文章编号:1004-0609(2007)12-1936-07
界面金属间化合物对
铜基Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu焊点拉伸断裂性能的影响
鞠国魁1,韦习成1, 2,孙 鹏2, 3,刘建影2, 3
(1. 上海大学 材料科学与工程学院, 上海 200072;
2. 上海大学 中瑞联合微系统集成技术中心 新型显示技术与应用集成教育部重点实验室, 上海 200072;
3. SMIT Center, Chalmers University of Technology, 412-96 G?teborg, Sweden)
摘 要:研究了Cu/Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/Cu焊点在(150±1)℃时效温度下,0~1 000 h不同时间时效后焊点的拉伸断裂性能以及界面金属间化合物(IMC)的组织形态和成分。结果表明:随着时效时间的延长,焊点拉伸强度降低,拉伸断裂主要发生于Solder/IMC界面或/和IMC/IMC界面,而且断口形貌逐渐由韧窝状断口为主向解理型脆性断口转变。SEM研究发现,时效过程中界面IMC不断长大、增厚并呈针状或块状从Cu/Solder界面向焊点心部生长,时效1 000 h的焊点中IMC分层明显。半焊点结构为Cu/Cu3Sn/Cu6Sn5/Solder,同时,在靠近铜基体的IMC中有Kirkendall空洞存在。
关键词:金属间化合物;Cu/Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/Cu焊点;拉伸断裂;多层结构;柯肯达尔洞
中图分类号:TG 146 文献标识码:A
Effects of interfacial IMC on tensile fracture behavior of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder joints on copper substrates
JU Guo-kui1, WEI Xi-cheng1, 2, SUN Peng2, 3, LIU Johan2, 3
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China;
2. Key Laboratory of New Displays and System Integration, Ministry of Education,
Sino-Swedish Microsystem Integration Technology (SMIT) Centre, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China;
3. SMIT Center, Chalmers University of Technology, 412-96 G?teborg, Sweden)
Abstract: The tensile fracture behavior and the intermetallic compound’s(IMC’s) morphology and composition at the interface of Cu/Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/Cu solder joint specimens after aging at (150±1)℃ for 0-1 000 h were studied. The results show that, with the increasing aging time, the tensile fracture strength of the solder joints decreases and the crack initiates mostly at the interfaces between the solder and IMC layer or/and IMC and IMC layer. The morphology of fracture surface changes from dimple-like to cleavage-like surfaces. SEM analysis indicates that the needle-like or block-like interfacial IMC forms at the interface of Cu/solder and grows into the solder matrix. After being aged for 1 000 h, the obvious IMC multilayer structure is observed, which is defined as Cu/Cu3Sn/Cu6Sn5/solder structure for the half-joints. Moreover, the Kirkendall voids can be observed in the multilayer structure close to the copper substrate. These voids are possibly one of the factors of the tensile fracture mechanism.
Key words: intermetallic compound (IMC); Cu/Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/Cu joint; tensile fracture; multilayer structure; Kirkendall void
电子封装工艺中,焊点界面的IMC(intermetallic compound)的形成机制是焊接时液态焊料与焊盘的化学冶金反应,服役时IMC的演变机制是元素的固态扩散[1]。Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu焊料的熔点及Sn含量都高于Sn-37Pb焊料,回流焊时较高的峰值温度导致Cu、Ni等UBM(under bump metallization)层在无铅焊料中的溶解速率提高,焊点界面更易形成大量IMC[2-4]。依焊料组分不同,IMC的成分、组元和结构均会发生相应改变,例如,在Cu/SnAgCu界面可形成Cu6Sn5或Cu3Sn[5-6];在Cu-Ni(P)/Solder界面可形成Ni3Sn4等[7]。当T/Tm≥0.5(T为时效温度,Tm为焊料熔点)时,焊料与Cu基板间的元素互扩散作用加强,导致界面IMC的进一步生长[8]。Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu的熔点为223 ℃,在器件存储、使用过程中(T/Tm=300 K/500 K=0.6≥0.5),其IMC厚度仍会随时间的延长而不断增加。
研究表明[9-11],焊点界面结合力的强弱很大程度上取决于焊接过程中焊料和焊盘表面冶金反应所生成的IMC,但由于IMC与焊料本体的物理性质差异,其形态、大小、厚度等都会影响焊点的变形协调性,机械应力或热应力亦会在焊点相界面、焊盘界面、工艺缺陷(如空洞)和Kirkendall孔等弱界面处形成应力集中,进而发展形成微裂纹,使焊点脆化或弱化,疲劳性能下降,最终导致焊点可靠性降低甚至早期断 裂[12]。因此,焊点界面的IMC研究一直是电子产品封装可靠性研究重点关注的议题。
目前研究机械疲劳条件下焊点可靠性的方法主要是采用剪切实验,但剪切面间的摩擦作用破坏了焊点断裂表面[13],不易获得焊点断裂机理的真实信息。如果采用拉伸实验的方法则不仅可获得可靠的界面结合强度数据和完整、清晰的拉伸断口形貌;而且在拉伸过程中试样截面方向的应力分布均匀,焊料、焊盘、界面的受力状态一致,失效将发生在焊点最薄弱处,有利于准确判断失效机理和影响焊点可靠性的因素。
本文作者在工业纯(99.9%)的铜棒材端面利用 Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu焊料制成焊点,然后对在150 ℃的时效温度下经不同时效时间处理后的焊点进行拉伸实验,研究界面IMC对焊点拉伸断裂强度及断裂机理的影响,为无铅焊点的可靠性研究提供实验基础。
1 实验
实验采用工业纯(99.9%)的铜棒,将其截取制成 d 6 mm×50 mm的试棒,用硝酸溶液除去表面氧化层。Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu块状焊料采用法国Avantec化工公司产品,将其线切割成d 6 mm×4 mm的薄片,然后将铜试棒和焊料片(涂覆德国助焊剂KesterRTacky soldering flux)装夹在自行研制的模拟焊接平台上,焊接5 min(在(250±5))℃保温约1 min),出炉空冷至室温。图1所示为制备的试样原型。

图1 制备的Cu/Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/Cu试样照片
Fig.1 Image of prepared Cu/Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/Cu sample
时效实验依据JREDEC(Joint Electron Device Engineering Council) 2004年11月发布的High Temperature Storage Life标准(JESD22-A103C),将制成的试样在150 ℃(精度±1 ℃)下分别时效24、168、500和1 000 h,每个时效时间4个试样(各组的平均焊层厚度分别为:0 h,1.54 mm;24 h,1.48 mm;168 h,1.53 mm;500 h,1.54 mm;1 000 h,1.50 mm;)。拉伸实验在CMT5305型微机控制万能拉伸实验机上进行,拉伸速率0.02 mm/s。随后将断裂的试样冷镶嵌制成金相样,机械磨削、抛光并经94%C2H5OH+ 4%HNO3+2%HCl (体积分数)腐蚀。用Hitachi S-570 扫描电镜(SEM)分析拉伸断口形貌和界面的IMC,用SEM附带的EDAX-phoenix检测IMC的成分和元素的扩散分布。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 时效对Cu/Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder界面拉伸强度的影响
图2所示为在150 ℃,经不同时效时间后焊点的拉伸强度。由图2可以看出,焊点的拉伸强度随着时效时间的延长而下降,其指数关系为σ=24.2+36exp(-t/180)。时效400 h前的焊点结合强度下降显著,当超过400 h后,拉伸强度的降幅趋于平缓,这与IMC的生长趋势相吻合。众所周知,一方面焊点界面形成的IMC保证了焊料与焊盘的可靠连接,焊料中弥散分布的微小IMC可以改善焊料的蠕变和疲劳抗力,而且扇贝状IMC也有利于改善焊点与焊盘的连接强度;另一方面,如果粗大的IMC在界面呈较厚的层状分布则会降低界面的力学协调性,在热循环或外力作用下界面易于产生应力集中,并在IMC与焊料界面累积缺陷,弱化了界面强度,最终导致断裂失效[14]。因此,在焊点界面上的IMC厚度适当有利于提高焊点可靠性,但IMC的过度生长则对焊点可靠性不利。

图2 焊点拉伸强度与时效时间的关系
Fig.2 Tensile strength as function of aging time
2.2 不同时效时间后焊点的断口形貌
焊点的断裂失效模式主要取决于焊点结构和焊点微观组织,而裂纹的形成与生长途径受焊点结构、焊料成分、基板以及加载模式、应力状态等因素的影响。由于焊料和基板间的IMC弱化了界面,焊点在短时时效后的破坏大多发生在界面靠焊料一侧。Rzerhard 等[15]通过有限元模拟对CSP器件的应力应变进行分析发现,裂纹通常发生在焊点内部IMC与焊料形成的界面处、焊料内部接近IMC边界处以及IMC层内部。
图3所示为不同时间时效后的拉伸断口形貌。 时效24 h后的断口上可见残留的焊料周围分布着大量的韧窝,只有部分断口比较平整,说明短时时效后少量弥散分布的IMC颗粒有利于增强焊点的结合强度,断裂主要发生在IMC/solder界面;时效168 h后,韧窝状断口明显减少,平整断口逐渐增多,仅在晶界处分布了少量残余焊料,在IMC/solder的界面的断裂和IMC/IMC界面的断裂并存;当时效时间达到500 h后,平整的解理断口开始占据主导地位,韧断痕迹很少;时效1 000 h的焊点断口上脆断基本覆盖了整个断面,韧断特征完全消失。由于时效时间的延长导致IMC的过度生长,进而严重恶化了焊点的拉伸强度,拉伸断裂最终完全起裂于最脆弱的IMC/IMC界面。

图3 不同时效时间后焊点的断口形貌
Fig.3 Morphologies of fracture surface after different aging time: (a) 24 h; (b) 168 h; (c) 500 h; (d) 1 000 h
因此,随着时效时间的延长,焊点拉伸强度逐步降低,断裂起点由Solder/IMC界面转至IMC/IMC界面,断裂方式由韧性断裂转变为了脆性断裂。
2.3 焊点界面的SEM分析
2.3.1 界面IMC的组织与成分
图4 (a)和(b)所示分别为150 ℃下Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu焊点时效0 h和24 h后的界面SEM照片,直线CD表示Cu/IMC界面。24 h时效后试样的IMC平均厚度明显厚于未时效试样,且沿Cu/Solder界面呈不规则锯齿状向焊料内部凸进。图4(c)所示为E点的EDS峰。
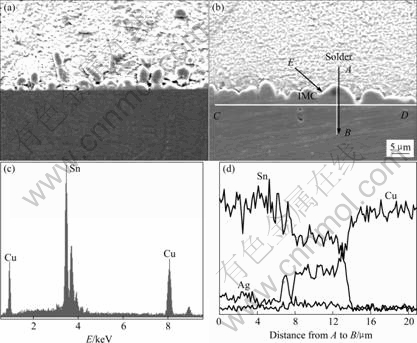
图4 焊点短时间时效后0 h的SEM像(a),24 h的SEM像(b),E点成分峰(c),沿AB线的成分分布(d)
Fig.4 SEM image after aging for 0 h (a), SEM image after aging for 24 h (b), element apices of point E (c) and line scan profiles along line AB (d) after short time aging
由图4可以看出,E点IMC的组成元素为Cu和Sn,其原子比为59.0?41.0,成分接近Cu6Sn5相。图4(d)所示为沿直线AB方向的线扫描结果,Cu和Sn成分沿AB线呈现梯形分布,与Solder/Cu界面上IMC厚度对应部分的Cu量明显高于焊点内部,而Sn量则比焊点内部的低。这说明Cu原子大量由Cu基盘向焊料内部扩散,与IMC的生长方向和浓度梯度一致;相对于Cu原子的扩散而言,Sn原子的分布恰好相反,在IMC层中的Sn原子明显少于焊点心部,而且在心部与IMC之间的Sn峰略高于心部,说明Sn原子在Cu原子向焊点内部扩散时,Sn原子也向心部扩散,这是一种明显的上坡扩散,因为Cu原子与Sn原子结合形成Cu6Sn5时,将多余的Sn排入了心部。本研究结果与实际的SnAgCu焊点界面的IMC的形态、厚度和组织形貌和成分均完全相同[10],说明本模拟焊点的方法完全能够真实地反映实际焊点。
图5(a)所示为焊点时效500 h后的截面SEM像,图5(b)所示为其对应的3种元素面扫描,图5(c)所示为图5(a)中F点的EDS分析。由图可以清楚地看到在焊料基体的晶界处有很多细小的颗粒,结合图5(c),其成分接近Ag3Sn相,而且发现此处多为沿晶断裂或解理断裂。从图5(b)中的颗粒分布处可以明显地看到Ag的富集和Sn的偏析,同时在焊料与Cu基体的界面富集着一层薄薄的Cu元素,说明了此处存在Sn-Cu化合物。

图5 焊点500 h时效后SEM像(a),面扫描(b),悬浮颗粒F的成分峰(c)
Fig.5 SEM image (a), element distribution map (b) and element apices of suspended grain F (c) after aging for 500 h
在Sn-Ag-Cu合金中,添加Ag可降低焊料的熔点,同时可改善焊料的润湿性及界面结合强度。但Ag与Sn会反应生成如图5所示的颗粒状或针状Ag3Sn。随着Ag含量增加,Ag3Sn逐渐细化,合金强度提高,在Ag含量为3.5%(共晶点)时,强度达到最高。当Ag 含量超过3.5%后,随着Ag含量的进一步增加,Ag3Sn逐渐以片状生长并会诱发焊料基体的开裂[16]。裂纹通常从焊点内部沿着Ag3Sn与焊料的界面扩展,产生沿晶断裂。大颗粒的Ag3Sn本身对拉伸强度没有影响,但却给裂纹的快速扩展提供了通道,从而降低了焊点的韧性,最终导致脆性断裂。尤其当焊点承受热/机械应力时,枝状Ag3Sn会严重影响焊点的力学性能[15]。
2.3.2 IMC的多层结构
图6 (a)所示为焊点时效1 000 h后的SEM像(未标明的成分峰是为增强试样镶料导电性而喷镀的金薄层)。在焊料基体的晶界处可见大量亮白色的颗粒状Ag3Sn,IMC的平均厚度约7.5 μm。界面处的IMC的上层A点和下层B点的成分分析表明,A点的成分接近Cu6Sn5相(η),B点的成分接近Cu3Sn相(ε)。这说明界面形成的IMC明显表现为两层结构:Cu6Sn5层位于焊料一侧,Cu3Sn层位于Cu基板和Cu6Sn5之间。梁英等[17]利用Thermo-Calc软件对Sn-Ag二元共晶焊料与Cu基板的界面反应的模拟计算发现,在较高时效温度下,Sn-Ag系共晶焊料与Cu基板首先反应析出Cu6Sn5中间相,随着反应的继续进行,在靠近Cu基体一侧又会生成Cu3Sn,Cu3Sn是在热力学条件趋于平衡时形成的,这层IMC较薄。图6中波浪状Cu3Sn(ε)相的厚度约为3.5 μm,而短时时效试样中并未发现明显的ε相,实验结果与梁英等[16]的理论计算吻合。同时,Henderson等[18]对Sn-Ag-Cu 焊料(SnAgCu+0.1%- 0.7%Zn)的研究也发现在Cu焊盘与焊料间存在类似的IMC结构,他们的研究显示,焊点经过150 ℃、500 h的时效后,Solder/Cu界面的Cu6Sn5厚度与Cu3Sn厚度几乎相当,界面处的Cu6Sn5以初始的贝壳状向焊料内部生长,逐渐转变成大的波浪状,形成了IMC与焊料边界的锯齿状粗糙形貌。
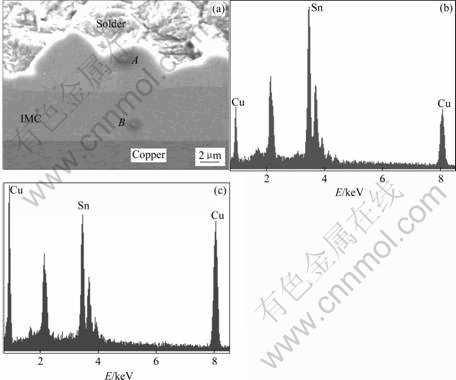
图6 焊点1000 h时效后SEM像(a),A点成分峰(b),B点成分峰(c)
Fig.6 SEM image (a), element apices of point A (b) and element apices of point B (c) after aging for 1 000 h
Solder/Cu界面IMC的形成一般分为两个阶段:在焊接过程中,Cu基板与液态焊料之间形成的IMC;焊后的Cu基板与焊料之间固态扩散形成的IMC。在焊接过程中,当Cu基板与液态焊料发生冶金接触后,固态Cu便开始向液态焊料中扩散,紧邻Cu基板的一层液态焊料中的Cu原子达到饱和。从热力学角度而言,虽然存在亚稳态的过饱和,但当Cu原子处于局部平衡时,便形成了Cu6Sn5(η相)。它消耗了处于饱和态的液体焊料中的Cu,促发基板上的Cu向液态焊料中的进一步扩散。随着Cu6Sn5的形成和向焊点内部的生长,在Cu/Solder界面上就形成了一层连续的、一定厚度的IMC,抑制了基板上的Cu向液态焊料的进一步扩散。尽管此时固态的Sn与Cu6Sn5处于平衡态,但固态Cu与Cu6Sn5仍处于非平衡状态。这意味着一旦热力学或者动力学条件满足,在Cu/Cu6Sn5界面便会通过固相扩散形成Cu3Sn(ε相)。由于≥0.5,焊后固态的Cu和Sn的扩散仍继续进行[8],以Cu穿过Cu3Sn层和Cu6Sn5层向焊点心部的扩散为主。当Cu扩散至Cu3Sn/Cu6Sn5和Cu6Sn5/Solder界面时,这两类IMC就继续向焊料中生长,厚度同步增加但不一定同幅。据此确定Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu焊点经长时间时效后的半焊点结构为Solder/Cu6Sn5(η)/Cu3Sn(ε)/Cu。
综上所述,在回流和时效过程中形成的多层结构的IMC间的结合强度较低增加了焊点的内部缺陷,导致焊点在外力作用下易从多层结构的IMC界面起裂甚至脆性断裂[19]。
结合图3(a)可以看出,短时时效后焊点的破坏主要是Cu/Solder界面处靠Cu6Sn5层一边的断裂。随着时效时间的延长,焊点破坏主要表现为在Cu6Sn5/Cu3Sn界面的脱层开裂,如图3(c)和(d)中的颗粒被拔出的痕迹。因此合理的界面组织控制对于焊点的可靠性提高是非常重要的,也是值得进一步研究的。
2.3.3 Kirkendall孔洞
经1 000 h时效处理后的焊点界面的SEM研究发现,在IMC层中有Kirkendall空洞存在,如图7所示。这些孔洞位于Cu3Sn(ε)层中靠近Cu6Sn5(η)层的一侧,结合图2和图3(d)可以推断,在Cu6Sn5(η)/Cu3Sn(ε)层中的Kirkendall空洞是影响焊点拉伸性能的重要因素之一。常俊玲等[20]认为,相对于SnPb焊料而言, Sn-Ag-Cu 焊料可以延缓焊点界面的Kirkendall空洞的形成。本文研究结果也表明(图7),尽管经过了1 000 h的高温时效,但在焊点界面并未发现大量的Kirkendall孔洞,说明Sn-Ag-Cu焊料确实具有一定的抑制Kirkendall孔洞形成的能力。

图7 焊点1 000 h时效后IMC层的Kirkendall空洞
Fig.7 Kirkendall voids on IMC layer after aging time 1 000 h
Kirkendall空洞的形成一方面与界面IMC的生长速率加快有关;另一方面由于长时间时效后在Sn-Ag-Cu焊料中Cu6Sn5和Ag3Sn的存在影响了Sn中Cu的溶解度和界面IMC的生长[10]。从原子水平而言,1个Sn原子与3个Cu原子形成Cu3Sn时体积净减小8.2%,5个Sn原子与6个Cu原子形成Cu6Sn5时体积净减小10%。由于基板中的Cu原子向焊料中扩散,遗留在基板与焊点界面的原子空位难以完全由焊料中向界面扩散的原子占据,即在存在1个原子的扩散通量差的情况下,便会在界面上形成部分永久空位。当这些空位在Cu/Cu3Sn界面和Cu3Sn内部聚集到一定程度便形成了Kirkenall空洞。随着进一步的时效,Kirkendall空洞会逐渐长大、聚合并沿着Cu/Cu3Sn界面层形成脱层或诱发Cu3Sn内部裂纹的萌生,进而直接影响焊点的可靠性。尽管人们一直关注焊点中的Kirkendall孔洞的形成机理及与焊点可靠性的关系[10],但至今尚无统一的观点,本研究中Kirkendall孔洞对断裂机理的影响也还需深入探讨。
3 结论
1) 随着时效时间的延长IMC的厚度增加,焊点拉伸断裂强度明显下降。
2) 随着时效过程中的焊点界面上IMC的厚度增加,拉伸断裂由Solder/IMC界面向IMC/IMC界面过渡,断裂机理由韧性断裂过渡为脆性断裂,时效时间超过500 h后的断口形貌基本为类解理状。
3) 长时时效后的半焊点结构为Cu/Cu3Sn(ε)/ Cu6Sn5(η)/Solder,同时在IMC层中分布着少量的Kirkendall空洞。
REFERENCES
[1] Li G Y, Chen B L. Formation and growth kinetics of interfacial intermetallics in Pb-free solder joint[J]. IEEE Trans on Components and Packaging Technologies, 2003, 26(3): 651-658.
[2] Tu K N, Zeng K. Tin-lead (SnPb) solder reaction in flip chip technology[J]. Materi Sci Eng R, 2001, 34(1): 40-58.
[3] 吴文云, 邱小明, 殷世强. Bi、Ag对Sn-Zn无铅钎料性能与组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(1): 158-163.
WU Wen-yun, QIU Xiao-ming, YIN Shi-qiang. Influence of Bi, Ag on microstructure and properties of Sn-Zn lead-free solder[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(1): 158-163.
[4] 韦习成, 鞠国魁, 孙 鹏. 高温、高湿环境中时效时Sn-Zn基无铅焊点的显微组织演化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(7): 1177-1183.
WEI Xi-cheng, JU Guo-kui, SUN Peng. Microstructure evolution of Sn-Zn based lead-free solder joints aged in humid atmosphere at high temperature[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(7): 1177-1183.
[5] Abtew M, Selvaduray G. Lead-free solders in microelectronics[J]. Mater Sci Eng R, 2000, 27(5/6): 95-141.
[6] Nakamura Y, Sakakibara Y, WatanabeY, Amamoto Y. Microstructure of solder joints with lead-free solders[J]. Soldering and Surface Mount Technology, 1998, 10(1): 10-12.
[7] Kim K S, Ryu K W, Yu C H, Kim L M. The formation and growth of intermetallic compounds and shear strength at Sn-Zn solder/Au-Ni-Cu interfaces[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2005, 45(3/4): 647-655.
[8] Islam M N, Chan Y C, Rizvi M J, Jillek W. Investigation of interfacial reactions of Sn-Zn based and Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder alloys as replacement for Sn-Pb solder[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 400(3/4): 136-144.
[9] Duan N, Scheer J, Bielen J, Van Kleef M. The influence of Sn-Cu-Ni(Au) and Sn-Au intermetallic compounds on the solder joint reliability of flip chips on low temperature co-fired ceramic substrates[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2003, 8(43): 13-17.
[10] Zeng K, Tu K N. Six cases of reliability study of Pb-free solder joints in electronic packaging technology[J]. Materials Science and Technology R, 2002, 3(8): 55-101.
[11] Foley J C, Gickler A, Leprevost F H, Brown D. Analysis of ring and plug shear strengths for comparison of lead-free solders[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2000, 29(10): 1258-1263.
[12] Salam B, Ekere N N, Rajkumar D. Study of the interface microstructure of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solders and the effect of solder volume on intermetallic layer formation[C]//2001 Electronic Components and Technology Conference. Oxlando, USA: Institue of Electrical and Electronic Engineers Inc., 2001: 471-477.
[13] Prakash K H, Sritharan T. Tensile fracture of tin-lead solder joints in copper[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 379: 277-285.
[14] Mon H, FD B. ITRI project on electroless nickel/immersion gold joint cracking[J]. Circuit World, 2000, 26(2): 10-16.
[15] Rzepka S, Hufer E E. Stress analysis and design optimization of a wafer-level CSP by FEM simulations and experiments[C]// Electron Compon Technol Conf. IEEE, 2001.
[16] Kang S K. Ag3Sn plate formation in the solidification of near ternary eutectic Sn-Ag-Cu alloys[J]. Miner Metals Mater Soc, 2003, 55(6): 61-65.
[17] 梁 英,孙凤莲,王丽凤. Sn-Ag共晶钎料与Cu基板界面反应的热力学计算[J]. 哈尔滨理工大学学报, 2005, 10(5): 80-83.
LIANG Ying, SUN Feng-lian, WANG Li-feng. Thermodynamic calculation analysis of interfacial reaction between Sn-Ag and Cu substrate[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2005, 10(5): 80-83.
[18] Henderson D W, Cho S, Yu J. Interfacial reactions of Sn-Ag-Cu solders modified by minor Zn alloying addition[R]. RC23558 (W0503-054), USA: IBM , 2005-03-09.
[19] Petar R. Reliability and failure analysis of Sn-Ag-Cu solder interconnections for PSGA packages on Ni/Au surface finish[J]. IEEE Trans Electron Packg Manuf, 2004, 4(1): 5-10.
[20] 常俊玲, 刘晓庆, 谢晓明. SnAgCu(SnPb)/N和SnAgCu (SnPb)/Cu界面金属间化合物在热冲击过程中的生长规律[J]. 功能材料与器件学, 2005, 11(4): 446-450.
CHANG Jun-ling, LIU Xiao-qing, XIE Xiao-ming. Growth behavior of IMC at SnAgCu(SnPb)/Ni and SnAgCu(SnPb)/Cu interface during thermal shock[J]. Journal of Functional Materials and Devices, 2005, 11(4): 446-450.
基金项目:上海市教育委员会科研基金资助项目(06ZR011);上海大学研究生创新基金资助项目(2007)
收稿日期:2007-04-17;修订日期:2007-08-22
通讯作者:韦习成, 研究员,博士;电话:021-56331377;传真:021-56331977; E-mail: wxc1028@staff.shu.edu.cn
(编辑 李向群)