、Si3N4(分析纯,质量分数为99.9%,安徽摩凯新材料公司生产)以及Y2O3和La2O3(4N,湖南稀土所)为原料,按照设计的化学组成计算出相应的原料质量,称取各原料粉末,充分混合均匀后,球磨10 h,过75 μm筛后,装入坩埚中,坩埚上部加高纯石墨盖,置于密封性良好的气氛电阻炉中,根据成分的不同分别加热到1 550~1 650 ℃保温2 h,熔化结束后经1 h匀速降温至1 000 ℃,退火2 h,经过10 h匀速冷却到200 ℃,然后随炉冷却。在整个实验过程中,用高纯N2作保护气氛。将制成的样品切割成要求的尺寸进行各种测试。
表1 氧氮玻璃样品的组成
Table 1 Compositions of oxynitride glasses
1.2 结构与性能测试
用Rigaku D/max 2550 PC型全自动X线衍射仪测定各个样品的X线衍射图谱。实验条件如下:Cu靶,扫描范围为10°~80°,扫描速度为8 (°)/min,测试温度为室温。玻璃的微观形貌通过FEI Quanta-200型扫描电镜进行分析检测,在SEM测试之前,玻璃样品先进行金相抛光处理,抛光后的样品进行喷铂金处理以增加样品的导电性。用美国NICOLET 6700型傅里叶红外光谱分析仪测试样品的红外(IR)光谱,测试在室温下进行,采用KBr为参比物,玻璃样品粉末(过孔径为45 μm筛)和KBr的质量比为1:50,测试范围为400~4 000 cm-1,分辨率为4 cm-1。用日本TAS 100 型热分析仪测量样品的热膨胀系数曲线和玻璃转变温度,样品直径×长度为5 mm×20 mm,采用Al2O3为参比物,加热速度为10 ℃/min,测试过程采用高纯氩气保护测试温度范围为25~1 100 ℃,对25~800 ℃时玻璃热膨胀系数进行对比。用德国NETZECH DSC 404 型差示扫描量热仪测定样品的DSC曲线,加热速度为10 ℃/min,测试过程采用高纯氩气保护,测试范围为25~1 400 ℃,由DSC曲线获得玻璃样品的析晶温度。采用HV-5型维氏显微硬度仪测量氧氮玻璃的维氏显微硬度。样品的长×宽×高为10 mm×10 mm×5 mm,载荷为20 N,受载时间15 s,每个试样取10个测试点,显微硬度取其平均值。用长春CSS-44100型电子万能试验机测量玻璃样品的抗弯 强度,样品长×宽×高为25 mm×4 mm×4 mm,跨距为14.5 mm,每个样品测量5次,抗弯强度取其平均值。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 玻璃的成形
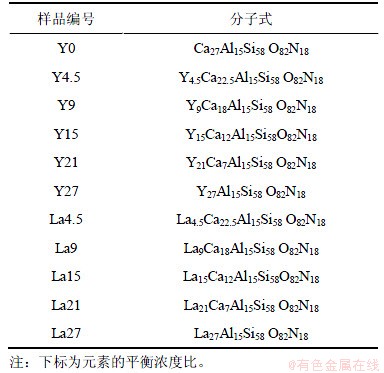
对所有Y-Ca-Si-Al-O-N和La-Ca-Si-Al-O-N体系的玻璃样品进行XRD测试以确定它们的无定形态。结果表明,对于Ca27Al15Si58O82N18氧氮玻璃而言,Ca元素可以被稀土La或者Y完全取代。La取代Ca后,引起玻璃颜色的改变,这取决于La的含量。玻璃样品从低La含量的浅灰色半透明到高La含量的灰黑色半透明,透明度随La含量的增加而呈逐渐下降的趋势。Y元素取代Ca对玻璃的颜色和透明度的影响不大。图1所示为玻璃样品Y15和La15的XRD图谱。可见,样品的XRD图谱表现为明显的散射峰,说明在检测范围内并未发现任何晶相物质。图2所示为玻璃样品Y15的SEM照片。由图2可以看出:样品为均匀的玻璃相,并未发现有任何晶相。
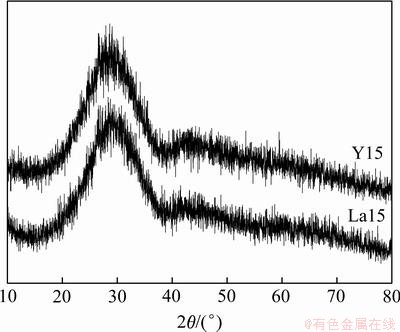
图1 玻璃样品Y15和La15的XRD图谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of glass samples Y15 and La15

图2 玻璃样品的SEM像
Fig.2 SEM images of glass samples
2.2 玻璃的红外光谱
图3和图4所示分别为掺Y和掺La玻璃样品在400~1 800 cm-1范围内的红外吸收光谱。从图3和图4可见:玻璃样品在此范围内有若干个明显的吸收谱带;位于1 640 cm-1附近的吸收峰对应吸附水的H—O—H弯曲振动模式。与玻璃结构有关的IR光谱的吸收峰主要位于1 500~400 cm-1范围内,该范围是本文主要要讨论的波数范围。
由图3可见:掺Y的氧氮玻璃样品的红外吸收光谱中可观察到4个较为明显的红外吸收谱带,其波数范围分别为位于1 640 cm-1附近的吸收峰,最强的吸收谱带在1 200~900 cm-1,750~600 cm-1和较弱的吸收谱带450~550 cm-1处;随着Y与Ca摩尔比的增加,其中450~550 cm-1和650~750 cm-1处的2个吸收谱带逐渐变宽、变钝,Y完全取代Ca后,450~550 cm-1处不再有明显的峰形,而650~750 cm-1吸收谱带有向低波数移动的趋势,吸收峰逐渐减弱,Y完全取代Ca后该谱带接近于消失。而1 200~900 cm-1处强吸收谱带则随着Y与Ca摩尔比的增加逐渐变宽,当Y全部取代Ca后,该吸收谱带分裂成2个吸收峰。对于氧氮玻璃,当N进入氧化物玻璃结构并与Si原子成键形成SiO3N5-四面体时,3个SiO3N5-四面体共用1个顶点,邻近的Si—O—Si键发生扭曲变形,导致O—Si—O键的弯曲振动(800 cm-1处)和Si—O—Si键的伸缩振动变宽[19]。同时,由于Si—O键和Si—N键的红外吸收峰分别位于1 100 cm-1和900 cm-1处,氧氮玻璃中的1 200~900 cm-1宽吸收谱带有两者共同的作用,而1 100 cm-1和900 cm-1处吸收峰比较接近,使得两者并连在一起。
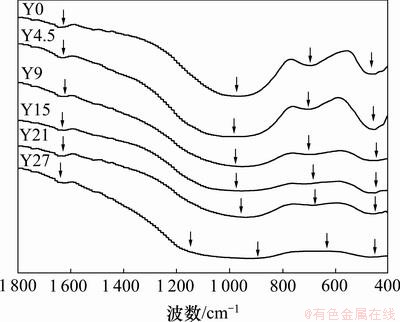
图3 玻璃样品Y0,Y4.5,Y9,Y15,Y21和Y27的IR图谱
Fig.3 IR spectra of glass samples Y0, Y4.5, Y9, Y15, Y21 and Y27
文献[20]在对掺Mg的Y-Si-Al-O-N玻璃的红外光谱分析中指出,1 200~900 cm-1处宽吸收峰分别是由900,1 050和1 100 cm-1处吸收峰叠加的结果,而氧氮玻璃中的非桥氧-桥氧摩尔比在很大程度上决定了最大吸收峰的位置和强度。本实验中,1 200~900 cm-1宽吸收峰的振动强度随着Y逐步取代Ca而逐渐降低。同时,随着Y平衡浓度比的增加,氧氮玻璃在1 200~900 cm-1之间的吸收峰呈现变宽的倾向,最终随着Y完全取代Ca后分裂成2个宽吸收峰。由此可以推断:随着Y逐步取代Ca,由于Y离子的半径比Ca离子的半径小,其阳离子场强比Ca离子的场强大,部分Y离子在玻璃网络结构中具有类似于Al原子的作用,参与网络体的形成,由此而产生出更多的桥键。Y—O键对应的红外光谱吸收峰位于780 cm-1附近,而[AlO4]四面体中的Al—O键位于730 cm-1附近,[AlO6]八面体中的Al—O键的振动位于650 cm-1附 近[20]。而Si—N和Si—O键的红外振动峰都位于900~1 200 cm-1处,因此,Y27样品的波数900~1 200 cm-1之间吸收峰趋于平缓,可能是这些化学键振动的峰值较为接近,叠加后产生的结果。图4所示为La-Ca-Si- Al-O-N氧氮玻璃在波数范围为1 800~400 cm-1的红外吸收光谱。从图4可见:La-Ca-Si-Al-O-N氧氮玻璃样品有4~5个较为明显的吸收峰,分别在1 630 cm-1,900~1 100 cm-1,650~750 cm-1,450~470 cm-1和415~440 cm-1处。峰值位于1 630 cm-1处附近的吸收峰同样归属于吸附水的H—O—H弯曲振动,而900~1 100 cm-1处的峰归属于Si—O键和Si—N键伸缩振动的吸收峰叠加的结果。650~700 cm-1处对应Al—O键的伸缩振动,450~470 cm-1,415~440 cm-1可能对应Si—O键等的弯曲振动。随着La逐步取代Ca原子,红外光谱的峰形、吸收峰的位置和强度的变化不十分明显,说明La原子与Ca原子在玻璃中所起的作用类似,La取代Ca后对玻璃的网络结构影响不大。此外,与La-Ca-Si-Al-O-N体系氧氮玻璃相比,Y-Ca-Si-Al-O-N体系氧氮玻璃的红外光谱多了415~440 cm-1处的峰。由于La—O键的振动峰大约在475 cm-1附近,故可能是La—O键与Si—O键等的弯曲振动的吸收峰发生了叠加的结果。
图4 氧氮玻璃样品La4.5,La9,La15,La21和La27的IR图谱
Fig.4 IR spectra of glasses samples La4.5, La9, La15, La21 and La27
通过对比图3和图4可知:Y在玻璃结构中所起的作用与La相比有本质的不同。当Y平衡浓度比较低时,Y与La和Ca的作用类似,在玻璃仅作修饰体离子,而当Y平衡浓度比较高时,部分Y3+与Al3+的作用类似;作为中间体参与玻璃网络的形成,增加玻璃中桥氧的数量,从而影响玻璃的网络结构。这一点在红外光谱中有明显的体现,较高的Y平衡浓度比对Si—O键、Si—N键的红外光谱(900~1 200 cm-1)产生了较大的影响,使得峰形变宽并向低波数移动。而La和Ca一样,在玻璃网络中只能作为修饰体离子,对玻璃网络结构的影响相对较小。
2.3 玻璃的热性能
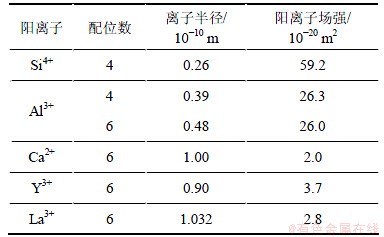
表2所示为玻璃中不同的阳离子的本质特征参数,包括阳离子的配位数,离子半径(r)和阳离子场强(CFS)[7, 21]。Weldon等[13]认为氧氮玻璃的性能与玻璃成分中的阳离子场强有关。由于本实验中涉及的玻璃成分中的Si和Al的平衡浓度比保持不变,分别以Y或者La逐步取代Ca原子,变化的是Y与Ca摩尔比或La与Ca摩尔比,因此在研究玻璃的结构和性能的变化时只考虑Y3+,La3+和Ca2+的阳离子场强,而不考虑Si和Al的阳离子场强。由表2可知,本实验所研究的玻璃中的阳离子场强从大到小的顺序为Y3+,La3+和Ca2+。阳离子场强与阳离子电荷成正比,与离子间距的平方成反比,它表示阳离子与氧阴离子间的吸引力。因此,不同阳离子场强的原子在玻璃中所起的作用不同。
表2 玻璃中不同的阳离子的本质特征
Table 2 Intrinsic characteristics of different cations present in glasses
本实验中通过测量玻璃的热膨胀曲线获得的样品的玻璃转变温度。热膨胀系数可表征物质的一种热力学性能。玻璃转变温度是在原子自由度松弛转换处的温度。在玻璃转变温度点,玻璃系统由黏性液体行为转变成固体行为,对于硅酸盐玻璃,较高的玻璃转变温度与高的化学键强和较高的网络聚合度有关。表3、图5和图6所示分别为玻璃样品的热膨胀系数或玻璃转变温度分别随Y平衡浓度比或La平衡浓度比的变化曲线。玻璃的热膨胀系数取决于玻璃的热振动的不对称的振幅。热膨胀系数降低表明玻璃网络的刚度增加。非桥氧键数的增加可能弱化了玻璃的结构,增大了热膨胀系数,而网络形成体阳离子的配位数的变化可能引起热膨胀系数的增加或降低,这取决于其对玻璃结构的影响。将测试的数据对玻璃的热膨胀系数与Y或La平衡浓度比的关系进行线性拟合,得到经验公式:
对于Y-Ca-Si-Al-O-N玻璃,
α=6.89-0.061·[Y]×10-6 (1)
对于La-Ca-Si-Al-O-N玻璃,
α=6.89-0.033·[La]×10-6 (2)
式中:[Y]和[La]分别代表Y 和La的平衡浓度。由经验公式可以看出:Y对玻璃热膨胀系数的影响要比La大得多。热膨胀系数随对应稀土阳离子场强的增大而减小,这主要是由于稀土氧化物在玻璃中起网络修饰体的作用有关。此外,由于稀土阳离子属于高场强的网络修饰体,对玻璃的网络具有一定的聚集作用,因此随着添加的稀土离子的阳离子场强的增大对应的氧氮玻璃的热膨胀系数呈降低的趋势。
表3 Y或La对Ca-Si-Al-O-N系氧氮玻璃的物理性能、机械性能和热性能的影响
Table 3 Effects of Y or La on physical, mechanical and thermal properties of Ca-Si-Al-O-N oxynitride glasses
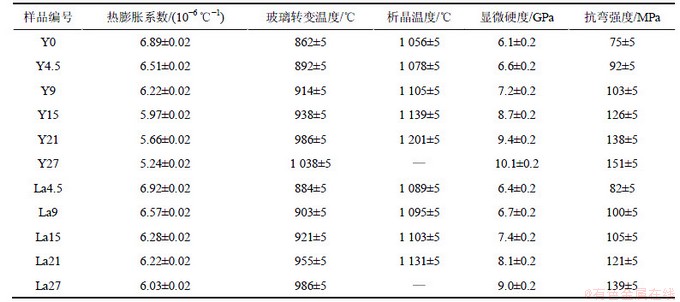
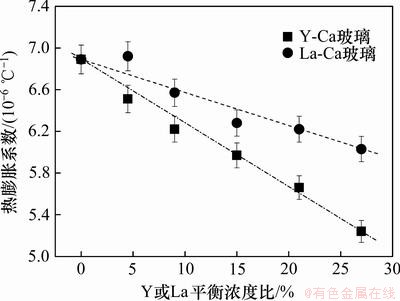
图5 RE-Ca-Si-Al-O-N氧氮玻璃的热膨胀系数随La或Y平衡浓度比的变化曲线
Fig.5 Thermal expansion coefficient versus La (or Y) content for RE-Ca-Si-Al-O-N glasses
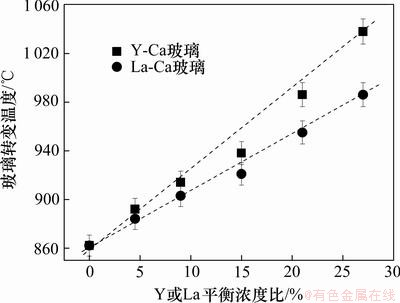
图6 RE-Ca-Si-Al-O-N氧氮玻璃的玻璃转变温度(Tg)随La或Y平衡浓度比的变化曲线
Fig.6 Glass transition temperature (Tg) versus La (or Y) content for RE-Ca-Si-Al-O-N glasses
从表3可以看出:所研究的氧氮玻璃的玻璃转变温度为862~1 038 ℃,热膨胀系数为5.24×10-6~ 6.92×10-6 ℃-1。当Y平衡浓度比从0增加到27%时,Tg从862 ℃增加到1 038 ℃,增加了176 ℃,而当La平衡浓度比从0增加到27%时,Tg从862 ℃增加到986 ℃,增加了124 ℃,表明Y平衡浓度比对玻璃转变温度的影响比La平衡浓度比的影响要大的多。将测试的数据对Tg随Y或La平衡浓度比的关系进行线性拟合,得到经验公式:
对于含Y的玻璃,
Tg=862+6.52·[Y] (3)
对于含La的玻璃,
Tg=862+ 4.59·[La] (4)
对于氧氮玻璃而言,网络形成体中的氧原子被3价的氮原子所取代,Si—N键的形成增加了玻璃的网络强度,使得玻璃网络更加紧密。同时,玻璃的热膨胀系数和玻璃转变温度还取决于阳离子的配位数和各元素之间的键合力。玻璃中非桥氧数越少,阳离子场强越大、配位数越高,玻璃的转变温度就越高。稀土Y或La取代Ca-Si-Al-O-N玻璃中的Ca使玻璃转变温度Tg升高可解释为:一方面,Y3+或La3+的阳离子场强要比Ca2+的高,从而吸引阴离子的有效力也增强;另一方面,玻璃的结构研究表明当玻璃改性体Y取代Ca时,部分Y(8配位)参与玻璃网络形成增加了桥氧数,从而使Tg升高(如图6所示)。而La只以6配位的形式存在于玻璃网络中,不能参与玻璃网络形成而只能作为修饰体离子存在,因此,Y对玻璃转变温度的影响较大。
图7所示为样品Y0,Y15,La15和Y21的DSC曲线,各个样品的析晶峰温度见表3。析晶峰温度的数据来源于样品的DSC曲线,DSC曲线中的放热峰的峰值温度定为析晶温度。从图7可以看出:样品的析晶峰温度分别随稀土含量的增加而升高,峰形随之明显变宽变缓,析晶倾向下降,热稳定性增加。从表3可以看出,当Y平衡浓度比从0增加到21%时,Tc从1 056 ℃增加到1 201 ℃,与此同时,析晶峰的峰形逐渐变宽变钝,当Y完全取代Ca后,DSC曲线中已无明显的析晶峰。这说明稀土Y2O3的加入降低了玻璃的析晶倾向,提高了玻璃的热稳定性。与Y含量对氧氮玻璃析晶温度的影响类似,La取代Ca也提高了玻璃的析晶温度。而当La平衡浓度比从0增加到21%时,Tc从1 056 ℃增加到1 131 ℃,表明:Y平衡浓度比对玻璃析晶温度的影响比La平衡浓度比的影响更大。析晶温度也与玻璃的结构有关,Y3+或La3+的阳离子场强要比Ca2+的高,吸引阴离子的有效力也增强,玻璃在加热的过程中,发生离子迁移的难度增加,使得玻璃网络在受热过程中更加稳定。因此,玻璃的析晶温度逐渐增加,而析晶倾向逐渐减弱。
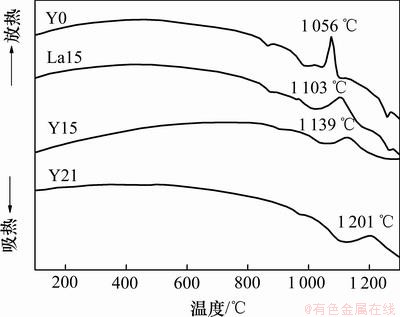
图7 玻璃样品Y0,La15,Y15,Y21的DSC曲线
Fig.7 DSC curves of glasses samples Y0, La15, Y15 and Y21
2.4 玻璃的机械性能
氧氮玻璃样品的维氏显微硬度随Y或La平衡浓度比的变化趋势如图8所示。本实验制备的氧氮玻璃的维氏硬度为6.1~10.1 GPa。由图8可以看出,玻璃的硬度随Y平衡浓度比或La平衡浓度比的增加而近似呈线性增加。
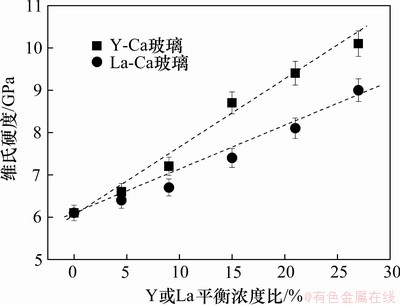
图8 RE-Ca-Si-Al-O-N氧氮玻璃的维氏硬度随La或Y平衡浓度比的变化曲线
Fig.8 Vickers hardness versus La (or Y) content for RE-Ca-Si-Al-O-N glasses
Y取代Ca原子导致硬度增加可能是由于Y占据玻璃的网络连接位置,部分Y原子参与构成玻璃网络形成体,加强了玻璃的网状连接影响了玻璃的网状堆积结构,使得玻璃的结构更加紧密,从而增大了玻璃的硬度。对于Y系列氧氮玻璃,其维氏硬度随玻璃中Y的平衡浓度基本呈线性变化。在Y-Ca-Si- Al-O-N 氧氮玻璃中,玻璃的硬度不仅取决于玻璃形成体[Si, Al]与阴离子(O,N)之间的键强,还取决于玻璃改性体[Y, Ca]与阴离子之间的键强。6配位Y3+的阳离子场强(CFS)要比6 配位Ca2+的大,在Y-Ca-Si-Al-O-N 氧氮玻璃中,Y取代Ca后使玻璃网络连接更加紧密,进而提高玻璃的显微硬度。在一般情况下,La与Y对氧氮玻璃结构的作用有一定的类似,但是,La的相对分子质量比Y的大,且离子半径要比Y3+ 的大(如表2所示),其离子本性与Y有一定的差异,La原子和Y原子在玻璃中所起的作用不完全相同。对比La-Ca氧氮玻璃和Y-Ca氧氮玻璃的显微硬度可以发现,添加Y对氧氮玻璃显微硬度的影响程度比添加La对氧氮玻璃的影响大。可能的原因是,La的半径比Y的大,且同配位数下的阳离子场强比Y的小,且只能作为修饰体,不能参与形成玻璃的网络结构。
本实验制备的Y-Ca和La-Ca体系的氧氮玻璃的抗弯强度为75~139MPa。目前,关于氧氮玻璃抗弯强度的研究较少。文献[22]研究发现,Li-Si-Al-O-N体系氧氮玻璃的抗弯强度为110~150 MPa,该体系中氧氮玻璃的氮含量较高。氧氮玻璃样品的抗弯强度随玻璃样品中Y或La平衡浓度比的变化趋势如图9所示。从图9可以看出:对于La-Ca-Si-Al-O-N体系氧氮玻璃,抗弯强度随La平衡浓度比的增加而大致呈线性增加。对Y-Ca-Si-Al-O-N体系氧氮玻璃系列玻璃来说,抗弯强度与Y平衡浓度比的关系也近似呈线性增加的趋势,与显微硬度的变化趋势类似,Y的作用比La的作用更明显。因此,Y或La的引入在一定程度上提高了Ca-Si-Al-O-N体系氧氮玻璃的机械性能。
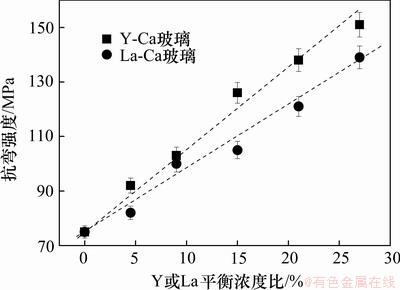
图9 RE-Ca-Si-Al-O-N氧氮玻璃的抗弯强度随La或Y平衡浓度比的变化
Fig.9 Bending strength versus La (or Y) content for RE-Ca-Si-Al-O-N glasses
3 结论
(1) 在相对较低的温度下(1 550~1 650 ℃)制备了RE-Ca-Si-Al-O-N(RE=Y, La)体系氧氮玻璃,XRD和SEM测试结果表明所制备的样品均为玻璃。
(2) 所制备的氧氮玻璃的力学性能及热性能比普通玻璃的好,有望应用于透明装甲车的硬质面板材料。
(3) 所制备的氧氮玻璃最强的IR光谱的吸收峰波数位于900~1 200 cm-1之间,对应主要的化学键为Si—O键及Si—N键。Y的引入对玻璃的网络结构产生了较大的影响,而La对玻璃结构的影响相对较小;随着Y或La逐步取代玻璃中的Ca,2个体系氧氮玻璃的玻璃转变温度、析晶温度、显微硬度、抗弯强度均呈近似线性增加的趋势,而热膨胀系数则随之呈下降趋势。这是因为Y3+的离子半径比La3+的小,而阳离子场强比La3+的大,因此,Y和La在玻璃网络中的所起的作用不同。
参考文献:
[1] Jack K H. Review: Sialons and related nitrogen ceramics[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1976, 11(6): 1135-1158.
[2] Hampshire S, Drew R A L, Jack K H. Viscosities, glass transition temperatures, and microhardness of Y-Si-A1-O-N glasses[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1984, 67(3): C46-C47.
[3] Hampshire S, Pomeroy M J. Grain boundary glasses in silicon nitride: A review of chemistry, properties and crystallization[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2012, 32(9): 1925-1932.
[4] Wakihara T, Tatami J, Komeya K, et al. Effect of TiO2 addition on thermal and mechanical properties of Y-Si-Al-O-N glasses[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2012, 32(6): 1157-1161.
[5] Ali S, Jonson B. Preparation of oxynitride glasses from woody biofuel ashes[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2010, 356(50/51): 2774-2777.
[6] Peterson I M, Tien T Y. Thermal expansion and glass transition temperatures of Y-Mg-Si-Al-O-N glasses[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1995, 78(7): 1977-1979.
[7] Lofaj F, Satet R, Hoffmann M J, et al. Thermal expansion and glass transition temperature of the rare-earth doped oxynitride glasses[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2004, 24(12): 3377-3385.
[8] Drew R A L, Hampshire S, Jack K H. Nitrogen glasses[J]. Proceedings of the British Ceramic Society, 1981, 31: 119-132.
[9] Ohashi M, Nakamura K, Hirao K, et al. Formation and properties of Ln-Si-O-N glasses (Ln=lanthanides or Y)[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1995, 78(1): 71-76.
[10] Ramesh R, Nestor E, Pomeroy M J, et al. Formation of Ln-Si-Al-O-N glasses and their properties[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1997, 17(15): 1933-1939.
[11] Graaf D, Rol S, Hintzen H T, et al. Mixed oxidation states of Yb and Sm in Si-Al-O-N glasses[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26 (13): 2497-2501.
[12] Rocherulle J, Matecki M, Delugeard Y. Heat capacity measurements of Mg-Y-Si-Al-O-N glasses[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1998, 238(1/2): 51-56.
[13] Weldon L, Pomeroy M J, Hampshire S. Glasses in the rare-earth sialon systems[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 1996, 118/119: 241-248.
[14] Klement R, Rol S, Mikulikova R, et al. Transparent armour materials[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2008, 28(5): 1091-1095.
[15] Medvedovski E. Ballistic performance of armour ceramics: Influence of design and structure. Part 1[J]. Ceramics International, 2010, 36(7): 2103-2115.
[16] Gueguen Y, Sharafat A, Grins J, et al. Viscosity of high-nitrogen content Ca-Si-O-N glasses[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(16): 3455-3458.
[17] Sharafat A, Grins J, Esmaeilzadeh S. Hardness and refractive index of Ca-Si-O-N glasses[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2009, 355(4/5): 301-304.
[18] Mitomo M, Laubach B. Preparation of Ca-Si-Al-O-N oxynitride glass powders[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1987, 6(12): 1434-1439.
[19] Brinker C J, Haaland D M, Loehman R E. Oxynitride glasses prepared from gel and melts[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1983, 56(1/2/3): 179-184.
[20] LI X Y, LU A X, XIAO Z H, et al. The influences of cations on the properties of Y-Mg-Si-Al-O-N glasses[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2008, 354(31): 3678-3684.
[21] Pomeroy M J, Nestor E, Ramesh R, et al. Properties and crystallization of rare-earth Si-Al-O-N glasses containing mixed trivalent modifiers[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2005, 88(4): 875-881.
[22] YAO L, FANG Q, HU G, et al. Preparation and properties of some Li-Si-Al-O-N glasses[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1983, 56(1/2/3): 167-172.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2012-12-15;修回日期:2013-02-22
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51272288);湖南省研究生创新项目(CX2011B108)
通信作者:卢安贤(1960-),男,湖南郴州人,博士,教授,从事无机非金属材料研究,电话:0731-88830351;E-mail: axlu@csu.edu.cn