文章编号:1004-0609(2011)01-0110-08
合金元素钨对新型Co-Al-W合金热腐蚀行为的影响
徐仰涛 1, 2, 夏天东1, 2, 闫健强1, 2
(1. 兰州理工大学 甘肃省有色金属新材料省部共建国家重点实验室, 兰州 730050;
2. 兰州理工大学 有色金属合金及加工教育部重点实验室, 兰州 730050)
摘 要: 研究Co-Al-W和商用MAN900合金在800 ℃ 75%Na2SO4+25%NaCl混合熔盐中的腐蚀动力学及热腐蚀行为。结果表明:7.5 W、9.8 W和10.7 W合金经热腐蚀后质量增加量比MAN900合金的质量增加量少,Co-Al-W合金的耐热腐蚀能力比MAN900合金的耐热腐蚀能力强。Co-Al-W合金在熔盐中腐蚀膜结构分成3层,即呈蓬松状由富钴氧化物Co3O4组成的腐蚀膜最外层,由Co、Al、W复杂氧化物组成的中间过渡层和主要由Al及Co氧化物组成较致密的腐蚀膜内层。随着腐蚀时间的增加,合金腐蚀膜最外层由于脱落逐渐变薄;中间过渡层厚度逐渐增加,该层中各元素分布趋于均匀、稳定;腐蚀膜内层致密性增加使该层增厚不明显。
关键词: Co-Al-W合金; 合金元素钨; 热腐蚀
中图分类号: TG172.6; TG146.1 文献标志码:A
Effect of alloying element tungsten on hot corrosion behavior of novel Co-Al-W superalloys
XU Yang-tao1, 2, XIA Tian-dong1, 2, YAN Jian-qiang1, 2
(1. State Key Laboratory of Gansu Advanced Non-ferrous Metal Materials,
Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou 730050, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Non-ferrous Metal Alloys, Ministry of Education,
Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou 730050, China)
Abstract: The hot corrosion kinetics and hot corrosion behavior of Co-Al-W and MAN900 superalloys at 800 ℃ in 75%Na2SO4+25%NaCl molten salt were studied. The results show that the mass gains of 7.5 W, 9.8 W and 10.7 W alloys are less than those of MAN900 superalloy. The hot corrosion resistance of Co-Al-W superalloys is superior to that of MAN900 superalloys. The hot corrosion oxide scale of Co-Al-W superalloys is made up of three layers, that are, the external corrosion layer consisting of Co oxide (Co3O4), the intermediate mixed oxides layer composed of complex oxide and nonuniform-barren oxide layer of Co, Al, W and an internal attacked layer with different compounds of Co, Al and O. With the increase of corrosion time, the intermediate mixed oxide layer becomes thicker, the external layer becomes thinner and internal layer almost has no change, but compactness of internal layer increases gradually.
Key words: Co-Al-W superalloys; alloying element tungsten; hot corrosion
高温腐蚀作为多学科的交叉点,其研究必然会促进相关学科的发展[1]。为此,许多研究者对新研制的合金在其力学性能研究取得一定进展的前提下,对其热腐蚀性能进行大量研究[2-6],提出高温腐蚀的一般机理[7-8]。 但由于影响合金热腐蚀的因素非常复杂,如合金的组成、合金的制备工艺、沉积物的量、腐蚀温度及腐蚀方式等[9],不同合金在不同腐蚀条件下其耐腐蚀性能会有很大差异,因此,模拟合金使用环境并对其耐腐蚀性能进行研究,是评价合金应用的重要工 作[10]。
最近,SATO等[11]发现了具有L12结构、较稳定γ′-Co3(Al,W)相沉淀强化的新型Co-Al-W合金。随后,SUZUKI等[12]用悬浮感应熔炼方法制备了Co-Al-W- Ta和Co-Al-W合金。他们发现,在连续两相(γ′+γ)微观结构中,细晶粒、多边形、有规则连续密排的γ′相沉积在γ-Co基体上。由于钴基合金具有良好的抗氧化、耐腐蚀和耐磨损性能,常用于制造燃气涡轮机的叶片[13]。因此,用γ′-Co3(Al,W)相沉淀强化的Co-Al-W合金将成为在高温、强腐蚀磨损、强氧化性环境(如汽化煤装置、发电系统,常为高硫含量的劣质油和燃气)中满足“极端”使用要求的高温合金[11-12]。但至今未见有关新型Co-Al-W合金热腐蚀行为和钨对其热腐蚀行为影响的报道。
为此,本文作者研究Manaurite900(MAN900)和真空电弧熔炼不同钨含量Co-Al-W合金在800 ℃ 75%Na2SO4 +25% NaCl混合熔盐中的腐蚀行为,为新型Co-Al-W合金在“极端”条件中使用提供科学依据和理论指导。
1 实验
真空电弧熔炼制备Co-Al-W合金的原料为钨粉(0.98 μm,纯度99.8%)、铝粉(3.59 μm, 纯度99.5%)和钴粉(4.5 μm, 纯度99.0%)。按表1中合金理论含量(摩尔分数,%)进行配料。用METTLER AE240型电子天平称取粉末30 g经QM-1SP4行星式球磨机混合均匀(球料比1.3:1,转速250 r/min,球磨3 h)后在岛津万能材料实验机上用自制模具压制试样(压坯压力90 MPa)。压制试样在石墨坩埚中用WS-4非自耗电弧熔炼炉熔炼(氩气保护)制备Co-Al-W合金。用能量色散X荧光光谱仪(EDXRF)分析合金成分,其结果如表1所列。为表述方便,本实验均以钨的摩尔分数(%)表示合金。所制备的合金经(1 623 K,2 h)+(1 123 K,2 h)均质化和时效处理。商用Manaurite900合金化学成分为:w(C) 0.10%~0.18%,n(S)/n(P)≤ 0.03, w(Mn)≤ 1.5%, w(Si)≤0.5%, w(Cr)19%~23%, w(Nb) 0.8%~1.2%, w(Ni) 31%~33%,其余为Fe。
将合金加工成15 mm×12 mm×3 mm的薄片,用400#~1 000#水砂纸打磨后在乙醇和丙酮混合溶液中用KQ-250D超声波清洗仪清洗,干燥后在试样表面涂敷75%Na2SO4+25%NaCl饱和水溶液,控制涂盐量为0.9~1.2 mg/cm2,直至获得一层均匀的混合盐膜。将涂盐试样与烘烤至质量恒定、洗净的瓷舟一起放入KSF 15-16型意丰电炉(控温精度为±2 ℃)在800 ℃进行热腐蚀试验。腐蚀时间为2、4、8、12、16和20 h,不同腐蚀时间后取出磁舟在DT-100光电分析天平(感量为0.1 mg)称质量,试验值为3个试样的平均值。
用JSM-6700F型扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和EPMA-1600型电子探针分析仪分析腐蚀产物的组成、微观形貌和元素分布。
2 结果及分析
2.1 合金微观形貌
图1所示为真空电弧熔炼制备Co-Al-W和商用MAN900合金的微观形貌。由图1(a)可知,7.5 W合金微观组织由γ-Co基体及γ′-Co3(Al,W)强化相和少量碳化物共同组成。合金微观组织中呈不规则多边形状、边长大小不等、与γ-Co基体界面连续的是强化相,γ′-Co3(Al, W)强化相是在合金固溶和时效处理过程中逐渐形成的。这与SATO等[11]发现的新型Co-Al-W合金中γ′强化相的形态和分布形式相同。由图1(b)可知,MAN 900合金微观组织是典型的柱状晶组织,组织均匀,晶界上分布骨干状一次碳化物,断续相间,也有少量二次碳化物呈弥散分布。
2.2 腐蚀动力学
图2所示为7.5 W、9.8 W、10.7 W和MAN900合金在800 ℃ 75%Na2SO4+25%NaCl熔盐中的质量 变化(Δm) (见图2(a))及其平方(见图2(b))随时间(t)变
表1 真空电弧熔炼法制备Co-Al-W合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of Co-Al-W superalloys by vacuum arc melting

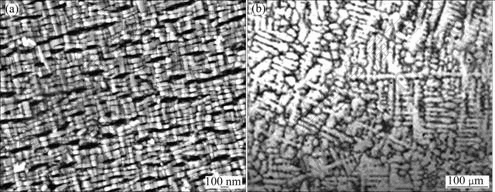
图1 7.5 W(a)和MAN900(b)合金的微观形貌
Fig.1 Micrographs of 7.5 W (a) and MAN900 (b) superalloys
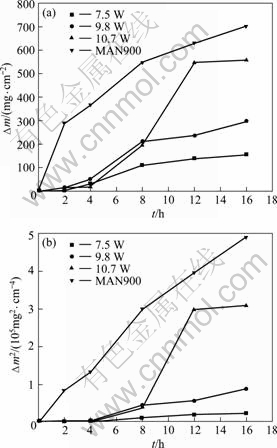
图2 7.5 W、9.8 W、10.7 W和MAN900合金热腐蚀动力学曲线
Fig.2 Kinetic curves of hot corrosion of 7.5W、9.8W、10.7W and MAN900 superalloys: (a) ?m—t; (b) ?m2—t
化的热腐蚀动力学曲线。由图2可知,合金腐蚀质量变化随腐蚀时间的增加而增大,MAN900合金的质量变化最大,7.5 W和9.8 W合金的质量变化较小,其耐热腐蚀能力优于MAN900合金的耐热腐蚀能力。合金腐蚀质量变化梯度随腐蚀时间的增加逐渐减小,这与合金表面腐蚀膜的形成速度、腐蚀膜的类型及腐蚀膜的致密度对基体合金的保护程度有关。一般来说,合金热腐蚀过程分为起始阶段和增长阶段,由于涂盐腐蚀是一种加速腐蚀,起始阶段的时间较短[14]。腐蚀初期(<8 h),腐蚀质量增加很快。随着腐蚀的进行,腐蚀时质量增加逐渐平稳。10.7 W合金的热腐蚀质量增加在12~16 h时非常缓慢,甚至出现质量损失现象[10]。质量损失是保护性腐蚀膜的挥发或破裂[15]及在腐蚀过程中反应产生挥发性物质[16]所致。
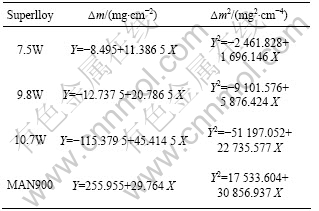
利用Origin软件对图2中曲线进行拟合,结果如表2所列,方程形式为Y2=A+BX,其中:Y代表单位面积的腐蚀质量变化;X代表腐蚀时间。由表2可知,合金在800 ℃的熔盐中的腐蚀速度由快到慢的顺序为:MAN900、10.7 W、9.8 W和7.5 W。由此可见,Co-Al-W合金耐热腐蚀能力较强。
表2 7.5W、9.8W、10.7W和MAN900合金腐蚀动力学曲线拟合结果
Table 2 Fitting results of corrosion dynamic curves of 7.5 W、9.8 W、10.7 W and MAN900 superalloys
2.3 XRD分析
表3所列为合金在800 ℃ 75%Na2SO4+25%NaCl熔盐中静态腐蚀2和16 h后的XRD分析结果。由表3可知,Co-Al-W合金在熔盐中腐蚀2 h后,除存在表面残留盐(Na2SO4、NaCl)外,这有两类化合物:一类是含氧化合物CoO、CoWO4和Co2AlO4;另一类是硫化物Co9S8。当合金涂盐腐蚀时间增至16 h时,Al2O3的特征峰减弱,其他氧化物、硫化物峰位没有变化,但强度增强,并出现Co9S8的多个衍射峰。说明随着腐蚀时间的增加,硫化物逐渐增多[10]。
表3 合金在800 ℃ 75%Na2SO4+25%NaCL熔盐中腐蚀不同时间后表面热腐蚀膜的组成
Table 3 Phase constitutions of hot corrosion of superalloys corroded in 75%Na2SO4+ 25%NaCl at 800 ℃ for different times
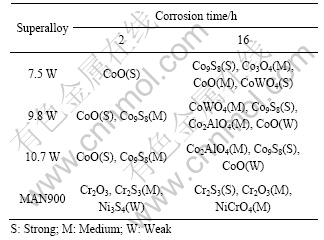
由表3可知,当腐蚀时间为2~16 h时,腐蚀产物较复杂。表3所列腐蚀产物不包含涂盐。由于X射线穿透深度的限制,表3所列氧化物和硫化物主要存在于表面和次表面。因此,Co-Al-W合金经800 ℃熔盐热腐蚀后,腐蚀产物主要为Co的含氧化合物及硫化物。由于CoO的激活能高于Co3O4的激活能,高温下优先氧化成CoAl2O4,因此,CoO保护膜的耐高温热腐蚀能力较强[17]。
2.4 形貌分析
2.4.1 宏观形貌
图3所示为7.5W、9.8W和10.7W合金分别腐蚀4、8和12 h后的宏观形貌。由图3可知,随着腐蚀时间的增加,合金表面形成一层完整而致密的腐蚀膜,腐蚀产物颗粒细小。随着腐蚀时间的增加,合金表面腐蚀膜逐渐呈蓬松状突起,外表面变得越来越不规则,腐蚀膜脱落程度越来越严重。腐蚀膜脱落后表面呈灰黑色,在合金表面有形状和深度不同的蚀孔出现。
2.4.2 微观形貌
图4所示为7.5W合金在熔盐中腐蚀后表面腐蚀膜的微观形貌。由图4(a)可知,7.5W合金腐蚀2 h后表面出现蓬松状腐蚀膜团聚、氧化皮鼓包和开裂现象。由图4(b)可知,合金热腐蚀4 h后,表层出现蚀坑和沿晶界开裂现象。这是由于熔盐热腐蚀导致腐蚀膜热应力集中而破坏其形态,进而引起腐蚀膜沿晶界开裂。根据合金热腐蚀机理,热腐蚀分为两个阶段,即腐蚀初始阶段和腐蚀扩展(加速)阶段。LUTHRA[18]将Co基合金发生热腐蚀的机制总结为Co或Co的氧化物在
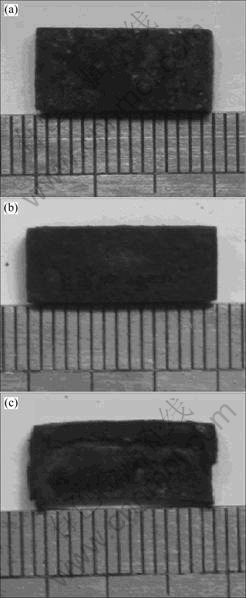
图3 合金分别腐蚀不同时间后的宏观形貌
Fig.3 Surface morphologies of different superalloys corroded for different times: (a) 7.5W, 4 h; (b) 9.8W, 8 h; (c) 10.7W, 12 h
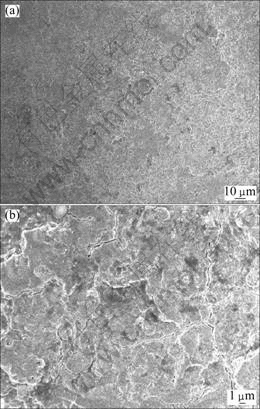
图4 7.5W合金腐蚀2和4 h后的微观形貌
Fig.4 Morphologies of 7.5W superalloy after hot corrosion at 800 ℃ for different times: (a) 2 h; (b) 4 h
合金表面发生溶解并由此阻止保护性氧化膜的形成。在腐蚀初始阶段,合金中Co的含量高,在试样表面迅速生成一层Co3O4膜。合金中Mo和A1等含量低的元素发生内氧化,并在Co3O4膜的内侧分布较多。随着腐蚀的进行,合金表面腐蚀膜逐渐增厚,腐蚀膜内侧贫Co化加剧,使得其他元素含量显著提高,在该条件下,Co元素在腐蚀膜中的扩散速率增大。Co在腐蚀膜/熔盐界面溶解并重新在液态盐膜中析出氧化物,熔盐中的Mo3+和Al3+可能参与了Co2+/Co3+还原反应并以氧化物的形式在熔盐中析出[18]。在整个腐蚀过程中,Co和CoO在合金表面液态混合熔盐的溶解使得合金的腐蚀程度增加[19]。
2.4.3 横截面形貌
图5所示为7.5W、9.8W和MAN900合金在75%Na2SO4+25%NaCl熔盐中腐蚀的横截面形貌。由图5可知,3种合金在熔盐中腐蚀膜结构分3层:呈蓬松状腐蚀膜最外层、相对致密的中间过渡层和致密的腐蚀膜内层。
图6所示为7.5W、9.8W和MAN900合金分别腐蚀不同时间后的线扫描元素分布。由图6(a)和(b)可知,

图5 不同合金经腐蚀不同时间后的横截面形貌
Fig.5 Cross-sectional micrographs of different superalloys after corroded for different times: (a) 7.5W, 4 h; (b) 9.8W, 8 h; (c) MAN900, 2 h
7.5W合金腐蚀4 h后,表面腐蚀膜最外层为富钴氧化物,Al和W含量较低;中间过渡层由Co、Al和W复杂氧化物组成,Co和Al氧化膜交替存在,但贫Co;腐蚀膜内层由Al和Co氧化物组成,Al含量高于但Co含量低于中间层中各元素含量。由图6(c)和(d)可知,9.8 W合金腐蚀2 h后,腐蚀膜最外层亦为富钴氧化物,其他元素含量很低;中间过渡层是Co和Al的复杂氧化物层,W含量很低;腐蚀膜内层由Co氧化物组成,Al含量低于过渡层中的Al含量。由图6(e)和(f)可知,MAN900合金在熔盐中热腐蚀膜也分为3层。最外层和最内层为Cr的氧化物,Ni含量低于中间过渡层中的Ni含量。中间过渡层为Ni、Cr、Mn和Si的复杂氧化物层,其Cr含量远低于腐蚀膜内、外层中的Cr含量。
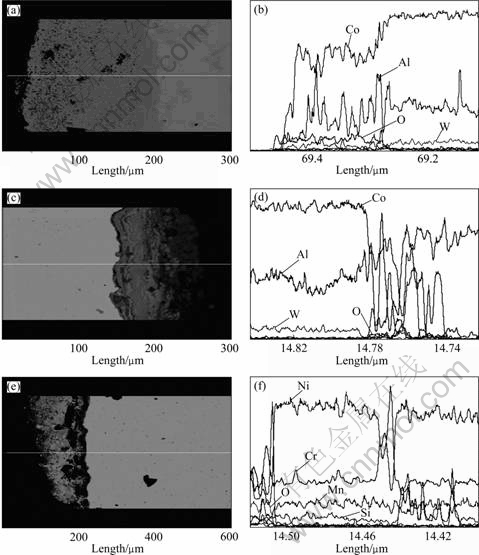
图6 7.5W、9.8W和MAN900合金腐蚀不同时间后腐蚀膜及其线扫描元素分布
Fig.6 Cross-sectional micrographs and liner scanning element distribution of different superalloys corroded for different times: (a), (b) 7.5W, 4 h; (c), (d) 9.8W, 2 h; (e), (f) MAN900, 2 h
3 讨论
从Co-Al-W合金在熔盐中腐蚀动力学曲线及其拟合结果可知(见图2和表2),随着腐蚀时间的增加,该合金腐蚀质量增加较MAN900的小,耐热腐蚀性能优于MAN900合金的耐热腐蚀性能。从图4~6合金表面腐蚀膜形态及元素分布来看,随着腐蚀时间的增加,合金表面出现蓬松状腐蚀膜团聚、开裂和脱落现象,腐蚀膜最外层由于脱落逐渐变薄;中间过渡层氧化物种类较复杂,但随着腐蚀时间的增加,各元素分布趋于均匀、稳定,腐蚀膜致密性逐渐增加。Al元素形成的氧化膜(Al2O3)比较致密,可对腐蚀膜内层起隔离氧和基体接触的保护作用,所以,未出现腐蚀膜和基体分层、开裂和蚀孔穿透腐蚀膜的现象。
ZHANG等[20]对几种合金化元素在钴基高温合金中所起作用的研究时发现,元素Al可以促使合金在凝固过程中形成γ′相,也能提高合金的抗热腐蚀能力。合金凝固过程中Mo、Al在枝晶间区域偏析,而Co、W元素分布在枝晶上。Al元素在氧化性气氛中形成更稳定的氧化膜使合金腐蚀膜更加致密和稳定。对于钴基高温合金的热腐蚀来说,合金中富钴元素容易在氧化环境中生成CoO和Co3O4,这两种钴的氧化物主要通过Co沿晶格向外扩散生成。根据热腐蚀机制的电化学模型[21],阳极发生深度氧化反应,逐渐形成Co2+和Co3+离子,但其在氧化物/熔盐界面氧活度低。Co2+在热力学上是稳定的,在熔盐中向外迁移,并在熔盐/气体界面发生氧化反应。在靠近气相的局部熔盐区,Co3+和O2-的浓度积超过其溶度积,于是,它们相互结合,以疏松的Co3O4粒子形成沉积[22]。在氧化物/熔盐界面,由于氧参与阴极还原反应,氧活度将明显降低,硫活度明显升高。硫通过溶解-扩散机制或含硫气体分子(如SO2)经致密氧化层中的疏松、孔洞、裂纹及氧化物晶界缺陷向内迁移,在具有足够还原性的合金/氧化物界面和致密氧化层中发生还原反应形成硫化 物[22],熔盐加速物质扩散是通过形成硫化物实现的。
一般认为,硫化物的形成有两种方式[23]:一种是SO42-先被还原成单质硫,单质硫通过腐蚀膜中的物理缺陷渗透到合金基体前沿形成硫化物;另一种是在较低的氧势下,金属直接与SO42-反应形成硫化物与氧化物,这些硫化物会因氧势升高而转变为氧化物,从而将硫推向更深的前沿,生成新的硫化物 [23]。另外,由于表面腐蚀层存在裂纹等缺陷,Na2SO4中的硫可以通过缺陷扩散至氧化层、基体界面及基体内部,由于氧势低而生成硫化物,也可能是Na2SO4熔体在氧化层和基体界面发生SO42-还原反应,进而在Co贫化区发生反应生成内氧化物和内硫化物[24]。
4 结论
1) 在800 ℃75%Na2SO4+25%NaCl熔盐中,Co- Al-W合金的腐蚀质量增加比MAN900的腐蚀质量增加小,合金耐热腐蚀能力较强,其中7.5W和9.8W合金的腐蚀质量增加最小。
2) Co-Al-W合金在熔盐中腐蚀膜结构分为3层:即呈蓬松状由富钴氧化物组成的腐蚀膜最外层;由Co、Al和W复杂氧化物组成的中间过渡层和由Al和Co氧化物组成较致密的最内层。 MAN900合金在熔盐中的腐蚀膜也分为3层:最外层和最内层为Cr的氧化物,Ni含量较低;中间过渡层为Ni、Cr、Mn和Si组成的复杂氧化物,Cr含量较低。
3) 随着腐蚀时间的增加,合金腐蚀膜最外层由于脱落逐渐变薄,中间过渡层厚度逐渐增加,各元素在该层中分布趋于均匀、稳定,腐蚀膜内层致密性增加使该层增厚不明显。
References
[1] 陈 磊, 王富岗. 抗高温氧化合金的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2002, 16(5): 27-29.
CHEN Lei, WANG Fu-gang. Process in study on anti-high temperature oxidation alloy[J]. Materials Review, 2002, 16(5): 27-29.
[2] KAI W, LEE C H, LEE T W, WU C H. Sulfidation behavior of Inconel 738 superalloy at 500-900 ℃[J]. Oxidation of Metals, 2001, 56(1/2): 51-71.
[3] MISRA R D K, SIVAKUMAR R. Effect of NaCl vapor on the oxidation of Ni-Cr alloy[J]. Oxidation of Metals, 1986, 25(1/2): 83-92.
[4] ZHU Ri-zhang, GUO Man-jiu, ZUO Yu. Study of the mechanism of internal sulfidation-internal oxidation during hot corrosion of Ni-base alloys[J]. Oxidation of Metals, 1987, 27(5/6): 253-265.
[5] BOURHIS Y, JOHN C S. Na2SO4 and NaCl-induced hot corrosion of six nickel-base superalloys[J] . Oxidation of Metals, 1975, 9(6): 507-528.
[6] KAMESWA S R. The role of NaCl in the hot-corrosion behavior of nimonic alloy 90[J]. Oxidation of Metals, 1986, 26(1/2): 33-44.
[7] CUI H, ZHANG J S, MURATA Y. Hot corrosion behavior of Ni-based superalloy with higher Cr contents. Part Ⅱ: Mechanism of hot corrosion behavior[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing: English Edition, 1996, 3(2): 91-98.
[8] 黄乾尧, 李汉康. 高温合金[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2000: 100-133.
HUANG Qian-yao, LI Han-kang. High temperature alloy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2000: 100-133.
[9] RAPP R I A. Hot corrosion of materials: A fluxing mechanism[J].Corrosion Science, 2002, 44(2): 209-221.
[10] 李 云, 郭建亭, 袁 超, 杨洪才, 徐 宁, 申志明. 镍基铸造高温合金K35的热腐蚀行为[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2005, 25(4): 250-255.
LI Yun, GUO Jian-ting, YUAN Chao, YANG Hong-cai, XU Ning, SHEN Zhi-ming. Hot corrosion of nickel-base cast superalloy K35 at 800 ℃[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2005, 25(4): 250-255.
[11] SATO J, OMORI T, OIKAWA K, OHNUMA I, KAINUMA R, ISHIDA K. Cobalt-base high-temperature alloys[J]. Science, 2006, 312: 90-93.
[12] SUZUKI A, DENOLF G C, POLLOCK T M. Flow stress anomalies in γ/γ′ two-phase Co-Al-W-base alloys[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 56(5): 385-388.
[13] BELTRAN A M. Superalloys Ⅱ[M]. New York: Wiley, 1987: 135.
[14] 李树索, 韩雅芳, 肖程波, 宋尽霞. Ni3Al基合金IC6及MCrAlY包覆涂层的抗腐蚀性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(6): 1451-1455.
LI Shu-suo, HAN Ya-fang, XIAO Cheng-bo, SONG Jin-xia. Corrosion resistances of Ni3Al based alloy IC6 and MCrAlY overlay coatings[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(6): 1451-1455.
[15] ECER G M, MEIER G H. Oxidation of high-chromium Ni-Cr alloys[J]. Oxidation of Metals, 1979, 13(2): 119-158.
[16] BEN-ABDERRAZIK G, MOULIN G, HUNTZ A M. Relation between impurities and oxide-scale growth mechanisms on Ni-34Cr and Ni-20Cr alloys.Ⅰ: Influence of C, Mn, and Si [J]. Oxidation of Metals, 1990, 33 (3/4): 191-235.
[17] 刘培生, 陈国锋, 梁开明. DZ40M钴基合金的高温氧化[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 1999, 19(6): 339-344.
LIU Pei-sheng, CHEN Guo-feng, LIANG Kai-ming. High temperature oxidation of DZ40M alloy[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 1999, 19(6): 339-344.
[18] LUTHRA K L. Low temperature hot corrosion of cobalt-base alloys. part Ⅰ: Morphology of the reaction product[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1982, 13: 1843-1852.
[19] 赵双群, 谢锡善, GAYLORD D S. 新型镍基高温合金在模拟燃煤锅炉环境中的腐蚀[J]. 金属学报, 2004, 40(6): 659-663.
ZHAO Shuang-qun, XIE Xi-shan, GAYLORD D S. Corrosion of a new nickel base superalloy in coal-fired boiler environments[J]. Acta Metallrugica Sinica, 2004, 40(6): 659-663.
[20] ZHANG J S, HU Z Q, MURATA Y, MORINAGA M, YUKAWA N. Design and development of hot-resistant nickel-base single crystal superalloys by the d-electrons alloy design theory. part Ⅱ: Effects of refractory metals Ti, Ta and Nb on microstructure and properties[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1993, 24: 2451-2463.
[21] 李美栓. 金属的高温腐蚀[M] .北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2001: 391-392.
LI Mei-shuan. High temperature corrosion of metals[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industrial Press, 2001: 391-392.
[22] 苏 勇, 孙长波, 尹 丽. Co及Co-10Ce合金在900 ℃空气中的热腐蚀行为研究[J]. 辽宁化工, 2006, 35(8): 439-441.
SU Yong, SUN Chang-bo, YIN Li. Study on hot corrosion of Co and Co-10Ce alloy in air at 900 ℃[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2006, 35(8): 439-441.
[23] 王淑荷, 郭建廷, 赖万慧, 谭明辉, 李 辉, 孙 超. NiAl- 20%atFe合金的高温氧化与热腐蚀行为[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 1995, 15(2): 135-140.
WANG Shu-he, GUO Jian-ting, LAI Wan-hui, TAN Ming-hui, LI Hui, SUN Chao. High temperature oxidation and hot corrosion behavior of NiAl-20%at Fe alloy[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 1995, 15(2): 135-140.
[24] 赵双群, 谢锡善. 新型Ni-Cr-Co基高温合金的热腐蚀行为[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2006, 14(5): 507-509.
ZHAO Shuang-qun, XIE Xi-shan. Hot corrosion behaviors of new Ni-Cr-Co base superalloy[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2006, 14(5): 507-509.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:2009年中国科学院西部之光计划资助项目(0901ZBB066);甘肃省中青年科技基金计划项目(099RJYA018); 兰州理工大学优秀青年教师培养计划项目(1001ZCX009); 兰州理工大学博士科研启动基金资助项目(01-0282)
收稿日期:2009-12-31; 修订日期:2010-05-13
通信作者:徐仰涛, 讲师, 博士研究生; 电话: 0931-2973563; E-mail: xuyt@lut.cn