微通道内纳米流体换热与压降特性
宁常军,罗小平
(华南理工大学 机械与汽车工程学院,广东 广州,510640)
摘要:为研究微通道换热和压降特性的影响因素,在当量直径分别为0.923 1,1.333 3和2.000 0 mm的矩形微通道内,以0.1%和0.5%(体积分数)的Al2O3-H2O纳米流体为实验工质,进行无相变以及沸腾传热与流阻特性实验研究,分析雷诺数对努塞尔数和单相流动压降的影响。研究结果表明:增加纳米粒子体积分数对摩擦压降影响较小,而努塞尔数则得到较大提高;在2.0 mm宽槽道内,纳米流体的换热系数比水的换热系数高18%;而0.6 mm宽槽道的换热系数比2.0 mm宽槽道的换热系数提高了近2倍;随着槽道尺寸的减少,摩擦压降显著增大;当雷诺数为800时,0.6 mm和1.0 mm宽槽道摩擦压降分别是2.0 mm宽槽道摩擦压降的23.3倍和4.4倍;热流密度和质量流量增大都将导致摩擦压降增大。
关键词:微通道;纳米流体;阻力特性;换热系数;热流密度
中图分类号:TK 124 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2012)08-3000-07
Heat transfer and pressure drop of Al2O3 nanofluids in microchannels
NING Chang-jun,LUO Xiao-ping
(School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China)
Abstract: The single-phase and two-phase flow and heat transfer characteristics were experimentally investigated through the aluminum-based rectangular microchannels with different hydraulic diameter of 0.923 1, 1.333 3 and 2.000 0 mm, using Al2O3-H2O nanofluids with particle of 0, 0.1% and 0.5% (volume fraction) as the working fluids. The effect of the Reynolds number, the heat flux density, the size of the channel and the nanoparticle concentration on the pressure drop and convective heat transfer were investigated. The results show that the Nusselt number increases considerably as the nanoparticle volume fraction increases slightly but causes little extra pressure drop. The heat transfer coefficient of nanofluid rises by 18% than that of deionized water in 2.0 mm width channel. The heat transfer coefficient in 0.6 mm width channel is double higher than that in 2.0 mm width channel. With the decrease of the channel width, the pressure drop rises rapidly. The pressure drops of fluids in 0.6 and 1.0 mm width channels are 23.3 and 4.4 times of that in 2.0 mm width channel, respectively (Re=800). The pressure drop and flow friction of the nanofluids are also influenced by the heat flux density and mass velocity.
Key words: micro-channel; nanofluid; resistance characteristic; heat transfer coefficient; heat flux density
微通道换热器是一种强化换热装置,其结构紧凑、换热系数高,在空间有限而换热强度要求较高的领域具有广阔的应用前景,如航天机舱内热环境控制、微电子机械系统(MEMS)、大规模集成电路的冷却[1-2],是取代风冷技术最好的电子器件冷却技术之一。自Choi等[3]提出纳米流体的概念以后,高导热性能的纳米流体应用于微通道,进一步提高了其传热性能。由于换热性能好,微通道内纳米流体的流动和传热特性越来越受到重视[4-6]。Tuckerman等[1]在硅制VLSI芯片的背面蚀刻了微矩形结构通道,通水冷却,热流密度达到790 W/cm2,并认为,通道当量直径越小,换热能力越高,但通道尺寸的缩小又受换热工质黏度的限制。Wen等[7]测量了A12O3-H2O的对流换热系数,发现在水中加入A12O3纳米粒子,层流状态下显著增大了对流换热系数。研究表明[8-9]:与基液相比,纳米流体具有较高的换热系数,且没有带来过大的额外压降损失。目前,关于纳米流体的流动与传热机理还存在许多分歧。Bowers等[10]对R-113在微通道内的流动沸腾压降进行了比较研究,结果表明:当进入旺盛核态沸腾后,随着外加负荷的增加,微通道内的压降突然增加,表现出与常规尺度完全不同的压降特性。Ravigururajan[11]发现:当换热系数很高时,质量流速对压降的影响不大;而当壁面过热度升高时,换热系数随之下降,此时压降急剧升高,认为这是通道内产生大量气泡的缘故。本文作者主要研究Al2O3-H2O纳米流体在当量直径分别为0.923,1.333和2.0 mm的矩形微通道中的流动与换热特性,分析不同流量、不同热流密度、不同体积分数以及雷诺数Re对流体流动和换热的影响。
1 实验设备与方法
1.1 实验系统
实验系统如图1所示。实验段槽道竖直安放在实验架上,实验工质在水箱中被加热到预定温度,并通过PID温控仪保持温度恒定,然后经热水泵输送,一部分经旁通阀回流到水箱,另一部分经转子流量计通过试验段后返回到水箱。转子流量计适用于介质温度为0~120 ℃,量程为0~100 L/h,测量误差在1%以内。为防止意外混入实验工质的较大粒径的杂质进入试验段堵塞槽道,实验工质先经过过滤网以去除较大粒径固体杂质,但是,纳米流体中的纳米级粒子却可以顺利通过过滤网。试验段设有温度和压力传感器,实验数据由数据采集模块实时读取并保存。
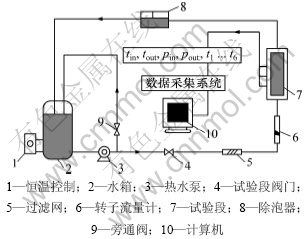
图1 实验系统示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of test device
试验段结构如图2所示。微槽主体材料为铝,矩形通道采用电火花线切割机床加工,加工精度达6级以上。进出口测温采用铠装型Pt1000热电阻,壁面测温采用6个铠装型Pt100热电阻,其精度都为0.1%;进出口压力变送器的量程为0~100 kPa。加热板和微槽主体之间通过导热硅脂均匀连接,整个试验段由保温棉包裹,以减少热量损失。试验段参数如表1所示。表1中:L为槽道长度;n为试验段内槽道个数;Dε为槽道当量直径;δ为壁面测温孔对之间的距离,试验段开有3对壁面测温孔,并且上面一排壁面测温孔距槽底壁面的距离为δ′;Wch,Hch和Ww分别为槽道宽、高和槽道间距。

图2 试验段结构图
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of test section
表1 3种试验段的几何参数
Table 1 Geometric parameters of test section

1.2 纳米流体的配置及其热物理性质
先在水中加入一定量的醋酸,然后添加纳米颗粒,采用超声振荡使粒子均匀地分散在基液中。A12O3纳米颗粒为球形,粒径为20~30 nm,实验配置了0.1%和0.5%(体积分数)的纳米流体,并分别称为纳米流体1和纳米流体2。由于纳米颗粒的加入,纳米流体相对与基液其输运参数也产生了变化。
密度为[12]:
 (1)
(1)
比热容为[13]:
 (2)
(2)
黏度为[14]:
 (3)
(3)
使用LVDV-Ⅱ型旋转黏度计对纳米流体的实际黏度进行测量,并对式(3)进行修正:
 (4)
(4)
导热系数为[15]:
 (5)
(5)
其中:φ为纳米颗粒体积分数;角标nf,f和p分别代表纳米流体、基液和纳米颗粒。
A12O3-H2O纳米流体热物性参数如表2所示。
表2 A12O3-H2O纳米流体热物性参数
Table 2 Thermophysical properties of nanofluids

2 实验结果及分析
2.1 强制对流传热
在实验前,首先对实验系统进行热平衡计算,计算电加热板输入功率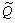 和实验工质获得的热功率
和实验工质获得的热功率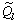 的偏差,工质吸收的热量
的偏差,工质吸收的热量 。其中:
。其中: 为质量通量;(cp)nf为工质的比定压热容;tin和tout分别为工质的进口温度和出口温度。热平衡偏差为[16]:
为质量通量;(cp)nf为工质的比定压热容;tin和tout分别为工质的进口温度和出口温度。热平衡偏差为[16]:
 (6)
(6)
经计算,热平衡偏差在6%内。工质与微通道壁面间的平均换热系数h为:
 (7)
(7)
其中: 为传热总面积;Δtm为微通道壁面与工质间的平均温差。由于热平衡偏差在6%内,因此,可以忽略侧壁面的散热而认为槽道基底为一维热传导。由于铝的导热性较好,因此可以假设某一横截面处,微通道四周壁面的温度相等[1]。通过以上简化,可计算槽道底部壁面处的温度
为传热总面积;Δtm为微通道壁面与工质间的平均温差。由于热平衡偏差在6%内,因此,可以忽略侧壁面的散热而认为槽道基底为一维热传导。由于铝的导热性较好,因此可以假设某一横截面处,微通道四周壁面的温度相等[1]。通过以上简化,可计算槽道底部壁面处的温度 :
:
 (8)
(8)
其中:Δti为第i对壁面测温孔测得的温度差;ti1为第i对壁面测温孔靠近槽道底部的传感器测得的温度,i取值为1,2和3。因此Δtm定义为:
 (9)
(9)
雷诺数Re为:
 (10)
(10)
 (11)
(11)
其中:u为流体平均流速。努塞尔数Nu表示对流传热系数与导热系数的比率,其计算如下:
 (12)
(12)
以下各图中数据使用的都是经3次重复实验所采集的平均值。热流密度为34.75 kW/m2,tin=60 ℃时平均换热系数与流量的关系如图3所示。从图3可以看出:质量流量对传热系数影响较小;在2.0 mm宽的槽道中,与水的换热系数相比,纳米流体2的换热系数提高了近18%;在1.0 mm宽的槽道中,提高了12%;在0.6 mm宽的槽道中,提高了8%。这说明随着槽道尺寸的减小,与水相比,纳米流体强化传热的效果不再那么明显。而0.6 mm宽槽道的换热系数比2.0 mm宽槽道的换热系数高2倍以上。即当槽道当量直径减小时,由于槽道尺寸的减小带来的强化传热起主导作用,而纳米颗粒强化传热的效果不再那么明显,这与文献[17]的预测结果相同。因此,若能将槽道尺寸做得足够小,就可以不再使用纳米流体作为强化传热的方式,尤其当温度接近工质饱和温度时,纳米颗粒易产生沉降和吸附[17]。而Chen等[18]在当量直径为158 μm的槽道中,以体积分数为0.2%~0.4%的CuO-H2O纳米流体进行对流换热,结果显示:在较低流量下,纳米流体的对流换热能力较强,能带走更多的热量;随着流量的增大,换热能力只与流量有关,而纳米颗粒强化换热的作用不再明显。平均换热系数与热流密度的关系如图4所示。图4可以看出:在实验范围内,换热系数与热流密度呈线性增长,并且槽道越小,增长趋势越快。不同宽度槽道中,努塞尔数Nu与雷诺数Re的关系如图5所示。从图5可以看出,在实验范围内,Nu随Re的增大而增大,纳米流体的Nu比去离子水的Nu大,这与[17]的结果一致。Ho等[6]在截面为0.800 mm×0.283 mm(长×宽)矩形通道中以0,1%和2%(体积分数)的纳米流体进行实验,纳米流体的Nu相对于水的Nu提高了40%左右;而与水相比,图5中纳米流体的Nu仅提高10%,可能是由于纳米流体2的体积分数较小,仅为0.5%。

图3 平均换热系数与流量的关系
Fig.3 Relationship between average heat transfer coefficient and flow in different channel with different working fluid

图4 平均换热系数与热流密度的关系
Fig.4 Relationship between average heat transfer coefficient and heat flux density in different channel with different working fluid
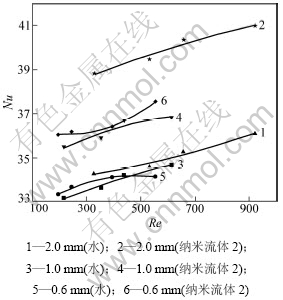
图5 不同宽度槽道中努塞尔数与雷诺数的关系
Fig.5 Relationship between Nu and Re in different channel with different working fluid
2.2 无相变阻力特性试验
分别采用体积分数为0.1%和0.5%的纳米流体为试验工质,进口温度为60 ℃,测试其在3种槽道下的阻力特性。试验测得的压力包括3部分:(1) 在微通道进出口处,流道突然缩小与扩大产生的局部压差;(2) 由于槽道竖直安放,工质自下往上流动,因此存在由重力引起的压力降;(3) 所测量压差的主要部分是沿程损失。因此,有如下关系:
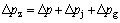 (13)
(13)
其中:Δpz为测量的总压力降;Δpj为局部压力降;Δpg为重力引起的压力降;Δp为槽道沿程压力降,并且:
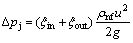 (14)
(14)
 (15)
(15)
其中:ξin取0.5,为管入口阻力系数;ξout取1,为管出口阻力系数;g为重力加速度。经计算得局部压力降Δpj很小,可以忽略不计。并且摩擦阻力系数f可由下式计算:
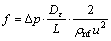 (16)
(16)
图6所示为槽道压降与雷诺数关系的拟合曲线。从图6可以看出:单个槽道的摩擦压降随雷诺数的增大而增大,并且在实验范围内呈一次线性关系;随着槽道尺寸的减少,压降显著增加,当雷诺数Re为600时,1.0 mm宽槽道压降比2.0 mm宽槽道压降增大了4.7倍,0.6 mm宽槽道压降比2.0 mm宽槽道的压降升高了24.4倍,并且0.6 mm宽槽道压降随雷诺数的增加而显著增大,即若增加流量,则槽道中的压降显著增加,若减小槽道尺寸,流动压降也显著增加。在相同雷诺数下,纳米流体1比纳米流体2的压降略小,但相差不大,这与文献[8-9]中的结论一致,纳米颗粒的加入并不会带来过大的压降损失。图7所示为摩擦阻力系数随雷诺数的关系曲线。可见:摩擦阻力系数随雷诺数Re的增大而减小,并且2.0 mm槽道的泊松数接近64;在相同雷诺数下,0.6 mm宽槽道摩擦阻力系数最大,2.0 mm宽槽道的摩擦阻力系数最小。通过对每条曲线的趋势进行拟合得出泊松数与3种槽道的关系如表3所示。Ho等[6]在截面为0.800 mm×0.283 mm矩形通道中和Wu等[17]在当量直径为0.194 5 mm的微通道中,使用Al2O3-H2O纳米流体作为工质,获得了类似的结论。
2.3 沸腾阻力特性试验
进行沸腾换热实验时,首先将水箱中的纳米流体加热到接近沸腾的95 ℃,调整试验段底部加热板电功率,然后调节旁通阀和试验段阀门,由小到大缓慢改变工质流量,待系统状态稳定后,采集温度、流量和压力数据。采集完所有流量状态的数据后,再调整加热板功率,所有状态测试完毕后,更换槽道重复实验过程。进入微通道的工质处于过冷状态,因此,通道中工质的流动通常有单相流段Lsub和两相流段Ltp。 Lsub可由下式计算[19]:
 (17)
(17)
其中:W为整个微槽试验段总宽度;tsat为介质的饱和温度;qeff为有效热流密度,
 (18)
(18)

图6 不同槽道中压降与雷诺数的关系图
Fig.6 Relationship between Re and Δp in different channel with different working fluid
表3 不同槽道中流体泊松数
Table 3 Poisson number of fluid in different channels
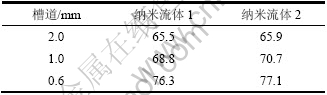
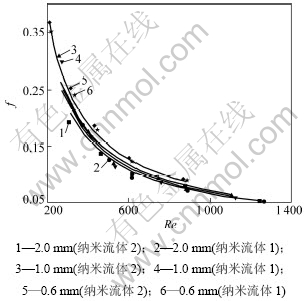
图7 摩擦阻力系数与雷诺数关系图
Fig.7 Relationship between Re and f
因此,单个微通道中两相段长度为:
Ltp=L-Lsub (19)
出口干度xout可由下式求得[19]:
 (20)
(20)
其中:C为槽道截面周长;z为所计算点处距入口的距离;Δh1g为水的汽化潜热。同时,沸腾试验的重力压降也分单相段的重力压降Δpg,sp和两相段的重力压降Δpg,tp,由于 ,因此,两相实验的重力压降Δpg为[19]:
,因此,两相实验的重力压降Δpg为[19]:

 (21)
(21)
其中:ρcm为流量密度,ρg和ρl分别为气相和液相的密度。又由式(20)得 ,因此,式(21)为:
,因此,式(21)为:

扣除重力压降Δpg后,两相段长度的压降由加速度压降和摩擦压降组成:
 (22)
(22)
且
 (23)
(23)
式中:Δpsp为单相段压降;Δptp为两相段压降。可将式(16)中的L改为Lsub,摩擦阻力系数采用单相阻力特性,从而求得Δpsp。加速度压降Δptp,a[20]为:
 (24)
(24)
 (25)
(25)
其中:vl和vg分别为液相和气相的比容;αout为空饱率。图8所示为两相压降与热流密度的关系,其中进口温度为95 ℃。从图8可以看出:随着热流密度、质量流量以及纳米颗粒体积分数的增大,两相摩擦压降也增大;对于流量为154 kg/(m2·s)的纳米流体1,当热流密度为42 kW/m2时,3种槽道的压降分别为1.2,2.7,7.0 kPa;当热流密度为50 kW/m2时,3种槽道的摩擦压降分别为1.5,3.0,12.0 kPa。可见:随着槽道尺寸的减小,两相摩擦压降成倍增加,并且小槽道内两相摩擦压降随热流密度和质量流量的增大而显著增大。
2.4 误差分析
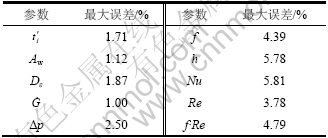
在实验过程中产生误差的因素较多,环境温度的变化对实验有加热或降温作用,因此,实验采取了严格的保温措施。根据实验仪器的测量精度,可得尺寸、温度、压力和流量等参数的最大误差。同时,利用误差传递原理计算Nu,Re和摩擦阻力系数等的最大误差,具体结果如表4所示。

图8 两相摩擦压降与热流密度的关系
Fig.8 Relationship between two-phase frictional pressure drop and heat flux density in different channels
表4 直接测量和间接测量参数的误差
Table 4 Measured and deduced parameter errors
3 结论
(1) 在实验范围内,质量流量对传热系数的影响较小,最大流量相对于最小流量提高的传热系数低于2%。努塞尔数随质量流量的增加而增大。但是,随着流量的增大,摩擦压降成倍增加。
(2) 在沸腾流动下,当热流密度为50 kW/m2、流量为154 kg/(m2·s)时,1.0 mm宽槽道内纳米流体1的两相摩擦压降比2.0 mm宽槽道的大2倍,0.6 mm宽槽道的两相摩擦压降比2.0 mm宽槽道的大8倍,在同一槽道内,两相摩擦压降随着热流密度、质量流速的增大而增大。
(3) 随着槽道尺寸的减小,尺寸效应变得明显。0.6 mm宽槽道的换热系数比2.0 mm宽槽道的换热系数高2倍以上。当工质流量、热流密度增加时,小槽道的压降显著增大。在单相流情况下,2.0 mm宽槽道的泊松数为65.5,最接近经典理论值的64,而其他2种槽道泊松数分别为68.8和76.3。
参考文献:
[1] Tuckerman D B, Pease R F W. High-performance heat sink for VLSI[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 1981, 2(5): 126-129.
[2] Kandlikar S G. Fundamental issues related to flow boiling in minichannels and microchannel[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2002, 26: 389-407.
[3] Choi S U S, Eastman J A. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles[C]//International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exhibition, San Francisco, 1995: 12-17.
[4] Wang B X, Peng X F. Experimental investigation on liquid forced-convection heat transfer through microchannels[J]. Int J Heat and Mass Transfer, 1994, 37: 73-82.
[5] Morini G L. Single-phase convective heat transfer in microchannels: A review of experimental results[J]. Int J Thermal Sci, 2004, 43(7): 631-651.
[6] Ho C J, Wei L C. An Experimental investigation of forced convective cooling performance of a microchannel heat sink with Al2O3-water nanofluid[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2010, 30: 96-103.
[7] WEN Dong-sheng, DING Yu-long. Experimental investigation into convective heat transfer of nanofluids at the entrance region under laminar flow conditions[J]. Int J Heat and Mass Transfer, 2004, 47(24): 5181-5188.
[8] CHEN Rei-yu, HUANG Guan-ming. Analysis of microchannel heat sink performance using nanofluids[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2005, 25(17): 3104-3114.
[9] Daungthongsuk W, Wongwises S. A critical review of convective heat transfer of nanofluids[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2007, 11(5): 797-817.
[10] Bowers M B, Mudawar I. High flux boiling in low flow rate, low pressure drop mini-Channel and micro-channel heat sink[J]. Int J of Heat Mass Transfer, 1994, 37(2): 321-332.
[11] Ravigururajan T S. Impact of channel geometry on two-phase flow heat transfer characteristics of refrigerants in microchannel heat exchangers[J]. J Heat Transfer, 1998, 120(2): 485-491.
[12] Drew D A, Passman S I. Theory of multicomponent fluids[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1998: 1-235.
[13] Xuan Y, Roetzel W. Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids[J]. Int J Heat and Mass Transfer, 2000, 43(19): 3701-3707.
[14] Batchelor H C. The effect of brownian motion on the bulk stress in a suspension of spherical particles[J]. Fluid Mech, 1977: 83-97.
[15] Maxwell J C. A treatise on electricity and magnetism[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Oxfor University Press, 1904: 435.
[16] 费业泰. 误差理论与数据处理[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1995: 1-200.
FEI Ye-tai. The theory of error and data processing[M]. Beijing: China Mechine Press, 1995, 1-200.
[17] WU Xin-yu, WU Hui-ying. Pressure drop and heat transfer of Al2O3-H2O nanofluids through silicon microchannels[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2009, 19(10): 1-10.
[18] Chen R, Chuang J. Experimental microchannel heat sink performance studies using nanofluids[J]. Int J Therm Sci, 2007, 46: 57-66.
[19] 鲁钟琪. 两相流与沸腾传热[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2002: 1-310.
LU Zhong-qi. Two-phase and boiling heat transfer[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2002: 1-310.
[20] Mishima K, Hibiki T. Some characteristics of air water two-phase flow in small diameter vertical tubes[J]. Int J Multiphase Flow, 1996, 22: 703-712.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2011-08-01;修回日期:2011-11-24
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(20676039)
通信作者:罗小平(1967-),男,江西南昌人,教授,从事微尺度相变传热机理方面的研究;电话:020-22236616;E-mail:mmxpluo@scut.edu.cn