文章编号:1004-0609(2013)11-3260-07
SiCl4-Zn体系硅化学气相沉积的化学机理
谢 刚1, 2,侯彦青2,宋东明2, 3,林 艳2,崔 焱1
(1. 云南冶金集团总公司技术中心,昆明 650031;
2. 昆明理工大学 冶金与能源工程学院,昆明 650093;
3. 昆明冶研新材料股份有限公司,昆明 650031)
摘 要:基于MP2/6-311G(d,p)方法,计算并得到SiCl4锌还原各反应通道上各驻点的几何构型、振动频率和能量。根据密度泛函理论,采用广义密度梯度近似和总体能量平面波赝势方法结合周期性平板模型,研究反应驻点在Si(100)面上的吸附、解离及锌还原过程。结果表明:衬底硅参与SiCl4锌还原反应,SiCl4易在顶位吸附解离成—SiCl3和—Cl自由基;当硅基表面有—Cl自由基吸附时,气相中的Zn原子或硅基面吸附的—ZnCl自由基更容易与—Cl自由基结合,而不是与含氯的硅自由基(—SiCln,n=1~3)结合。
关键词:多晶硅;密度泛函理论;锌还原;反应机理
中图分类号:O641 文献标志码:A
Chemical mechanism for silicon chemical vapor deposition in SiCl4-Zn system
XIE Gang1, 2, HOU Yan-qing2, SONG Dong-ming2, 3, LIN Yan2, CUI Yan1
(1. The Technique Center of Yunnan Metallurgy Co., Ltd., Kunming 650031, China;
2. Faculty of Metallurgical and Energy Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093, China;
3. Kunming Yeyan New-Material Co., Ltd., Kunming 650031, China)
Abstract: The channel geometries, vibration frequencies and energy of all stagnations zinc reduction reaction for SiCl4 were calculated through the MP2/6-311G(d, p) method. According to density functional theory, the effects of adsorption, dissociation and zinc reduction of stagnation in the Si(100) surface were studied using the generalized gradient approximation density and total energy plane wave pseudo-potential method combined with periodic slab model. The results show that silicon substrate can participate in zinc reduction reaction of SiCl4, SiCl4 can be absorbed in top sites easily and dissociate into freed radical —SiCl3 and —Cl. When there is —Cl radical adsorbed on the surface of silicon, atom Zn or free radical —ZnCl, which is absorbed on the base silicon, tends to combine with —Cl rather silicon chloride (—SiCln, n=1-3).
Key words: polycrystalline silicon; density functional theory; zinc reduction; reaction mechanisms
近几年来,在严峻的能源替代形势和日益完善的法规政策的强力推动下,太阳能光伏发电产业得到飞速发展。高纯多晶硅作为太阳能电池的关键性材料,被列为重要的战略资源。新一代低成本多晶硅工艺技术研究空前活跃,除了传统工艺(电子级和太阳能级兼容)及技术升级外[1-3],还相继涌现出冶金法[4-8]、锌还原法[9-11]、钠还原法、硅石碳热还原法[12]、气液沉积法[13]、熔盐电解法[14]及无氯技术[15]等专门生产太阳能级多晶硅的新工艺。其中,SiCl4锌还原法因具有设备投资门槛低(仅为西门子法的1/3)、生产耗电量少(约为西门子法的1/3)、SiCl4利用转化率高以及可作为西门子法尾气回收的辅助工艺等优点而备受关注。关于该反应体系的工艺论证及实验研究已有许多报道,但对其反应机理,尤其是硅表面上SiCl4与锌作用并最后生成硅的异相反应机理研究尚未见报道。本文作者采用二阶Moller-Plesset方法和密度泛函理论方法对该反应的微观机理进行了理论探讨,以期寻找最佳反应途径,为实验工作提供必要的理论依据。
1 模型的建立及计算方法
1.1 计算模型
表面计算模型一般分为簇模型和平面模型。簇模型很难对晶体表面的周期性、复杂性以及Fermi能级进行描述。根据文献资料,Si(100)晶向出现的几率较大,具有一定的代表性[16-19]。在此,选取3×3 Si(100)周期性两层平板模型来研究硅表面上SiCl4与锌作用并最后生成硅的还原反应机理。为满足DFT计算所要求的周期性边界条件,用一定厚度的真空层将各超包隔开。考虑到各反应驻点在表面的吸附,选取的真空层厚度为1 nm,以消除层和层间的相互作用。Si(100)基体的具体构型如图1所示。
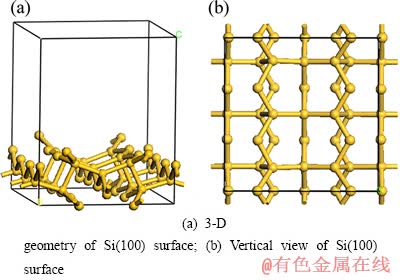
图1 Si (100) 基面的优化构型
Fig. 1 Optimized geometries of Si (100) surface
1.2 计算方法
采用Gaussian 03软件的MP2/6-311G(d,p)方法对SiCln(n=1~4)的几何结构进行优化,并计算其振动频率和能量。在确定SiCln(n=1~4)几何结构的基础上,采用Material Studio软件的CASTEP模块对SiCl4锌还原过程涉及到的各种反应物、过渡态和产物进行了几何构型全优化。交换关联能的近似方法选用广义梯度近似(Generalized gradient approximation,GGA),梯度函数选用PBE (Perdew burke ernzerhof)函数。实现密度泛函的方法是总体能量平面波赝势方法,赝势采用超软赝势。几何优化的计算精度为中等,平面波基截断能量设为Ecut=285.0 eV。平面波基截断能量为Ecut=310.0 eV。过渡态计算采用Complete LST/QST方法,该方法将线性同步过渡(Linear synchronous transition,LST)/四级同步过渡(Qaud-stage synchronous transition,QST)算法结合使用,是一种较为有效的过渡态搜索技术。最后根据计算得到的各过渡态构型,内禀反应坐标(IRC)对进行解析,验证反应势能面上各过渡态与反应物、产物之间的连接关系。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 SiCln(n=1~4)的基态结构
为了确定SiCl4锌还原各反应通道上的稳定驻点,对SiCln(n=1~4)的构型在MP2/6-311G(d,p)下进行几何优化、能量和频率计算,将能量最低且最低振动频率为正值的结构确定为反应的基态稳定驻点。
表1 SiCln(n=1~4)的基态结构和振动频率及能量
Table 1 Energy and vibration frequency of ground state structures of SiCln(n=1-4)
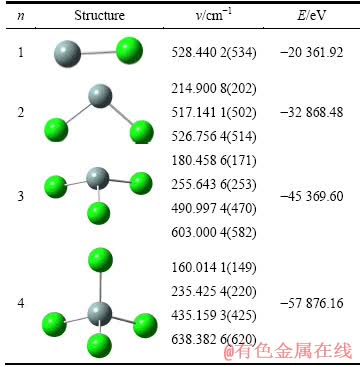
首先,采用上述计算方法对已经过实验验证的SiCl4的结构及振动光谱进行了计算。计算结果表明:SiCl4中Si—Cl键键长为0.201 98 nm,Cl—Si—Cl键角为109.471 2°,振动频率分别为160.014 1、235.425 4、435.159 3和638.382 6 cm-1,理论计算值均较为接近实验值[20]。SiCl计算得到的振动频率为528.440 2 cm-1,也和文献报道的实验测定值534 cm-1基本一致。说明所选择的计算方法能反映真实体系的情况,因此,采用该方法进一步对SiCln(n=1~4)的几何构型进行了计算。表l给出了计算所得的SiCln (n=1~4)的基态稳定结构、最高振动频率及能量,表中括号里的数值为SiCln(n=1~4)振动频率的实验测定值[21]。
从表1可知,自由基—SiCl、—SiCl2、—SiCl3和—SiCl4的几何结构分别为直线型、V形、三角锥形和四面体;振动频率均不存在虚频,说明SiCln(n=1~4)的结构都为势能面上的稳定驻点。
2.2 SiCl4在Si(100)面上的吸附
SiCl4与锌的还原反应主要在硅表面进行,而后还原生成的Si原子进入基体晶格,因此,应先讨论SiCl4在硅晶面上的吸附情况。SiCl4在Si(100)晶面上主要有4种吸附位置,其中,A代表顶位,B代表桥位,C代表穴位1,D代表穴位2。SiCl4分子采用上述MP2/6-311G(d,p)计算得到的几何构型,Si(100)层晶模型先进行预优化后,再分别对4种吸附构型的稳定性、吸附能及成键情况进行了理论计算。计算得到的吸附稳定构型如图2所示。
从图2可以看出,SiCl4分子在Si(100)面上吸附时,与基体Si原子有相互作用,相邻顶位上的Si原子与SiCl4上的1个Cl原子产生键合,使SiCl4上对应的Si—Cl键的键长由基态时的0.201 98 nm分别伸长为0.413 559、0.486 75、0.375 754和0.434 805 nm。
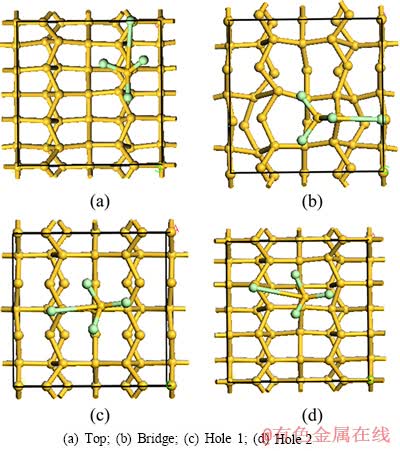
图2 SiCl4分子在Si(100)表面不同吸附模式的俯视图
Fig. 2 Top views of SiCl4 molecule after adsorption on Si(100) surface at different sites
吸附能为吸附前后体系总能量的变化,其符号和大小可表示吸附发生的可能性和吸附强度。吸附能的计算公式如下:
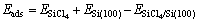 (1)
(1)
式中: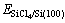 、
、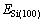 和
和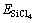 分别表示SiCl4/Si (100)体系、净Si(100)面和自由SiCl4分子的能量,其值为正时表示吸附体系是稳定的。相应的吸附能和SiCl4分子的Mulliken电荷布居数列于表2中。
分别表示SiCl4/Si (100)体系、净Si(100)面和自由SiCl4分子的能量,其值为正时表示吸附体系是稳定的。相应的吸附能和SiCl4分子的Mulliken电荷布居数列于表2中。
根据表2的计算结果,当SiCl4在Si(100)上发生顶位吸附时,吸附能最大,吸附构型最稳定。电子云密度分布能直接反映体系中电荷的空间分布,为了更直观地判断吸附SiCl4分子与表层Si原子之间的相互作用本质,分别绘制各吸附构型的电荷密度分布和差分电荷密度分布图,如图3所示。
从吸附构型的Mulliken电荷和差分电荷密度分布图可知,SiCl4在Si(100)面的吸附为解离吸附,SiCl4中的1个Si—Cl键断裂,离解的—Cl自由基与相邻硅基顶位上的Si原子形成共价键合,吸附方程可表示为
SiCl4+sites→ —SiCl3+ —Cl (2)
计算获得的吸附机理与现有的实验研究结论一致,NALWA[20]和 等[22]曾采用激光诱导热脱附和程序升温脱附法证实SiCl4在硅表面的脱吸附为解离吸附。
等[22]曾采用激光诱导热脱附和程序升温脱附法证实SiCl4在硅表面的脱吸附为解离吸附。
2.3 SiCl4锌还原反应的途径
根据上述的计算结果,SiCl4在Si(100)面上发生顶位吸附时能量最低,且吸附时发生离解反应,反应产物为吸附在Si(100)面上的—SiCl3和—Cl自由基。因此SiCl4锌还原反应前存在前置解离反应,参与锌还原的最初反应物实际上应为—SiCl3。而因其最低振动频率为正值,—SiCl3、—SiCl2和—SiCl自由基均证实是势能面上的稳定驻点,故在本计算中,锌还原的反应途径按SiCl4→ —SiCl3→ —SiCl2→ —SiCl→Si的顺序进行。SiCl4锌还原反应途径中各反应物、过渡态和产物的优化构型和能量见图4。
分析图4中各反应途径的活化能垒,在Zn还原过程中,Zn原子还原—SiCln(n=1~3)时,该反应逆过程的活化能垒总是高于正过程的活化能垒,因此,对应的反应偏向于正过程,即SiCln生成硅的趋势较好;与之相反,当—ZnCl自由基还原—SiCln(n=1~3)时,反应逆过程的活化能垒总是低于正过程的活化能垒,此时—SiCln较难生成硅。此外,由于Zn/—ZnCl与—SiCln上的—Cl反应时比其与硅基体上的—Cl自由基反应需要更高的能量,所以,当硅基表面有—Cl自由基吸附时,Zn/—ZnCl更倾向于与—Cl自由基结合,而不是与—SiCln结合。
表2 SiCl4在Si(100)面吸附的几何构型参数、吸附能和Mulliken电荷
Table 2 Optimized geometrical parameter,adsorption energies and Mulliken charges of SiCl4 adsorption on Si(100) surface
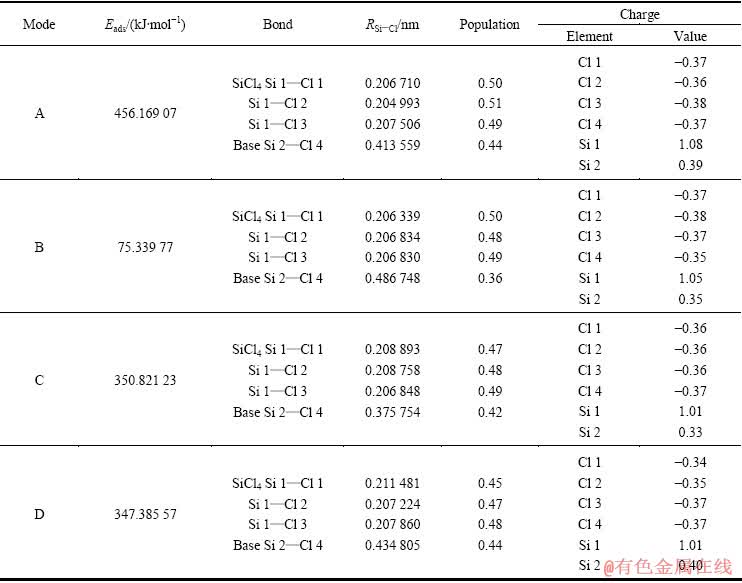
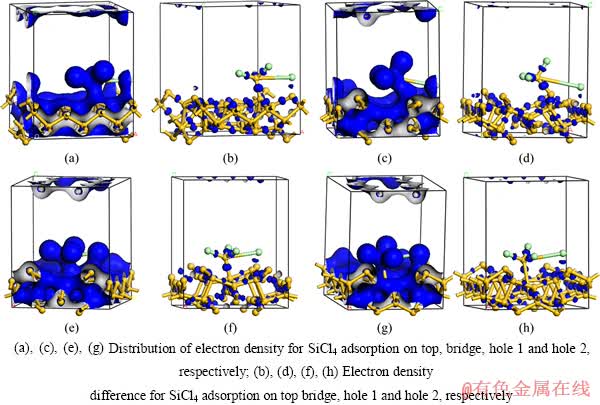
图3 SiCl4在Si(100)面吸附的电荷密度分布和差分电荷密度分布
Fig. 3 Distribution of electron density and electron density difference of SiCl4 adsorption on Si(100) surface
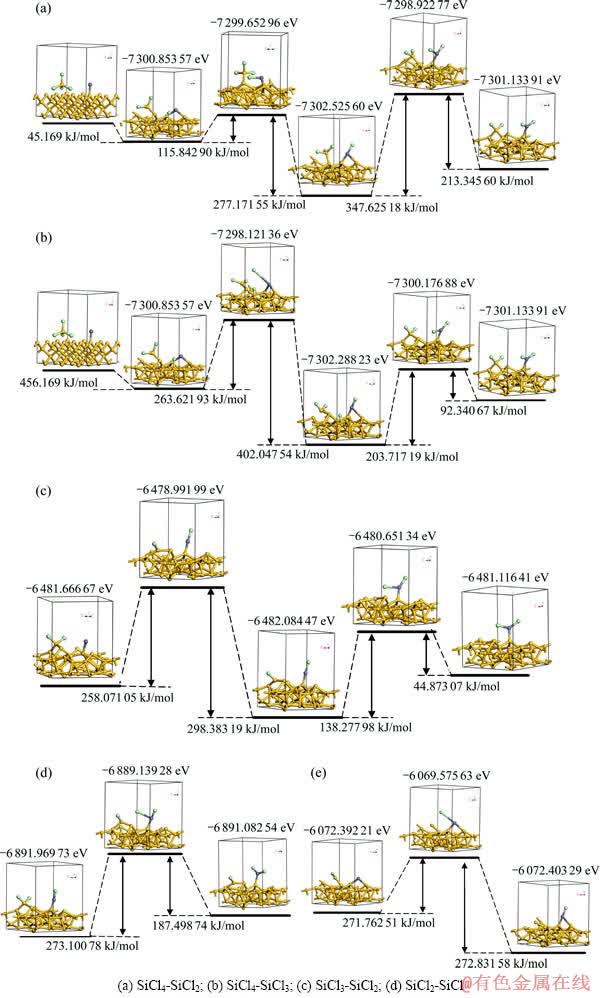
图4 SiCl4锌还原过程各反应物、过渡态和产物几何构型、反应途径及能垒
Fig. 4 Geometric configurations of reactants, transition states and products and reaction path ways and energy barriers during zinc reduction of SiCl4
综合以上研究结果,SiCl4锌还原的最佳反应途径可表示为
SiCl4+sites→ —SiCl3+ —Cl (3)
—SiCln+ —Zn→ —SiCln-1+ —ZnCl (4)
—ZnCl+—Cl ZnCl2 (5)
ZnCl2 (5)
根据式(3)~(5)可知,采用SiCl4锌还原法生产多晶硅时,为了获得较高的SiCl4转化率,体系中的锌蒸气应过量以满足硅基表面上有足够的Zn原子用于还原—SiCln自由基(n=1~3),且应促使生成的ZnCl2尽快从硅基表面脱附,以减少逆反应的发生,并使硅表面上占据顶位的—Cl自由基尽快脱除,为SiCl4的解离吸附创造条件。
3 结论
1) SiCl、SiCl2、SiCl3和SiCl4的几何结构分别为直线型、V形、三角锥形和四面体;振动频率均不存在虚频,说明SiCln(n=1~4)的结构都为势能面上的稳定驻点。
2) SiCl4在Si(100)面上发生解离吸附,吸附位为顶位时体系能量最低且有较大吸附能,吸附反应为
SiCl4+sites→—SiCl3+ —Cl。
3) SiCl4锌还原的最佳反应途径如下:
SiCl4+sites→—SiCl3+ —Cl
—SiCln+ —Zn→—SiCln-1+ —ZnCl
—ZnCl+ —Cl ZnCl2
ZnCl2
REFERENCES
[1] 马文会, 戴永年, 杨 斌, 刘大春, 王 华. 太阳能级硅制备新技术研究进展[J]. 新材料产业, 2006, 10: 12-16.
MA Wen-hui, DAI Yong-nian, YANG Bin, LIU Da-chun, WANG Hua. Research process on new techniques of solar-grade silicon[J]. New Material Industry, 2006, 10: 12-16.
[2] BALAJI S, DU J, WHIT C M, ERIK B. Multi-scale modeling and control of fluidized beds for the production of solar grade silicon[J]. Powder Technology, 2010, 199(1): 23-31.
[3] 温 雅, 胡仰栋, 单廷亮. 改良西门子法多晶硅生产中分离工艺的改进[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2008, 25(2): 154-159.
WEN Ya, HU Yang-dong, SHAN Ting-liang. Improvements of separating process in polycrystalline Si production by modified siemens arts and crafts[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2008, 25(2): 154-159.
[4] MUKASHEV B N, ABDULLIN K A, TAMENDAROV M F, TURMAGAMBETOV T S, BEKETOV B A, PAGE M R, KLINE D M. A metallurgical route to produce upgraded silicon and monosilane[J]. Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells, 2009, 93(10): 1785-1791.
[5] 马晓东, 张 剑, 李廷举. 冶金法制备太阳能级多晶硅的研究进展[J]. 铸造技术, 2008, 29(9): 1288-1291.
MA Xiao-dong, ZHANG Jian, LI Ting-ju. Research process on metallurgical processing of solar grade multicrystalline silicon[J]. Foundry Technology, 2008, 29(9): 1288-1291.
[6] 罗大伟, 张国粱, 张 剑, 李 军, 李廷举. 冶金法制备太阳能级硅的原理及研究进展[J]. 铸造技术, 2008, 29(12): 1721-1726.
LUO Da-wei, ZHANG Guo-liang, ZHANG Jian, LI Jun, LI Ting-ju. Principle and research process on preparation solar grade (SoG) silicon by metallurgical route[J]. Foundry Technology, 2008, 29(12): 1721-1726.
[7] 吕 东, 马文会, 伍继君, 杨 斌, 戴永年. 冶金法制备太阳能级多晶硅新工艺原理及研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2009, 23(3): 30-33.
 Dong, MA Wen-hui, WU Ji-jun, YANG Bai, DAI Yong-nian. New process principle and research advances of production of solar grade poly silicon by metallurgical method[J]. Materials Review, 2009, 23(3): 30-33.
Dong, MA Wen-hui, WU Ji-jun, YANG Bai, DAI Yong-nian. New process principle and research advances of production of solar grade poly silicon by metallurgical method[J]. Materials Review, 2009, 23(3): 30-33.
[8] 于站良, 马文会, 戴永年, 杨 斌, 魏奎先. 太阳能级硅制备新工艺研究进展[J]. 轻金属, 2006, 3: 43-47.
YU Zhan-liang, MA Wen-hui, DAI Yong-nian, YANG Bin, WEI Kui-xian. Research process for novel techniques of solar grade silicon[J]. Light Metals, 2006, 3: 43-47.
[9] SEIFERT D A, BROWNING M F. Pilot-scale development of the zinc reduction process for production of high-purity silicon[J]. Processing of Energy and Metallic Minerals, 1981: 104-115.
[10] 张鸣剑, 李润源, 代红云. 太阳能多晶硅制备新技术研发进展[J]. 新材料产业, 2008, 6: 29-34.
ZHANG Min-jian, LI Run-yuan, DAI Hong-yun. Research process on new techniques of solar grade silicon[J]. New Material Industry, 2008, 6: 29-34.
[11] 汪光裕, 丁国江, 艾 波. 四氯化硅在西门子多晶硅生产流程内部的循环利用[J]. 东方电气评论, 2008, 22(4): 70-72.
WANG Guang-yu, DING Guo-jiang, AI Bo. Circular utilization of silicon tetrachloride in production of polycrystalline silicon by siemens process[J]. Dongfang Electric Review, 2008, 22(4): 70-72.
[12] 龙桂花, 吴 彬, 韩 松, 丘克强. 太阳能级多晶硅生产技术发展现状及展望[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(S1): s387-s392.
LONG Gui-hua, WU Bin, HAN Song, QIU Ke-qiang. Development status and prospect of solar grade silicon production technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(S1): s387-s392.
[13] BRAGA A F B, MOREIRA S P, ZAMPOERI P R, BACCHIN J M G, MEI P R. New processes for the production of solar-grade polycrystalline silicon: A review[J]. Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells, 2008, 92(4): 418-424.
[14] 郭 瑾, 李积和. 国内外多晶硅工业现状[J]. 上海有色金属, 2007, 28(1): 20-25.
GUO Jin, LI Ji-he. Present status of polysilicon industries at home and abroad[J]. Shanghai Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 28(1): 20-25.
[15] 梁骏吾. 电子级多晶硅的生产工艺[J]. 中国工程科学, 2000, 2(12): 34-39.
LIANG Jun-wu. The production technology of electronic grade plycrustalline silicon[J]. Chinese Engineering Science, 2000, 2(12): 34-39.
[16] MENDICINO M A, SEEBAUER E G. Adsorption of chlorine on Si(100)[J]. Applied Surface Science, 1993, 68(3): 285-290.
[17] DARLINGTON B, FOSTER M, CAMPION A. Adsorption and reactions of diethylsilane on Si(100)[J]. Surface Science, 1994, 304(1/2): 407-402.
[18] MENDICINO M A, SEEBAUER E G. Adsorption of TiCl4 on Si(100)[J]. Surface Science, 1992, 277(1/2): 89-96.
[19] SAKAMOTO H, TAKAKUWA Y, HORI T, TETSUHIRO H, NOBUO M. First-order isothermal desorption kinetics of chlorine on SiH2Cl2-adsorbed Si(100) surface[J]. Applied Surface Science, 1994, 75(1/4): 27-32.
[20] NALWA H. Silicon-based material and devices[J]. Two-Volume Set, 2001, 170: 1-2.
[21] SU M D, H. SCHLEGEL B. An ab initio MO study of the thermal decomposition of chlorinated monosilanes, SiH4-nCln (n=0-4)[J]. J Phys Chem, 1993, 97(39): 9981-9985.
[22]  A, PAUL D F, THOMAL E. Reactions of chlorine with Si(100) and Si(111): Adsorption and desorption kinetics[J]. Surface science, 1994, 312(3): 284-300.
A, PAUL D F, THOMAL E. Reactions of chlorine with Si(100) and Si(111): Adsorption and desorption kinetics[J]. Surface science, 1994, 312(3): 284-300.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50574045)
收稿日期:2012-05-04;修订日期:2013-09-20
通信作者:侯彦青,博士;电话:15987198926;E-mail:hhounyanqing@163.com