DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.06.043
波浪荷载作用下原状软黏土动力特性和基于能量方法的孔压研究
杨彦豪1, 2,周建1, 2,温晓贵1, 2,严佳佳1, 2,曹洋1, 2
(1. 浙江大学 滨海和城市岩土工程研究中心,浙江 杭州,310058;
2. 浙江大学 软土与环境土工教育部重点实验室,浙江 杭州,310058)
摘要:针对杭州原状软黏土,利用浙江大学5 Hz空心圆柱扭剪仪进行等向固结条件下的主应力轴旋转试验以研究波浪荷载作用下软黏土的动力特性。探讨不同频率和循环应力比条件下土体的应变发展、模量衰减等动力特性。采用能量方法,研究频率和循环应力比对孔隙水压力与损耗能关系的影响,并对不同条件下土体的崩塌能进行对比分析。研究结果表明:在主应力轴旋转条件下,原状软黏土存在一个门槛循环应力比,当循环应力比小于该值时,应变只在较小范围内发展,土体模量呈“急剧—平稳”的衰减规律;当循环应力比大于该值时,应变曲线会因土体达到结构崩塌而出现1个激增点,此时土体模量呈“急剧—平稳—急剧”的衰减规律,并且频率越低或循环应力比越大,应变发展及模量衰减速度越快,达到结构崩塌所需要的循环次数越少。频率和循环应力比对原状软黏土的孔压与损耗能关系及崩塌能均有影响,且频率越低或循环应力比越大,孔压随损耗能发展越快,结构崩塌时的崩塌能也越小。频率和循环应力比是通过改变损耗能中两部分能量所占的比例来实现对孔压与损耗能关系及崩塌能的影响。
关键词:主应力轴旋转;原状软黏土;频率;循环应力比;损耗能量;孔压;崩塌能
中图分类号:TU411 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)06-2309-08
Dynamic characteristics of isotropically consolidated intact soft clay and study of pore water pressure based on energy method under wave loading
YANG Yanhao1, 2, ZHOU Jian1, 2, WEN Xiaogui1, 2, YAN Jiajia1, 2, CAO Yang1, 2
(1. Research Center of Coastal and Urban Geotechnical Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
2. Key Laboratory of Soft Soils and Geoenvironmental Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China)
Abstract: A series of tests with principal stress rotation were carried out on 5 Hz ZJU-HCA to investigate the dynamic characteristics of isotropically consolidated Hangzhou intact soft clay under wave loading. The dynamic characteristics such as the development of strain and degradation of modulus were studied under different frequencies or cyclic stress ratios. Furthermore, the relationship between pore water pressure and the dissipated energy as well as the collapse energy were analyzed based on energy method. The result show that under principal stress rotation, there exists a threshold cyclic stress ratio in the intact soft clay. When the cyclic stress ratio is smaller than the threshold value, the strains only develop in a small range and the modulus of the soft clay attenuates in a sharp-steady mode; when it is larger than the threshed value, there is an abrupt point in the strain verse cyclic number line due to the structural collapse of soil. Meanwhile the modulus decreases in a sharp-steady-sharp way, and the lower the frequency or the larger the cyclic stress ratio is, the faster the strains develop and the modulus degenerates, the fewer cyclic numbers required to achieve the structural collapse. Frequency and cyclic stress ratio have some influence on the relationship between pore water pressure and dissipated energy as well as the collapse energy, that is, the lower the frequency or the larger the cyclic stress ratio, the faster the pore water pressure develops with dissipated energy, and the less the collapse energy. The frequency and cyclic stress ratio affect the relationship between pore water pressure and dissipation energy as well as the collapse energy through changing the percentage of the two parts energy.
Key words: principal stress rotation; intact clay; frequency; cyclic stress ratio; dissipated energy; pore water pressure; collapse energy
在海洋工程中最重要的荷载是波浪荷载。波浪荷载以循环压力波的形式作用于海床上,其主要特点是主应力轴循环旋转,大、小主应力之差幅值不变[1]。我国沿海地区海洋建筑物地基表层大都有数米厚的软黏土覆盖,在波浪荷载作用下,海床土体往往会产生应变开展、孔压累积并伴随强度和模量衰减等现象,引起地基的压缩、破坏和失稳,甚至使坐落于海床上的结构物发生破坏[2]。因此,研究波浪荷载作用下软黏土海床地基的动力稳定性对于近海和海岸工程具有非常重要的意义。波浪荷载引起的主应力轴旋转对土体的应变、强度和孔压等特性具有显著的影响。沈瑞福等[3]利用双向振动仪对波浪荷载下土体动强度进行研究,发现考虑动主应力轴旋转影响的砂土动强度较常规动扭剪试验降低15%左右;Ishihara等[4]通过动单剪仪,研究不同应力路径对饱和砂土的动强度的影响;张健等[5]对模拟波浪荷载下粉土的孔压特性进行了研究,并给出了孔压随振次的经验公式;栾茂田等[6]研究了不同循环应力路径对饱和黏土的应力-应变关系和强度特性的影响,结果表明耦合循环荷载下黏土扭转剪切分量和正向偏差分量的应力-应变关系曲线与应力路径有关,且随着振动次数的增加逐渐疏松,割线模量Es和Gs不断衰减。循环荷载会引起土体内部的结构破坏、颗粒重新排列,从而引起孔压累积,该过程需消耗能量,因此,孔压的开展与能量之间有着内在关系。能量为标量且与应力和应变均有关[7],故以能量法研究孔压具有一定的优越性。Towata等[8]针对Toyoura砂进行了包括主应力旋转在内的不同应力路径下循环剪切试验,结果表明孔压发展与剪切功之间具有唯一的对应关系;Yan等[9]从能量角度出发,通过循环三轴、循环扭剪和主应力轴旋转试验,研究了不同循环应力比、频率、相对密实度和循环应力路径对粉土孔压开展的影响,研究表明,崩塌能可以作为土体的循环强度标准,孔压比与损耗能关系与频率、密实度和应力路径有关,与循环应力比无关,最后给出了一个基于能量的孔压增长模型。郭莹等[10]利用多功能剪切仪针对福建标准砂进行了多种复杂循环剪切试验,分别研究了循环剪切应力路径、初始主应力方向、初始偏应力、初始中主应力系数等因素对孔压与累积耗散能关系的影响,并建立了孔压增长的能量模式。综上可知,关于波浪荷载下土体动力特性研究已有较多的成果,试验对象从砂土、粉土到黏土,研究内容从应变开展、强度衰减到孔压发展规律。但多数该类试验条件均假设频率或循环应力比固定,从而忽略了波浪荷载下不同频率和循环应力比对土体动力特性的影响。此外,虽然能量法在砂土的孔压研究方面取得了一定的进展,但原状软黏土的这方面研究还较少。基于上述研究现状和问题,本文作者利用空心圆柱扭剪仪(HCA),对杭州原状软黏土在等向固结条件下进行了主应力轴旋转试验,研究不同频率和循环应力比条件下原状软黏土的应变开展、模量衰减等动力特性。采用能量方法探讨频率和循环应力比对孔压与损耗能量关系的影响,并对不同条件下软黏土的崩塌能进行对比分析。
1 试验设计
1.1 试验仪器及用土
使用浙江大学ZJU-HCA空心圆柱扭剪仪。该仪器可对空心圆柱试样施加独立控制的轴力、扭矩和内、外压力,从而实现主应力轴连续旋转等复杂试验应力路径[11]。郑鸿镔[12]对该仪器试验结果的可靠性进行了分析,表明该仪器在实现主应力轴旋转等复杂应力路径时具有足够的精度,试验结果具有很好的可靠性和可重复性。
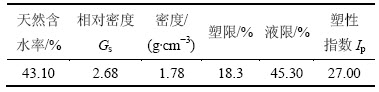
试验用土为取自杭州某基坑开挖工地的原状软黏土块,取土面位于地表以下7 m处,地下水位位于地表以下约1 m处,此处土体的有效应力约为150 kPa。土体的基本物理参数如表1所示。通过专用制样设备将原状软黏土块制备成200 mm×100 mm×60 mm(高度×外径×内径)的空心试样,原状土取样及空心试样的制样方法参见文献[11]。试样经反压饱和后孔压系数B都能达到0.97以上,固结完成条件参考“土工试验规程”,当试样每小时排水量稳定小于100 mm3时即认为排水固结完成,所有试样的有效固结压力为150 kPa(内压和外压均为200 kPa,反压50 kPa),等向固结完成后进行相应应力路径条件下的不排水循环剪切试验。
表1 土体基本物理参数
Table 1 Physical-mechanical parameters of soil
1.2 加载应力路径
各试样在固结完成后进行不排水主应力轴旋转试验,控制循环扭矩比循环竖向荷载的相位滞后90°,且使循环轴向应力幅值的一半(σz-σθ)/2与循环扭转剪应力幅值τzθ相等,从而保证循环耦合试验中的应力路径始终为圆形,以期模拟海洋波浪荷载在海床中所形成的主应力轴连续旋转应力路径。试验中预设与实际应力路径如图1所示。
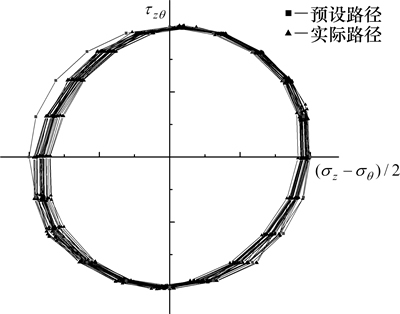
图1 预设与实际应力路径
Fig. 1 Preset and actual stress path
1.3 试验方案
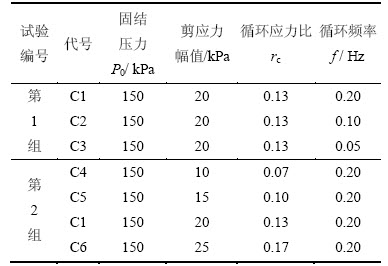
为了研究波浪荷载作用下频率和循环应力比对原状黏土动力特性的影响,分别设计了2组试验。第1组试验考察频率的影响,鉴于波浪荷载频率一般介于0.05~0.20 Hz之间[13],该组试验在循环应力比为rc=0.13的条件下,对频率f=0.05,0.10,0.20 Hz 3种情况进行主应力轴连续旋转试验;第2组考察了循环应力水平的影响,在频率f=0.2 Hz的条件下,对循环应力比rc=0.07,0.10,0.13,0.17共4种情况进行主应力轴循环旋转试验。其中rc为剪应力幅值与前期固结压力之比(rc=q/P0),具体试验方案及参数设置如表2所示。
表2 试验方案
Table 2 Test program
试验采用应力控制方式,当试样固结完成后,在不排水条件下进行主应力轴旋转,加载过程中当试样出现明显剪切带,或者进行了10 000次循环而试样仍不产生明显变形,认为试验结束。
2 结果及分析
主应力轴旋转条件下,原状软黏土中的应变和孔压都会随应力的循环变化而波动,同时随时间或循环次数而不断增长。本文取每个循环中的峰值应变和孔压,以表征其变化特性。
2.1 应变发展特性
空心圆柱试样受到主应力轴旋转作用时,会产生轴向应变εz、径向应变εr、环向应变εθ和扭剪应变γzθ。但εz,εr和εθ的发展规律基本相似,且εz最大。因此本文只给出εz和γzθ随循环数的变化曲线,如图2所示。
由图2(a)和图2(b)可知在本文讨论的频率和循环应力比范围内,当循环应力比为0.07时,应变只在较小范围内发展;而当循环应力比为0.10,0.13和0.17时,应变随循环数的变化曲线可以分为2个阶段:1) 循环数较小时各应变增长速度较慢;2) 达到某一临界循环周数时,各应变曲线均出现1个激增点,此后急剧增加。在rc=0.07和rc=0.10之间必然存在1个临界值,当循环应力比小于该值时应变发展特征与rc=0.07时相似,而当循环应力比大于该值时,应变发展特征与rc=0.1等相似。参考周建[14]针对杭州饱和软黏土提出的门槛循环应力比概念,确定该临界值为本试验条件下的门槛循环应力比。
Alarcon-Guzman等[15]在研究砂土的剪切特性时,引入了结构崩塌概念,认为土体结构崩塌时,由土体结构承担的应力快速转移至孔隙水,这使得有效应力突然降低而孔压迅速升高,土体在短时间内产生很大变形。本文中,在不排水条件下,当饱和软黏土的应变和孔压增长到一定程度时,若继续施加循环荷载,其内部的土体结构将加速破坏,孔压迅速升高,同时颗粒间的相互作用急剧减弱,外部表现为各个方向的应变同时快速增加,即出现图2中各应变的转折点,此时试样开始出现较为明显的剪切带。借鉴砂土在循环荷载作用下的研究[15],将本文中应变的激增点命名为结构崩塌点,选取曲线中曲率最大处确定该点。
由图2可知:当循环应力比大于门槛循环应力比时,循环应力比越大或频率越低,各应变发展速度越快,试样也越先达到结构崩塌而出现应变转折。这与动三轴试验的结论相似,但是相比于动三轴试验结果,本试验中试样崩塌时所需的循环次数较少,说明主应力轴连续旋转会加速土体的应变发展,这与类似应力路径条件下砂土的试验结果一致[16]。
2.2 模量的衰减
动三轴试验研究结果表明土体在循环荷载作用下会发生软化现象[17-18],一般采用轴向压缩模量的衰减来表示土体的软化规律。本文中试样受到轴力和扭矩的共同作用,轴向压缩模量衰减的同时剪切模量也会衰减,故采用轴向压缩模量和剪切模量共同描述土体模量的衰减。
轴向压缩模量EN和剪切模量GN的定义如下:
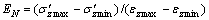 (1)
(1)
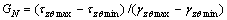 (2)
(2)
式中:EN和GN分别为第N次循环的缩模量和剪切模量;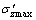 和
和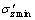 分别为第N个循环周期内的最大、最小轴向有效应力;
分别为第N个循环周期内的最大、最小轴向有效应力;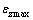 和
和 分别为第N个循环周期内的最大、最小轴向应变;τzθmax和τzθmin分别为第N个循环周期内的最大、最小剪应力;γzθmax和γzθmin分别为第N个循环周期内的最大、最小剪应变。
分别为第N个循环周期内的最大、最小轴向应变;τzθmax和τzθmin分别为第N个循环周期内的最大、最小剪应力;γzθmax和γzθmin分别为第N个循环周期内的最大、最小剪应变。
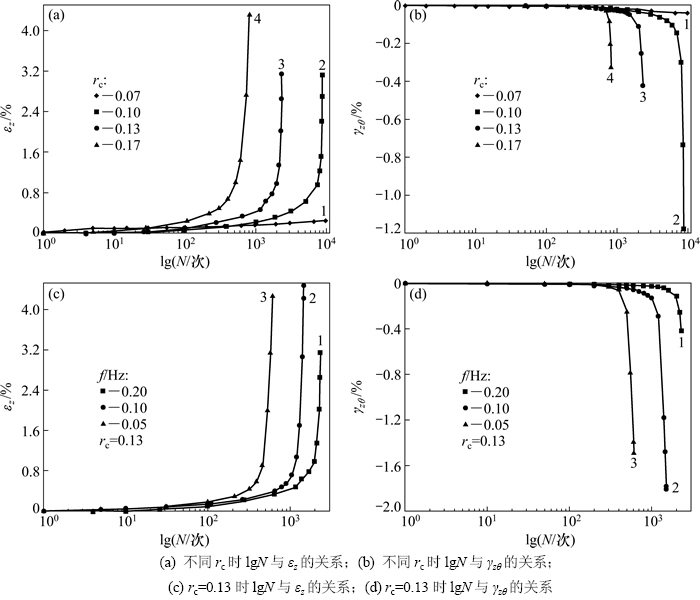
图2 应变与循环次数的关系
Fig. 2 Relationships between stain and cyclic number
定义软化指数为
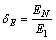 (3)
(3)
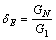 (4)
(4)
式中:δE和δG分别为压缩模量和剪切模量的软化指数。
图3所示为不同频率和循环应力比下压缩模量和剪切模量的软化指数随循环数的变化曲线。从图3可以看出:在循环加载过程中,各试样压缩模量和剪切模量均不断衰减,且两者的衰减规律基本相同;当循环应力比小于门槛循环应力比时,两模量呈“急剧—平稳”的衰减规律,即循环加载初期土体模量急剧衰减至初始模量的70%左右;此后,随着循环数的增加土体模量的衰减速度逐渐减慢,最后模量基本不变化;而当循环应力比大于门槛值时,两模量呈“急剧—平稳—急剧” 的衰减规律,即加载初期土体模量急剧衰减至50%左右,之后随着循环数的增加土体模量的衰减速度逐渐降低,当衰减到初始模量的20%左右时其衰减速度再次急剧增加,这与前面提到的土体结构崩塌点相对应,可见模量的第2次急剧衰减是土体到达结构崩塌点造成的。结构崩塌后试样的残余模量只有初始模量的10%左右,在整个循环加载过程中,压缩模量的衰减速率要稍快于剪切模量。而且频率越低或循环应力比越大,土体模量衰减速率越快,达到结构崩塌所需要的循环次数也越少。
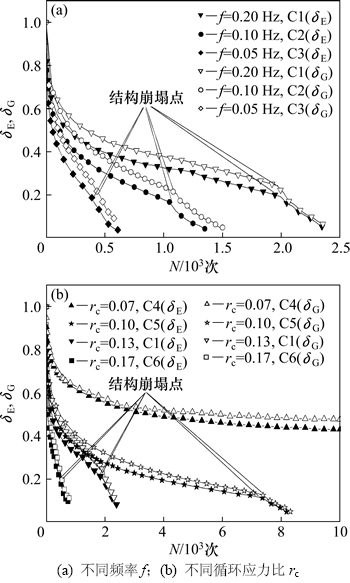
图3 软化指数δE和δG与循环数N的关系
Fig. 3 Relationships between degradation index and cyclic number
2.3 基于能量方法的孔压研究
一般认为,荷载所做的功一部分释放,一部分被土体吸收,其中被吸收的能量称为损耗能。本文采用能量方法,研究土体结构崩塌前不同频率和循环应力比对原状软黏土孔压累积与损耗能关系的影响, 并对结构崩塌时所需的崩塌能进行对比分析。
若试样单位体积内的损耗能变化为dWS,则
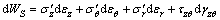 (5)
(5)
式中: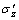 ,
,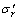 ,
,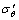 和
和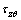 分别为有效轴向应力、有效径向应力、有效环向应力和剪应力;dεz,dεr,dεθ和dγzθ分别为εz,εr,εθ,γzθ对应的应变增量。对式(5)积分,得单元体的损耗能WS:
分别为有效轴向应力、有效径向应力、有效环向应力和剪应力;dεz,dεr,dεθ和dγzθ分别为εz,εr,εθ,γzθ对应的应变增量。对式(5)积分,得单元体的损耗能WS:
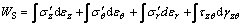 (6)
(6)
图4(a)和图5(a)所示分别为不同频率和循环应力比条件下软黏土结构崩塌前孔隙水压力u与损耗能WS的关系曲线。可以看出这2图中各曲线形状十分相似,且基本可以分为2个阶段:第1阶段孔压随损耗能快速增长;第2阶段孔压随损耗能的增长速度逐渐减慢,最后基本不变。说明孔隙水压力与损耗能之间存在某种内在关系,这与有关试验结果是相同的[9-10]。
2.3.1 频率的影响
由图4(a)可知:起始时较少的损耗能变化就会引起孔压剧烈上升,此时频率基本不影响孔压与损耗能关系。但是,随着损耗能的增加,3条曲线间的差异逐渐显露出来,并且频率越低,孔压随损耗能发展越快。从图4(a)可以看出不同频率条件下土体结构崩塌时的崩塌能WSC并不相同,为了研究频率对结构崩塌能的影响,作出结构崩塌能与频率的关系曲线,如图4(b)所示。从图4(b)可见:崩塌能随频率的提高而不断增大。Yan等[9]利用能量方法对长江粉砂进行研究,探讨频率与崩塌能关系,将其结果绘到图4(b)中,频率对软黏土和粉土崩塌能的影响规律基本相同。
2.3.2 循环应力比的影响
不同循环应力比下孔压与损耗能的关系如图5(a)所示。从图5(a)可见:与频率对该关系的影响相似,开始阶段,循环应力比基本无影响。但是,当损耗能达到一定程度后,3条曲线开始分岔,且循环应力比越大,孔压随损耗能发展越快。图5(b)所示为循环应力比与土体结构崩塌能的关系,可以看出:随循环应力比的减小,土体所需要的崩塌能越来越大。然而,Towate等[8]通过Toyoura砂的试验发现孔压与损耗能关系不受剪应力峰值影响。沈扬等[9]对粉土的研究认为结构崩塌能与循环应力比无关,但是如果考虑到结构崩塌时的崩塌孔压不同,那么孔压与损耗能关系会受到循环应力比的影响。由此可见,循环应力比对不同类型土体的影响存在一定的差异性。
已有研究[20]认为循环荷载作用下,一部分损耗能用于颗粒重排列、团粒破碎和土体结构变形,这导致土体产生塑性应变进而引起孔压上升;其余部分用于提高土体内能(如热能、土颗粒的动能和表面能等),这部分能量与土体的应变有关,应变越大,克服颗粒间摩擦所需要的损耗能越多,该部分能量也就越大。上述2部分能量在不同频率和循环应力比条件下所占损耗能的比例不同,这是影响孔压与损耗能关系和崩塌能的直接原因。从图4(a)和图5(a)可知:3条曲线几乎都是在孔压为22 kPa时开始分岔,此时对应的损耗能约为8 kJ。结合图2可知:分岔之前由于各应变均较小,几乎全部损耗能都用于第1部分能量消耗,孔压快速开展且只与损耗能有关,因此,所有曲线几乎重合;随着应变的增长,第2部分能量的消耗逐渐增多,从而使孔压增长速度减慢。这就导致了孔压随损耗能的增长曲线呈先快后慢的模式。
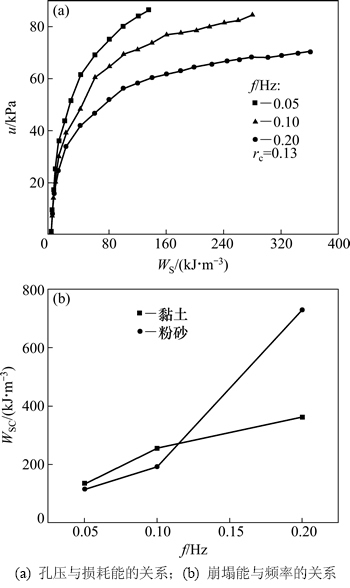
图4 频率f对孔压u与损耗能WS关系及崩塌能WSC的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of frequency on relationship among pore water pressure, dissipated energy and collapse energy
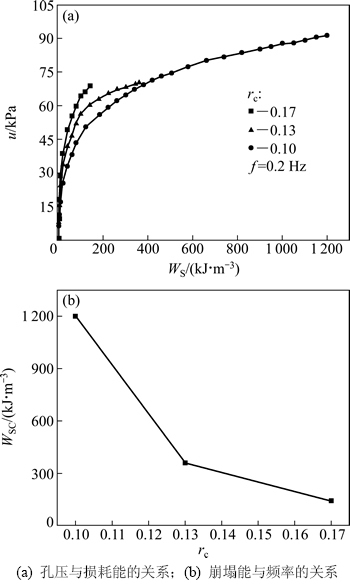
图5 循环应力比rc对孔压u与损耗能WS关系及崩塌能WSC的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of cyclic stress ratio on relationship among pore water pressure, dissipated energy and collapse energy
频率和循环应力比是通过影响损耗能中两部分能量所占的比例来实现对孔压与损耗能关系及崩塌能的影响。当循环应力比较小时,颗粒重排列、团粒破碎和土体结构变形将变得困难,用于产生孔压的能量相对较少,大部分能量被用于产生热能、土颗粒的动能和表面能等。因此,循环应力比越小,后期孔压随损耗能增长速度越慢,土体的达到结构崩塌时所需要的崩塌能越高。若循环应力比低于门槛循环应力比,则后期损耗能将全部用于第2部分的能量消耗,应变将基本不发展,土体始终无法达到结构崩塌点,这与本文C4组试验结果是吻合的。
3 结论
1) 在主应力轴旋转条件下,原状软黏土存在1个门槛循环应力比,当循环应力比小于该值时,随循环数增加,应变只在较小范围内开展;当循环应力比大于门槛循环比时,应变会因土体达到结构崩塌而出现一个激增点,且频率越低或循环应力比越大,应变发展及模量衰减速率越快,到达结构崩塌所需要的循环数越少。
2) 随循环数增加,竖向压缩模量和剪切模量的衰减规律基本相同,但前者稍快于后者。当循环应力比小于门槛循环应力比时,两模量呈“急剧—平稳”的衰减规律;当循环应力比大于门槛循环应力比时,两模量呈“急剧—平稳—急剧”的衰减规律。模量的第二次急剧衰减是土体到达结构崩塌点造成的。
3) 在主应力轴旋转条件下,频率和循环应力比对原状软黏土的孔压与损耗能关系以及崩塌能均有影响:频率越低或循环应力比越大,孔压随损耗能发展越快,结构崩塌时的崩塌能也越小。本文中频率对孔压与损耗能关系以及崩塌能的影响同已有的部分研究结果相似,但循环应力比对不同类型土体的影响却存在一定的差异。一部分损耗能被用于生成塑性应变进而使孔压升高,另一部分转化为土体的内能。频率和循环应力比是通过影响损耗能中2部分能量所占的比例来实现对孔压与损耗能关系及崩塌能的影响。
参考文献:
[1] 聂影. 复杂应力条件下饱和重塑黏土动力特性试验研究[D]. 大连:大连理工大学土木水利学院, 2008: 10-11.
NIE Ying. Experimental study on dynamic behavior of saturated clay under complex stress condition[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology. School of Civil and Hydraulic Engineering, 2008: 10-11.
[2] MADSEN O S. Wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in a porous bed[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, American Society of Civil Engineering, 1978, 28(4): 377-393.
[3] 沈瑞福, 王洪瑾, 周克骥, 等. 动主应力旋转下砂土孔隙水压力发展及海床稳定性判断[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1994, 16(3): 70-78.
SHEN Ruifu, WANG Hongjin, ZHOU Keji, et al. Building up of pore pressure under cyclic rotation of principal stress and evaluation of stability of seabed deposit[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1994, 16(3): 70-78.
[4] Ishihara K, Yamazaki F. Cyclic simple tests on saturated sand in multi-directional loading[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1980, 20(1): 45-49.
[5] 张健, 高玉峰, 沈扬, 等. 波浪荷载作用下饱和粉土反正弦孔压拟合参数影响因素分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2011, 32(2): 727-732.
ZHANG Jian, GAO Yufeng, SHEN Yang, et al. Factor analysis of fitting parameter for saturated silt arcsin pore water pressure under wave loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(2): 727-732.
[6] 栾茂田, 聂影, 杨庆, 等. 不同应力路径下饱和黏土耦合循环剪切特性[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(7): 1927-1932.
LUAN Maotian, NIE Ying, YANG Qing, et al. Study of coupling cyclic test of saturated clay under different stress paths[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(7): 1927-1932.
[7] Baziar M H, Sharafi H. Assessment of silty sand liquefaction potential using hollow torsional tests: An energy approach[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2011, 31(7): 857-865.
[8] Towhata I, Ishihara K. Shear work and pore water pressure in undrained shear[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1985, 25(3): 73-84.
[9] YAN Jun, SHEN Yang, HUANG Guofa, et al. Energy-based method for analyzing the collapse characteristics of silt subjected to changes of principal stress orientation[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 2011, 39(5): 123-131.
[10] 郭莹, 刘艳华, 栾茂田, 等. 复杂应力条件下饱和松砂振动孔隙水压力增长的能量模式[J]. 岩土工程报报, 2005, 27(12): 1380-1385.
GUO Ying, LIU Yanhua, LUAN Maotian, et al. Energy-based model of vibration-induced pore water pressure build-up of saturated loose sand under complex stress condition[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2005, 27(12): 1380-138.
[11] 沈扬. 考虑主应力方向变化的原状软黏土试验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学建筑工程学院, 2007: 27-29.
SHEN Yang. Experimental study on effect of variation of principal stress orientation on undisturbed soft clay[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University. Architectural Engineering Institute, 2007: 27-29.
[12] 郑鸿镔. 主应力轴旋转下重塑黏土与原状黏土特性试验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学建筑工程学院, 2010: 29-33.
ZHENG Hongbin. Experimental study of reconstituted clay and intact clay under principal stress rotation[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University. Architectural Engineering Institute, 2010: 29-33.
[13] CHEN Yunmin, JI Meixiu, HUANG Bo. Effect of cyclic loading frequency on undrained behaviors of undisturbed marine clay[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2004, 18(4): 643-651.
[14] 周建. 循环荷载作用下饱和软黏土特性研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学建筑工程学院, 1998: 36-37.
ZHOU Jian. Properties of saturated clay under cyclic loading[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University. Architectural Engineering Institute, 1998: 36-37.
[15] Alarcon-Guzman A, Leonards G A, Chameau J L. Undrained monotonic and cyclic strength of sands[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1988, 114(10): 1089-1108.
[16] Ishihara K, Towhata I. Sand response to cyclic rotation of principal stress direction as induced by wave loads[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1983, 23(4): 11-26.
[17] 刘飞禹, 蔡袁强, 徐长节, 等. 循环荷载下软土动弹性模量衰减规律研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2008, 42(9): 1479-1483.
LIU Feiyu, CAI Yuanqiang, XU Changjie, et al. Degradation of dynamic elastic modulus of soft clay under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2008, 42(9): 1479-1483.
[18] 蔡袁强, 陈静, 王军. 循环荷载下各向异性软黏土应变-软化模型[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2008, 42(6): 1058-10.
CAI Yuanqiang, CHEN Jing, WANG Jun. Strain- degradation model for anisotropic soft clay under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2008, 42(6): 1058-1064.
[19] 沈扬, 闫俊, 张朋举, 等. 主应力方向变化路径下等压固结粉土强度特性差异和能量评价方法研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 32(增刊1): 118-123.
SHEN Yang, YAN Jun, ZHANG Pengju, et al. Strength characteristics of isotropically consolidated silt under change of principal stress orientation and correlative evaluation method with collapse energy[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(Suup.1): 118-123.
[20] Voznesensky E A, Nordal S. Dynamic instability of clays: an energy approach[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 1999, 18(2): 125-133.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2014-04-13;修回日期:2014-07-20
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(50778162,51178422)(Projects (50778162, 51178422)supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:周建,博士,副教授,从事软黏土力学、非饱和土本构模型及地基处理等研究;E-mail:dzhoujian@yahoo.com