DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.09.048
铝基微通道内纳米流体饱和沸腾及可视化研究
罗小平,涂华营,邓君
(华南理工大学 机械与汽车工程学院,广东 广州,510640)
摘要:分别以去离子水及质量分数为0.3%,0.6%和0.9% Al2O3纳米流体为工质,在截面宽×高为0.3 mm×2.0 mm矩形铝基微通道内进行沸腾换热实验,并利用高速摄像仪进行可视化研究,分析热流密度、雷诺数、壁面粗糙度对流体传热系数的影响,探究流体流型变化与气泡生长规律。研究结果表明:纳米流体与去离子水的饱和沸腾传热系数随热流密度的增加而快速增大,努塞尔数Nu随雷诺数Re增大而增大但增幅不同,质量分数为0.3%,0.6%和0.9%的3种纳米流体的Nu比去离子水的Nu分别提高约8%,13%和16%;在相同热流密度及质量流速条件下,纳米流体与去离子水的传热系数均随传热壁面粗糙度的增加而增大;流体流型的变化呈现周期性,增大热流密度,可缩短气泡生长周期,泡状流比例增加。
关键词:微通道;纳米流体;传热系数;粗糙度;可视化
中图分类号:TK124 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)09-3520-07
Saturated boiling and visualization of nanofluids in aluminum-based microchannels
LUO Xiaoping, TU Huaying, DENG Jun
(School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China)
Abstract: The boiling heat transfer characteristics were experimentally investigated through aluminum-based rectangular microchannels with the size of 0.3 mm×2.0 mm, using Al2O3-H2O nanofluids with particle of 0, 0.3%, 0.6%, 0.9% (mass fraction) as the working fluids, and the visualization was studied by using high speed camera device. The influence of heat flux, Re and wall roughness on the fluid heat transfer coefficients was discussed, and the variations of stream pattern and the bubbles’growth were investigated. The results show that the saturated boiling heat transfer coefficients of nanofluids and deionized water both increase significantly with the increase of mass flow rate. The values of Nu increase with the increase of Re. But the amount of increase is different. The Nu of nanofluids with particle of 0.3%, 0.6% and 0.9% are 8%, 13% and 16% higher than those of deionized water. With the same heat flux density and mass velocity, the heat transfer coefficient of two working fluids both increase with the increase of roughness of the channels. The stream pattern changes periodically, and the growth cycle of the bubbles will be shorter when heat flux density increases.
Key words: microchannel; nanofluid; heat transfer coefficient; roughness; visualization
受现代社会高新科技的快速发展的推动,微电机系统、精密农业机械、生物医学等科技产品朝着高度集成化的方向发展,由于它们的热流密度较高,微空间的传热冷却问题亟待解决[1]。在此背景下,以微尺度相变理论为基础的微通道内两相流动沸腾传热的研究变得极具研究潜力,微空间内的高效散热问题也受到新型科技产品的青睐。Dai等[2-3]发现将高导热性能的纳米流体应用于微通道中,利用工质的相变潜热使元件的换热表面保持在安全温度以下,可大大提高电子元件的工作寿命。近年来,人们对微尺度传热的研究已取得了一定的成果。Qu等[4-5]致力于研究微通道换热器内两相流沸腾流动传热,他们发现在热力学平衡干度零点附近,流型突然转变为环流,传热的主导机理为强制对流沸腾传热,同时他们建立了环流预测模型。Lee等[6]进行了硅基微通道内的饱和沸腾传热及压降的实验研究,修正得到了适合其实验条件的传热系数计算公式。Kim等[7-8]基于前人的实验研究数据,建立起微通道传热的数据库,并利用数据库数据对先前的传热系数计算公式进行了验证性评价。常威等[9]对竖直微通道内水沸腾过程中气泡的生长形态及传热特性进行了数值模拟。但截至目前仍然没有一个普适的统一理论模型来深入解释沸腾传热的本质机理。本文作者通过矩形微槽道内Al2O3纳米流体的换热实验,旨在研究纳米流体流动沸腾过程中热流密度、壁面粗糙度等因素对微通道流体沸腾换热效果所产生的影响,同时利用高速摄像仪进行气泡生长及流型变化的可视化研究。通过探讨微通道内纳米流体沸腾传热机理,以期对已有沸腾理论进行补充和完善。
1 实验设备及方法
1.1 实验系统
图1所示为实验系统示意图。整个实验平台包括水箱、高温水泵、转子流量计、实验段、除泡器、传感器、数据采集卡、计算机、高速摄像仪等设备。流体及信号流向如图1中箭头所示。工质由高温热水泵从水箱中抽出,一部分通过回流管道流回水箱,另一部分流经过滤网和转子流量计后进入实验段。设计回流旁路可方便控制实验段流量和压力。从实验段流出的工质已是气液两相的混合流,经过除泡处理后再流回水箱,实现循环实验。高速摄像系统置于试验段侧面。
实验段采用一体式结构,材质均为铝合金,能够保证实验段具有良好的传热性能。实验段开有4对壁面测温孔,采用铠装型Pt100热电阻进行测温。加热板和槽道基体之间通过导热硅脂连接,整个实验段由保温棉包裹,以减少热量损失。
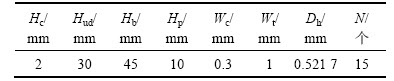
图2所示为实验段通道截面示意图,具体参数取值如表1所示。图2和表1中:N为槽道个数;Wc为槽道宽;Wt为槽道间距;Hc为槽道高;Hp为盖板厚度;Hb为基座厚度;Hud为上下测温点间距;Hwu为上测温点到槽道底部的距离;Dh为槽道水力直径。

图1 实验系统示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of experimental system

图2 微通道横截面示意图
Fig. 2 Microchannels’cross section
表1 槽道尺寸参数的取值
Table 1 Geometric parameters of test section
1.2 纳米流体的配置及其热物理性质
实验所用水基Al2O3纳米流体采用共混法[10]制备。为防止纳米流体产生团聚现象,在流体中加入体积分数约1%的醋酸,形成纳米粒子悬浮液,搅拌10~20 min形成含纳米粒子颗粒的水溶胶,辅以超声波震荡仪进行振动,使纳米粒子均匀、稳定地分散在液体介质中。
若纳米颗粒黏度过高,则在实验过程中可能会附着在槽道壁面而降低传热性能,因此,实验配置的Al2O3纳米颗粒质量分数较少,分别为0.3%,0.6%和0.9%。同时由于纳米粒子直径极小,这样避免了通道的磨损或阻塞,也几乎不会影响系统的阻力损失。
实验中所用纳米流体的相关物性参数计算式为[11]:
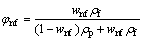 (1)
(1)
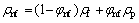 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
 (4)
(4)
式中:下标nf表示纳米流体;f表示去离子水;p表示纳米颗粒;ρ为密度;λ为导热系数;μ为黏度;w为质量分数;φ为体积分数。
实验采用LVDV-П型旋转黏度计对Al2O3纳米流体实际黏度[12]进行测量。3种浓度的纳米流体及去离子水在饱和温度下的物性参数如表2所示。
1.3 微槽道壁面粗糙度的表征
图像灰度在空间以纹理变化形式生成的图案是对真实物体表面固有特征的体现,表面的微小起伏不平以及凹坑、破碎等细微缺陷也可表现为不同的纹理基元排布规律。统计并分析表面数字图像的灰度直方图,可以掌握壁面纹理和灰度信息,从而评定壁面粗糙度情况[13]。
灰质化处理主要是消除图像中RGB的色彩信息,本文选用1种常见的加权平均算法:
 (5)
(5)
式中:Y为某一像素点灰度信息;Red,Gre和Blu为该像素点三原色分量。
对于本次实验,中值滤波可表述为:
 (6)
(6)
经上述处理后,得到灰度计算公式。
灰度均值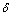 为
为
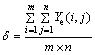 (7)
(7)
灰度均方差 为
为
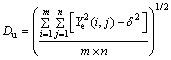 (8)
(8)
在本实验研究中,选用灰度均方差 来表征微通道传热壁面表面的形貌,即壁面粗糙度。
来表征微通道传热壁面表面的形貌,即壁面粗糙度。
1.4 数据处理
本实验中由于铝导热性能较好,热平衡偏差较小,且在通道饱和沸腾区域内,壁面温度相对稳定因而可以认为在铝制基座内的热量均沿如图2所示截面传递,而忽略通道壁面沿流动方向的热传递[14]。
流动工质与微通道壁面之间的传热系数为
 (9)
(9)
式中:A为对流换热面积,即微通道底面和两侧总面积;Q为流动工质带走的总热量,
 (10)
(10)
ΔTm为流体与壁面的平均温差,
 (11)
(11)
有效热流密度为
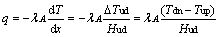 (12)
(12)
雷诺数Re为
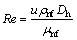 (13)
(13)
表2 纳米流体物性参数
Table 2 Thermophysical properties of Al2O3-H2O nanofluids

式中:u为流体平均流速,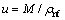 ;Dh为槽道水力直径;λA为铝制基座的导热系数。
;Dh为槽道水力直径;λA为铝制基座的导热系数。
努塞尔数Nu为对流传热系数与导热系数的比率:
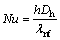 (14)
(14)
2 实验结果及分析
2.1 热流密度对传热的影响
泡核沸腾传热机理的一个重要特征是传热系数随热流密度的变化较快。实验探究热流密度对纳米流体传热的影响,得到纳米流体在不同热流密度下的传热系数。图3所示为纳米流体质量流速为198.14 kg/(m2·s)时, 0.3 mm×2.0 mm微通道传热系数与热流密度的关系。
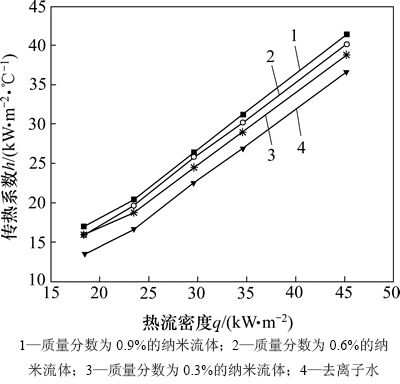
图3 流动沸腾传热系数与热流密度的关系
Fig. 3 Relationship between heat transfer coefficient of saturated flow boiling and heat flux
显然,纳米流体与去离子水的传热系数均随热流密度的增加而快速增加。这个结论与文献[15]提出的中沸腾数理论结果相吻合。并且热流密度增加时,壁面与流体间的瞬时温差增大,气化核心产生气泡的速度以及气泡脱离直径增加,使液体所受扰动加剧,增强了流体与壁面的换热。此结论也将在可视化研究中得到体现。在本实验中,泡核沸腾传热机理起到主导作用。
另外,由图3可以发现,在相同的质量流速下,纳米流体的换热系数比去离子水的换热系数高14%左右。可见加入纳米颗粒会增加流体的导热系数,同时由于颗粒之间、颗粒与基液以及颗粒与壁面之间的相互作用及碰撞会增加流体分子之间动量和能量的交换,从而强化了传热。
2.2 雷诺数对努塞尔数的影响
根据实验中所得的测温点温度以及质量流量结果,计算得到实验时流体的对流换热准则数Nu,将实验结果绘制成Nu-Re图(见图4),这在一定程度上反映流体传热效率的变化情况。图4中流体热流密度为29.6 kW/m2。
由图4可得:在本实验条件下,纳米流体与去离子水的Nu均随Re的增大而增大,并在Re较大时,Nu有增长加快的趋势,这也从侧面反映出流体质量流量增大使传热效果得到改善。对比相同Re时纳米流体与去离子水的Nu可发现,纳米流体比去离子水的Nu大,并且纳米颗粒质量分数越高,Nu越大,质量分数为0.9%,0.6%和0.3%的3种纳米流体Nu相比于去离子水约分别高16%,13%和8%。这与Wu等[16]的研究结果相似。这是由于流体中纳米颗粒含量增加所导致的对流传热效应大于热传导效应,从而使流体的传热效果得到增强。

图4 努塞尔数随雷诺数变化曲线
Fig. 4 Relationship between Nu number and Re number
2.3 通道壁面粗糙度对传热的影响
采用化学抛光的方法来改变通道内传热壁面的粗糙度,计算相应的灰度均方差Du,Du越大,对应的表面纹理变化就越剧烈,表面粗糙度越大[17]。经计算,原始传热壁面及2次抛光后传热壁面的平均Du分别为51.2,38.7和25.3。经过抛光处理后的传热壁面粗糙度逐渐减小,也即越来越光滑。
图5所示为质量分数0.3%纳米流体在不同传热壁面粗糙度条件下,通道内饱和流动沸腾传热系数随质量流速的变化关系。在相同热流密度及质量流速时,2种工质的传热系数均随传热壁面粗糙度的增加而增大。当工质为去离子水且q=23.50 kW/m2时,Du=25.3表征的壁面(即2次抛光处理后),相对于原始壁面(Du=51.2),传热系数平均下降约12.53%;当工质为纳米流体时,在相同条件下,传热系数平均下降为8.07%,显然下降幅度比去离子水的下降幅度小。当热流密度为其他值时可得到同样的结论。由此可见,传热壁面粗糙度对去离子水的影响相对较大。
粗糙度对流动沸腾传热产生影响主要有2个方面的原因。一方面,从气泡动力学角度来看,传热壁面粗糙度越大时,壁面在沸腾过程中能够产生更多的活跃核化点,而气泡正是从这些活跃核化点生成,同时传热壁面越粗糙,形成气泡的空腔变大,气泡的脱离直径更小,脱离频率更快,而在本次实验条件下,泡核沸腾传热起主导作用,因而带来了传热系数的增大;另一方面,靠近壁面处,流体由于黏力的作用会形成一定厚度的边界层,而粗糙度增大会对该边界层产生扰动作用,该作用甚至能够使流体在较低流速下进入湍流状态。

图5 不同壁面粗糙度条件下的传热系数
Fig. 5 Heat transfer coefficients from different wall roughness
2.4 流体气泡流型可视化研究
利用高速摄影仪对微槽道内两相流沸腾传热过程中的气泡生长过程以及流型变化情况进行拍摄记录,并在工控机上进行图像数据分析。
图6所示为去离子水在不同热流密度、质量流速为295.74 kg/(m2·s)时,距入口约160 mm处通道内气泡的生长情况。对比气泡生长过程,可以发现从槽道壁面脱离的气泡在随着流体向上运动的过程中都是逐渐变大的,但生长速度不同,生长周期不同。测量气泡在生长过程中不同时刻的直径,得到不同热流密度下的气泡直径变化规律如图7所示。
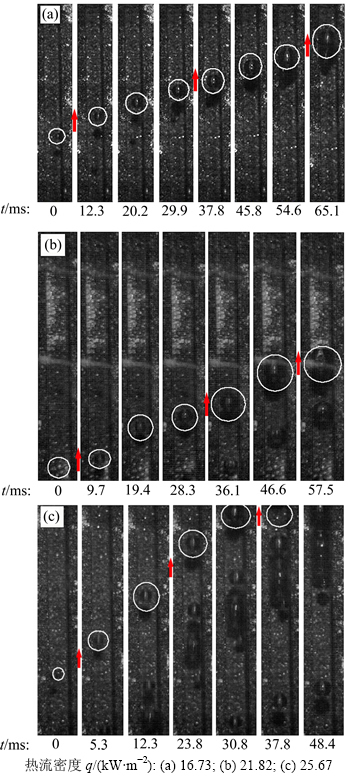
图6 气泡生长过程
Fig. 6 Development processes of bubbles
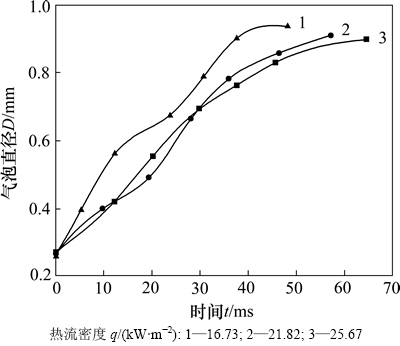
图7 不同热流密度下气泡生长速度
Fig. 7 Velocity diagram of bubbles with different heat fluxes
从图6可见:当q为16.73 kW/m2时,气泡从刚刚脱离壁面到长大并最终发生形变所用时间约为 65.1 ms,且成长过程比较均匀;当q为21.82 kW/m2时,气泡的生长周期为57.5 ms,以至于挤压到壁面发生形变,并有与其他气泡合并的趋势;当q增大到25.67 kW/m2时,可以发现整个槽道内气泡数目明显增多,并已经开始和后边的气泡接触及合并,这时气泡生长周期缩短至48.4 ms。在这里引入气泡生长速率,即图7所示曲线的斜率,可以看出q为25.67 kW/m2时,曲线平均斜率最大,即生长速度最快;q为21.82 kW/m2时的气泡生长速度次之,q为16.73 kW/m2时速度最慢。由此得到,随着热流密度的不断增大,气泡的生长速度逐渐加快,生长周期缩短。
研究发现,即便在几个不同的热流密度条件下,流体流型均以泡状流—弹状流—环状流—液态单相流方式进行,只是发生变化的周期所占比例不同。在单相流中,气泡又开始产生并向出口处移动,重新回到泡状流状态。但泡状流时,不同热流密度条件下气泡生成速度及脱离状态有所不同。在高热流密度条件下气泡脱离、上升速率较快,所以,产生的气泡大都为小气泡,不易形成弹状流,泡状流在整个周期中比例较大,由此加剧了泡核沸腾传热的效果。
3 结论
1) 在本实验条件下,纳米流体与去离子水的饱和沸腾传热系数均随热流密度的增加而增大,这是由汽化核心产生气泡的速度以及气泡的脱离直径增大引起;在相同条件下,纳米流体的换热系数比去离子水高14%左右,证明了纳米流体的强化换热效果。
2) 在流动沸腾过程中,纳米流体与去离子水的Nu均随Re的增大而增大。在定质量流速条件下,纳米流体的Nu比去离子水大,0.9%,0.6%和0.3%这3种质量分数的纳米流体与去离子水相比,其Nu约分别提高16%,13%和8%。
3) 在相同热流密度及质量流速条件下,纳米流体的传热系数随传热壁面粗糙度的增加而增大,传热壁面粗糙度对去离子水换热的影响比对纳米流体更明显。
4) 在微通道内流动沸腾过程中,流体流型以泡状流—弹状流—环状流—液态单相流方式周期性变化;随着热流密度的增大,气泡的生长速度加快,生长周期缩短,泡状流比例增加,从而强化了传热效果。
参考文献:
[1] Kandlikar S G. High flux heat removal with microchannels—A roadmap of challenges and opportunities[J]. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2005, 26(8): 5-14.
[2] DAI Wenting, LI Junming, CHEN Xiao, et al. Experiment investigation on convective heat transfer of copper oxide nanoparticle suspensions inside mini-diameter tubes[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2003, 24(4): 633-636.
[3] Lee J, Mudawar I. Assessment of the effectiveness of nanofluids for single-phase and two-phase heat transfer in microchannels[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2007, 50(3): 452-463.
[4] QU Weilin, Mudawar I. Flow boiling heat transfer in two-phase micro-channel heat sinks: Ⅰ. Experimental investigation and assessment of correlation methods[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2003, 46(15): 2755-2771.
[5] QU Weilin, Mudawar I. Flow boiling heat transfer in two-phase micro-channel heat sinks: Ⅱ. Annular two-phase flow model[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2003, 46(15): 2773-2784.
[6] Lee P S, Garimella S V. Saturated flow boiling heat transfer and pressure drop in silicon microchannel arrays[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2008, 51(3): 789-806.
[7] Kim S M, Mudawar I. Universal approach to predicting saturated flow boiling heat transfer in mini/micro-channels: Part Ⅰ. Dryout incipience quality[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 64: 1226-1238.
[8] Kim S M, Mudawar I. Universal approach to predicting saturated flow boiling heat transfer in mini/micro-channels: Part Ⅱ. Two-phase heat transfer coefficient[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 64: 1239-1256.
[9] 常威, 张树生, 程林, 等. 竖直矩形细通道内的水沸腾换热特性[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(2): 743-748.
CHANG Wei, ZHANG Shusheng, CHENG Lin, et al. Nucleate boiling heat transfer in vertical rectangular minichannel[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(2): 743-748
[10] 李强. 纳米流体强化传热机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学动力工程学院, 2004: 11-15.
LI Qiang. Investigation on enhanced heat transfer of nanofluids[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology. School of Power Engineering, 2004: 11-15.
[11] 宁常军, 罗小平. 微通道内纳米流体换热与压降特性[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(8): 3001-3006.
NING Changjun, LUO Xiaoping. Heat transfer and pressure drop of Al2O3 nanofluids in microchannels[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(8): 3001-3006.
[12] 彭小飞, 俞小莉, 夏立峰, 等. 低浓度纳米流体黏度变化规律试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2007, 38(4): 138-141.
PENG Xiaofei, YU Xiaoli, XIA Lifeng, et al. Viscosity of low concentration nanofluids[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2007, 38(4): 138-141.
[13] 时小军, 张玉琴, 张小辉. 基于机器视觉技术的研磨表面粗糙度检测[J]. 机械设计与研究, 2010, 26(3): 101-107.
SHI Xiaojun, ZHANG Yuqin, ZHANG Xiaohui. Measurement of lapped surface roughness based on machine vision technique[J]. Machine Design and Research, 2010, 26(3): 101-107.
[14] Bertsch S S, Groll E A, Garimella S V. Refrigerant flow boiling heat transfer in parallel microchannels as a function of local vapor quality[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2008, 51(19/20): 4775-4787.
[15] 甘云华. 硅基微通道内流动与传热的可视化测量及其规律的研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学热科学与能源工程系, 2006: 80-82.
GAN Yunhua. Visualization measurement and investigation of fluid flow and heat transfer in silicon microchannels[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China. Department of Thermal Science and Energy Engineering, 2006: 80-82.
[16] WU Xinyu, WU Huiying. Pressure drop and heat transfer of Al2O3-H2O nanofluids through silicon microchannels[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2009, 19(10): 1-10.
[17] 王健全, 田欣利, 郭昉, 等. 基于灰度信息的工程陶瓷磨削表面粗糙度评定[J]. 装甲兵工程学院学报, 2011, 25(3): 86-90.
WANG Jianquan, TIAN Xinli, GUO Fang, et al. Evaluation of ground surface roughness of engineering ceramics based on grayscale information[J]. Academy of Armored Force Engineering, 2011, 25(3): 86-90.
(编辑 罗金花)
收稿日期:2014-10-29;修回日期:2014-12-30
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(21276090) (Project(21276090) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:罗小平,教授,博士生导师,从事微尺度相变强化传热机理、微尺度热物理系统的拓扑学、分子动力学模拟等研究;E-mail: mmxpluo@scut.edu.cn