文章编号:1004-0609(2013)S1-s0545-05
热加工工艺对Ti-6Al-4V钛合金抗弹性能的影响
郑 超1,王富耻1,程兴旺1,付克勤1, 2
(1. 北京理工大学 材料科学与工程学院 冲击环境材料技术重点实验室,北京 100081;
2. 中国兵器工业集团 第52研究所 烟台分所,烟台 264003)
摘 要:通过终点弹道实验,使用7.62 mm AP和长杆型穿甲弹垂直侵彻β区和α+β区锻造的40 mm厚的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板。结果表明:经α+β两相区锻造的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板抗弹性能优于经β区锻造的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板;长杆型穿甲弹对α+β两相区锻造的具有等轴组织的双层Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板的侵彻过程是弹体和靶板材料的相互消耗的过程,绝热剪切带的萌生扩展及其带内微裂纹的成核长大导致Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板弹坑附近材料的碎化破坏。
关键词:Ti-6Al-4V钛合金;热加工工艺;抗弹性能
中图分类号:TJ840.1 文献标志码:A
Effect of thermo-mechanical processing on ballistic performance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy
ZHENG Chao1, WANG Fu-chi1, CHENG Xing-wang1, FU Ke-qin1, 2
(1. National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Materials under Shock and Impact, School of Material Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China;
2. Yantai Branch of No. 52 Institute, China Ordnance Industry Group, Yantai 264003, China)
Abstract: The β region and α+β region forged Ti-6Al-4V plates with a thickness of 40 mm were impacted by 7.62 mm AP and long-rod penetrator. The ballistic performance of Ti-6Al-4V target forged in α+β region is optimum than that of the Ti-6Al-4V target forged in β region. Further, post ballistic metallurgical observations find that the white-etching bands occur both in the β region and α+β region forged Ti-6Al-4V targets impacted by 7.62 mm AP, and deformed bands only occur in target forged in α+β region. In the α+β region forged equiaxed Ti-6Al-4V target impacted by long-rod penetrator, the penetration of the projectile is a process of eroding of the penetrator and fragmentation of the target, in which adiabatic shear bands and adiabatic shear band cause cracks.
Key words: Ti-6Al-4V alloy; thermo-mechanical processing; ballistic performance
钛合金材料因其较高的比强度和较强的抗腐蚀能力深受世界各国防护材料研究者关注,自20世纪90年代至今,针对Ti-6Al-4V钛合金开展了大量的弹道冲击实验,实验表明:对于常规动能穿甲弹,Ti-6Al-4V钛合金抗弹性能比装甲钢的抗弹性能可以高出近80% [1-2]。
钛合金材料通常分为3类:α钛合金、α+β钛合金和β钛合金。Ti-6Al-4V钛合金是典型的α+β钛合金,其相变温度为990~1 000 ℃,屈服强度为800~1 000 MPa,抗拉强度为900~1 200 MPa,伸长率为8%~ 15%。针对Ti-6Al-4V钛合金抗弹性能的研究表明:绝热剪切带是Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板发生贯穿破坏的通道。LEPPIN[3]和GREBE等[4]研究了Ti-6Al-4V钛合金薄靶板的损伤特征,发现Ti-6Al-4V钛合金薄靶板以充塞和崩落破坏为主。LEE等[5-6]的研究发现,具有双态组织结构的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板抗弹性能优于具有等轴组织的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金。本文作者通过不同的热加工工艺获得了2类Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板,研究了其常规力学性能和抗弹性能,并对损伤后靶板开展了宏微观的损伤分析以认识热加工工艺对Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板抗弹性能的影响规律。
1 实验
实验使用的钛合金材料由航空材料研究院提供,2块Ti-6Al-4V钛合金板料分别经由β区和α+β区锻造获得,锻造所得靶板在机加工前使用的退火热处理制度为:800 ℃,保温1 h,空冷。
切取金相试样和静态拉伸试样,静拉伸试样取样及测试依据GBT 228—2002。金相试样经研磨抛光后,使用Kroll腐蚀液(H2O 88 mL, HF 2 mL, 和HNO3 10 ml)腐蚀5~10 s。使用Zeiss Z10光镜进行金相观察,使用光镜附带的金相分析软件Micro-image Analysis & Process测量组织结构中相的大小和比例等。室温静态拉伸实验在Instron万能试验机开展,实验应变率为10-3,静拉伸断口使用冷场发射扫描电镜Hitachi S- 4800观察。
将不同相区锻造后板料沿厚度方向切取150 mm×150 mm×40 mm靶板开展弹道冲击实验。终点弹道实验室如图1所示。实验中使用7.62 mm AP和长杆型穿甲弹垂直侵彻靶板,7.62 mm AP和长杆型穿甲弹弹芯如图1所示。质量约为5.1 g的7.62 mm AP弹芯由T12A钢制的,其硬度HRC约为65;质量为44.5 g的长杆型穿甲弹弹芯由93钨合金制的,其长径比约为13.9。弹靶实验中,弹体速度有测速靶测得,7.62 mm AP弹速约为(840±10) m/s,长杆型穿甲弹弹速约为1 300 m/s。损伤后靶板沿弹坑中线剖开,一半用于弹坑宏观损伤特征的分析,另一半用于弹坑微观损伤特征的分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 微观组织结构
经β区和α+β区锻造的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金板料的微观组织结构如图2所示。由图2可以看到:经β区锻造的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金板料具有典型的片层组织结构特征,在片层状的α相间分布着晶间β相,在本研究中标记为L;而经α+β区锻造的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金板料为典型的等轴组织结构,等轴α相间分布着晶间β相,本研究中标记为E[7]。在片层组织板料L中,β相的体积分数为36.3%,α相区尺寸和α片层宽度分别为200~ 500 μm和3~5 μm;在等轴组织板料E中,β相的体积分数为32.8%,等轴α相的大小约为20 μm。
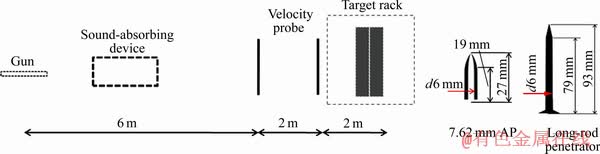
图1 终点弹道实验室和弹芯示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of terminal ballistic laboratory

图2 Ti-6Al-4V钛合金板材的组织结构
Fig. 2 Microstructures of forged Ti-6Al-4V plates
2.2 力学性能和抗弹性能
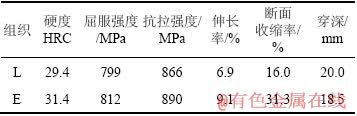
具有片层组织的板料L和具有等轴组织的板料E的硬度、静态拉伸性能和7.62 mm AP侵彻条件下的穿深如表1所示。等轴组织E无论硬度、屈服强度、抗拉强度、伸长率或断面收缩率,均优于片层组织L。等轴组织E所获得优异的强塑性的匹配来源于组织结构中等轴α相的作用。值得注意的是,等轴组织E较之片层组织L 抗拉强度的提高不如其伸长率提高的那么明显。等轴组织E较之片层组织L抗拉强度提高仅3%,而伸长率提高达32%。2种锻造工艺获得的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金板料在塑形变形能力上的区别在其静拉伸断口的观察中得到了进一步的证实。图3所示为2种Ti-6Al-4V钛合金板料的静拉伸断口扫描电镜照片。由图3可以看到:等轴组织E静拉伸断口是以韧窝为特征的塑性断裂模式,而片层组织L静拉伸断口是以韧窝和台阶为特征的韧性和脆性相结合的断裂模式[8]。由表1可见,2种锻造工艺所得Ti-6Al-4V钛合金板料的抗弹性能差异性显见,等轴组织靶板较片层组织靶板穿深要小,表明了经由α+β两相区锻造的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板抗弹性能优于经由β区锻造的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板。
表1 Ti-6Al-4V钛合金板材的力学性能和抗弹性能
Table 1 Mechanical properties and ballistic performance of forged Ti-6Al-4V plates
2.3 Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板的宏微观损伤分析
图4所示为经7.62 mm AP和长杆型穿甲弹侵彻后Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板的宏观损伤照片。弹体侵彻方向均有右向左,7.62 mm AP垂直侵彻了单层的具有等轴组织和片层组织的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板,长杆型穿甲弹侵彻了双层的等轴组织靶板。由图4可以看到:对于7.62 mm AP的侵彻,40 mm Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板可以被看做半无限靶板,板厚弹径比高达6.67,从而2种组织靶板均形成了同弹芯尺寸相近的弹坑,如图4(a)和(b)所示;而对于长杆型穿甲弹,双层的等轴组织Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板没有被击穿,但是,在第2层靶板背面可以观察到明显的背部突起,形成的弹坑直径约为7~8 mm,略大于弹芯直径为6 mm,如图4(c)和(d)所示。

图3 Ti-6Al-4V钛合金板材的静拉伸断口形貌
Fig. 3 Fractographs of forged Ti-6Al-4V plates

图4 Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板宏观损伤照片
Fig. 4 Macro-damage of forged Ti-6Al-4V plates

图5 经7.62 mm AP侵彻后Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板的微观损伤特征
Fig. 5 Micro-damage characteristic of forged Ti-6Al-4V plates impacted by 7.62 mm AP

图6 经长杆型穿甲弹侵彻后具有等轴组织的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板的微观损伤
Fig. 6 Micro-damages of double-layered Ti-6Al-4V targets having equiaxed microstructure impacted by 105 simulating penetrator
图5所示为经7.62 mm AP侵彻后的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金单层靶板微观损伤特征。取样位置如图4方框所示。动能弹侵入靶板瞬间,弹靶前沿形成冲击波分别向弹体和靶板内传播;弹体进一步侵入靶板形成弹坑的过程使得靶板材料处于高应变率作用下,众所周知,Ti-6Al-4V钛合金材料在这种加载条件下易于形成绝热剪切带。绝热剪切带一般依据其在光镜下的特征,被分为白亮带和形变带,且绝热剪切带往往是材料发生破坏的通道。在具有等轴组织Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板E和具有片层组织的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板L中,具有白亮特征的剪切带均被观察到,且带内没有微裂纹的萌生,这被认为是半无限厚的靶板随着板厚的增加其衰减冲击波的能力增强,同时靶板增厚约束了弹坑附近材料的变形,这2个因素共同作用使得前述靶板在剪切带内没有形成微裂纹。图6所示为经长杆型穿甲弹侵彻后的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金双层靶板微观损伤特征,取样位置A-D如图4所示。从微观损伤照片图6中B和C位置可以看到碎化的材料。这些碎化的材料显然是由于弹坑附近形成的大量的绝热剪切带及带内微裂纹的萌生长大直至贯通连接所致。值得注意的是,在等轴组织靶板E中A-D处,类似7.62 mm AP侵彻后的等轴组织靶板E中所观察到的,大量的形变带也被观察到,如红色方框所示。等轴组织靶板E所呈现的较之片层组织靶板高的抗弹性能可能就是由于其内大量形变带的形成使得具有白亮特征的剪切带形成得以推迟,从而提高了靶板的承载能力。
3 结论
1) α+β区锻造的具有等轴组织的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板抗弹性能优于β区锻造的具有片层组织的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金靶板。
2) 靶板中均形成了具有白亮特征的剪切带,而等轴组织靶板中还观察到了形变带的产生。
3) 杆式弹侵彻过程是弹体动能和弹靶材料相互消耗的过程,靶板中绝热剪切带的形成和其带内微裂纹的萌生扩展直至贯通促成了弹坑材料的破碎并消耗弹体能量。
REFERENCES
[1] MONTGOMERY J S, WELL G H, ROOPCHAND B, OGILVY J W. Low-cost titanium armors for combat vehicles [J]. JOM, 1997: 45-47.
[2] MONTGOMERY J S, WELL G H. Titanium armor applications in combat vehicles [J]. JOM, 2001: 29-32.
[3] LEPPIN S, WOODWARD R L. Perforation mechanisms in thin titanium alloy targets [J]. Int J Impact Eng, 1986, 4(2): 107-115.
[4] GREBE H A, PAK H R, MEYERS M A. Adiabatic shear localization in titanium and Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Metall Trans A, 1985, 16A: 761-775.
[5] LEE D G, KIM S, LEE S, LEE C S. Effects of microstructural morphology on quasi-static and dynamic deformation behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2001, 32: 315-324.
[6] LEE D G, LEE Y H, LEE S, LEE C S. Dynamic deformation behavior and ballistic impact properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy having equiaxed and bimodal microstructures [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2004, 35: 3103-3112.
[7] LUTJERING G, WILLIAMS J C. Titanium [M]. Beilin: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2007: 203-216.
[8] JOSHI V A. Titanium alloys: An atlas of structures and fracture features [M]. Baca Raton: CRC Press, 2006: 59-69.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2013-07-28;修订日期:2013-10-10
通信作者:程兴旺,副教授,博士;电话:010-68913951;E-mail: chengxw@bit.edu.cn