文章编号:1004-0609(2011)11-2812-07
锰酸锂电池储存后容量衰减机理
刘云建1, 2, 3, 宋 杨1, 魏洪兵1, 王彩娟1, 赵 永1, 金 挺1, 李新海3, 郭华军3
(1. 吴江出入境检验检疫局,吴江 215200;2. 江苏大学 材料科学与工程学院,镇江 212013;
3. 中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,长沙 410083 )
摘 要:采用商品化的LiMn2O4制作锰酸锂/石墨电池,研究其储存性能,并对储存前后的正极、负极和电解液进行表征分析。结果表明:半荷电常温储存一个月,电池容量衰减3.7%,循环性能得到改善。X射线衍射和透射电镜结果表明:LiMn2O4晶格发生收缩,正极表面形成一层固体电解质(SEI)膜。交流阻抗研究表明:正极阻抗由储存前的62.69 Ω增大到储存后的84.64 Ω,负极阻抗由储存前的183.1 Ω增大到储存后的301 Ω。红外光谱分析表明:电解液溶剂和电解质盐均不同程度地发生了分解,锰酸锂电池储存后容量衰减主要是由电极极化、Mn溶解、电解液分解、负极SEI膜增厚等原因造成。
关键词:锰酸锂电池;储存;容量衰减;机理
中图分类号:TM91.2 文献标志码:A
Capacity fading mechanism of LiMn2O4 cell after storage
LIU Yun-jian1, 2, 3, SONG Yang1, WEI Hong-bing1, WANG Cai-juan1, ZHAO Yong1, JIN Ting1, LI Xin-hai3, GUO Hua-jun3
(1. Wujiang Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine Bureau, Wujiang 215200, China;
2. School of Material Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China;
3. School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The power battery was manufactured with the commercial LiMn2O4 and graphite. The storage performance of LiMn2O4 battery was tested. The cathode, anode and electrolyte before and after storage were characterized. The result shows that the capacity fading ratio of LiMn2O4 battery at half-charged state is 3.7%, but the cycling performance is improved after storage. XRD results show that the crystal lattice of LiMn2O4 shrinks. TEM results show that the surface of LiMn2O4 particles is covered with SEI film. The cathode impedance increases from 62.69 Ω to 84.64 Ω and that of anode increases from 183.1 Ω to 301 Ω. FT-IR results show that the solvent and solutes of electrolyte decompose at a certain degree after storage. The polarization, Mn dissolution, electrolyte decomposition and the incrassation of anode SEI are responsible for the capacity fading of LiMn2O4 battery after storage.
Key words: LiMn2O4 battery; storage; capacity fading; mechanism
锰酸锂因为其原材料丰富,价格便宜,安全性好,环境友好等优点,一直被人们认为是锂离子动力电池理想的正极材料。但是锰酸锂材料也存在循环性能和储存性能差等缺点。研究者通过在16d的位置掺杂金属离子[1-5]来稳定LMin2O4的尖晶石结构, 或者通过表面包覆[6-7]减少锰的溶解,循环性能得到了一定的改善。但是在锰酸锂电池的制作、运输和使用过程中,不可避免会存在荷电储存搁置的问题。最近研究发现锰酸锂电池储存后不可逆容量损失严重[8-10]。目前,国内外研究者对锰酸锂电池储存后容量衰减及机理研究尚不够系统和深入。
本文作者系统地研究了锰酸锂电池在荷电储存后电化学性能以及电极材料的结构变化。并通过对储存前后锰酸锂电池正、负极和电解液等关键材料的检测和电化学分析,系统地研究了锰酸锂电池储存后容量衰减的机理。
1 实验
1.1 LiMn2O4的形貌和结构分析
利用X射线衍射仪(Rigaku公司,日本)对LiMn2O4样品进行物相分析,以Cu Kα靶作为辐射源,电压为40 kV,电流50 mA,步宽0.02°,扫描速度2 (?)/min,扫描范围(2θ)为10°~90°。
用JSM-5600型扫描电子显微镜对LiMn2O4的表面形貌进行表征。
1.2 LiMn2O4电池的制作
首先将LiMn2O4、导电剂、PVDF在80 ℃真空烘烤6 h,然后按照一定的比例进行搅拌,然后涂布在集流体铝薄上,经过120 ℃真空脱气烘干压膜,然后制成小片,负极采用人造改性石墨。正、负极和隔膜通过卷绕,装入钢壳,脉冲脱气24 h,注液,由1 mol/L LiPF6和体积比为1:1:1的EC+DMC+EMC配成1 L电解液,搁置后预充、化成。
1.3 LiMn2O4的储存
将化成后的电池充电至半荷电状态,然后在室温下储存28 d,储存后将电池放电至3.0 V,然后再在3.0~4.2 V之间进行充放电循环100次。充放电电流分别为1/3C和0.5C。
1.4 红外光谱分析
将储存后的锰酸锂电池钢壳上的防爆膜划破,用毛细管取出电解液,快速进行红外光谱分析。使用的仪器为美国Nicolet公司生产的AVATAR 370,配备动态准直干涉仪,溴化钾分束器,DTGS检测器。文中采用中红外波段,波数精度为4 cm-1,区间为 4 000~400 cm-1,其结果是测量16次累加得平均数。
1.5 电化学测试
交流阻抗测试采用三电极体系,测试仪器为上海辰华CHI660电化学工作站。频率为0.01~100 kHz。
2 结果与讨论
图1所示为锰酸锂电池储存前后的放电曲线。由图1可看出,储存前后的放电曲线基本保持重合,储存后LiMn2O4的放电曲线仍能看出两个明显的放电平台,表明储存后LiMn2O4的尖晶石基本结构仍未改变。储存后LiMn2O4的放电容量为101.1 mA·h/g,不可逆容量损失为3.9 mA·h/g,容量恢复率为96.3%。该结果表明,锰酸锂电池充半电,在常温下搁置一个月后, 3.7%的容量永久损失而得不到恢复。
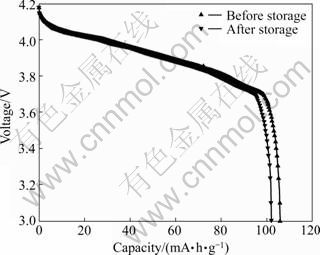
图1 锰酸锂电池储存前后的放电曲线
Fig.1 Discharge curves of LiMn2O4 electrode before and after storage
图2所示为锰酸锂电池半荷电态储存前后的循环性能曲线。锰酸锂电池储存前后100次循环容量保持率分别为91.1和94.1%。由此可见,锰酸锂电池储存后,其循环稳定性得到改善。根据循环性能曲线斜率的变化可以看出,随着循环次数的增加,储存前后锰酸锂电池循环后的差异将进一步被放大。
储存前后锰酸锂的XRD谱如图3所示。其中图3(a)所示为10°~90°的XRD谱,图3(b)所示为35°~40°的XRD谱。从图3(a)中可以看出,储存后LiMn2O4依旧保持着良好的尖晶石结构。从图3(b)中可以明显地看出,储存后尖晶石的各条衍射峰都向高角度漂移,并且衍射峰都发生宽化。具体特征峰的2θ位置参数列于表1中。
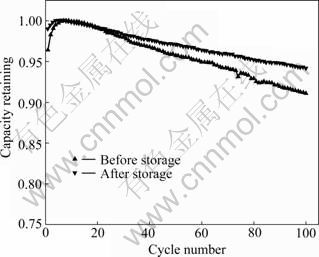
图2 锰酸锂电池储存前后的循环性能
Fig.2 Cycling performance of LiMn2O4 battery at room temperature before and after storage
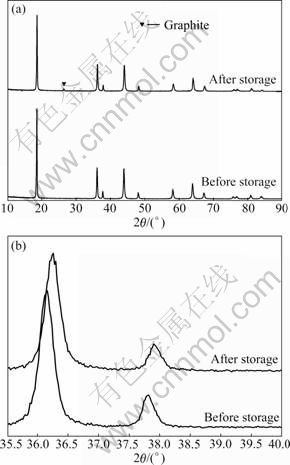
图3 LiMn2O4电极储存前后的XRD谱
Fig.3 XRD patterns of LiMn2O4 before (a) and after (b) storage
表1 储存前后LiMn2O4特征峰出现的2θ位置比较
Table 1 Comparison of 2θ for characteristic peak of LiMn2O4 before and after storage
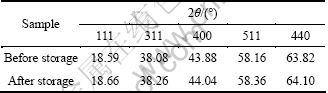
根据表1中的数据以及布拉格公式和晶面间距公式,计算得到储存前后的LiMn2O4的晶胞参数分别为8.240×10-10 m和8.217×10-10 m。该结果表明,经过储存后,LiMn2O4的晶胞发生了收缩,Mn—O键长变短,尖晶石结构的稳定性得到了增强。
图4所示为锰酸锂电池储存后正极材料的SEM像。由图4可以看出,储存后,原来锰酸锂材料表面的细小颗粒已经消失,颗粒的棱角变光滑,正极表面还存在一种絮状物质。这是因为在储存过程中,电解液对LiMn2O4的侵蚀,造成锰酸锂的溶解,并在正极表面形成絮状物质。

图4 LiMn2O4电极储存前后的SEM像
Fig.4 SEM images of LiMn2O4 electrode before (a) and after (b) storage
最近研究证明,在正极表面确实存在一层类似负极表面的固体电解质膜(Solid electrolyte interface, SEI)[11]。该层膜的主要成分以烷基酯锂(R-CO3Li)为主,R-CO3Li、Li2CO3、LiF和MnO2[12]等共存的钝化膜。在半电池中,R-CO3Li主要来自于溶剂与金属锂电极的反应[13-14]:
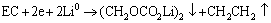 (1)
(1)
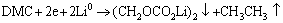 (2)
(2)
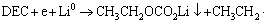 (3)
(3)
关于烷基酯锂(R-CO3Li)的生成,AURBACH等[14]曾提出“漂移说”,认为在半电池中,正极的钝化膜实际上可能产生于金属锂对电极,并随着电解液铺散开来,最后漂移到正极并沉积下来。但是事实上,钝化膜也可能由溶剂与Li+直接反应产生[13]:
 (4)
(4)
为了进一步验证沉积在正极材料表面MnO2以及正极表面SEI膜的正确性以及存在状态,本文作者比较研究了储存前后锰酸锂电池正极材料的透射电镜(TEM)图,如图5所示。从图5可以清楚地看到,储存前,LiMn2O4颗粒的表面比较光滑(见图5(a)),只是表面有少量的絮状物质附着在颗粒表面;但是储存后(见图5(b)),LiMn2O4颗粒表面包覆了一层30~50 nm厚的包覆层,并且该包覆层比较均匀严实地包覆在颗粒表面。

图5 储存前后的LiMn2O4的TEM像
Fig.5 TEM images of LiMn2O4 electrode before (a) and after (b) storage
图6所示为储存前后的锰酸锂电极的交流阻抗谱图以及模拟图。从图6中可以看出,图谱均由两个半圆和一条直线组成。高频区的半圆代表锂离子在电极和电解液界面处吸附形成表面双电层的阻抗,中频区的半圆代表的是锂离子在正极材料/电解液界面发生的电荷转移反应阻抗,低频区的直线代表的是锂离子在固相正极材料内部的扩散。
从图6中可以看出,模拟曲线和实测曲线比较吻合,模拟效果较好。图7所示为LiMn2O4电极等效电路图。表2所列为图7等效电路图中各个元器件的模拟参数。从表2中可看出,储存前后,锂离子在电解液中迁移的阻抗由5.01 Ω增大到5.81 Ω,锂离子在电极和电解液界面处吸附形成表面的层电阻由20.28 Ω增大到53.31 Ω,而锂离子在正极材料/电解液界面发生电荷转移反应电阻则由37.4 Ω减小到25.52 Ω。锂离子在嵌锂过程中总的阻抗由储存前的62.69 Ω增大到储存后的84.64 Ω。
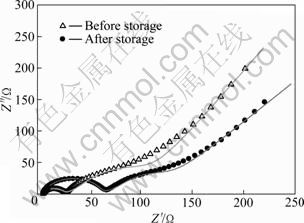
图6 LiMn2O4电极储存前后的交流阻抗谱
Fig.6 AC impedance of LiMn2O4 electrode before and after storage
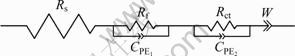
图7 LiMn2O4电极等效电路图
Fig.7 AC impedance of LiMn2O4 electrode
表2 LiMn2O4电极储存前后阻抗参数拟合结果
Table 2 Impedance parameters of equipment circuit of LiMn2O4 electrode before and after storage

电极和电解液界面处吸附形成表面层电阻增大的原因则是因为在储存过程中,LiMn2O4电极表面形成的SEI膜以及由Mn溶剂而产生的MnO2,引起LiMn2O4在储存后表面钝化膜变厚[12],反应式如下:
2LiMn2O4+4H+→3λ-MnO2(solid)+
Mn2+(liquid)+2Li+(liquid)+2H2O (5)
进而导致锂离子在电极表面形成双电层的阻抗增大,从而造成储存后锂离子的扩散困难,容量损失。
图8所示为锰酸锂电池负极材料储存前后的交流阻抗图谱。从图8中可以看出,储存前后负极阻抗图谱均由高频区的半圆和低频区的直线组成,并且储存之后负极阻抗明显增大。经过非线性模拟,储存前后负极的阻抗分别为183.1和310 Ω。负极阻抗增大后,将使锂离子的脱/嵌阻力增大,在整个电池体系中则表现为在充放电过程中电极极化增大。负极阻抗增大的原因可能是在储存过程中,负极电位较低,电解液溶剂不断地在负极表面发生分解并沉积在负极表面,使得负极表面的SEI膜不断增厚。SEI膜增厚给电池带来以下两个方面的影响:1) SEI膜的形成过程中,消耗了电池体系中的活性锂,进而降低了锂离子电池的储存后的放电容量;2) SEI厚度增厚,使得Li+在脱嵌过程中的扩散距离增长,扩散更加困难,并造成极化现象增大。此外在储存过程中,也有一部分的Mn2+被还原成Mn单质而沉积在负极表面[12],Mn可能堵塞了Li+的脱嵌通道,造成Li+的脱嵌困难,进而影响了储存后电池的放电比容量。
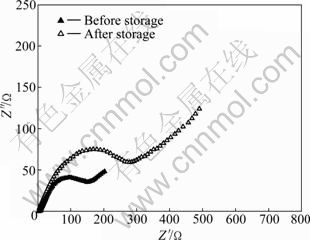
图8 锰酸锂电池负极的交流阻抗谱
Fig.8 AC impedance of anode in LiMn2O4 battery
图9所示为锰酸锂电池储存前后电解液的红外光谱(FT-IR)。图9(a)是2 200~4 000 cm-1区间的吸收图,图9(b)所示为400~2 200 cm-1区间的吸收图。图中 3 000 cm-1和2 925 cm-1代表的是C—H键的吸收峰, 846 cm-1和559 cm-1的吸收峰代表的是LiPF6。 776 cm-1代表混合溶剂中CO2的反对称弯曲振动模式。1 805和1 774 cm-1属于代表电解液的CO2伸缩振动模式。1636、1 558、1 485(1 482) cm-1和721 cm-1代表的是ROCO2Li中典型的CO2伸缩振动模式的红外光谱吸收峰[15]。这表明,在电解液中也存在ROCO2Li。总体来说,储存前后电解液的各吸收峰位置基本不变。
从图9中可以看出,储存后,代表LiPF6的846和559 cm-1的吸收峰强度要比储存之前的要小,这表明储存之后锰酸锂电池电解液中LiPF6的浓度要小于储存之前的,这是因为在储存过程中,LiPF6发生分解导致其浓度降低[16]。
此外,代表ROCO2Li的吸收峰(例如1 636、1 485 (1 482) cm-1和721 cm-1)强度在储存之后,也发生了一定程度的弱化,这表明在储存过程中,一部分ROCO2Li沉积在了正负极表面,形成SEI膜。由此可见,SEI膜的成分之一ROCO2Li也可能在锂离子传输过程中和溶剂反应生成。具体反应如下:
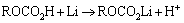 (6)
(6)
然后,生成的ROCO2Li在储存过程中再沉淀在正负极表面。该结果直接证明了吴川[11]的结论。
此外,在储存之后的红外光谱中,在1 178~1 400 cm-1之间,出现了新的吸收峰,如1 261 cm-1代表的是羟基的吸收峰,这表明经过储存之后,电解液分解,产生了新的小分子物质。
红外光谱图有效地表征了电解液在储存过程中的变化。在储存过程中,电解液溶剂和电解质盐均不同程度的发生了分解,影响了电解液的成分组成和性质(导电率、酸度和水分等),进而影响了锰酸锂电池储存后的容量。
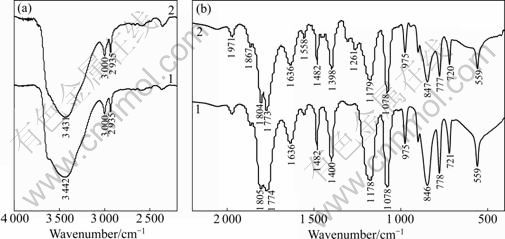
图9 储存前后锰酸锂电池电解液的FT-IR谱
Fig.9 FT-IR spectra of electrolyte in battery: 1—Before storage; 2—After storage
根据以上的研究表明,锰酸锂电池在储存之后,正极、负极和电解液都发生了明显的变化。其中正极和负极的电极阻抗都明显增大,电解液也发生了一定程度的分解。因此储存之后锰酸锂电池容量衰减的机理可能有以下几个方面。
1) 电极极化。储存后正负极表面SEI膜不断增厚,极化现象增大,导致锂离子扩散困难;电池充电过程中正极和负极的极化电压增大,电池在相同的充电制度下,储存后的电池充入的电量减少,因此造成放电容量降低。
2) 正极材料结构的变化。在储存过程中,Mn的溶解直接导致电池中活性物质减少。
3) 电解液的分解。在储存过程中,电解质盐LiPF6和溶剂都发生了一定程度的分解,导致电解液的电导率下降,进而导致锰酸锂电池充放电极化增大,电池容量下降。
4) 负极SEI膜的变化。储存过程中负极表面的SEI膜在不断的增厚,在SEI膜形成增厚的过程中,不断地消耗电池体系内的活性锂,Mn单质沉积在负极表面,堵塞了Li+的脱嵌通道,因此导致储存后锰酸锂电池容量降低。
3 结论
1) 将锰酸锂电池半荷电常温储存一个月,电池容量衰减3.7%,但是循环性能得到改善,储存前后100次循环容量保持率分别为91.1和94.1%。
2) 储存后LiMn2O4晶格发生收缩,存前后的LiMn2O4的晶胞参数分别为8.240×10-10 m和8.217×10-10 m。
3) 储存后正负极阻抗明显增大。正极阻抗分别由储存前的62.69 Ω增大到储存后的84.64 Ω,负极阻抗由储存前的183.1 Ω增大到301 Ω。
4) 储存后电解液溶剂和电解质盐均发生了不同程度的分解。
REFERENCES
[1] AMINE K, TUKAMOTO H, YASUDA H. Preparation and electrochemical investigation of LiMn2-xMexO4 (Me: Ni, Fe, and x=0.5, 1) cathode materials for secondary lithium batteries[J]. J Power Sources, 1997, 68(2): 604-608.
[2] HONG Y S, HAN C H, KIM K. Structural and electrochemical properties of the spinel Li(Mn2-xLix/4Co3x/4)O4[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2001, 139(1/2): 75-81.
[3] 李运娇, 常建卫, 李洪桂. 富锂型掺钴尖晶石锂锰氧化物的结构与电化学性能[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 35(3): 381-385.
LI Yun-jiao, CHANG Jian-wei, LI Hong-gui. Structure and electrochemical performance of Li-rich spinel lithium manganese oxide with doping cobalt[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2004, 35(3): 381-385.
[4] ALCANTARA R, JARABA M, LAVELA P. New LiNiyCo1–2yMn1+yO4 spinel oxide solid solutions as 5 V electrode material for Li-ion batteries[J]. J Electrochem Soc A, 2004, 151(1): 53-58.
[5] 何向明, 蒲微华, 蔡 砚, 王晓青, 姜长印, 万春荣. 球形尖晶石LiMn2O4惨杂钇的性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2005, 63(19): 1853-1856.
HE Xiang-ming, PU Wei-hua, CAI Yan, WANG Xiao-qing, JIANG Chang-yin, WAN Chun-rong. Study on yttrium doping of spherical spinel LiMn2O4[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2005, 63(19): 1853-1856.
[6] EFTEKHARI A. Aluminum oxide as a multi-function agent for improving battery performance of LiMn2O4 cathode[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2004, 167 (3/4): 237-242.
[7] 吴 川, 吴 锋, 白 莹. 金属氧化物包覆LiMn2O4的红外光谱及光电子能谱研究[J]. 光散射学报, 2006, 17(4): 396-401.
WU Chuan, WU Feng, BAI Ying. Fourier transition infrared spectroscopic and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic studies on metal oxide-coated LiMn2O4[J]. Chinese Journal of Light Scattering, 2006, 17(4): 396-401.
[8] YAMANE H, SAITOH M, SANO M. Cycle performance in each state-of-charge in LiMn2O4[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2002, 149(10): 1514-1519.
[9] TAKAHASHI K, SAITOH M, ASAKURA N. Electrochemical properties of lithium manganese oxides with different surface areas for lithium ion batteries[J]. J Power Sources, 2004, 136(1): 115-121.
[10] LIU Yun-jian, LI Xin-hai, GUO Hua-jun. Performance and capacity fading reason of LiMn2O4/graphite battery after storing at high temperature[J]. Rare Metals, 2009, 28(5): 322-327.
[11] 吴 川. 动力电池及其关键材料的研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2005.
WU Chuan. Stuydy on the pwoer battery and pivotal materials [D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2005.
[12] LIU Yun-jian, LI Xin-hai, GUO Hua-jun. Electrochemical performance and capacity fading reason of LiMn2O4/graphite batteries stored at room temperature[J]. J Power Sources, 2009, 189(2): 721-725.
[13] AURBACH D, DAROUX M. L, FAGUY P W. Identification of surface films formed on lithium in dimethoxyethane and tetrahydrofuran solutions[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1988, 135(8): 1863-1871.
[14] AURBACH D, DAROUX M L, FAGUY P W. Identification of surface films formed on lithium in propylene carbonate solutions[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1987, 134(5): 1611-1616.
[15] 胡传跃. 锂离子电池非水电解液的行为研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2005.
HU Chuan-yue. Study on the electrolyte of Li-ion battery [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2005.
[16] AMATUCCI G G, BLYR A, SIGALA C, ALFONSE P, TARASCON J M. Surface treatments of Li1+xMn2-xO4 spinels for improved elevated temperature performance[J].Solid State Ionics, 1997, 104(1): 13-17.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB613607);国家质检总局科研项目(2008IK260-6);江苏省自然科学基金资助项目(BK2011530); 江苏大学高级人才启动基金(10JDG041);
收稿日期:2010-10-28;修订日期:2011-05-19
通信作者:刘云建,讲师,博士;电话: 13505282025; E-mail: lyjian122331@yahoo.com.cn