文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-01-0162-09
铝电解槽电解质与内衬换热系数的数值计算
杨 帅,李 劼,张红亮,邹 忠,赖延清
(中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:铝电解槽内电解质与内衬界面传热系数直接决定电解槽热平衡。基于多相流理论及壁函数方法,建立了铝电解槽电解质与内衬界面的换热系数计算数学模型,在商业数值计算软件上实现对传热推动力、传热系数分布的计算。研究结果表明:阳极气泡的作用处于主导地位,但电磁力的作用也不能被忽略,在进行换热系数计算时,需同时考虑二者的共同影响;在电解槽的大面及小面槽帮处,换热系数的分布主要受电解质流动的影响,而对于阳极底部则由于气泡层的阻碍使得此区域的传热系数较小;阳极开槽会增大电解质与阳极的换热系数,但会一定程度上减小电解质与槽帮的换热系数。
关键词:铝电解槽;数值计算;换热系数
中图分类号:TF821 文献标志码:A
工业铝电解槽是一个巨大的热生成器,由电能转化而成的热量维持了电解所需的温度。热量的生成区域集中在阳极与铝液间的极间电解质层,来源主要包括电解质的欧姆压降和气泡压降。极间产生的热量随着电解质和气泡的流动而向外传递,热量向槽外传递过程的第一步就是电解质与包括阳极、槽帮伸腿、铝液等界面的对流传热。热量只有在经过正常的对流传热进入内衬后,才能经过内衬材料的热传导而流向槽外表面,继而通过槽外表面换热最终散失到环境中。由于通过气泡逸出、阳极更换以及出铝等操作带走少部分热量外,几乎其他所有的热量都需要经过电解质与内衬的换热,因此,弄清楚电解质与内衬的换热状况也是电-热场仿真的必要条件[1-3]。
为了获得电解质与内衬的换热系数,许多研究者在此方面展开了相关的实验或模拟研究。SOLHEIM[4]总结了国际上对于电解槽内电解质与槽帮进行对流换热的研究结果,结果表明:在1980年代中期以前,研究者所获得的结果普遍在500 W/(m2·K)以下,而在之后,大部分的研究者所获得的结果都在其两倍以上,作者认为这很难以解释。但可以考虑到,槽型升级和工艺变化在一定程度可以解释这种区别。KHOKHLOV等[5]基于SOLHEIM等[6]对于电解质传热系数的实验数据进行了反推,建立了一种半经验模型对电解质与槽帮、铝液的传热系数计算。然而在其模型中,没有能够体现磁流体运动的影响,因此很难解释电解质的流动对于传热系数的影响,也就难以解释为何其计算所得的数据相对于前人的研究要大一些。BECH等[7]通过运用CFD方法建立了铝电解槽电流分布与对流的数值计算模型,对其电场与热场进行了数值计算,其计算结果验证了KHOKHLOV等[5]所建立的半经验模型在其所研究槽型上的准确性,但并未对槽型间的差别进行分析。SEVERO等[8-9]等提出了用数值仿真的方法进行铝电解槽熔体与槽帮的对流换热进行计算,并且对部分结构参数对于换热系数的影响做了分析。其计算结果与实测值对比发现与实测结果吻合良好,但对于电解质部分与内衬的换热考虑不周全,忽略了电磁力的作用及气泡层所带来的阻碍问题。DUPUIS等[10-11]认为,在500 kA铝电解槽的熔体与槽帮的传热系数应该在2000 W/(m2·K)以上,因此,其提出一个基于TAYLOR等[12]以及FLETCHER[13]研究成果的假推公式用以计算这部分的换热系数,但也并未对其计算结果进行足够的影响因素分析。WANG等[14]研究了换极对于电解质与内衬传热的问题,但并未给出内衬换热系数的具体计算方法。虽然上述研究都深刻认识到了电解质与内衬传热的重要性,然而在获得这部分换热系数的研究中,绝大多数均未能考虑到实际工业电解槽内极为复杂的流动因素,或者是在进行新电解槽设计过程中无法通过理论计算得到结果以辅助电解槽的热平衡设计,特别是对推动电解质流动的电磁力与气泡运动的作用未进行深入的分析,难以通过理论的计算评估电解槽磁-流场设计对于热平衡的影响。因此,在实际的铝电解槽热场仿真与设计中,电解质与内衬换热系数的设定仍然不能考虑本身所开发电解槽特性的影响。
为了更为准确和完善地计算铝电解槽与内衬的换热系数从而进行电解槽的完整电-热场模拟,本文作者通过建立铝电解槽电解质与内衬界面换热系数数学模型,以某500 kA电解槽的实例实现对电解质与内衬界面换热系数的仿真计算,并对推动电解质运动的电磁力因素与气泡因素对计算结果的影响进行了分析,并以阳极开槽对于换热系数的影响进行了数值计算,结果可为铝电解槽的电-热场设计提供必要的理论与工具支撑。
1 电解质与内衬换热的数学建模
1.1 电解质与内衬传热过程及其简化
铝电解槽内的流体是一种典型的多相流体,包含连续的电解质与铝液相、离散的阳极气泡相和氧化铝颗粒相,本文作者采用欧拉-欧拉法描述电解质的流动。此外,基于欧拉-欧拉法的多相流模型又可分为均相模型和非均相模型两种。前者假定相间曳力足够大,计算区域内除温度场和各相体积分数外,所有相的速度场、压力场和其他标量场均相同。然而铝电解内流体的行为存在明显差异,不符合均相模型的前提,因此需要采用非均相模型进行研究。
基于上述阐述,数学模型可以进行一定的假设与简化,电解质可视为恒温的不可压缩流动,且槽帮形状保持恒定;阳极底掌平整,极距保持恒定;阳极气体为具有相等直径的气体颗粒,故可处理为离散相。因此,本模型中包含有连续电解质相和离散阳极气泡相,又由于热量主要产生在电解质内,电解质本身与铝液存在相间对流传热,因此把电解质与铝液的相界面换热系数也考虑在内。
1.2 流体流动数学物理方程
基于欧拉-欧拉法的电解质-气泡两相流模型通过求解由简化的时均Navier-Stokes方程组所表述的质量守恒、动量守恒以及能量守恒三项基本规律模拟三维的电解质-气泡两相流,其中质量守恒、动量守恒的数学表达式的微分形式可表述为
 (1)
(1)
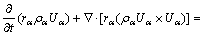
 (2)
(2)
式中:rα、ρα、μα, eff、Pα和Uα分别表示α相的体积分数、密度、有效黏度、压强和流速;其中有效黏度为分子黏度μα和湍流黏度μT之和;Mα为相与相之间的内部表面作用力;Sα为外部体积作用力。
用于进行电解质与内衬界面换热系数计算的模型包括了电解质相和阳极气泡相。槽内电解质相所受的外部作用力除重力场引起的浮力外主要是由电磁场与导电流体作用产生的电磁力FEM,内部作用力主要是电解质和气泡间的相间曳力Mb。b为电解质相,p为阳极气泡相,可以对各相所受的力进行描述,具体如式(3)~(5)所示:
 (3)
(3)
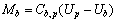 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
式中:Cb,p可认为是电解质与气泡之间的摩擦因数,与多相流中离散相颗粒对连续向的曳力计算理论对比可对Cb,p进行计算,计算方法如式(6)所示。
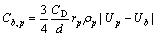 (6)
(6)
式中:CD本为无量纲曳力系数。
式(3)中的电磁力是本模型最为重要的外作用力,通过对电解槽的电磁场进行仿真可以获得电解质区域的电场J和磁场分布B,应用式(7)可计算获得电磁力:
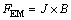 (7)
(7)
此外,在考虑流体流动与传热的关系时,流体还服从能量守恒定律,因此,本模型的流体相能量方程形式可以简化为如式(8)所示:
 (8)
(8)
式中:T、cp、λ、μT分别表示流体的温度、定压比热容、导热系数和湍流黏度;σT湍流普朗特数,按经验可取0.9~1.0;Q为流体的热源项。
1.3 流体流动湍流模型
本文作者采用均相标准k-ε湍流模型,湍动能k及湍流耗散率ε可通过联立式(9)~(10)获得:
 (9)
(9)
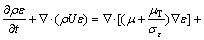
 (10)
(10)
其中:
 (11)
(11)
 (12)
(12)
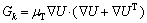 (13)
(13)
式中:经验常数cμ=0.09,C1=1.44,C2=1.92,σk=1.0,σε=1.3。
1.4 近壁面传热与壁函数
由于流体的流速在固体壁面附近迅速下降并直至趋于零,因而在近壁面区域的流动状况与流体主体有很大的区别,其湍流状况不再适合使用描述流体主体的高雷诺数的k-ε湍流模型进行近壁面流动的描述,一般采用壁函数对流体流动的边界层进行近似处理[15]。
对于铝电解槽电解质与内衬的换热来说,可以用牛顿表面冷却定律进行理论上的描述和计算,其表达形式如式(14)所示。
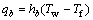 (14)
(14)
式中:qb、hb、Tw和Tf分别为热流密度、换热系数、表面温度和流体温度,本文作者所要研究的,就是如何利用数值仿真方法求解电解质与内衬界面换热系数hb的问题。
在近壁面的流体边界层内部,流体的温度可用无量纲温度T+表示,它在边界层中服从黏性子层的对数分布,表达形式如式(15)所示:
 (15)
(15)
式中:ρ、cp和uτ分别为流体的密度、定压比热容和黏性子层内的无量纲摩擦速度。对式(15)进行变化可得式(16)。
 (16)
(16)
对比式(15)和式(16)可获得换热系数hb的计算式(17)。
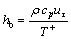 (17)
(17)
采用壁函数时,在近壁面处的黏性子层内不进行网格划分,把离壁面最近的第一层节点划分在流体的旺盛湍流区域内,其无量纲近壁面流速服从对数分布,表达式如式(18)所示。
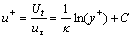 (18)
(18)
式中:κ为冯·卡门系数,取0.4~0.42;y+为无量纲近壁距离;C为与壁面粗糙度相关的经验常数一般取值4.9~5.6,本处取值为5.2;Ut为在壁面距离Δy处的切向速度,其来源为来自于流场计算值。其中Δy的值并非实际的物理距离,其定义在k-ε湍流模型中的表达式如式(19)所示:
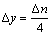 (19)
(19)
式中:Δn为壁面与近壁面第一层节点的距离。
此外,无量纲近壁距离y+的计算方法如式(20)所示:
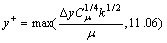 (20)
(20)
根据式(19)和式(20),并结合流场的强湍流区的计算结果,则可以对式(18)进行化简求出uτ。
与近壁面处的黏性子层内的流速规律一致,无量纲温度T+同样符合对数分布,其计算方法在不同的湍流模型中有不同的形式,根据KADER等[16]的研究,在k-ε湍流模型中的定义如式(21)~(22)所示:
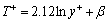 (21)
(21)
 (22)
(22)
式中:Pr为普兰特数,计算方法如式(23)所示:
 (23)
(23)
结合近壁面的修正k-ε湍流模型,以及在旺盛湍流区域内求出的Ut,电解质与内衬界面的换热系数hb可以得到求解。此外,由于在阳极周围存在着气泡的流动,因此,阳极部分表面会被气泡所覆盖,使得该部分电解质微观上与阳极的接触并不充分,更重要的是这部分电解质已经不是纯电解质而更类似于气泡与电解质混合的中间相。对此种情况下的换热系数尚无标准方法描述,本文作者提出一种简化方法计算此种情况下的综合换热系数(h),形式如式(24)所示:
 (24)
(24)
式中:hb、hp分别为电解质和气泡与阳极的换热系数;rb、rp分别为换热面处的电解质与气泡的体积分数。
1.5 材料属性与边界条件
由上述分析可知,需要给定的材料属性包括电解质和阳极气泡的密度、分子黏度、热容、导热系数。然而对于电解质来说,由于其组分差异较大,因此,需要对特定的计算对象设定符合其材料属性的特定取值[17]。
电解质流动及其与内衬界面的综合换热系数hc计算模型的边界条件见表1。
表1 计算换热系数的边界条件
Table 1 Boundary conditions of calculation for heat transfer coefficient

2 换热系数的数值计算实现
2.1 数值计算方法简介
以上建立的铝电解槽电解质与内衬界面换热系数计算模型需要对电解质所受的电磁力进行考虑,此电磁力通过利用电磁场的数值仿真所获得的电场和磁场进行计算。随后在商业数值计算平台上导入建立的电解质区域网格,依据前述模型进行相应设置,实现对模型的数值计算。
2.2 模型应用实例
以某500 kA槽为研究对象,实现对于电解质与内衬界面的换热系数计算。建模及计算中所需的基本结构与工艺参数如表2。
表2 500 kA槽基本结构与工艺参数
Table 2 Structure and process parameters of 500 kA cell

在计算阳极气泡的质量源时,阳极气体主要由CO2和CO组成,通常CO2的体积分数约为75%~80%,CO的体积分数约为20%~25%,本文作者取CO2的体积分数78%,CO的体积分数为22%,利用式(25)即可计算的质量流量。对于阳极气泡的当量直径,参考前人的研究取在2 cm[18]。实例500 kA槽电解质与内衬 界面换热系数计算网格如图1所示。
在以上所述的基础上,对该500kA槽的电解质与内衬界面换热系数进行计算,获得电解质与内衬界面换热系数的分布结果。图2所示为计算所得的整个电解质区域与内衬在界面上的综合换热系数分布。
 (25)
(25)

图1 500 kA槽电解质与内衬界面换热系数计算网格
Fig. 1 Computational mesh of bath-lining heat transfer coefficient for 500 kA cell

图2 500 kA槽电解质与内衬界面换热系数分布
Fig. 2 Bath-lining heat transfer coefficient distribution in 500 kA cell
由图2可知,整个换热区域的换热系数大小差异较大,最大值约为2947 W/(m2·K)。同时,从图2中可知,换热系数在不同的换热区域体现出不同的分布特性,例如在阳极底部区域的换热系数大部分分布在300 W/(m2·K)左右;对于与大面槽帮的换热界面,换热系数则大部分分布在1300~1900 W/(m2·K)左右。由于本文作者主要关注建模电解质与内衬换热系数的建模方法,因此,并未对换热系数的分布特征进行深入分析,讨论重点主要集中在对于换热系数建模过程中影响因素的探讨。
3 电解质与内衬换热推动因素分析
为了探索电解质与内衬的换热过程的特征,解释其对流换热情况的深层次原因,需要对电解质与内衬换热的推动因素进行研究。本文作者分别计算500 kA电解槽在仅电磁力、仅阳极气泡以及两者共同作用下的电解质与内衬界面换热系数的特征,探索二者在推动槽内传热过程中所起的作用。
3.1 电磁力作用下的槽内换热系数
不考虑阳极气泡相的存在,在仅有电磁力作用计算得到电解质与内衬界面的换热系数分布,并以电解质与阳极底部的换热系数进行分析。图3所示为仅考虑电磁力作用时的电解质与阳极底部换热系数分布,图4为极间距离阳极底面7 mm截面上的电解质流速分布。
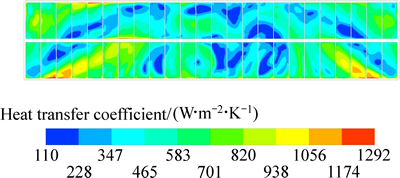
图3 仅电磁力作用时电解质与阳极底面换热系数分布
Fig. 3 Bath-anode bottom heat transfer coefficient distribution under EMFs driving
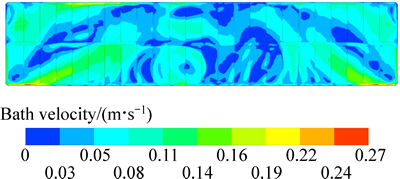
图4 仅电磁力作用时距阳极底面7 mm截面上的电解质流速分布
Fig. 4 Bath velocity distribution in 7 mm below anode bottom under EMFs driving
由图3可知,仅电磁力作用时500 kA槽电解质与阳极底面的换热系数最大值为1292 W/(m2·K),最小值为110 W/(m2·K);从换热系数分布的绝对值上来看分布的不均匀,并且几乎没有任何规律;从换热分布的数值区间来看,换热系数分布范围不集中,但换热系数大于1000 W/(m2·K)的换热区域面积占比较小,大部分分布在110~1056 W/(m2·K)的范围内,区域平均换热系数为501 W/(m2·K)。此外,对比图3和4可知,电解质的流动形态与电解质与阳极底部的换热系数形态具有很强对应性,并且在大小上具有正相关关系,电解质流速大的部位对应的换热系数也较大。因此,电磁力推动电解质运动是一项影响对流换热系数的重要因素,其分布对于电磁力的作用有高度依赖性。
3.2 阳极气泡作用下的槽内换热系数
不考虑电磁力的作用,在仅有阳极气泡作用时计算得到电解质与内衬界面的换热系数分布。图5所示为仅考虑阳极气泡作用时的电解质与阳极底部换热系数分布,图6所示为极间距离阳极底面7 mm截面上电解质的流速分布。
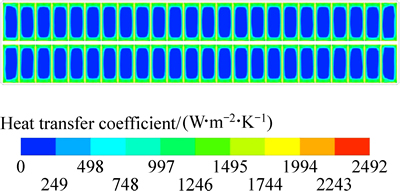
图5 仅气泡作用时电解质与阳极底面的换热系数分布
Fig. 5 Heat transfer coefficient distribution of bath-anode bottom of under bubble driving
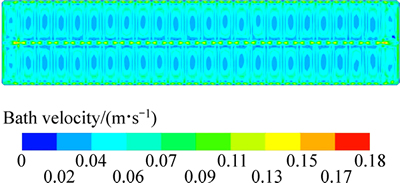
图6 仅气泡作用时距阳极底面7 mm截面上的电解质流速分布
Fig. 6 Bath velocity distribution in 7 mm below anode bottom under bubble driving
由图5可知,仅阳极气泡作用时,500 kA槽电解质与阳极底面的换热系数最大值为2492 W/(m2·K),最小值为0,相对于仅电磁力作用时最大值几乎大了一倍,较小部分区域也更大;从换热系数分布的绝对值上来看分布的很不均匀,但存在阳极底部投影区的中部位置较小,边缘逐渐增大的规律;从整体分布形态上看,换热系数的分布左右或者上下对称;从换热分布的数值区间来看,换热系数分布范围较为分散,但阳极底部大部分区域的换热系数小于250 W/(m2·K);整个区域的平均换热系数为482 W/(m2·K)。对比图5和6可知,在仅有阳极气泡作用下,电解质的流动形态与电解质与阳极底部的换热系数形态具有一定的对应性,但这种联系仅体现在趋势上的一致性。这是由于气泡在阳极底掌的积存,导致此部分的实际流体介质已不单纯为熔融电解质,而是具有较高含量的气泡-电解质混合相。由于气泡已经达到较高的含量,流体的性质改变已经是不能忽略的因素,因此,这部分混合相与阳极底面的换热特征相对于纯电解质相已发生了巨大的变化,气泡的存在减弱了实际微观过程中此部分流体与阳极的接触性能及本身的传热性能,因而虽然临近此部分的电解质流速并不低,但换热系数相对纯的电解质要小一些。
3.3 气泡与电磁力共同作用下的槽内换热系数
由以上的分析可知,在仅考虑电磁力的作用,电解质与阳极底部的换热系数分布与近壁面的电解质流速存在紧密的正相关关系,表明电解质的流动是驱动热量向内衬传递的核心因素;然而在仅有阳极气泡作用时计算得到电解质与内衬界面的换热系数却由于气泡在阳极底部的积存效应而较小,其实质是气泡层的存在部分隔绝了电解质与阳极底面的接触或接触时间,这表明阳极底掌处积存在的气泡会在一定程度上减小电解质与阳极底部的传热性能。可以看出,两种因素的影响较为复杂,各有其特点,因此在进行槽内换热系数计算时,应对电磁力和阳极气泡同时考虑。表3为仅考虑电磁力作用、仅考虑阳极气泡作用以及考虑两者共同作用下的电解质与内衬界面换热系数在各区域的均值。
表3 不同推动因素计算所得的槽内各区域换热系数均值
Table 3 Average value of heat transfer coefficient in different areas under different driving factor

由表3可知,在仅考虑电磁力或仅考虑阳极气泡的作用时,电解质与阳极底部换热系数大小的计算值相差不大,总体在500 W/(m2·K)上下,表明虽然气泡是电解质运动的主要推动因素,但对于阳极底部的传热来说,气泡层的阻隔作用仍然是热量向阳极传递的重要阻力;对于大面槽帮、小面槽帮和熔体界面的传热系数,考虑阳极气泡或者两者同时考虑时计算值明显要大于仅考虑电磁力的作用,几乎达到仅电磁力作用时的2~3倍,表明气泡是驱动热量随电解质运动向内衬传递的最主要驱动力;在电磁力与阳极气泡两者同时考虑时比仅考虑阳极气泡作用的计算值要大,其中差异最小的是熔体界面处的传热系数,约大了1.4%,次之为大面槽帮处传热系数,约增大7.5%,差异最大的是小面槽帮处的换热系数,增大约14.8%,表明电磁力的作用也在不同程度上加强了热量向内衬的传递。从上述计算和分析来看,电磁力和阳极气泡都对热量向内衬结构的传递起了推动作用,其中阳极气泡的作用处于主导地位,但电磁力的作用也不能被忽略。因此,在进行电解质与内衬界面的换热系数计算时,需要对两者同时进行考虑。
3.4 阳极开槽对换热系数电解质与内衬换热系数的影响
考虑到500 kA电解槽使用1800 mm长、740 mm宽的大型阳极,假设不对阳极气泡的排放进行促进加强,可以想象将在阳极底部形成厚且大的气泡层,因此,在应用这种大型阳极碳块时一般会采取一些促进阳极气泡排放的措施,例如对阳极进行开槽。本文作者课题组[19]就阳极开槽对气泡排放的促进作用进行了一系列的研究,证明开槽得当时可以大量减少积存在电解质中的气泡。考虑对这种大型阳极碳块进行开槽处理,计算开槽对电解质与内衬界面换热系数的影响,图7所示为500 kA槽阳极开槽后电解质与阳极底部换热系数分布。

图7 500 kA槽阳极开槽后电解质与阳极底部换热系数分布
Fig. 7 Heat transfer coefficient distribution of bath-anode bottom in 500 kA cell after anodes cutting
比较图5与7可知,500 kA槽阳极开槽后电解质与阳极底部换热界面上的换热系数的分布形态与正常阳极基本一致,即在每个阳极的底掌中部位置,换热系数普遍较小,但换热系数较小的总面积要明显小于正常阳极;在每个阳极底掌的边缘位置,换热系数比中部位置要大得多,并且面积要大于正常阳极。这是由于在阳极开槽后气泡层的厚度和体积要小于正常阳极,因此,对此部分电解质的性质和传热能力的影响要相对而言小得多,从而可在界面出获得更大的换热系数。此外,表4所列为开槽与正常阳极两种情况下电解质与内衬界面的换热系数在各区域的均值。
表4 不同阳极槽槽内各区域换热系数均值
Table 4 Average value of heat transfer coefficient in different areas using different anodes
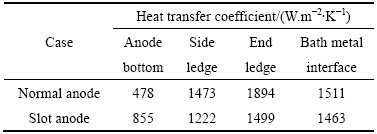
由表4可知,阳极开槽会在一定程度上影响电解质与内衬界面的换热系数。对于阳极底部来说,由于开槽会大量减少气泡在底掌处的积存,因此该区域的换热系数有所增大,在本500 kA槽的实例中换热系数由478 W/(m2·K)增至855 W/(m2·K),增大78.87%;对此,可以合理推测在进行阳极开槽后,顶部的保温应该得到适度的加强,才能弥补由于开槽所带来的散热部分变化;而对于大面槽帮和小面槽帮来说,阳极的开槽会减小电解质与槽帮的换热系数,幅度分别在17.04%和20.86%,从而减小了电解质向侧部的传热能力,这是由于气泡对电解质的搅动作用很强,开槽会加快气泡的排放因而减弱了气泡对阳极周围电解质流动的影响,致使这些区域换热系数减小;电解质与铝液间熔体界面的传热系数所受影响很小,这是由于气泡的运动轨迹主要是向上的,影响区域集中在气泡的流动区域,也即阳极块的周围,因而对气泡层以下区域电解质流动的影响相对较小的缘故。
4 结论
1) 基于多相流动理论、湍流模型以及壁函数结合的方法,同时考虑电磁力作用和气泡运动建立了铝电解槽电解质与内衬界面的换热系数计算数学模型,开展了500 kA铝电解槽熔体与槽帮与内衬换热系数的数值计算。
2) 电磁力和阳极气泡都对热量由电解质向内衬结构的传递起了推动作用,其中阳极气泡的作用处于主导地位,但电磁力的作用也不能被忽略,在进行电解质与内衬界面的换热系数计算时,需要对两者同时进行考虑。
3) 电解质与内衬界面的换热系数针对各个区域其分布特性不同,在槽的大面及小面槽帮处,换热系数的分布主要受电解质流动的影响,而对于阳极底部则会因为此部分流体中气泡含量较大而改变了区域的流体性质、减弱了实际微观过程中此部分流体与阳极的接触性能,使得此区域的传热系数较小。
4) 阳极开槽会减少气泡在底掌处的积存,从而增大此区域的换热系数;同时,开槽会加快气泡排放因而减弱阳极周围电解质流动,致使槽帮区域换热系数减小;而电解质与铝液间熔体界面的传热系数则由于受气泡影响较小而变化不大。
REFERENCES
[1] 李 劼, 张红亮, 徐宇杰. 现代大型铝电解槽内复杂物理场的仿真计算与优化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(10): 2594-2606.
LI Jie, ZHANG Hong-liang, XU Yu-jie. Simulated computation and optimization of comprehensive physical fields in modern large-scale aluminium reduction cells[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(10): 2594-2606.
[2] 杨 帅, 张红亮, 邹 忠, 赖延清, 李 劼. 铝电解槽槽体与环境界面换热系数的计算[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(2): 515-522.
YANG Shuai, ZHANG Hong-liang, ZOU Zhong, LAI Yan-qing, LI Jie. Calculation of heat transfer coefficient between aluminum reduction cell surface and surroundings[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(2): 515-522.
[3] 徐宇杰, 李 劼, 尹诚刚, 杨 帅, 张红亮, 吕晓军. 铝电解槽电-热强耦合建模方法[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(1): 239-245.
XU Yu-jie, LI Jie, YIN Cheng-gang, YANG Shuai, ZHANG Hong-liang,  Xiao-jun. Method of strongly coupled modeling and computing for thermal-electrical field in aluminium reduction cells[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(1): 239-245.
Xiao-jun. Method of strongly coupled modeling and computing for thermal-electrical field in aluminium reduction cells[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(1): 239-245.
[4] SOLHEIM A. Some aspects of heat transfer between bath and side ledge in aluminum reduction cells[C]//LINDSAY J. Light Metals 2011. San Diego, CA: TMS(The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 2011: 381-386
[5] KHOKLOV V A, FILATOV E A, SOLHEIM A, THONSTAD J. Thermal conductivity in cryolitic melts-new data and Its influence on heat transfer in aluminium cells[C]//WELCH B J. Light Metals 1998. San Antonio, TX: TMS(The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 1998: 501-506
[6] SOLHEIM A, THONSTAD J. Model experiments of heat transfer coefficients between bath and side ledge in aluminium cells[C]//ADKINS E M. Light Metals 1983. Atlanta, GA: Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1983: 425-435.
[7] BECH K, JOHANSEN S T, SOLHEIM A, HAARBERG T. Coupled current distribution and convection simulator for electrolysis cells[C]//ANJIER J L. Light Metals 2013. New Orleans, LA: TMS(The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 2013: 396-401.
[8] SEVERO D S, GUSBERTI V. A modeling approach to estimate bath and metal heat transfer coefficients[C]//BEARNE G. Light Metals 2009. San Francisco, CA: TMS(The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 2009: 557-562.
[9] GUSBERTI V, SEVERO D S, WELCH B J, SKYLLAS-KAZACOS M. Modeling the mass and energy balance of different aluminium smelting cell technologies[C]//SUAREZ C E. Light Metals 2012. Orlando, FL: TMS(The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 2012: 929-934.
[10] DUPUIS M, BOJAREVICS V. Weakly coupled thermo-electric and MHD mathematical models of an aluminum electrolysis cell[C]//KVANDE H. Light Metals 2005. San Francisco, CA: TMS(The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 2005: 449-454.
[11] DUPUIS M. Mathematical modelling of aluminum reduction cell potshell deformation[C]//JOHNSON J A. Light Metals 2010. Warrendale, PA: TMS(The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 2010: 417-422.
[12] TAYLOR M P, WELCH B J. The measurement of heat transfer coefficient between cryolite and ledge[J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1989, 18(2): 391-398.
[13] FLETCHER T E. The role of convective heat transfer in sidewall ledging[D]. Toronto, Canada: University of Toronto, 1995.
[14] WANG Q, LI B Q, FAFAD M. Effect of anode change on heat transfer and magneto-hydrodynamic flow in aluminum reduction cell[J]. JOM, 2016, 68(2): 610-622.
[15] 岑可法, 樊建人. 工程气固多相流动的理论[M]. 杭州: 浙江大学出版社, 1989.
CHEN Ke-fa, FAN Jian-ren. Engineering theory and calculation of the gas-solid multiphase flow[M]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Press, 1989.
[16] KADER B A. Temperature and concentration profiles in fully turbulent boundary layers[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1981, 24(9): 1541-1544.
[17] 冯乃祥, 孙 阳, 刘 刚. 铝电解槽热场、磁场和流场及其数值计算[M]. 沈阳: 东北大学出版社, 2001.
FENG Nai-xiang, SUN Yang, LIU Gang. The thermo, magnetic and fluid field and it’s numerical calculation in aluminum reduction cell[M]. Shenyang: Northeastern University Press, 2001.
[18] LI Jie, XU Yu-jie, ZHANG Hong-liang, LAI Yan-qing. An inhomogeneous three-phase model for the flow in aluminium reduction cells[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2011, 37(1): 46-54.
[19] 杨 帅, 张红亮, 徐宇杰, 张翮辉, 邹 忠, 李 劼, 赖延清. 铝电解槽预焙阳极开槽对气泡排出的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(12): 4617-4625.
YANG Shuai, ZHANG Hong-liang, XU Yu-jie, ZHANG He-hui, ZOU Zhong, LI Jie, LAI Yan-qing. Effects of slot cutting at prebaked anodes on bubble elimination in aluminum reduction cell[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(12): 4617-4625.
Numerical simulation of heat transfer coefficient between bath and lining in aluminum reduction cell
YANG Shuai, LI Jie, ZHANG Hong-liang, ZOU Zhong, LAI Yan-qing
(School of Metallurgy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The heat transfer coefficient between the bath and lining determines the heat balance in aluminum reduction cell. Based on the multiphase theory, turbulence model and wall function method, a numerical simulation model of heat transfer coefficient between the bath and lining was built and calculated in comercial codes. The heat transfer driving force and the heat transfer distribution were calculated. The results show that the anode bubbles are the main driving force, while the influence of electromagnetic force can’t be ignored, both of them need to be considered in the calculation of heat transfer coefficient. Moreover, the heat transfer coefficient is determined by the bath flow in cell sides and ends, while it is small in the anode bottom because of the obsturction effect of the anode bubbles. Anode cutting will increase the heat transfer coefficient between bath and anode, however, reduce the heat transfer coefficient between bath and aideledge.
Key words: aluminum electrolysis; numerical simulation; heat transfer coefficient
Foundation item: Project(61533020) supported by Key Project of National Nature Science Foundation of China; Project (51574289) supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2015CXS017) supported by Innovation-driven Plan in Central South University, China
Received date: 2015-12-28; Accepted date: 2016-04-25
Corresponding author: LI Jie; Tel: +86-731-88830474; E-mail: csulijie@123.com
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金重点资助项目(61533020);国家自然科学基金面上资助项目(51574289);中南大学“创新驱动计划”项目资助(2015CXS017)
收稿日期:2015-12-28;修订日期:2016-04-25
通信作者:李 劼,教授,博士;电话:0731-88830474;E-mail:csulijie@126.com