Influence of welding processes on microstructure, tensile and impact properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy joints
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2011年第6期
论文作者:T. S. BALASUBRAMANIAN V. BALASUBRAMANIAN M. A. MUTHUMANIKKAM
文章页码:1253 - 1262
关键词:钛合金;钨电极惰性气体保护焊接;激光束焊接;电子束焊接
Key words:titanium alloy; gas tungsten arc welding; laser beam welding; electron beam welding
摘 要:钛合金由于具有高比强度、优越的耐腐蚀性和出色的耐热性等优良特性,已成功应用于航空航天、造船和化学工业。尽管钛合金具有合适的可焊性特点,但焊接方法极大地影响焊接接头性能。焊接过程中热循环将会影响焊接金属凝固、相转变和微观组织。采用钨电极惰性气体保护焊接(GTAW)、激光束焊接(LBW)和电子束焊接(EBW)方法制备Ti-6Al-4V合金的焊接接头。EBW焊接接头的强度高于GTAW和LBW接头的强度,但GTAW接头较其它两种接头具有较高的断裂韧性。焊接接头的拉伸和冲击性能与焊接金属的微观组织有关。
Abstract:
Titanium alloys have been successfully applied for aerospace, ship and chemical industries because they possess many good characteristics such as high specific strength, superior corrosion resistance and excellent high temperature resistance. Though these alloys show reasonable weldability characteristics, the joint properties are greatly influenced by the welding processes. Weld thermal cycle of the processes will control the weld metal solidification and subsequent phase transformation and resultant microstructure. The welded joints of Ti-6Al-4V alloy were fabricated by gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), laser beam welding (LBW) and electron beam welding (EBW) processes. The joints fabricated by EBW process exhibit higher strength compared with the GTAW and LBW joints; but the joints by GTAW process exhibit higher impact toughness compared with the LBW and EBW joints. The resultant tensile and impact properties of the welded joints were correlated with the weld metal microstructures.

T. S. BALASUBRAMANIAN1, M. BALAKRISHNAN2, V. BALASUBRAMANIAN2, M. A. MUTHU MANICKAM1
1. Combat Vehicle Research and Development Establishment (CVRDE), Avadi, Chennai- 600 054, India;
2. Center for Materials Joining Research (CEMAJOR), Department of Manufacturing Engineering,
Annamalai University, Annamalainagar 608 002, Tamil Nadu, India
Received 19 June 2010; accepted 6 September 2010
Abstract: Titanium alloys have been successfully applied for aerospace, ship and chemical industries because they possess many good characteristics such as high specific strength, superior corrosion resistance and excellent high temperature resistance. Though these alloys show reasonable weldability characteristics, the joint properties are greatly influenced by the welding processes. Weld thermal cycle of the processes will control the weld metal solidification and subsequent phase transformation and resultant microstructure. The welded joints of Ti-6Al-4V alloy were fabricated by gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), laser beam welding (LBW) and electron beam welding (EBW) processes. The joints fabricated by EBW process exhibit higher strength compared with the GTAW and LBW joints; but the joints by GTAW process exhibit higher impact toughness compared with the LBW and EBW joints. The resultant tensile and impact properties of the welded joints were correlated with the weld metal microstructures.
Key words: titanium alloy; gas tungsten arc welding; laser beam welding; electron beam welding
1 Introduction
Titanium alloys have been successfully applied for aerospace, ship, desalination of sea water, biomechanics and chemical industries because they possess many good characteristics such as high specific strength, corrosion resistance, and toughness, low thermal expansion rate, high temperature creep resistance [1]. Presently, Ti-6Al-4V is one of the most widely used titanium alloys, accounting for more than half of all titanium tonnage in the world, and no other titanium alloys threaten its dominant position [2-3]. The Ti-6Al-4V alloy is commonly used in nuclear engineering, civil industries and medically implanted materials, transportable bridge girders, military vehicles, road tankers, and space vehicles, for its above said significant properties [4-5].
The welding technology of titanium is complicated due to the fact that at temperatures above 550 °C, and particularly in the molten stage, it is known to be very reactive towards atmospheric gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, carbon or hydrogen causing severe embrittlement. Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) is the most preferred welding method for reactive materials like titanium alloy due to its comparatively easier applicability and better economy [6]. However, it is widely understood that the GTAW of titanium alloy exhibits columnar grains in the weld pool, which often results in inferior mechanical properties and may lead to hot cracking [6]. To overcome these problems, the high energy beam welding process like laser beam welding (LBW) and electron beam welding (EBW) is considered in this work.
Numerous experiments have demonstrated that laser welding permits the manufacture of precision welded joints with a high depth-to-width ratio and a high welding speed. Laser welding has been used as one of the major manufacturing processes in the medical device industry because it offers number of advantages such as precision and noncontact processing, with a small heat affected zone (HAZ), consistent and reliable joints [7]. Owing to these advantages, laser beam welding has been widely applied in industrial production [8]. EBW is highly suited for joining titanium, as the high vacuum inside the chamber where the process is carried out, shields hot metal from contamination. Moreover, joint depth can be achieved with high beam power density and low heat input, when compared with arc welding processes [9].
MOHANDAS et al [10] investigated the fusion zone microstructure and porosity in electron beam welds of α + β titanium alloy and reported that the porosity at low welding speed was low and the scale of martensite lath depended on the welding speed. The early work by SUNDERASAN et al [11] showed the influence of DC and AC pulsing on the solidification structure of α + β titanium alloy welds and the effect of grain refinement on tensile behaviour. QI et al [1] studied the microstructure, properties and technical parameters of welding of 0.5 mm-thick sheets of commercial pure titanium by GTAW, LBW and EBW processes. The influence of temperature below 450 °C on the tensile properties of LBW of dual phase Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy was investigated by WANG et al [12]. WU et al [13] investigated the microstructure evaluation and fracture behavior for EBW of Ti-6Al-4V and reported the disordered and short needle morphology of weld microstructure makes the fracture mechanism complex. SARESH et al [9] investigated the effects of electron beam welding on thick Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy and found that the joint quality of single sided partial penetration welds can be improved by using two passes double side welding technique with lesser beam power. BALASUBRAMANIAN et al [14] developed mathematical models to predict the tensile properties of pulsed current gas tungsten arc welded Ti-6Al-4V alloy. CAO and JAHAZI [15] reported the effect of welding speed on surface morphology and shape, welding defects, microstructure, hardness and tensile properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy welded using a high-power Nd:YAG laser.
From the literature review, it is understood that the extensive research work has been carried out on welding of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. However, most of the published information is focusing on any one of the welding process. There is no literature available comparing the tensile properties and microstructural features of GTAW, LBW and EBW joints of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Hence, the present investigation is carried out to compare the tensile properties and microstructural characteristics of GTAW, LBW and EBW joints of Ti-6Al-4V alloy.
2 Experimental
The rolled plates of 5.4 mm-thick Ti-6Al-4V alloy were used as base material to fabricate the joints. The chemical composition and mechanical properties of the base metal (BM) are presented in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. The base metal contains elongated grains of α (light etched) and transformed β (dark etched) containing some amount of acicular α. The β phase is distributed at the boundaries of the α phase. Single ‘V’ butt joint configuration was prepared to fabricate the joints using GTAW process. Square butt joint configuration was prepared to fabricate the joints using LBW and EBW processes. The optimized welding parameters were obtained by trial experiments. Few welding trials were carried out on 5.4 mm-thick rolled plates of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. The welding parameters were varied to get defect free and full penetration joints. The welding parameters, which resulted in defect free and full penetration joint, were taken as optimized welding parameters. The optimized welding parameters (presented in Table 3) were used to fabricate the joints. Necessary care was taken to avoid joint distortion during welding. The welding was carried out normally to the rolling direction of the base metal.
Table 1 Chemical composition of base metal (mass fraction, %)
![]()
Table 2 Mechanical properties of base metal

The welded joints were sliced using wire-cut electric discharge machining (WEDM) as shown in Fig. 1 to prepare the tensile and impact test specimens. Two types of tensile specimens (smooth and notch) were prepared to evaluate the transverse tensile properties. The smooth (unnotched) tensile specimens were prepared to evaluate yield strength, tensile strength, elongation and reduction in cross sectional area. The notched tensile specimens were prepared to evaluate notch tensile strength and notch strength ratio of the joints. The notched bar impact specimens were prepared to evaluate the impact toughness of the base metal and joints. The tensile and impact specimens were prepared according to the ASTM E8M—04 and ASTM E23—04 standards, respectively. Tensile testing was carried out using 100 kN electro mechanically controlled universal testing machine (Maker: FIE-Blue Star, India; Model: UNITEK-94100). The 0.2% offset yield strength was derived from the load displacement curve. The specimens for metallographic examination were sectioned to the required sizes from the joint comprising weld metal, HAZ and base metal regions and polished using different grades of emery papers. Final polishing was done using the diamond compound (1 mm in particle size) in the disc polishing machine. Specimens were etched with Kroll’s reagent to reveal the micro and macrostructure. The microstructural analysis was done by optical microscope (OM) observation (MEIJI Japan; Model: ML7100). Hardness measurement was done across the weld center line by Vickers micro hardness tester (SHIMADZU, Japan Model: HMV-2T) with 0.49 N load and 15 s dwell time. The fractured surfaces of impact and tensile (both smooth and notched) specimens were analyzed through scanning electron microscope (HITACHI, S400N).
Table 3 Welding parameters used to fabricate joints


Fig. 1 Scheme of welding with respect to rolling direction and extraction of specimens(ST: Smooth tensile; NT: Notch tensile) (unit: mm)
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Macrostructure
The macrographs shown in Fig. 2 clearly reveal the difference in weld bead geometry of the three different welding processes. GTAW joint possesses the widest weld fusion zone (FZ) among the three welding processes (Fig. 2(a)). LBW joint possesses the narrowest weld FZ and narrow HAZ among the three welding processes (Fig. 2(b)). The reverse triangle shape and clear fusion line appear in LBW joint [1]. The sample welded using EBW process shows the weld FZ of intermediate width between the other two processes (Fig. 2(c)). The small narrow undercuts at the toe ends of EBW seams are also observed and are the characteristic nature of the process.
In GTAW process, the resultant bead structure is a coarser one due to high heat input leading to the slower cooling rate. The wider arc column (the process characteristic) is also a reason for this wide FZ. In LBW process, the energy density is comparatively higher than that in GTAW process. The high self quenching rates that are associated with this process certainly promote the fast cooling rates[15]. This could be attributed to the narrow FZ. Due to the metal vapour in the weld from LBW, the macrograph (Fig. 2(b)) shows the symmetrical undercut on both (the top and bottom) surfaces of the weld. The center of the FZ joint (Fig. 2(c)) presents a convex shape attributed to volume contraction, surface tension and phase transformation. This defect cannot be eliminated even though LBW parameters are changed[12]. Comparatively higher energy density is involved in EBW process and the welding is carried out in vacuum, so no heat is expected to be lost by convection to the surrounding atmosphere [10]. This could be attributed to the increased FZ width compared with the LBW joints.

Fig. 2 Macrographs of different welded joints: (a) GTAW joint; (b) LBW joint; (c) EBW joint (1, 5—Unaffected base metal; 2, 4—HAZ; 3—Weld fusion zone
3.2 Microstructure
Optical micrographs of weld region and HAZ region of the joints are presented in Fig. 3. The fusion zone microstructure of GTAW joint (Fig. 3(a)) contains the coarse serrate and acicular α structures of grain boundary α, massive α, and Widmanst?tten α + β. HAZ microstructure of the GTAW joint consists of the coarse distorted serrate and acicular α structures of grain boundary α, coarse α + β structure (Fig. 3(b)). The microstructure of LBW joint shows fine acicular α′structure (Fig. 3(c)). HAZ microstructure of the LBW joint shows the intermediate α + β structure (Fig. 3(d)). Figure 3(e) reveals the EBW joint microstructure and it shows the serrate and regular plate-shaped α structures. The equiaxed grains appear at the matrix. The HAZ microstructure of EBW joint shows the fine α + β structure (Fig. 3(f))[16]. The formation of the acicular grains is due to the fast cooling rate by LBW process and the plate-like α is due to the slow cooling rate in EBW process[1].
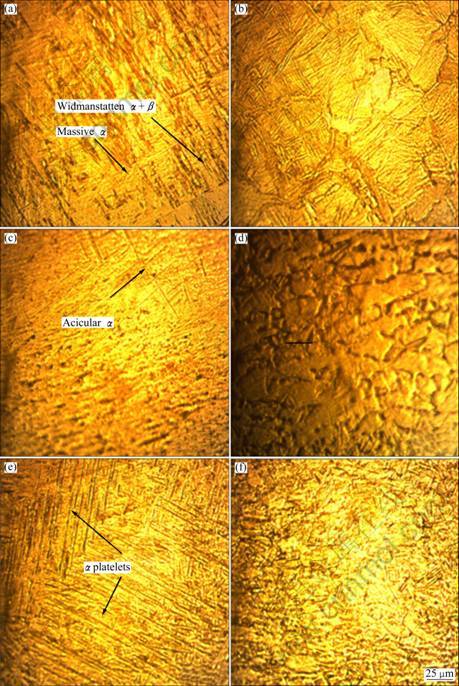
Fig. 3 Optical micrographs of weld metal and HAZ: (a) Weld metal, GTAW; (b) HAZ, GTAW; (c) Weld metal, LBW; (d) HAZ, LBW; (e) Weld metal, EBW; (f) HAZ, EBW
The grain size of the weld region is influenced by the heat of the welding process. Of the three welding processes used in this investigation to fabricate the joints, the GTAW process has higher heat input compared with the LBW and EBW processes (Table 3). Higher heat input will lead to slower cooling rate, and slow cooling rate will result in coarser microstructure in this welds. In LBW joint the presence of martensitic structure is also observed. The high self-quenching rate associated with the laser beam welding process certainly promotes the less diffusion transformation of the β phase into martensitic microstructure. The boundaries of the prior β grains are clearly revealed in the FZ (Fig. 2(c)). The small fusion zone exhibits coarse columnar β grains that grow opposite to the heat flow direction and then undergo martensitic transformation upon cooling.
3.3 Tensile properties
Table 4 presents the transverse tensile properties of the welded joints. In each condition three tensile specimens of each joint were tested and the average of the results is presented in Table 4. The yield strength and tensile strength of parent metal are 969 and 1 002 MPa, respectively. But the yield strength and tensile strength of GTAW joints are 893 and 939 MPa, respectively. This indicates that there is 6% reduction due to GTAW process. Similarly, the yield strength and tensile strength of LBW joints are 959 and 982 MPa, respectively, which are 2% lower than those of the parent metal. However, the yield strength and tensile strength of EBW joints are 960 and 1 000 MPa, respectively. Of the three types of welded joints, the joints fabricated by EBW process exhibit higher strength values, and the enhancement in strength value is approximately 6.1% compared with GTAW joints and 2% compared with LBW joints.
The elongation and reduction in cross-sectional area of parent metal are 2.7% and 34.55%, respectively. But the elongation and reduction in cross-sectional area of GTAW joints are 10.15% and 17.48%, respectively. This suggests that there is a 73% increment in ductility due to GTAW process. Similarly, the elongation and reduction in cross-sectional area of LBW joints are 15% and 32%, respectively, which are 82% higher than those of the parent metal. However, the elongation and reduction in cross-sectional area of EBW joints are 7.7% and 21.78%, respectively. Of the three types of welded joints, the joints fabricated by LBW exhibit higher ductility values, and the improvement in ductility is approximately 32% compared with GTAW joints and 48.66% compared with EBW joints.
The notch tensile strength (NTS) of parent metal is 1 236 MPa. But the notch tensile strength of GTAW joint is 1 047 MPa. This reveals that the reduction in NTS is approximately 15% due to GTAW process. Similarly, the NTS of LBW joint is 1 148 MPa and the NTS of EBW joint is 1 077 MPa. Of the three types of welded joints, the joints fabricated by EBW exhibit higher NTS values, and the enhancement is 9% compared with GTAW process and 6% compared with EBW process.
Another notch tensile parameter, notoh strength ratio (NSR), is found to be greater than unity (>1) for all the joints. This suggests that the Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy is insensitive to notches and is a notoch ductile material. The NSR is 1.23 for the parent metal, but it is 1.11, 1.16 and 1.07 for GTAW, LBW and EBW joints, respectively. Of the three types of welded joints, the joints fabricated by LBW exhibit a relatively higher NSR (1.16), and the improvement in NSR is 4.3% compared with GTAW process and 7.7% compared with EBW process.
The joint efficiency of GTAW joints is approximately 93.7% and the joint efficiency of LBW joints is 98.1%. Of the three types of welded joints, the joints fabricated by EBW process exhibit a relatively higher joint efficiency (99.81%). The joint efficiency of the EBW joints is 6.12% higher than that of the GTAW joints and 2% higher than that of the LBW joints.
Transverse tensile properties of the welded joints presented in Table 4 indicate that the EBW joints exhibit superior tensile properties compared with GTAW and LBW joints. During tensile tests, all the specimens invariably failed in the unwelded region. This indicates that the weld region is comparatively stronger than other regions and the joint properties are controlled by weld region chemical composition and microstructure. The higher strength of the base metal is mainly attributed to the presence of elongated grains of α and transformed β containing some amount of acicular α. In fusion welding, the dilution of base metal in weld metal is a common phenomenon. The grain size of the weld region also plays a major role in deciding the joint properties of titanium alloys that are dictated by the amount, size, shape and morphology of α phase and density of α-β interfaces. The lowest strength in GTAW joint may be attributed to the presence of coarse serrate structures of grain boundary α, massive α, and Widmanst?tten α + β. The highest strength of EBW joint could be contributed to the weld metal microstructure containing fine serrate and regular plate-shaped α microstructures. Intermediate strength achieved by the LBW joint might be attributed to the acicular morphology of the joint.
Table 4 Mechanical properties of weld metal

3.4 Impact toughness properties
Three Charpy impact toughness test specimen results were averaged and the results are presented in Table 4. The impact properties of base metal is 16 J at room temperature. When it welds with GTAW process, the weld metal toughness exhibits 15 J which is 3% lower than that of the base metal, and the highest impact strength is achieved by welding compared with the other two welding processes. The impact toughnesses of LBW and EBW joints are 10 J, respectively. The equal value of impact toughness might be contributed to the inherent nature of high energy density processes.
3.5 Hardness
The hardness across the weld cross section was measured using a Vickers micro-hardness testing machine, and the values are presented in Fig. 4. The hardness of base metal in its initial condition is VHN 372. But the hardness values of the GTAW, LBW and EBW joints in the weld metal region are VHN 390, VHN 463 and VHN 488, respectively. This suggests that the hardness is increased by VHN 18, VHN 91 and VHN 116 in the weld metal regions of GTAW and LBW and EBW joints respectively due to welding thermal cycle. They are 1.04 times, 1.24 times and 1.32 times greater than those of the base metal for GTAW, LBW and EBW joints, respectively. Figure 4 shows the hardness variations across the weld. The micro-hardness decreases from centre of welded joint to matrix invariably in all the joints.
From Fig. 4, it can be understood that the increases of micro-hardness in the weld zone and the decrease of hardness towards the base metal are due to the presence of coarse distorted microstructure in all the three joints. The micro-hardness values are less significant in affecting the mechanical properties because the inherent nature of the process selected has more influencing factors. The widths of the FZ were observed to be 4.0-8.0, 0.7-1.5 and 3.0-6.0 mm for GTAW, LBW and EBW joints, respectively. Similarly, the widths of the HAZ were observed to be 4.0, 0.2 and 1.5 mm for GTAW, LBW and EBW joints, respectively. The hardness profiles (Figs.4(b), (c)) of both LBW and EBW joints are in agreement with the resultant strength properties at intermediate and the highest strength levels, respectively.
3.6 Fracture surface
The fractured surfaces of the impact and tensile test specimens of base metal and welded joints were analyzed using a scanning electron microscope and the fractographs are displayed in Figs.5-6. The modes of failure for the impact test base metal and the joints are ductile with microvoid coalescence in all cases (Fig. 5). There is an appreciable difference in the size of the dimples of the base metal with respect to the welded joints. It is evident from the fractograph of the base metal (Fig. 5(a)) that the dimples are finer than those in the welded joints (Figs.5(b)-(d)).

Fig. 4 Micro-hardness profiles across weld centre line: (a) GTAW joint; (b) LBW joint; (c) EBW joint
The fracture surface morphologies of the impact test joints exhibit tensile over-load failure invariably in all the three joints. From Fig. 5(b), it is observed that the entire surface shows dimpled fracture of fine and equiaxed α phase that ruptured in ductile shear[17]. Figure 5(c) shows the presence of the dimples with various sizes, and some secondary cracking is detectable. The structure is continuous β phase with dispersed α phase of tensile-overload fracture, which is dimpled and has aligned elongated cavities suggesting localized slip. Figure 5(d) shows the various sized dimples and few micro pores. These micro pores are the inherent nature of the EB welded titanium alloy[10].

Fig. 5 Fractographs of impact test specimens: (a) BM; (b) GTAW joint; (c) LBW joint; (d) EBW joint
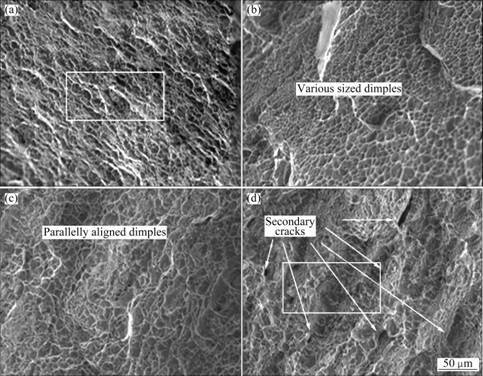
Fig. 6 Fractographs of tensile test specimens: (a) BM; (b) GTAW joint; (c) LBW joint; (d) EBW joint
The modes of failure for the tensile tested base metal and the welded joints are ductile with microvoid coalescence in all cases (Fig. 6). Figure 6(a) shows the finer equiaxed dimple structure. The size variation of the dimples can be observed in Fig. 6(b). The parallelly aligned finer dimples with grain boundary α could be the reason for the highest ductility with intermediate tensile strength for the LBW joint (Fig. 6(c)). The EBW joint fractograph (Fig. 6(d)) reveals the finer dimples, but at the same time the presence of numerous secondary cracks can also be observed. The preferred nucleation site may be the presence of micro pores in this joint. The size variation of the dimple is also observed.
From Fig. 5(a), the dimples are relatively uniform in size, without any extremely large ones. A few inclusions are evident. Few secondary dimples can be observed at the lip of the dimples or at the valley of the dimples (Fig. 7). This could be the reason for the high impact strength for the base metal. It can be seen from Fig. 8 that the presence of α phase ruptures and the secondary dimples is evident. This might be the reason for the higher impact energy absorption for the GTAW joint. The size variation of dimples and secondary cracks might be the reason for the drop of impact energy absorption of LBW joint compared with the base metal and GTAW joint. For the EBW joint the various sized dimples and the presence of micropores are the main contributors of the resultant impact toughness.
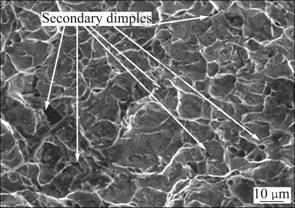
Fig. 7 Fractograph of fracture toughness test specimen of base metal
Though the finer dimples are the characteristic feature of fractured surface of the base metal (Fig. 6(a)), Figure 9 shows the presence of secondary cracking and some micropores. Due to these reasons the higher tensile strength and lower ductility might be achieved in the base metal. In addition to the small dimples, there are some micro cracks and micropores presented in EBW tensile tested fractograph. In Fig. 10, small dimples are evident at the edges and within the larger dimples. This could be the main reason for the improvement in tensile strength of the EBW joint. The various size dimples could be attributed to the drop in tensile strength of the GTAW joint (Fig. 6(b)).

Fig. 8 Fractograph of fracture toughness specimen of GTAW joint

Fig. 9 Fractograph of tensile specimen of base metal

Fig. 10 Fractograph of tensile (smooth) specimen of EBW joint
All the fractographs reveal that the similar features are inhibited by the fractured surface of the impact and tensile specimens indicating the ductile mode of failure. Fine dimples are the characteristic feature of ductile materials and hence the joints show a higher ductility compared with the base metal. The dimple size exhibits a directly proportional relationship with the strength and ductility, i.e. if the dimple size is finer, the strength and ductility of the respective joint are higher and vice versa [18-19].
4 Conclusions
1) In the three welded joints, the joints fabricated by EBW process exhibit higher strength, and the enhancement of strength is approximately 6% compared with GTAW joints, and 2% compared with LBW joints. The presence of fine serrate and regular plate-shaped α microstructures and the resultant hardness in EBW joints are the key for the enhancement of the tensile strength of this joint.
2) In the three welded joints, the joints fabricated by GTAW process exhibit 35% higher impact toughness compared with the joints fabricated by LBW and EBW processes due to the presence of coarse serrate and acicular α structures of grain boundary α, massive α, and Widmanst?tten α + β weld metal microstructure.
3) The hardness is higher in the weld metal region than in the HAZ and BM regions. Lower hardness is recorded in the GTAW joints (HV 403) and the higher hardness is recorded in the EBW joints (HV 509).
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to record their sincere thanks to the Combat Vehicle Research and Development Establishment (CVRDE), Avadi, Chennai, Government of India for providing financial support to carry out this investigation through a Contract Acquisition for Research Services project, No. CVRDE/MMG/09-10/ 0043/CARS. The authors also register their sincere thanks to Defense Research and Development Laboratory (DMRL), Hyderabad, for effective fabrication of the joints.
References
[1] QI Yun-lian, DENG Ju, HONG Quan, ZENG Li-ying. Electron beam welding, laser beam welding and gas tungsten arc welding of titanium sheet [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 280: 177-181.
[2] CAIAZZO F, CURCIO F, DAURELIO G, MINUTOLO F M C. Ti-6Al-4V sheets lap and butt joints carried out by CO2 laser: Mechanical and morphological characterization [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2004, 149(1-3): 546-552.
[3] CASALINO G, CURCIO F, MINUTOLO F M C. Investigation on Ti-6Al-4V laser welding using statistical and Taguchi approaches [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2005, 167(2-3): 422-428.
[4] BALASUBRAMANIAN M, JAYABALAN V, BALASUBRAMA- NIAN V. A mathematical model to predict impact toughness of pulsed-current gas tungsten arc-welded titanium alloy [J]. Int J Adv Manuf Techno, 2008, 35: 852-858.
[5] ZHANG Shuang-yin, LIN Xin, CHEN Jing, HUANG Wei-dong, Heat treated microstructure and mechanical properties of laser solid forming of Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Rare metals, 2009, 28(6): 537-544.
[6] BALASUBRAMANIAN M, JAYABALAN V, BALASUBRAMA- NIAN V. Prediction and optimization of pulsed current gas tungsten arc welding process parameters to obtain sound weld pool geometry in titanium alloy using lexicographic method [J]. ASM International, JMEPEG, 2009, 18: 871-877.
[7] NOOLUA N J, KERRA H W, ZHOUA Y, XIEB J. Laser weldability of Pt and Ti alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 397: 8-15.
[8] WANG S H, WEI M D, TSAY L W. Tensile properties of LBW welds in Ti-6Al-V alloy at evaluated temperatures below 450 °C [J]. Materials Letters, 2003, 57: 1815-1823.
[9] SARESH N, GOPALAKRISHNA PILLAI M, JOSE M. Investigations into the effects of electron beam welding on thick Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 192-193: 83-88.
[10] MOHANDAS T, BANERJEE D, KUTUMBA RAO V V. Fusion zone microstructure and porosity in electron beam welds of an a + b titanium alloy [J]. Metal Trans A, 1998, 30: 789-98.
[11] SUNDARESAN S, JANAKI RAM G D, MADHUSUDHAN REDDY G. Microstructural refinement of weld fusion zones in α – β titanium alloys using pulsed current welding [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 262: 88-100.
[12] WANG S H, WEI M D, TSAY L W. Tensile properties of LBW welds in Ti-6Al-V alloy at evaluated temperatures below 450 °C [J]. Materials Letters, 2003, 57: 1815-1823.
[13] WU Hui-qiang, FENG Ji-cai, HE Jing-shan. Microstructure evolution and fracture behaviour for electron beam welding of Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Bull Mater Sci, 2004, 27(4): 387-392.
[14] BALASUBRAMANIAN M, JAYABALAN V, BALASUBRAMA- NIAN V. Developing mathematical models to predict tensile properties of pulsed current gas tungsten arc welded Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Materials and Design, 2008, 29: 92-97.
[15] CAO X, JAHAZI M. Effect of welding speed on butt joint quality of Ti-6Al-4V alloy welded using a high-power Nd:YAG laser [J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2009, 47: 1231-1241.
[16] ASM handbook. Metallography and microstructures[M]. Volume 9. 968-1015.
[17] ASM handbook. Fractography [M]. Volume 12. 768-793.
[18] NOOLUA N J, KERRA H W, ZHOUA Y, XIEB J. Laser weldability of Pt and Ti alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 397: 8-15.
[19] MAGUDEESWARAN G, BALASUBRAMANIAN V, BALASUBRAMANIAN T S, MADHUSUDHAN REDDY G. Effect of welding consumables on tensile impact properties of shielded metal arc welded high strength, quenched and tempered steel joints[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2008, 13: 97-105.
T. S. BALASUBRAMANIAN1, V. BALASUBRAMANIAN2, M. A. MUTHUMANIKKAM1
1. Combat Vehicle Research and Development Establishment (CVRDE), Avadi, Chennai- 600 054, India;
2. Center for Materials Joining Research (CEMAJOR), Department of Manufacturing Engineering,
Annamalai University, Annamalainagar 608 002, Tamil Nadu, India
摘 要:钛合金由于具有高比强度、优越的耐腐蚀性和出色的耐热性等优良特性,已成功应用于航空航天、造船和化学工业。尽管钛合金具有合适的可焊性特点,但焊接方法极大地影响焊接接头性能。焊接过程中热循环将会影响焊接金属凝固、相转变和微观组织。采用钨电极惰性气体保护焊接(GTAW)、激光束焊接(LBW)和电子束焊接(EBW)方法制备Ti-6Al-4V合金的焊接接头。EBW焊接接头的强度高于GTAW和LBW接头的强度,但GTAW接头较其它两种接头具有较高的断裂韧性。焊接接头的拉伸和冲击性能与焊接金属的微观组织有关。
关键词:钛合金;钨电极惰性气体保护焊接;激光束焊接;电子束焊接
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Corresponding author: V. BALASUBRAMANIAN; Tel: +91-4144-239734; Fax: +91-4144-238080/238275; E-mail: visvabalu@yahoo.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60850-9

