Al/Cu多层复合板的组织演化及其对力学性能的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第1期
论文作者:李小兵 祖国胤 王 平
文章页码:36 - 45
关键词:Al/Cu层状复合材料;轧制复合;界面;超细晶
Key words:Al/Cu laminated composite; roll bonding; interface; ultra-fine grain
摘 要:研究异步冷轧退火工艺制备的Al/Cu多层复合材料的组织演化及其对力学性能的影响。采用SEM和TEM分析界面组织,用界面剥离实验和拉伸实验测试复合板的力学性能。结果表明:异步冷轧复合工艺可以获得界面紧密连接的超细晶多层复合材料。退火促进Al和Cu连接界面上金属原子的扩散,甚至导致金属间化合物的生成。复合板的连接界面在300 °C退火时发生固溶强化现象,界面的连接强度达到最大,但是在更高温度退火时界面生成的金属间化合物导致连接性能急剧下降。在300 °C退火时,复合板组织发生再结晶并获得较高的抗拉强度;而在350 °C退火时,界面存在亚微米厚度的过渡层,有利于位错滑移运动,因此复合板获得较高的伸长率。
Abstract: The microstructural development and its effect on the mechanical properties of Al/Cu laminated composite produced by asymmetrical roll bonding and annealing were studied. The composite characterizations were conducted by transmission electron microscope (TEM), scanning electron microscope (SEM), peeling tests and tensile tests. It is found that the ultra-fine grained laminated composites with tight bonding interface are prepared by the roll bonding technique. The annealing prompts the atomic diffusion in the interface between dissimilar matrixes, and even causes the formation of intermetallic compounds. The interfacial bonding strength increases to the maximum value owing to the interfacial solution strengthening at 300 °C annealing, but sharply decreases by the damage effect of intermetallic compounds at elevated temperatures. The composites obtain high tensile strength due to the Al crystallization grains and Cu twins at 300 °C. At 350 °C annealing, however, the composites get high elongation by the interfacial interlayer with submicron thickness.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 36-45
Xiao-bing LI, Guo-yin ZU, Ping WANG
School of Materials and Metallurgy, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110004, China
Received 17 March 2014; accepted 14 July 2014
Abstract: The microstructural development and its effect on the mechanical properties of Al/Cu laminated composite produced by asymmetrical roll bonding and annealing were studied. The composite characterizations were conducted by transmission electron microscope (TEM), scanning electron microscope (SEM), peeling tests and tensile tests. It is found that the ultra-fine grained laminated composites with tight bonding interface are prepared by the roll bonding technique. The annealing prompts the atomic diffusion in the interface between dissimilar matrixes, and even causes the formation of intermetallic compounds. The interfacial bonding strength increases to the maximum value owing to the interfacial solution strengthening at 300 °C annealing, but sharply decreases by the damage effect of intermetallic compounds at elevated temperatures. The composites obtain high tensile strength due to the Al crystallization grains and Cu twins at 300 °C. At 350 °C annealing, however, the composites get high elongation by the interfacial interlayer with submicron thickness.
Key words: Al/Cu laminated composite; roll bonding; interface; ultra-fine grain
1 Introduction
Metallic laminated composites are attracting considerable attentions due to the significant interface effect on the mechanical performance [1]. The Al/Cu laminated composite provides a good combination of high conductivity, strength and corrosion resistance [2]. Many manufacturing technologies have been used to produce the Al/Cu composites [3,4]. Among them, roll bonding and diffusion bonding are preferable because of their low cost and reliability [5]. JAMAATI and TOROGHINEJAD [6] have summaried the processing parametres on roll bonding strength between dissimilar metals. Nowadays, the approaches for achieving bulk nanostructured metals from coarse-grained material are developed, including various severe plastic deformation (SPD) techniques such as equal-channel angular pressing, high-pressure torsion, accumulative roll bonding and asymmetric rolling [7].
The shape control of individual layer in laminated composites is difficult in the accumulative roll bonding processing. The thickness difference along the rolling direction is found between the layers [8]. It could induce serious heterogeneous properties to the laminated composites. Asymmetrical roll technique now gets an attention as its SPD capability. A single pass with large thickness reduction in asymmetrical roll bonding process is found to get a tight bonding between dissimilar metals at room temperature [9]. It is well known that the mechanical strength of material produced by SPD technique increases with the grain size decreasing from micron to submicron scale. Thus, the mechanical performance of laminates produced by the asymmetrical roll bonding can be promoted [10].
The interface in composite has been investigated broadly. LI et al [11] directly observed the dislocation slip in the interface of Cu/Nb multilayers according to the in situ nanoindentation experiments. YAJID et al [12] investigated the alloy phases in the metallic multilayers of Cu/Al/Ti composition during ex situ and in situ heating experiments according to transmission electron microscopy. CHEN et al [13] studied the influence of interfacial structure on the fracture behavior of cold roll bonded Al/Cu bimetal plate. RAWERS and PERRY [14] conducted the tensile tests of brittle intermetallic/ductile metallic microlaminates to study the strengthening and toughening effect by the bridge-crack deformation mechanism. However, very few publications have clearly reported the microstructural characterizations of the laminated composites through SPD manufacturing approach. Meanwhile, the effect of SPD and thermal diffusion on the microstructure of Al/Cu laminated composite is still ambiguous. LI et al [9,15] have taken some macroscopic characterizations of clad sheets, but many works are still required to clarify the relationship between the microstructure and mechanical performance of laminated composites.
In the present work, the asymmetrical cold roll bonding of Al and Cu metallic layers was conducted to get the ultra-fine grained laminated composite. Especially, the interfacial developments were observed before and after the thermal annealing. The deformation condition in asymmetrical roll bonding was analyzed to understand the microstructural development of laminated composites. Based on the interfacial bonding strength and tensile performance of the laminated composites, the microstructural effects on the mechanical properties of composites were discussed.
2 Experimental
The raw materials were fully annealed commercial purity copper and aluminum sheet with chemical compositions and mechanical properties listed in Table 1. They were cut into specimens with 25 mm in width and 150 mm in length. After degreasing and brush scratching the metal surface, the stacked metal layers were cold roll bonded in the asymmetrical mill with work-rolls diameter of 92 mm. The rotation velocity of the lower roll was 20 r/min and was 1.31 times faster than that of the upper roll. A single cold rolling pass for the multilayer was taken with the thickness reduction of 72%. The roll bonding process was illustrated in Fig. 1(a). Then, the as-rolled laminates were annealed at 300 °C, 350 °C and 400 °C, respectively, for 30 min in the resistance furnace.
Figure 1(b) indicates that the Al/Cu bimetallic laminated composite consists of three layers with individual thickness of about 250 μm. The microstructural observations of the ion-polished cross-sectional film were performed on a transmission electron microscope (TEM) Tecnai G2 20 with a 200 kV accelerating voltage. It is schematically illustrated in Fig. 1(b) that the observation zone locates in the interface and matrixes beside the interface.
Table 1 Specifications and mechanical properties of raw materials


Fig. 1 Schematic diagrams of asymmetrical roll bonding process (a), Al/Cu laminated composite with typical TEM observation zone in interface and matrixes (b) and tensile specimen (c)
In order to reveal the interface effect on the metallic bonding between dissimilar matrixes, the peeling strength tests were conducted on the materials testing system SANSCMT5000. As shown in Fig. 1(c), the tension specimens with gauge of 20 mm length and 10 mm width were made from the centre of laminated composites along the rolling direction. Tensile tests with strain rate of 8.3×10-3 s-1 were conducted on SANSCMT 5000 at room temperature. The elongation of the composites was calculated from the fractured specimens. Then the fracture behavior of the laminated composites was discussed according to the fracture observation.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructural development of laminated composites
Figure 2 shows the TEM micrographs of the as-rolled laminated composite. It is clear that the matrix grains in the composite are distinctly flatted under the deformation pressure and elongated in the transverse direction. The thickness of lamellar grains is about 0.2 μm in Al matrix and about 0.1 μm in Cu matrix. The grains in the interfacial zone are obvious in the submicron scale, and even smaller than the matrix grains. The clear interface between Cu and Al matrix presents a tight bonding without any microvoids.
In general, a remarkable shear deformation on the metal surfaces is imposed by the rotated rolls in the rolling deformation zone. It is found that the shear deformation can distribute in the whole bulk material, which is ascribed to the significant shear stress during asymmetrical roll process [16]. In addition, different metal flows owing to the different mechanical properties of dissimilar matrix enhance the interfacial shear deformation in roll bonding of the metallic multilayer. Therefore, the interfacial grains obtain a severe plastic deformation. Based on the SPD theory, the multiplication of a large amount of dislocations induces the formation of dislocation cell and then forms subgrain structure in the interface. Because of the low stacking fault energy (SFE) of Cu, twinning deformation mechanism plays an important role in the plastic deformation [17]. By contrast, the high SFE of Al is favorable to the dislocation interaction and annihilation, and then reduces the high-angle subgrain boundary.
According to the bonding mechanism of multilayer, the surface deformation in the matrix plays a crucial role in promoting the surface cracks and the extrusion of underlying metals. In the present work, the asymmetrical roll bonding with thickness reduction of 72% has a visible capability of promoting the surface deformation in matrixes to form a tight interfacial bonding between dissimilar metals.

Fig. 2 TEM images of bonding interface (a, b), Al matrix (c) and Cu matrix (d) in as-rolled laminated composite

Fig. 3 TEM images of bonding interface (a), Al matrix (b) and Cu matrix (c) in laminated composite annealed at 300 °C and twins in Cu matrix with inset of SAED pattern (d)
The TEM microstructures of the composites annealed at 300 °C are indicated in Fig. 3. An obvious recrystallization occurs in the Al matrix and induces the mixture of flatted grains and small grains of 0.1 μm size in Fig. 3(b). But the Cu grains mainly retain the elongated state. The inset of Fig. 3(d) shows the selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of the twin with the circle mark and well confirms the twinned Cu structure [18]. The microstructures of Al and Cu matrix reveal the occurrence of the recrystallization.
Especially, an interlayer with thickness of 0.1-0.2 μm forms in the interface. Because of the thermal activation of Cu and Al atoms at 300 °C, the atomic diffusion occurs between dissimilar matrixes. It then causes the formation of solid solution region in the interface and induces the significant interfacial lattice distortion. Finally, the interface reveals a near- amorphous structure in Fig. 3(a).
Figure 4 shows the microstructures of composites annealed at 350 °C. The Al matrix consists of nearly equiaxed grains with average grain size of 0.6 μm, while the Cu matrix contains a few of deformed grains without complete recrystallization. Moreover, an interfacial interlayer with 0.6 μm thickness forms between the dissimilar matrixes. The energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis result reveals that typical points of A and B have the fixed ratio of Cu and Al atoms, nearly similar to the chemical composition of intermetallic compounds CuAl2 and Cu9Al4, which indicates the possible compounds in the interlayer.
At high annealing temperature, the grains of composite grow promptly and the atomic diffusion is enhanced greatly. The activation energy for the migration of grain boundary and atomic motion is fulfilled by the thermal energy at 350 °C. The number of diffusion atoms in the bonding interface exceeds the saturation of the Cu-Al solid solution. Once the thermal activation is significant enough, the supersaturated solid solutions will transform into the intermetallic compounds. According to the Cu-Al binary alloy phase diagram, the formation sequence of various intermetallic compounds CuAl2, CuAl, Cu4Al3, Cu3Al2 and Cu9Al4 phases follows the thermodynamic conditions. The activation energies of CuAl2 and Cu9Al4 phase are 60.66 kJ/mol and 75.61 kJ/mol, respectively, which are the lowest in the five equilibrium compounds [19]. Therefore, the diffusion interlayer consists of the sublayer with CuAl2 and Cu9Al4 phase. The thicker sublayer with CuAl2 phase also proves its first formation and growth in comparison to Cu9Al4 phase.
The microstructures of the composite after 400 °C annealing are shown in Fig. 5. It is found that the average grain sizes of Al and Cu are 1.1 μm and 0.6 μm, respectively. The interfacial interlayer promptly grows up to 1.2 μm with three sublayers. The insets of SAED pattern in Fig. 5(a) confirm the intermetallic compounds to be CuAl2 and Cu9Al4 phases in the sublayer near the Al matrix and Cu matrix, respectively. Different from the result in Fig. 4, a new sublayer, confirmed as the intermetallic compound CuAl, exists between the initiated CuAl2 and Cu9Al4 phases. It is also notable that a few of microvoids exist in the CuAl sublayer, resulting from the damage effect of the significant volume differences and large plastic stresses among the hard and brittle intermetallic compounds [19].

Fig. 4 TEM images of bonding interface (a, b), Al matrix (c) and Cu matrix (d) in laminated composite after annealing at 350 °C

Fig. 5 TEM images of bonding interface (a, b), Al matrix (c) and Cu matrix (d) in laminated composite after annealing at 400 °C
3.2 Interfacial bonding strength of laminated composites
The peeling tests of the interface along the rolling direction directly reveal the interfacial bonding strength between dissimilar metals. The experimental results are listed in Table 2. It is found that the peeling strength increases up to the maximum value after 300 °C annealing and sharply decreases to the level below that of the as-rolled composites after 350 °C annealing. Finally, the peeling strength of the composites annealed at 400 °C is only 20% of the initial strength of as-rolled one. The results reveal that the peeling strength is very sensitive to the interfacial microstructure. The fracture surfaces after the peeling test are shown in Fig. 6. It is clear that the fracture modes are very different in the composites with different annealing temperatures. A lot of adhesive metals exist in the peeled Al and Cu surfaces, indicative of obvious ductile features for the composites after 300 °C annealing. By contrast, the cleavage fracture with several cracks forms in the composites after above 350 °C annealing.
Table 2 Peeling strength of bonding interface of laminated composites annealed at different temperatures

In as-rolled composites, the interfacial bonding mainly depends on the interfacial plastic deformation during the asymmetrical roll bonding. Therefore, the bonding strength could be enhanced by the large shear deformation and abundant extrusions of the underlying metals in the matrixes [10]. According to the classical bonding theory in metallic laminates, the extrusion plays a crucial role in the interfacial bonding. The bonding mechanism is proposed as the metallic interaction in the interface. A strong bonding forms in the interface of dissimilar metal matrixes after asymmetrical roll bonding process. However, the interfacial bonding strength is restricted by the significant residual stress caused by the plastic deformation at room temperature.
The annealing at low temperature can remove the interfacial residual stress and promote the interfacial atomic diffusion, and then the solution strengthening occurs in the interface and improves the interfacial bonding strength. Therefore, a high peeling strength is obtained in the composite annealed at 300 °C. Meanwhile, there is no overgrowth of the diffusion layer and formation of intermetallic compounds in the interface. In peeling tests, the interface is split by the large force once the strong metallic bonding between extruded metals is destroyed. Thus, there are several tearing ridges in the peeled surface of the as-rolled composite.
For the composites annealed at 350 °C, a rapid growth of the interlayer occurs in the interface, together with the formation of brittle intermetallic compounds. The interlayer is destructive to the interfacial bonding when a tensile stress is loaded on the normal direction of the interface. Finally, the peeling strength dramatically drops down to the value lower than the strength of as-rolled composite. The peeled fracture confirms the existence of the intermetallic compounds. The insets of Figs. 6(b) and (e) indicate that some microcracks exist in the peeled surfaces of the matrixes, which obviously proves the damage effect of the interfacial intermetallic compounds. However, some tearing ridges in the ring mark reveal that the interfacial interlayer with limited thickness and intermetallic compounds does not completely destroy the interfacial bonding [20-22].
By contrast, the peeled surfaces in Figs. 6(c) and (f) show the widespread cleavages without ductile tearing features. The stacked structure with cracks clearly exists in the Al matrix. The fracture behavior is reasonable according to the analysis of the interfacial interlayer shown in Fig. 5. Thus, the peeling strength of the composites after 400 °C annealing is very low due to the serious interface failure. Consequently, the annealing temperature should be 300 °C on the basis of the interfacial microstructure and bonding strength of laminated composites.
3.3 Tensile performance of laminated composites
The results of tensile tests of the laminated composites annealed at different temperatures are listed in Table 3. It is clear that the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of the composites decreases with the rise of annealing temperature, while the fractured elongation reveals a complex tendency. The typical engineering stress-strain curves of the laminated composites are shown in Fig. 7.

Fig. 6 Peeled fracture morphologies of Cu matrix (a-c) and Al matrix (d-f) in laminated composites annealed at different temperatures (The insets are the magnification of specific zone)
Table 3 Tensile strength and elongation of laminated composites
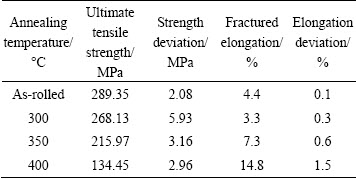
The composites have a strength of 289.35 MPa which is slightly higher than that of the as-received Cu sheet due to the existence of significant work-hardening in the as-rolled laminated composites. Meanwhile, the residual stress hinders the dislocations motion and induces the obvious tangling in the composites. The plastic deformation of composite is inhibited in the tensile process and then the premature yield occurs. However, the high SFE makes the dislocation cross-slip more easily in Al grain than in Cu grain, and induces the obvious dislocation pile-up in the Al grain boundary. Thus, the microcracks can be generated under the tensile load. After the connection and mergence with the neighbored microcracks, the cracks in the grain boundary induce the fracture of Al layer [23]. Finally, a lot of dimples form in the Al fracture as shown in Fig. 8(a). Furthermore, some junctions existing in the interface are in good agreement with the strong interfacial bonding.

Fig. 7 Engineering stress-engineering strain curves in tensile tests of laminated composites annealed at different temperatures

Fig. 8 Tensile fracture morphologies of laminated composites annealed at different temperatures
It is clear that the UTS value of the composites annealed at 300 °C is 268.13 MPa which is only 7.3% lower than that of the as-rolled composites. The result reveals that the full recovery of the composite can not be carried out after 300 °C annealing for 30 min, and also demonstrates that the plastic deformation of the composite is very severe during asymmetrical roll bonding. However, the fractured elongation is decreased. According to the microstructure shown in Fig. 3, the recrystallization occurs in the Al matrix and causes the mixture of large elongated grains with the small recrystallization. The dislocation is difficult to move across the boundary of mixed Al grains. As a result, the dislocation motion is hindered in the Al matrix. The non-uniform dimples in the Al fracture also prove the low ductility. Meanwhile, the interfacial atoms diffusion causes the formation of the solid solution with significant lattice distortion, and strengthens the composites but impedes the dislocation slip across the interface. Thus, the ductility of the laminated composites decreases. Furthermore, the interfacial pins in Fig. 8(b) indicate the high interfacial bonding strength. The interfacial bonding is improved by the interfacial atomic diffusion at 300 °C.
The composites annealed at 350 °C have the dramatically decreased strength and increased elongation, which can be ascribed to the obviously different microstructure of the composite. The deformed Al grains nearly become the equiaxed state due to the full recrystallization in 350 °C annealing process. The Cu grains also grow promptly. The recovery softening occurs in the deformed matrixes and then causes the UTS value to decrease distinctly [24]. The dislocation motion benefits from the uniform grain in the matrix and guarantees the plastic deformation of the composite. Owing to the large elongation, the Al fracture area with a lot of dimples is small. Most importantly, an interfacial interlayer with the submicron thickness exists between dissimilar matrixes. This interlayer makes the laminated composite an integrated structure in the tensile tests. Once the interfacial interlayer fractures, the composite obvious yields and causes the yield stage in the tensile stress-strain profiles as shown in Fig. 7. Then, the Al and Cu layer will be individually elongated until the failure by the tensile load. Furthermore, the yield strength of the composite is remarkably enhanced at 350 °C in comparison with the other annealing temperatures, which is the direct evidence of the advantage of the submicron interlayer in the interface. Meanwhile, the interlayer provides a good transition to the dislocation slip across the bonding interface and improves the ductility of the composites.
After 400 °C annealing, the tensile strength of the composites continues to decrease and the elongation slightly increases. The Al and Cu grains dramatically grow into the coarse state owing to the remarkable thermal activation. According to the Hall-Petch theory in terms of the dislocations pile-up, the large grain size makes a significant stress concentration in the grain boundary. Driving the dislocations transmission across grain boundary just requires a small external stress. The theory can be expressed as ss μ d-1/2, where ss is the yield strength and d is the grain size [25]. Therefore, the yield strength of the composite with coarse grains in matrixes reduces. However, the UTS value is obviously higher than the yield strength, which is ascribed to the stress strengthening effect.
Table 3 shows that the variation of strength and elongation of the composite annealed at 400 °C is remarkable in comparison with those of the composite annealed at 350 °C. The reason is likely to be that the prompt growth of the interfacial interlayer cannot strengthen the interface. And the microvoids in the interfacial interlayer are disadvantageous to the dislocation motion across the interface of dissimilar metals. A large crack existing in the interface of Al and Cu matrix confirms the bad interfacial bonding. The fragments on the matrix are detected as intermetallic compounds and aggravate the delamination. The laminated composites are separated into the individual layers to resist the tensile load. The Al matrix with a large deformation has a small fracture area, and no visible dimples form in the fracture.
4 Conclusions
1) The ultra-fine grained Al/Cu laminated composites with tight bonding interface are obtained by large plastic deformation in the asymmetrical roll bonding process. The abundant extrusion of underlying metal improves the interfacial bonding.
2) The high temperature annealing prompts the atomic diffusion and the formation of interfacial interlayer with intermetallic compounds. The maximum interfacial bonding strength of the composites is obtained by the solution strengthening effect of the interfacial diffusion at 300 °C.
3) The tensile strength of the composites increases with the decreasing grain size of matrixes. The interfacial interlayer with submicron thickness is helpful to the dislocation motion and improves the ductility of the composites. The excessive formation of intermetallic compounds induces the interface delamination and reduces the tensile properties of the composites.
References
[1] WANG J, MISRA A. An overview of interface-dominated deformation mechanisms in metallic multilayers [J]. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science, 2011, 15(1): 20-28.
[2] PENG X K, WUHRER R, HENESS G, YEUNG W Y. On the interface development and fracture behaviour of roll bonded copper aluminium metal laminates [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1999, 34(9): 2029-2038.
[3] LEE K S, KWON Y N. Solid-state bonding between Al and Cu by vacuum hot pressing [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(2): 341-346.
[4] LI Yun-tao, DU Ze-ye, MA Cheng-yong. Interfacial energy and match of cold pressure welded Ag/Ni and Al/Cu [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2002, 12(5): 814-817.
[5] LI L, NAGAI K, YIN F X. Progress in cold roll bonding of metals [J]. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2008, 9(2): 023001.
[6] JAMAATI R, TOROGHINEJAD M R. Cold roll bonding bond strengths: Review [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2011, 27(7): 1101-1108.
[7] ZHU Y T, VALIEV R Z, LANGDON T G, TSUJI N, LU K. Processing of nanostructured metals and alloys via plastic deformation [J]. MRS Bulletin, 2010, 35(12): 977-981.
[8] HSIEH C C, SHI M S, WU W T. Growth of intermetallic phases in Al/Cu composites at various annealing temperatures during the ARB process [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2012, 18(1): 1-6.
[9] LI X B, ZU G Y, DING M M, MU Y L, WANG P. Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu/Al clad sheet fabricated by asymmetrical roll bonding and annealing [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 529: 485-491.
[10] PAN D, GAO K, YU J. Cold roll bonding of bimetallic sheets and strips [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1989, 5(9): 934-939.
[11] LI N, WANG J, MISRA A, HUANG J Y. Direct observations of confined layer slip in Cu/Nb multilayers [J]. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 2012, 18(5): 1155-1162.
[12] YAJID M A M, BAGSHAW H, MOBUS G. In situ and ex situ transmission electron microscopy investigation of Cu-Al-Cu-Ti reactive metallic multilayer coatings [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2010, 25(6): 1196-1203.
[13] CHEN C Y, CHEN H L, HWANG W S. Influence of interfacial structure development on the fracture mechanism and bond strength of aluminum/copper bimetal plate [J]. Materials Transactions, 2006, 47(4): 1232-1239.
[14] RAWERS J, PERRY K. Crack initiation in laminated metal-intermetallic composites [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1996, 31(13): 3501-3506.
[15] LI X B, ZU G Y, WANG P. Interface strengthening of laminated composite produced by asymmetrical roll bonding [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 562: 96-100.
[16] WANG Jun-li, XU Rui-dong, WANG Shao-hua, QIAN Tian-cai, SHI Qing-nan. Formation mechanism and organizational controlling of ultra-fine-grain copper processed by asymmetrical accumulative rolling-bond and annealing [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(11): 2672-2678.
[17] SAN Xing-yuan, LIANG Xiao-guang, CHENG Lian-ping, SHEN Li, ZHU Xin-kun. Effect of stacking fault energy on mechanical properties of ultrafine-grain Cu and Cu-Al alloy processed by cold-rolling[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(4): 819-824.
[18] ROHATGI A, VECCHIO K S, GRAY G T. The influence of stacking fault energy on the mechanical behavior of Cu and Cu-Al alloys: Deformation twinning, work hardening, and dynamic recovery [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2001, 32(1): 135-145.
[19] XU H, LIU C, SILBERSCHMIDT V V, PRAMANA S S, WHITE T J, CHEN Z, ACOFF V L. Behavior of aluminum oxide, intermetallics and voids in Cu-Al wire bonds [J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(14): 5661-5673.
[20] LU Lin. Effect of diffusion heat treatment on structure of cold-rolled Cu-Al composite laminate interface [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2012. (in Chinese)
[21] MI Bing-xue. Study on the interface diffusion process of cold rolling Cu/Al clad metal sheet in annealing process [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2012. (in Chinese)
[22] WANG Da. Study on the bonding mechanism and interface reaction of Cu/Al layered composites [D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2011. (in Chinese)
[23] KUMAR K S, van SWYGENHOVEN H, SURESH S. Mechanical behavior of nanocrystalline metals and alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(19): 5743-5774.
[24] SHENG L Y, YANG F, XI T F, LAI C, YE H Q. Influence of heat treatment on interface of Cu/Al bimetal composite fabricated by cold rolling [J]. Composites Part B, 2011, 42(6): 1468-1473.
[25] MISRA A, KUNG H. Deformation behavior of nanostructured metallic multilayers [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2001, 3(4): 217-222.
李小兵,祖国胤,王 平
东北大学 材料与冶金学院,沈阳 110004
摘 要:研究异步冷轧退火工艺制备的Al/Cu多层复合材料的组织演化及其对力学性能的影响。采用SEM和TEM分析界面组织,用界面剥离实验和拉伸实验测试复合板的力学性能。结果表明:异步冷轧复合工艺可以获得界面紧密连接的超细晶多层复合材料。退火促进Al和Cu连接界面上金属原子的扩散,甚至导致金属间化合物的生成。复合板的连接界面在300 °C退火时发生固溶强化现象,界面的连接强度达到最大,但是在更高温度退火时界面生成的金属间化合物导致连接性能急剧下降。在300 °C退火时,复合板组织发生再结晶并获得较高的抗拉强度;而在350 °C退火时,界面存在亚微米厚度的过渡层,有利于位错滑移运动,因此复合板获得较高的伸长率。
关键词:Al/Cu层状复合材料;轧制复合;界面;超细晶
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Projects (50971038, 51174058) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Guo-yin ZU; Tel: +86-24-83686462; Fax: +86-24-83682912; E-mail: zugy@smm.neu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63576-2

