Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 1602-1607
Mechanism for capacity fading of 18650 cylindrical lithium ion batteries
Jian-liang CHENG, Xin-hai LI, Zhi-xing WANG, Hua-jun GUO
School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 7 April 2016; accepted 13 September 2016
Abstract: The mechanism for capacity fading of 18650 lithium ion full cells under room-temperature (RT) is discussed systematically. The capacity loss of 18650 cells is about 12.91% after 500 cycles. The cells after cycles are analyzed by XRD, SEM, EIS and CV. Impedance measurement shows an overall increase in the cell resistance upon cycling. Moreover, it also presents an increased charge-transfer resistance (Rct) for the cell cycled at RT. CV test shows that the reversibility of lithium ion insertion/extraction reaction is reduced. The capacity fading for the cells cycled can be explained by taking into account the repeated film formation over the surface of anode and the side reactions. The products of side reactions deposited on separator are able to reduce the porosity of separator. As a result, the migration resistance of lithium ion between the cathode and anode would be increased, leading the fading of capacity and potential.
Key words: 18650 lithium ion battery; capacity fading; cycle performance
1 Introduction
Because of the high energy, high power, and long lifetime, lithium-ion batteries have promoted the rapid development of electric vehicles (EV), hybrid electric vehicles (HEV) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV), and these new types of vehicles become more practical in order to alleviate the air pollution arising from the increasing number of automobiles [1-4]. 18650 secondary lithium-ion batteries are one of the typical cylindrical cells. Given their low costs and high automation level and good consistency, 18650 cells are considered to be widely used in EV, HEV and PHEV. For example, Tesla Model S cars are equipped with approximately 7000 pieces of 18650 cells that provide about 85 kW·h power.
Despite many advantages have been noticed, the capacity fading of lithium-ion batteries is inevitable due to the deterioration over time as the system is cycled repeatedly through multiple iterations of charge and discharge [5-7]. Considering the importance of life time of secondary lithium-ion battery, many researchers investigated the mechanism of capacity fading [8-11]. The capacity fading of Li-ion batteries can be attributed to the unexpected side reactions caused by electrolyte decomposition, structural changes, passive film formation and active material dissolution as well as corrosion of current collector during cycling process [12,13]. Several other capacity fading mechanisms namely complete exfoliation of the electrode material due to solvent co-intercalation [14] and electronic isolation of active mass [15] have also been clearly addressed. By the use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), ZHANG et al [16] investigated the capacity fading of commercially available LiCoO2 based Li-ion cells and found that the capacity loss was attributed to the higher impedance of LiCoO2 electrode with cycling, which results from continuous electrolyte oxidation under overcharging condition. PREMANAND et al [10] paid attention to the capacity fading of commercially available spinel based Li-ion cells. Their results indicate that the capacity fading of the cell depends on both the charging rate and the cut-off potential used to charge the cell and they attributed capacity fading to the structural degradation at the cathode and the decrease of active materials at both electrodes.
Although many mechanisms of capacity fading have been presented, it is hard to justify which one is the main reason due to different electrochemical systems as well as different shapes. Therefore, in this work, we focused on estimating the capacity fading mechanism of commercial 18650 cylindrical Li-ion cells for the purpose of enhanced lifetime. 18650 cylindrical Li-ion cells are widely used in the battery technology and are in a typical full-cell shape with fixed shape and size. Moreover, in order to increase the energy density and decrease the cost of Li-ion cell, LiNi0.5Mn0.3Co0.2O2 was selected as cathode materials to replace traditional LiCoO2 [17,18].
2 Experimental
The composition of the cathode electrode was 96% LiNi0.5Mn0.3Co0.2O2, 1% KS6, 1% SP and 2% (mass fraction) polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). The anode electrode was composed of 95.6% graphite with 1% SP, 1.4% CMC and 2.0% SBR. The rated capacity was about 2200 mA·h. 1 mol/L LiPF6 was used as the electrolyte in a 1:1 (volume ratio) mixture of ethylene carbonate (EC), and dimethyl carbonate (DMC). Celgard 2320, 20 μm in thickness, was used as a separator.
Charge–discharge studies were carried out in the potential range of 3.0-4.2 V, and discharge current was 1C. For charging, the conventional constant current–constant voltage (CC-CV) protocol was adopted. A direct current of 1C (2.3 A) was used to charge the cell during the constant current part and the cut-off voltage was set to be 4.2 V. Subsequently, the voltage was kept constant at 4.2 V till the current decreased to 0.02C (46 mA). By using this protocol, the cell could be completely charged to obtain the nominal capacity. Between charge and discharge, the cells were left at open circuit for 1 h to be stabilized.
Cycle voltammetry (CV) was conducted with electrochemical workstation (CHI6600). Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was carried out by means of a potentiostat galvanostat (Schlumberger SI 1286) and a frequency response analyzer (Schlumberger SI 1255). Scanning frequencies ranged from 50 kHz to 0.01 Hz, and perturbation amplitude was 5 mV. The impedance was measured at full charged states.
The morphological changes in both cathode and anode after different cycles were observed with a field emission SEM (FESEM, LEO-1530) at an accelerating voltage of 15 keV and coupled with an EDS (LEO-1550). Crystal structures of the graphite and LiNi0.5Mn0.3Co0.2O2 were identified by X-ray diffractometry (XRD, XD-5 with a Cu Kα target, wavelength 1.54056 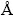 ). Diffraction data were collected by 4 (°)/min, ranging from 10° to 90°. Sample powders of anode and cathode were scraped off the current collector of electrodes.
). Diffraction data were collected by 4 (°)/min, ranging from 10° to 90°. Sample powders of anode and cathode were scraped off the current collector of electrodes.
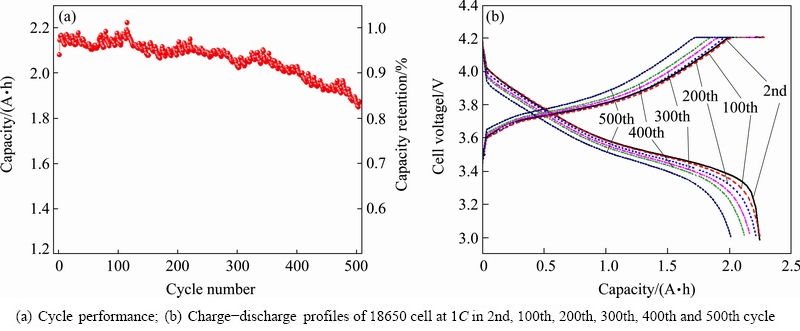
Fig. 1 Electrochemical performance of 18650 cells at 1C under room temperature
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Cycle performance
Figure 1(a) presents the cycle performance of 18650 cells when cycled at room temperature (RT). The capacity loss was about 1.03%, 2.24%, 3.61%, 7.41% and 12.91% for 100, 200, 300, 400 and 500 cycles, respectively. It is obvious that the capacity loss became more and more grievous along with the increase of cycle numbers. Figure 1(b) shows the charge- discharge curves obtained from different cycles. Comparing the discharge profiles of them, the voltage plateau decreases along with the increase of cycle number. The drop in the cell voltage at the beginning of discharge is found to increase with the cycle number, and the increase gradient becomes significantly larger with the increase of cycle number too. The charge curve trend shows opposite behavior in which the voltage plateau increases along with the increase of cycle number. As a result, as the cycling goes on, the electrode voltage polarization tends to be enlarged, indicating an increase in the high frequency impedance of the cell [19]. Moreover, the decrease in discharge voltage leads to a loss of power density of the cell.
3.2 Kinetics studies
Figure 2(a) shows the EIS results of the cells after 1, 300 and 500 cycles. The cell was tested at full charged state. The equivalent circuit used to fit the Nyquist plots is presented in the inset of Fig. 2(a), where Re represents the ohmic resistance of the cell, Rsf is the SEI film resistance and CPE1 is the corresponding capacitance to Rsf, Rct is the charge-transfer resistance, CPEdl is the double-layer capacitance, and W is the Warburg impedance. The semicircle in the high- frequency range corresponds to the surface film resistance and is composed of the smaller semicircle, which is mainly generated from the resistance and capacitance of the SEI. In the middle-frequency range, the semicircle resembles the charge-transfer resistance, and the linear section in the low-frequency range represents the solid-state lithium-ion diffusion in the bulk electrode particles. The semicircle high-frequency range almost remains the same after hundreds cycles, while the middle-frequency range semicircle increases significantly after cycles. The results indicated that the increase of charge-transfer resistance may be the primary reason for the capacity loss. The possible reason of the increase of Rct may be the incrassation of SEI film by the way of ceaseless dissolution or the decrease of activation sites. The increased Rct reflects that the electrochemical reaction becomes more and more difficult along with cycles. As a result, the cell experiences capacity fading. Figure 2(b) shows the cycle voltammetry results after 1 and 500 cycles, which show that the oxidation and reduction peak positions barely change after the cycles. However, the peak area reduces significantly after cycles, indicating a substantial reduction of reversibility of lithium ion.

Fig. 2 EIS results of full-charged cells with different cycle numbers (inset is equivalent circuit) (a) and cyclic voltammetry results after 1 and 500 cycles (b)

Fig. 3 XRD patterns of cathode (a, a′) and anode (b) before cycle and after 500 cycles
3.3 Morphological and structure changes
To investigate the structural and morphological change after cycles, the cycled cells were disassembled and washed with DMC solvent three times in Ar-filled glove box, and analyzed by SEM and XRD. As shown in Fig. 3, the XRD patterns reveal that there is hardly any difference between the electrodes before and after 500 cycles, all maintaining the pristine crystal structure. Carefully observing, we find that the peaks of cathode shift to low 2θ position, indicating a reduced cell parameter of cathode material after cycles. It may be due to the dissolution of transition metal ions into the electrolyte. In the SEM images of cycled electrodes (Fig. 4), many pores are found on the surface of anode, which might be caused by the transition metal ion dissolution. Moreover, in the SEM image of cycled cathode material (Fig. 4(c)), a lot of small particles are observed on the surface, which might be induced by electrode decomposition. Table 1 shows the compositions of different elements of the cathode and anode electrodes before cycle and after 500 cycles. For cathode, the contents of transition metal elements decrease slightly due to elemental dissolution in the electrolyte. Moreover, the content of O is increased, which indicates that on the cathode side, only the solvents decompose and deposit on the surface while the lithium salt is still in the liquid electrolyte [20]. For anode, element P can be detected after only one cycle and shows just a little increase with cycling going on because the SEI film is formed during the first cycle and tends to be stable during the following cycles. Elemental F is significantly increased with cycling, indicating continuous formation of LiF rather than LiPFx after the first cycle [21]. Therefore, the SEI becomes thicker and thicker, and finally hinders the charge and mass transfer of the cell. As a result, the cycle performance becomes worse at the later stage.
Figure 5 shows the SEM images of the separator before and after cycles. It can be obviously seen that the porosity of the separator is reduced after cycles, which is due to the long-time side reactions between electrode and electrolyte, the decomposition products are deposited on the surface of the separator, decreasing the pathways for Li+. As a result, the resistance of lithium ion movement between cathode and anode would be increased.
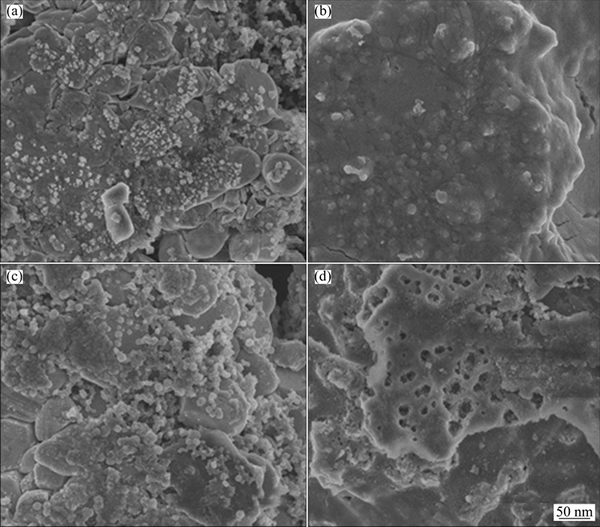
Fig. 4 SEM images of cathode (a, c) and anode (b, d) before cycle (a, b) and after 500 cycles (c, d)
Table 1 Compositions of different elements of cathode and anode electrodes before and after 500 cycles
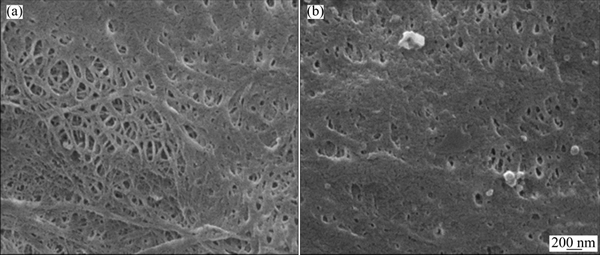
Fig. 5 SEM images of separator before cycle (a) and after (b) 500 cycles
4 Conclusions
1) The capacity loss of 18650 cells composed of LiNi0.5Mn0.3Co0.2O2 cathode and graphite anode was 1.03%, 2.24%, 3.61%, 7.41% and 12.91% for 100, 200, 300, 400 and 500 cycles, respectively.
2) Transition metal elements dissolution occurs during cycling, damaging the structure of cathode material.
3) SEI formation and LiF production on the surface of anode side brought a barrier against the diffusion of Li+ on the surface, increasing the reaction resistance of the cell.
References
[1] WANG J X, WANG Z X, SHEN L, LI X H, GUO H J, TANG W J, ZHU Z G. Synthesis and performance of LiVPO4F/C-based cathode material for lithium ion battery [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(6): 1718-1722.
[2] WANG J X, ZHANG Q B, LI X H, XU D G, WANG Z X, GUO H J, ZHANG K L. Three-dimensional hierarchical Co3O4/CuO nanowire heterostructure arrays on nickel foam for high-performance lithium ion batteries [J]. Nano Energy, 2014, 6: 19-26.
[3] WANG J X, ZHANG Q B, LI X H, ZHANG B, MAI L, ZHANG K L. Smart construction of three-dimensional hierarchical tubular transition metal oxide core/shell heterostructures with high-capacity and long- cycle-life lithium storage [J]. Nano Energy, 2015, 12: 437-446.
[4] LIU Z M, PENG W J, SHIH K, WANG J X, WANG Z X, GUO H J, YAN G J, LI X H, SONG L B. A MoS2 coating strategy to improve the comprehensive electrochemical performance of LiVPO4F [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 315: 294-301.
[5] YAN G C, LI X H, WANG Z X, GUO H J, XIONG X H. Beneficial effects of 1-propylphosphonic acid cyclic anhydride as an electrolyte additive on the electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 263: 231-238.
[6] NAKANISHI S, SUZUKI T, CUI Q, AKIKUSA J, NAKAMURA K. Effect of surface treatment for aluminum foils on discharge properties of lithium-ion battery [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(7): 2314-2319.
[7] YIN W M, ZHANG T T, ZHU Q, CHEN Q Q, LI G C, ZHANG L Z. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of Li3–2xMgxV2(PO4)3/C composite cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(6): 1978-1985.
[8] MUTO S, SASANO Y, TATSUMI K, SASAKI T, HORIBUCHI K, TAKEUCHI Y, UKYO Y. Capacity-fading mechanisms of LiNiO2- based lithium-ion batteries II: Diagnostic analysis by electron microscopy and spectroscopy [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society A, 2009, 156(5): 371-377.
[9] ARORA P, WHITE R E, DOYLE M. Capacity fade mechanisms and side reactions in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1998, 145(10): 3647-3667.
[10] PREMANAND R, DURAIRAJAN A, HARAN B, WHITE R, POPOV B. Studies on capacity fade of spinel-based Li-ion batteries [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society A, 2002, 149(1): 54-60.
[11] WANG J X, ZHANG Q B, LI X H, WANG Z X, ZHANG K L, GUO H J, YAN G C, HUANG B, HE Z J. A graphite functional layer covering the surface of LiMn2O4 electrode to improve its electrochemical performance [J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2013, 36: 6-9.
[12] ZHENG L Q, LI S J, ZHANG D F, LIN H J, MIAO Y Y, CHEN S W, LIU H B. Study on capacity fading of 18650 type LiCoO2-based lithium ion batteries during storage [J]. Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2015, 89(5): 894-897.
[13] SONG H S, CAO Z, CHEN X, LU H, JIA M, ZHANG Z A, LAI Y Q, LI J, LIU Y X. Capacity fade of LiFePO4/graphite cell at elevated temperature [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2013, 17(3): 599-605.
[14] KIM J H, PIECZONKA N P, LI Z, WU Y, HARRIS S, POWELL B R. Understanding the capacity fading mechanism in LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/ graphite Li-ion batteries [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 90: 556-562.
[15] WATANABE S, KINOSHITA M, HOSOKAWA T, MORIGAKI K, NAKURA K. Capacity fading of LiAlyNi1-x-yCoxO2 cathode for lithium-ion batteries during accelerated calendar and cycle life tests (effect of depth of discharge in charge–discharge cycling on the suppression of the micro-crack generation of LiAlyNi1-x-yCoxO2 particle) [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 260: 50-56.
[16] ZHANG D, HARAN B S, DURAIRAJAN A, WHITE R E, PODRAZHANSKY Y, POPOV B N. Studies on capacity fade of lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2000, 91(2): 122-129.
[17] HUANG Y, WANG Z X, LI X H, GUO H J, WANG J X. Synthesis of Ni0.8Co0.1Mn0.1(OH)2 precursor and electrochemical performance of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 cathode material for lithium batteries [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(7): 2253-2259.
[18] PAN C C, ZHU Y R, YANG Y C, HOU H S, JING M J, SONG W X, YANG X M, JI X B. Influences of transition metal on structural and electrochemical properties of Li[NixCoyMnz]O2 (0.6≤x≤0.8) cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(5): 1396-1402.
[19] LEE Y J, CHOI H Y, HA C W, YU J H, HWANG M J, DOH C H, CHOI J H. Cycle life modeling and the capacity fading mechanisms in a graphite/LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 cell [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2015, 45(5): 419-426.
[20] NAKURA K, ARIYOSHI K, YOSHIZAWA H, OHZUKU T, Characterization of lithium insertion electrodes and its verification: Prototype 18650 batteries consisting of LTO and LAMO [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society A, 2015, 162(4): 622-628.
[21] ECKER M, NIETO N, K BITZ S, SCHMALSTIEG J, BLANKE H, WARNECKE A, SAUER D U. Calendar and cycle life study of Li(NiMnCo)O2-based 18650 lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 248: 839-851.
18650型柱状锂离子电池的容量衰减机理
程建良,李新海,王志兴,郭华军
中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:研究18650商业化锂离子全电池在常温条件下的容量衰减机理。结果表明,经过500次循环后,18650柱状电池的容量衰减率为12.91%;对经循环后的电池采用XRD、SEM、EIS和CV进行表征。电化学交流阻抗图谱表明,随着循环的进行,电池的电阻特别是电荷转移电阻逐渐增加;同时,循环伏安测试表明,在循环的后期,电池的锂离子脱嵌可逆性能下降,导致容量衰减。这是因为,在正、负极材料界面处发生电解液与电极材料副反应,反复形成固态电解质界面膜。同时,副反应产物沉积一部分沉积在隔膜上,堵塞隔膜孔,阻碍锂离子的穿梭。因此,锂离子在正负极间的移动阻力增大,导致电池的容量衰减和电位衰减。
关键词:18650锂离子电池;容量衰减;循环性能
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (51574287) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2015CX001) supported by the Innovation- driven Plan in Central South University, China
Corresponding author: Xin-hai LI; Tel: +86-731-88836633; E-mail: xinhaili_csu@126.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60182-1