Mg2+掺杂对LiFePO4结构及电化学性能的影响
阮艳莉, 唐致远
(天津大学 化工学院, 天津 300072)
摘 要: 以MgAC2为掺杂源, 采用固相反应法在惰性气氛下合成了掺Mg的LiFePO4正极材料, 考察了Mg2+对于目标化合物物理及电化学性能的影响。 采用粉末X射线衍射和扫描电镜技术对产物的结构、 形貌及粒度等进行了表征, 通过恒电流充放电和交流阻抗技术对其电化学性能进行了研究。 结果表明: 少量的Mg2+掺杂并未影响产物结构, 但却有利于减小LiFePO4电荷转移过程中的阻抗, 克服该过程中的动力学限制。 在0.1C倍率下放电, 掺杂LiFePO4与未掺杂LiFePO4的初始放电容量分别为136.9和111.8mA·h/g, 循环50次后, 容量分别为135.6和83.9mA·h/g; 与未掺杂的LiFePO4相比, 掺镁后的LiFePO4具有更为优良的循环性能。
关键词: LiFePO4; 正极材料; Mg2+掺杂; 电化学性能 中图分类号: O614.111; O646; TM912.9
文献标识码: A
Effects of Mg2+ doping on structure and electrochemical performance of LiFePO4
RUAN Yan-li, TANG Zhi-yuan
(School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China)
Abstract: Stoichiometric Mg-doped lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) cathode material was synthesized by a solid-state reaction in an inert atmosphere which used MgAC2 as dopant. The effects of Mg2+ doping on the physical and electrochemical properties of as-synthesized cathode materials were investigated. The samples were characterized by powder X-ray diffractrometry, scanning electron microscopy, and their electrochemical performance was systematically measured by impedance response and constant current charge/discharge cycling tests. The results indicate that the low concentration Mg2+ doping does not affect the structure of the material but considerably improves its kinetics in terms of capacity delivery and cycle performance. At 0.1C discharging rate, the reversible specific capacities of the Mg-doped lithium iron phosphates and the undoped LiFePO4 are 140 and 128mA·h/g, respectively. After 50 cycles, the capacities are 135.6 and 83.9mA·h/g, respectively. Comparing to the undoped LiFePO4, the Mg-doped lithium iron phosphates also displays a more stable cycle performance.
Key words: LiFePO4; cathode material; Mg2+ doping; electrochemical performance
1997年Padhi等[1]的开拓性研究揭开了橄榄石型LiFePO4研究的序幕。 LiFePO4作为一种新型锂离子电池正极材料, 与常见的过渡金属氧化物正极材料, 如层状LiMO2(M=Co、 Ni、 Mn)及尖晶石LiMn2O4相比, 在价格、 安全性能及电化学性能等方面具有其独特的优势[2], 因而成为动力型锂离子电池的理想正极材料[3]。
LiFePO4的电导率为10-9~10-10S/cm[4], 其锂离子扩散系数(DLi+)为1.8×10-14cm2/s[5]。 对于受电导率及Li+扩散所控制的电极过程而言, 这较大地限制了LiFePO4的电化学性能, 阻碍了其在[CM(22]商业化电池中的应用。 研究表明, 这种导电性上[CM)] 的限制可以通过以下3种途径进行改善: 1) 合成形貌规则, 粒径小而均匀的颗粒[6]; 2) 包覆导电剂, 对颗粒表面进行改性[7, 8]; 3) 掺杂金属离子, 进行离子取代[9]。 其中, 对LiFePO4进行表面包覆改性, 可以获得细小而均匀的粉体, 并能在一定程度上改善其电化学性能, 但这种改善主要是通过提高活性物质颗粒之间以及活性物质与导电剂之间的电接触进行的[10]。 表面包覆改性对于LiFePO4晶格内部导电性的提高意义不大[11], 而且, 即使是低于1%(质量分数)导电剂碳的出现也会引起振实密度的明显下降[12]。 因此, 对LiFePO4进行离子掺杂以提高其晶格内部导电性具有了更为重要的意义。
目前, 国内外对于离子掺杂改性的研究还不甚成熟, 掺杂离子是如何影响LiFePO4的结构和电化学性能的也有待于进一步的探索。 本文作者以MgAC2为掺杂源, 采用固相反应法在750℃下合成了Mg2+掺杂的LiFePO4正极材料, 研究了Mg2+对于目标化合物物理及电化学性能的影响, 并分析了产生这种影响的原因, 旨在为进一步优化LiFePO4的性能提供理论依据。
1 实验
1.1 样品的制备
将LiCO3, FeC2O4·2H2O和NH4H2PO4(以上均为分析纯)按化学计量比称量, 加入适量丙酮分散, 球磨2h。 待原料混合均匀后, 放入石英坩锅中, 在氮气气氛下于350℃预热12h, 使原料完全分解。 冷却后充分研磨、 混匀, 在750℃焙烧24h。 缓慢降温, 冷却后研磨得到未掺杂的LiFePO4正极材料, 样品标记为LFP。 在混料时加入1%(摩尔分数)的MgAC2(分析纯), 按照上述合成方式合成掺杂样品, 样品标记为LMFP。
1.2 样品的表征
X射线衍射分析在PANalytical Xpert HighScore自动X射线衍射仪上进行。 Co Kα辐射(λ=0.178901nm), 40kV, 40mA, 扫描范围10°~80°。 扫描电镜测试在荷兰Philips XL-30环境扫描电子显微镜上进行, 加速电压20kV。
1.3 电化学性能测试
以自制的材料作为正极活性物质, 乙炔黑为导电剂, 60%的聚四氟乙烯乳液(PTFE)为粘结剂, 按照质量比为80∶15∶5混合。 用无水乙醇做分散剂, 超声波振荡15min, 使之混合均匀。 制成面积约1cm2, 厚度≤200μm的圆片并压在集流体铝箔上构成正极, 在真空干燥箱(DZG-404, 天津天宇技术实业有限公司)中120℃真空干燥12h。 以金属锂片作为负极, 进口聚丙烯微孔膜(Celgard 2300)作为隔膜, 以1mol/L LiPF6/碳酸乙烯酯(EC)、 碳酸二乙酯(DEC)、 碳酸二甲酯(DMC)(体积比为1∶1∶1)的混合溶液为电解液。 在充氩气的手套箱(ZKX3, 南京大学仪器厂)中装成2032型扣式电池。 用电池程控测试仪(PCBT-138-32D, 武汉力兴电源有限公司)在室温下以不同的倍率进行充放电循环测试, 电压范围为2.8~4.2V。 电池的交流阻抗(AC impedance)测试在电化学工作站(CHI 600, 上海辰华仪器公司)上进行, 频率范围为105~0.01Hz。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 X射线衍射分析
图1所示为LFP及LMFP的X射线衍射谱。 从图中可以看出, 这两种样品的衍射谱线或衍射数据与LiFePO4标准谱和数据(卡号: 01-083-2092)非常相似, 均具有橄榄石型晶体X射线衍射的特征, 且X射线衍射谱中并未观察到Mg2+或其它的杂质峰, 这说明Mg2+在LiFePO4结构中进行了有效掺杂, 形成了以LiFePO4为基质的橄榄石型结构固溶体。
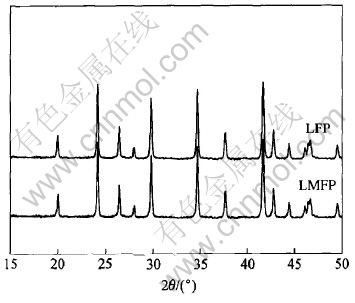
图1 掺杂前后LiFePO4粉末的X射线衍射谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of pure and doped LiFePO4 powders
在LMFP中, 掺杂的Mg2+更倾向于占据LiFePO4结构中M1(Li)的位置[9]。 由于是在惰性气氛下合成产物, 故产物不可能为富氧的化合物, 同时随着高价态Mg2+的进一步掺入, 为了保持电荷平衡, 产物必然为具有阳离子缺陷的化合物, 即在LiFePO4结构中M1(Li)或M2(Fe)位置上产生缺陷, 分别对应Li1-x-zMgxFePO4及Li1-x-MgxFe1-zPO4(z为阳离子缺陷浓度)的固溶体组成。 在高温下, Li+会以Li2O的形式逸出, 从而可能导致M1(Li)位置上的缺陷。 而缺失的Fe2+必然会生成杂相, 但在X射线图谱上却观测不到任何杂质峰, 因此认为在橄榄石结构中的M2(Fe)位置上不可能产生缺陷。 具有阳离子缺陷的Li1-x-z-MgxFePO4是一种较好的P型半导体材料[13], 晶格中的缺陷有利于Li+在LiFePO4固相中的扩散, 从而使得材料的电子导电能力也得到了增强[9]。
2.2 SEM表征
图2所示为两种样品的SEM像。 由图可以看出未掺杂LiFePO4的晶体生长完整, 颗粒比较大, 许多一次粒子聚集在一起, 形成较大的二次粒子, 而在掺杂的LiFePO4中, 许多粒子还保持了一次粒子的形态, 具有较小的粒径, 颗粒分布较为均匀,但颗粒表面较粗糙。 这说明掺杂Mg2+不仅在一定

图2 掺杂前后LiFePO4粉末的扫描电镜照片
Fig.2 SEM photos of pure and doped LiFePO4 powders
程度上降低了LiFePO4颗粒的大小, 还对其颗粒的表面形貌产生了影响。 晶体的颗粒越大, 材料的电性能越易受到Li+扩散的限制[14]。 因此, 较小的粒径将有助于材料比容量的发挥。 同时, 粗糙的表面有助于与导电剂更为紧密的接触, 便于形成良好的导电通路, 降低电极的内阻[15]。
2.3 电化学性能
图3所示为LFP及LMFP的首次放电曲线。 掺杂后的LMFP与LFP相比, 电化学性能有了很大改善。 在0.1C(1C=150mA·h/g)充放电倍率下, LFP的首次放电比容量为111.8 mA·h/g, LMFP的首放容量提高到了136.9mA·h/g。 同时, LMFP的首次库伦效率相对于LFP也有所提高, 分别为93.4%和87.2%。 Mg2+掺入后, 为了保持电荷平衡, LiFePO4与FePO4两相中均存在一定量的Fe2+/Fe3+混合价态[4], 这将有助于改善锂离子脱嵌过程中, LiFePO4与FePO4两相界面的电子导电性, 从而降低了首次充放电循环中容量的损失。
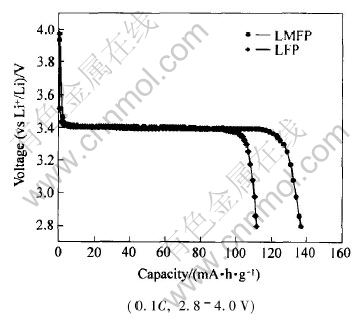
图3 掺杂前后LiFePO4的首次放电曲线
Fig.3 Discharge curves of pure and doped LiFePO4 in first cycle
图4所示为LFP及LMFP电极的循环伏安曲线, 其测量条件为室温, 扫描速度为0.1mV/s, 扫描电压区间为2.6~4.2V。 可以看出, 每条曲线都存在一对强的氧化还原峰, 分别对应着Li+在其中的脱出和嵌入过程。 从图中标出的电势数值可以看出, 掺杂后氧化峰位置从3.645V负移至3.617V, 而还原峰位置从3.241V正移至3.281V, 即掺杂后氧化还原峰之间的电势差Δφp减少, 从而使得LMFP电极的可逆性得到了提高, 进而预示其具有良好的充放电循环性能。

图4 掺杂前后LiFePO4电极的循环伏安曲线
Fig.4 Cycle voltammagram of pure and doped LiFePO4 electrode at scan rate 0.1mV/s
图5所示为LFP及LMFP样品的循环性能。 LMFP在起始的几次循环中存在材料的活化过程, 即随着循环次数的增加, 可逆容量不断提高。 在第5次循环时, 电池的比容量达到最大值, 141.6mA·h/g。 随后的几次循环中, 容量平稳衰减, 11次循环后, 衰减趋势逐渐减弱, 50次循环后, 容降率仅为2.6%。 LFP在第3次循环中达到其放电容量的最大值, 116mA·h/g, 从第7次循环开始, 容量不断下降。 50次循环后, 容量衰减至83.9mA·h/g, 容降率为55.8%。
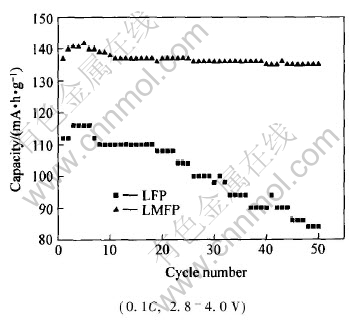
图5 掺杂前后LiFePO4的循环性能
Fig.5 Cycling performance of pure and doped LiFePO4
以上电化学性能研究结果表明, Mg2+掺杂不仅能够提高LiFePO4的初始放电容量, 对其循环性能的改善具有更为显著的作用。 为了进一步探讨掺杂离子在LiFePO4晶体中的作用, 本文作者采用交流阻抗技术考察了Mg2+掺杂对于LiFePO4充放电过程中电荷转移阻抗的影响。 图6所示为LFP及LMFP样品在充放电过程中的阻抗特性。 从图中可以看出两条曲线均由高频区的半圆和低频区的直线组成。 高频区的半圆是发生在电解质/氧化物电极界面的电荷传输反应所引起的阻抗, 低频区的直线则是锂离子在氧化物电极界面扩散所引起的Warburg阻抗。 掺入Mg2+后, LiFePO4在充放电过程中的电荷传输反应部分的阻抗值从约180Ω减小至约130Ω。 而电荷传输反应阻抗的减小有利于克服充放电过程中的动力学限制, 能够使LiFePO4活性颗粒中的嵌锂深度得到提高, 降低LiFePO4活性颗粒表面与内部存在的Li+浓度差, 避免了LiFePO4颗粒内部结晶结构发生扭曲而引起的容量下降, 从而改善了材料的循环性能。
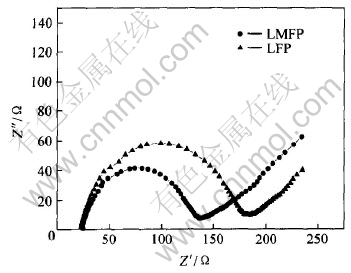
图6 掺杂前后LiFePO4电极的交流阻抗图谱
Fig.6 AC impedance spectroscopies of pure and doped LiFePO4
3 结论
1) 利用固相方法实现了Mg2+在LiFePO4结构中的有效掺杂, 形成了以LiFePO4为基质的橄榄石型结构固溶体Li0.99Mg0.01FePO4。
2) Mg2+掺杂不仅能够提高LiFePO4的初始放电容量, 对其循环性能的改善具有更为显著的作用。
3) 材料的首次充放电效率由掺杂前的87.2%提高到掺杂后的93.4%, 循环过程中容降率明显降低, 50次循环后, 由掺杂前的55.8%降为掺杂后的2.6%。 这主要是由于Mg2+掺入后, 在LiFePO4晶格中产生了阳离子缺陷, 形成了Fe2+/Fe3+混合价态, 有效改善了充放电过程中LiFePO4与FePO4两相界面的电子导电性, 从而提高了其电化学循环性能。
REFERENCES
[1] Padhi A K, Nanjundaswamy K S, Goodenough J B. Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1997, 144(4): 1188-1194.
[2]Hyung S K, Byung W C, Won I C. Cycling performance of LiFePO4 cathode material for lithium secondary batteries[J]. J Power Source, 2004, 132: 235-239.
[3]Takahashi M, Tobishima S, Takei K, et al. Reaction behavior of LiFePO4 as a cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 148: 283-289.
[4]Thuckeray M. An unexpected conductor[J]. Nat Mater, 2002, 1(2): 81-82.
[5]Prosini P P, Lisi M, Zane D, et al. Determination of the chemical coefficient of lithium in LiFePO4[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 148: 45-51.
[6]Yamada A, Chung S C, Hinokuma K. Optimized LiFePO4 for lithium battery cathodes[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2001, 148(3): A224-A229.
[7]Park K S, Son J T, Chung H T, et al. Surface modification by silver coating for improving electrochemical properties of LiFePO4[J]. Solid State Commun, 2004, 129: 311-314.
[8]Huang H, Yin S C, Nazar L F. Approaching theoretical capacity of LiFePO4 at room temperature at high rates [J]. Electrochem and Solid-State Lett, 2001, 4(10): A170-A172.
[9]Chung S Y, Bloking J T, Chiang Y M. Electronical conductive phosphor-olivines as lithium storage electrodes[J]. Nat Mater, 2002, 1(2): 123-128.
[10]Zane D, Carewska M, Scaccia S, et al. Factor affecting rate performance of undoped LiFePO4[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 49: 4259-4271.
[11]Wang G X, Bewlay S L, Konstantinov K, et al. Physical and electrochemical properties of doped lithium iron phosphate electrodes[J]. Electrachimica Acta, 2004, 50: 443-447.
[12]Chen Z, Dahn J R. Reducing carbon in LiFePO4/C composite electrodes to maximize specific energy, volumetric energy, and tap density[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2002, 149: A1184-A1189.
[13]Chung S Y, Chiang Y M. Microscale measurements of the electrical conductivity of doped LiFePO4[J]. Electrochem and Solid-State Lett, 2003, 6(12): A278-A281.
[14]Yoshinori A, Masahiro Y, Yasuo O. Non-aqueous Electrolyte Secondary Cell [P]. EP 1180811-A2, 2002.
[15]Huang H, Yin S C, Nazar L F. Approaching theoretical capacity of LiFePO4 at room temperature at high rates[J]. Electrochem and Solid-State Lett, 2001, 4(10): A170-A172.
(编辑龙怀中)
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金资助项目(20273047); 教育部博士点重点基金资助项目(20020056045)
收稿日期: 2005-05-15; 修订日期: 2005-06-28
作者简介: 阮艳莉(1977-), 女, 博士研究生.
通讯作者: 唐致远, 教授; 电话: 022-27892832; E-mail: zytang@tju.edu.cn