Densification and microstructure evolution during SPS consolidation process in W-Ni-Fe system
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2011年第3期
论文作者:胡可 李小强 杨超 李元元
文章页码:493 - 501
关键词:致密化行为;微观组织演变;SPS;W-Ni-Fe合金
Key words:densification behavior; microstructure evolution; SPS; W-Ni-Fe alloy
摘 要:采用放电等离子烧结(SPS)技术固结成形W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe(质量分数,%)混合粉末,研究不同加热速率对烧结致密化行为和微观组织演变规律的影响。结果表明,W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe合金的SPS致密化过程可以划分为三个阶段。初始不收缩阶段,快速加热导致粉末颗粒接触区产生瞬间放电,并在颗粒表面产生局部高温,强化后续烧结致密化;致密化过程主要发生在中期固相烧结阶段,缓慢加热有助于扩散更加充分;在后期瞬时液相烧结阶段,钨晶粒球化并迅速长大,且快速加热可获得更为细小的晶粒。
Abstract: Spark plasma sintering method (SPS) was used to consolidate mixed W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe (mass fraction, %) powders from commercial fine elemental powders, and both the densification behavior and microstructure evolution in sintering were investigated at different heating rates. The results show that the SPS densification process can be divided into three stages. At the initial unshrinking stage, fast heating generates instantaneous discharge and locally inhomogeneous temperature distribution in solid-state powder particles, enhancing later densification; during the intermediate solid state sintering stage, diffusion is more sufficient in the slow-heated SPS process; at the final transient liquid-phase sintering stage, tungsten grains become sphered and coarsen rapidly, but fast heating helps maintain rather small grain sizes.

HU Ke, LI Xiao-qiang, YANG Chao, LI Yuan-yuan
National Engineering Research Center of Near-Net-Shape Forming for Metallic Materials,
South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
Received 7 May 2010; accepted 6 December 2010
Abstract: Spark plasma sintering method (SPS) was used to consolidate mixed W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe (mass fraction, %) powders from commercial fine elemental powders, and both the densification behavior and microstructure evolution in sintering were investigated at different heating rates. The results show that the SPS densification process can be divided into three stages. At the initial unshrinking stage, fast heating generates instantaneous discharge and locally inhomogeneous temperature distribution in solid-state powder particles, enhancing later densification; during the intermediate solid state sintering stage, diffusion is more sufficient in the slow-heated SPS process; at the final transient liquid-phase sintering stage, tungsten grains become sphered and coarsen rapidly, but fast heating helps maintain rather small grain sizes.
Key words: densification behavior; microstructure evolution; SPS; W-Ni-Fe alloy
1 Introduction
W-Ni-Fe heavy alloys are a kind of composite materials, in which 86%-97% (mass fraction) of BCC structured W particles are generally embedded in the ductile Ni-Fe-W FCC matrix. These alloys are widely used as kinetic energy penetrators, counter weights, radiation shields and electrical contacts because of their high density, excellent strength and good ductility[1-3].
Recently, a newly arisen sintering technique called field assisted sintering technique (FAST), also known as spark plasma sintering (SPS) or pulsed electric current sintering, employs a pulsed direct current (DC) to intensify sintering and consolidate powders to near-full density at a relatively low temperature[4-6]. During SPS, pulsed electric current flows through the die and/or powder compact producing heat, which means this technique has a promising ability to sinter powders (especially nano-powders) in a significantly shorter processing time by using a much higher heating rate than those of traditional hot pressing or hot isostatic pressing. Thereby, grain growth in sintering can be essentially prevented, which will lead to improved mechanical properties[7].
Although SPS technique has been successfully used to prepare various materials systems[8-15], there are few reports on the application in tungsten heavy alloys. To better understand SPS mechanism in W-Ni-Fe system, this study focuses on the study of both the densification behavior and the microstructure evolution during sintering.
2 Experimental
2.1 Powder preparation
The characteristics of the as-received commercial W, Ni and Fe elemental powders in this study are given in Table 1. The W, Ni and Fe powders were weighted accurately to make up a desired stoichiometric composition of W-5.6%Ni-1.4%Fe (mass fraction, %). The weighed powders were subsequently mixed for 10 h. The SEM micrograph of the homogenously mixed powders is shown in Fig.1.
2.2 SPS experiments
All the sintering experiments were performed on an SPS-825 spark plasma sintering system (manufactured
Table 1 Characteristics of raw powders
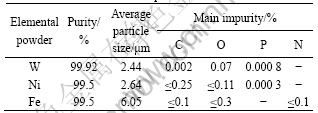
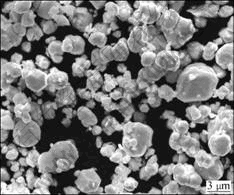
Fig.1 SEM micrograph of as-mixed powders
by Sumitomo Coal Mining Co. Ltd., Japan), with a sequence consisting of 12 pulses (with a pulse duration of 3.3 ms) followed by two periods of 0 current which was termed as 12:2 for the pulse sequence. For sintering, the process chamber was evacuated down to less than 6 Pa, and a constant pressure of 30 MPa was applied. 28.0 g mixed powders were moved in a graphite die with an internal diameter of 20.4 mm and a wall thickness of 15 mm, and then were mounted on the SPS equipment. During all the tests, temperature was obtained from an optical pyrometer focused on a hole (with a diameter of 2 mm and a distance of 1.5 mm near the inner wall of the female die) which was drilled into the graphite female die. Thus, the measured temperature was not the one in the powder bed. Recently, by comparing the results from SPS experiments and finite element modeling, R?THEL et al[16] found that when using a female graphite die with an internal diameter of 30 mm and a wall thickness of 10 or 15 mm, the temperature difference between the powder compact and the die wall was lower than 50 °C. In the present investigation, it is believed that the temperature difference between the one obtained from pyrometer and the powder compact will be much lower than 50 °C.
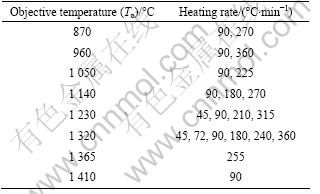
The heating from room temperature to 600 °C was controlled by a preset heating program and completed within 4 min. Above 600 °C, different heating schedules were used, as shown in Table 2. The holding time at objective temperature (To) was 0 min, that is to say, as soon as the temperature reached To, the electric current was shut off with the applied stress suppressed, and then the specimens were cooled down in the furnace.
Table 2 Heating schedules to consolidate as-mixed powers
Throughout sintering, the height variation of the powder compact ΔL was precisely measured (ΔL= LT-L0<0, where LT is the instantaneous height and L0 is the initial height of the powder compact). So the instantaneous relative density D can be computed[13]:
![]() (1)
(1)
where DT is the instantaneous relative density, Lf is the final height, LT is the instantaneous height and Df is the final relative density.
The instantaneous densification rate, that is the derivative of the instaneous relative density with respect to t, is then calculated, point by point, using the following well-known expression:
![]() (2)
(2)
All of the sintered specimens were ground and polished to remove any surface graphite contamination. Then the sintered density was determined by the Archimedes method. The final relative density was obtained using the apparent volume mass divided by the theoretical value of 17.71 g/cm3. The microstructure of specimens taken from fracture surfaces was examined by scanning electron microscopy (Quanta 200, FEI, Netherlands), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) phase analysis of the mixed powder and sintered samples was performed with a PANalytical X’Pert PRO X-ray diffractometer using Cu Kα radiation.
3 Results
Table 3 summarizes the relative densities of the W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe alloys sintered by SPS at various temperatures (To) and different heating rates. Figures 2-8 show the SEM micrographs of fracture surfaces of the sintered alloys, which reveal how the microstructure and densification behaviors evolved in response to sintering temperature and heating rate. Detailed explanations are
Table 3 Sintering conditions and relative densities for SPSed alloys
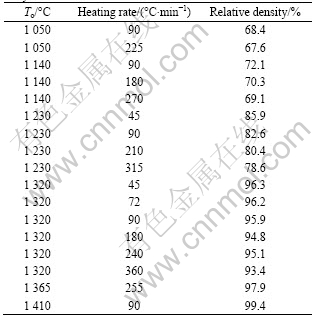

Fig.2 SEM images of fracture surfaces of alloys heated to 870 °C at various heating rates: (a) 90 °C/min; (b), (c) 270 °C/min
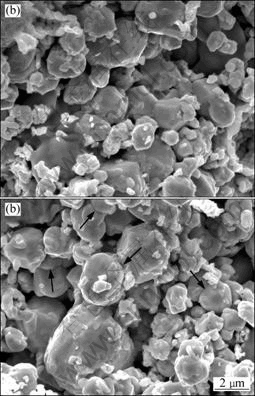
Fig.3 SEM images of fracture surfaces of alloys heated to 960 °C at various heating rates: (a) 90 °C/min; (b) 360 °C/min
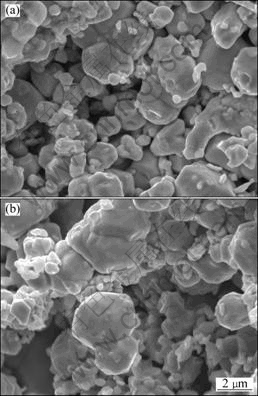
Fig.4 SEM images of fracture surfaces of alloys heated to 1 050 °C at various heating rates: (a) 90 °C/min; (b) 225 °C/min
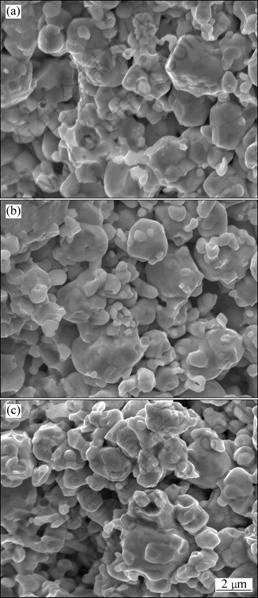
Fig.5 SEM images of fracture surfaces of alloys heated to 1 140 °C at various heating rates: (a) 90 °C/min; (b) 180 °C/min; (c) 270 °C/min
given below.
Both the slow-heated (90 °C/min) and the fast-heated (270 °C/min) specimens do not shrink when heated to 870 °C. SEM images shown in Fig.2 reveal that their microstructures are quite different. In the 270 °C/min-heated specimen, small bubbles appear on the W particle surfaces (Fig.2(b)) and local melting emerges on the W/particle-contact zones, resulting from extra- ordinarily high temperature on local particles surfaces (Fig.2(c)), but similar phenomenon is hardly observed in the microstructure of the 90 °C/min-heated alloy.
With To increasing to 960 °C, both the slow-heated (90 °C/min) and the fast-heated (360 °C/min) specimens undergo little densification, as shown in Fig.3. Part of Ni
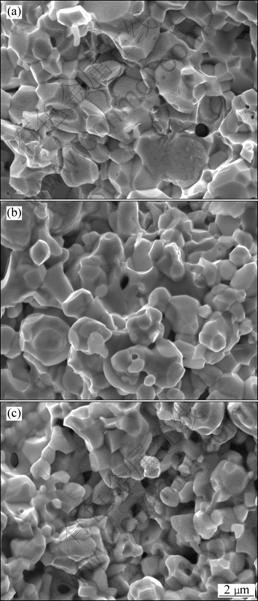
Fig.6 SEM images of fracture surfaces of alloys heated to 1 230 °C at various heating rates: (a) 90 °C/min; (b) 210 °C/min; (c) 315 °C/min
and Fe additives start to soften. In the 360 °C/min-heated specimen, sintering necks between neighbor particles extensively occur. However, necks hardly form in the 90 °C/min-heated sample. With To increasing to 1 050 °C, specimens are further densified and the sintering necks grow fast, as shown in Fig.4. The relative densities of the 90 °C/min-heated and 225 °C/min-heated specimens are 68.4% and 67.6%, respectively.
The results mentioned above show that a fast heating rate leads to particles activation and the sintering necks form and grow at a lower temperature. However, compared with a fast heating rate, slower heating rate is more conducive to the densification of the material when To is 1 140 °C or higher.
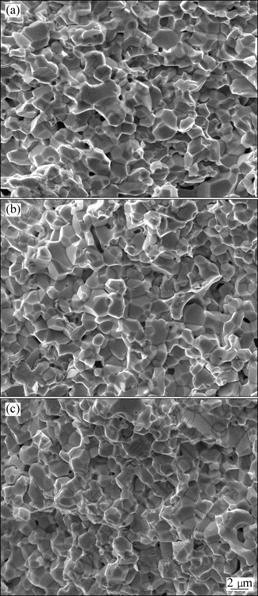
Fig.7 SEM images of fracture surfaces of alloys heated to 1 320 °C at various heating rates: (a) 90 °C/min; (b) 180 °C/min; (c) 360 °C/min
When To is 1 140 °C, the sintered densities at three different heating rates (90, 180 and 270 °C/min) increase to 72.1%, 70.3% and 69.1%, respectively. Obviously, the sintered density decreases when heating rate increases. Meanwhile, the SEM images (as shown in Fig.5) show that the microstructures of the specimens heated at three different heating rates are markedly different. For the 90 °C/min-heated specimen, the connection of sintering neck increases and some continuous pores site along the grain edges. With increasing heating rate, the densification rate decreases and more pores remain.
With To increasing to 1 230 °C, for the slow-heated sample (90 °C/min), the grains start to coarsen, and the pores become unstable and pinch off, leaving isolated
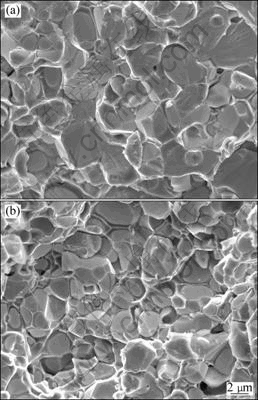
Fig.8 SEM images of fracture surfaces of alloys sintered with various parameters: (a) Heated at 90 °C/min to 1 410 °C; (b) Heated at 255 °C/min to 1 365 °C
pores, as shown in Fig.6. Increasing the heating rate, the grain growth can be prevented effectively, but at the same time, more isolative pores form and locate at grain corners. The morphologies are quite different between the slow-heated and fast-heated specimens. When To is 1 320 °C, all the sintered specimens with the three different heating rates of 90, 180 and 360 °C/min become quite dense and they have the almost same developed morphologies (Fig.7). For the three kinds of specimens, the sintered densities are 95.9%, 94.8% and 93.4%, respectively. That is to say, the slow-heated specimen has higher density than the fast-heated specimens. Viewing from the fracture surface morphology, all the three kinds of specimens can be characterized as W-W intergranular type in rupture, and no matter how the heating rate changes in the range of 90-360 °C/min, there are still a few pores isolated at the grain corners.
After sintering at higher To, quite different microstructures in both the slow-heated and fast-heated specimens are detected, which can be clearly seen by comparing Fig.7 with Fig.8. In Fig.8, tungsten grains are spheric and coarsened essentially, presenting a typical liquid-phase sintering microstructure. Although increasing the heating rate is favorable to inhibit grain coarsening in sintering, uneven microstructure forms at the same time.
4 Discussion
By analyzing the above microstructures, heating rate is affirmed to have great impact on consolidating the W-Ni-Fe heavy alloys. According to the different effects of heating rate on densification, the whole SPS process can be divided into three stages: the initial unshrinking stage, the intermediate solid state sintering stage and the final transient liquid-phase sintering stage.
At the initial unshrinking stage (To is below 900 °C), a fast heating rate can promote the later consolidation. To achieve a fast heating rate, a high current is needed to provide more energy for the powder compacts in the same heating duration. Before the densification takes place, high current passes through the powder compacts, generating instantaneous discharge at the particle-contact zones and locally inhomogeneous temperature distribution in the solid-state powder particles. In lots of research reports, the notion of the existence of plasma in SPS is only repeated routinely. Though there isn’t yet sufficient evidence to illustrate the plasma generation in the present study, the spark discharge plays a role of cleaning the particle-contact surfaces undoubtedly, providing a favorable path for the current[17]. Consequently, due to the extremely high temperature generated by the discharge on the particle surfaces, sintering necks firstly form between these particles. Simultaneously, low-melting Ni and Fe phases start to soften and the compact shrinks gradually. Resultantly, densification process begins to enter the next stage.
During the intermediate solid state sintering stage (To is between 900 and 1 320 °C), a fast heating rate provides a negative effect on the densification process. The relationship between the relative density and the temperature calculated by Eq.(1) is shown in Fig.9. Obviously, the densification processes are quite similar. In all cases, whatever the heating rate is, the samples start to be densified around 900 °C. At a given sintering temperature above 1 000 °C, the lower the heating rate is, the higher the relative density is. The results are consistent with the SEM images above. It can be interpreted that at a slower heating rate, the compact is exposed at elevated temperature for a longer time and shrinks more before reaching the final sintering temperature. Figure 10 shows the instantaneous densification rate as a function of sintering temperature and heating rate. At slow heating rates of 45 and 90 °C/min, the curves are relatively gentle, and the instantaneous densification rates reach the maximum from 1 050 to 1 250 °C. Increasing the heating rate makes the different curves superimpose at the beginning of densification (≤1 050 °C). However, if the sintering temperature is above 1 050 °C, the higher the heating rate is, the higher the instantaneous densification rate is.
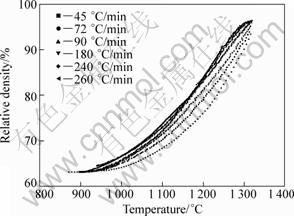
Fig.9 Relationship between relative density and temperature calculated by Eq.(1)
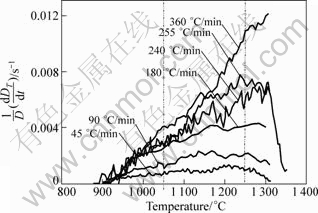
Fig.10 Instantaneous densification rate as function of sintering temperature relative to heating rate
In the second stage, solid-state diffusion dominates the whole sintering process. Ni and Fe are ensured to have lower activation energies for grain boundary diffusion and lattice diffusion[18]. By their interdiffusion, a FCC structured solid solution forms firstly. Figure 11 presents the XRD patterns from the mixed powders and he specimens sintered at various temperatures at a heating rate of 90 °C/min. When the sintering temperature is above 960 °C, (Fe, Ni) solid solution starts to appear. It means that the solid solution forms when the compact begins to shrink. Subsequently, the solid additive phase spreads by diffusion or viscous flow on the surface of W particles[19-20], resulting in the additive phase effectively fills the smaller pores between W particles. In view of longer time in heating the specimen at a slower heating rate, mass transfer is more sufficient in the slow-heated SPS process than that in the fast-heated SPS. It is also worthy remarking that the heating rate doesn’t affect the formation of (Fe, Ni) solid solution, as shown in Fig.12.
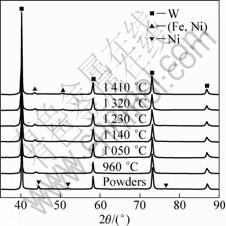
Fig.11 XRD patterns of mixed powders and specimens sintered at various temperatures at heating rate of 90 °C/min
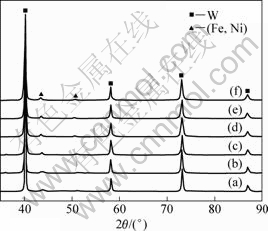
Fig.12 XRD patterns of specimens sintered at various heating rates and temperatures: (a) 90 °C /min, 960 °C; (b) 360 °C /min, 960 °C; (c) 90 °C /min, 1 140 °C; (d) 270 °C /min, 1 140 °C; (e) 90 °C /min, 1 320 °C; (f) 360 °C /min, 1 320 °C
The final stage is an unabiding stage. Therefore, it is termed transient liquid-phase sintering, which is different from the as-defined transient liquid phase sintering. Figure 13 shows the relative density as a function of sintering temperature. Obviously, there is difference in densification process between the slow-heated and fast- heated specimens. For the 90 °C/min-heated specimen, the sintered density remains in a flat state between 1320-1380 °C. With further increasing sintering temperature, liquid phase appears and the density increases. Nevertheless, an analogous phenomenon is not observed in the 255 °C/min-heated specimen. In other words, increasing heating rate causes the densification process accesses directly to the liquid-phase sintering before the solid state sintering completes. In the present study, two different heating rates of 45 and 270°C/min are used to heat the compacts until the liquid is squeezed out from the die cavity. From Fig.14, it is seen that liquid is squeezed out at about 1 430 °C for the 45 °C/min- heated specimen, while at about 1380 °C for the 270°C/min-heated specimen. Obviously, liquid phase forms at a lower temperature at a faster heating rate. It is noteworthy that the higher applied electric current inevitably leads to a larger sintering temperature difference between the experimental value (measured by an optical pyrometer) and the actual temperature in the center of the samples. In addition, ANSELMI- TAMBURINI et al[21] proved that a higher current caused a larger sintering temperature gradient in a specimen. Thereby, the liquid-phase sintering process in practice is often difficult to control precisely.
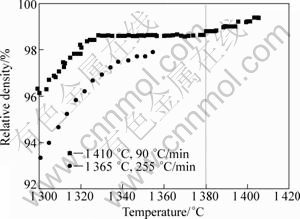
Fig.13 Relative density as function of sintering temperature calculated by Eq.(1)
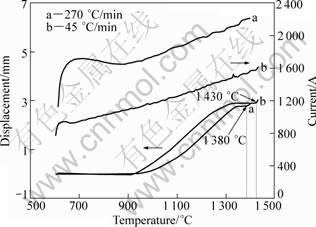
Fig.14 Variations of shrinkage displacement and current with sintering temperature at different heating rates
In this transient liquid-phase sintering stage, all the three main stages which dominate in liquid-phase sintering occur and complete quickly. The whole process can be described roughly as: firstly, good wetting spreads on the tungsten particles, particles shrink and rapidly rearrange as solid dissolves in the liquid, releasing liquid to fill the pores between the particles, and further densification occurs; then, the dissolution of sharp edges makes the tungsten particle surfaces smoother and spheroidized, reducing the interfacial energy; finally, the spherical tungsten particles coarsen by Ostwald ripening.
It should be stated that the above-mentioned delimiting way is rather arbitrary and the boundaries between the stages are actually not absolutely clear and difficult to define strictly. More detailed discussion of the solid state sintering and liquid-phase sintering is still further studied and will be reported elsewhere.
5 Conclusions
1) Mixed W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe powders were sintered via SPS method at various sintering temperatures between 870 and 1 410 °C at different heating rates.
2) According to the different effects of heating rate on densification, the whole SPS process is divided into three stages. At the initial unshrinking stage, fast heating generates instantaneous discharge at the particle-contact zones and locally inhomogeneous temperature distribution in the solid-state powder particles, essentially enhancing the following densification; densification process mainly takes place at the intermediate solid state sintering stage, and the matter transfer is more sufficient in the slow-heated SPS process; at the final transient liquid-phase sintering stage, tungsten grains spheroidize and coarsen rapidly, and fast heating results in smaller grain sizes.
References
[1] CAI W D, LI Y, DOWDING R J, MOHAMED F A, LAVERNIA E J. A review of tungsten-based alloys as kinetic energy penetrator materials [J]. Rev Particul Mater, 1995, 3: 71-131.
[2] YU Yang, HU Lian-xi, WANG Er-de. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a hot-hydrostatically extruded 93W-4.9Ni-2.1Fe alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 435-436(5): 620-624.
[3] GERMAN R M, Critical development in tungsten heavy alloys [C]//BOSE A, DOWDING R J. Proceedings of the International Conference on Tungsten and Tungsten Alloys. New Jersey: MPIF, 1992: 3.
[4] GROZA J R. Field assisted sintering [M]. Ohio: ASM, 1998: 583-589.
[5] GROZA J R. Field activation provides improved sintering [J]. Met Powder Rep, 2000, 55(7): 16-18.
[6] KANDUKURI S. A FAST winner for fully dense nano powders [J]. Met Powder Rep, 2008, 63(10): 22-27.
[7] VANMEENSEL K, LAPTEV A, HENNICKE J, VLEUGELS J, Van der BIEST O. Modelling of the temperature distribution during field assisted sintering [J]. Acta Mater, 2005, 53(16): 4379-4388.
[8] SRINIVASARAO B, OH-ISHI K, OHKUBO T, HONO K. Bimodally grained high-strength Fe fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering [J]. Acta Mater, 2009, 57(11): 3277-3286.
[9] SASAKI T T, OHKUBO T, HONO K. Microstructure and mechanical properties of bulk nanocrystalline Al-Fe alloy processed by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering [J]. Acta Mater, 2009, 57(12): 3529-3538.
[10] ZHAO J F, HOLLAND T, UNUVAR C, MUNIR Z A. Sparking plasma sintering of nanometric tungsten carbide [J]. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater, 2009, 27(1): 130-139.
[11] SHI Xiao-liang, YANG Hua, WANG Sheng. Spark plasma sintering of W-15Cu alloy from ultrafine composite powder prepared by spray drying and calcining-continuous reduction technology [J]. Mater Charact, 2009, 60(2): 133-137.
[12] CHAIM R, MARGULIS M. Densification maps for spark plasma sintering of nanocrystalline MgO ceramics [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 407(1-2): 180-187.
[13] BERNARD-GRANGER G, GUIZARD C. Spark plasma sintering of a commercially available granulated zirconia powder: I. Sintering path and hypotheses about the mechanism(s) controlling densification [J]. Acta Mater, 2007, 55(10): 3493-3504.
[14] BERNARD-GRANGER G, GUIZARD C, SURBLE S, BALDINOZZI G, ADDAD A. Spark plasma sintering of a commercially available granulated zirconia powder-II: Microstructure after sintering and ionic conductivity [J]. Acta Mater, 2008, 56(17): 4658-4672.
[15] CHAIMA R, SHLAYER A, ESTOURNES C. Densification of nanocrystalline Y2O3 ceramic powder by spark plasma sintering [J]. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2009, 29(1): 91-98.
[16] R?THEL J, HERRMANN M, BECKERT W. Temperature distribution for electrically conductive and non-conductive materials during Field Assisted Sintering (FAST) [J]. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2009, 29(8): 1419-1425.
[17] SONG X Y, LIU X M, ZHANG J X. Neck formation and self-adjusting mechanism of neck growth of conducting powders in spark plasma sintering [J]. J Am Ceram Soc, 2006, 89(2): 494-500.
[18] PARK S J, MARTIN J M, GUO J F, JOHNSON J L, GERMAN R M. Densification behavior of tungsten heavy alloy based on master sintering curve concept [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2006, 37(9): 2837-2848.
[19] DORE F, MARTIN C L, ALLIBERT C H. Apparent viscosity of W-Cu powder compacts during sintering [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 383(2): 390-398.
[20] MACEDO H R, SILVA A G P, MELO D M A. The spreading of cobalt, nickel and iron on tungsten carbide and the first stage of hard metal sintering [J]. Mater Lett, 2003, 57(24-25): 3924-3932.
[21] ANSELMI-TAMBURINI U, GENNARI S, GARAYA J E, MUNIR Z A. Fundamental investigations on the spark plasma sintering/ synthesis process II. Modeling of current and temperature distributions [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 394(1-2): 139-148.
胡 可,李小强,杨 超,李元元
华南理工大学 国家金属材料近净成形工程研究中心,广州 510640
摘 要:采用放电等离子烧结(SPS)技术固结成形W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe(质量分数,%)混合粉末,研究不同加热速率对烧结致密化行为和微观组织演变规律的影响。结果表明,W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe合金的SPS致密化过程可以划分为三个阶段。初始不收缩阶段,快速加热导致粉末颗粒接触区产生瞬间放电,并在颗粒表面产生局部高温,强化后续烧结致密化;致密化过程主要发生在中期固相烧结阶段,缓慢加热有助于扩散更加充分;在后期瞬时液相烧结阶段,钨晶粒球化并迅速长大,且快速加热可获得更为细小的晶粒。
关键词:致密化行为;微观组织演变;SPS;W-Ni-Fe合金
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
Foundation item: Project (2010CB635104) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project (2007AA03Z112) supported by the National High-Tech Research and Development Program of China; Project (9140A18040709JW1601) supported by the Advanced Research Fund of DOD, China; Project (2009ZZ0019) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China; Project (NCET-10-0364) supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University, China
Corresponding author: LI Xiao-qiang; Tel: +86-20-87110099; E-mail: lixq@scut.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60742-5

