铜模板微通道内CVD金刚石生长行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第6期
论文作者:刘学璋 张雄伟 余志明
文章页码:2009 - 2017
Key words:chemical vapor deposition; diamond; template; Cu substrate; microchannel
摘 要:主要活性基团(H, CH3·)的有效扩散与基体模板孔的深度限制了沟道或通道内金刚石的沉积。通过纳米金刚石悬浮液超声震荡加载籽晶,随后热丝化学气相沉积,在铜模板圆柱型微通道内成功制备出三维结构的金刚石膜。分别采用微区激光拉曼光谱和扫描电子显微镜表征金刚石膜,考察微通道深度对金刚石形貌、晶粒尺寸与膜生长速率的影响。结果显示:金刚石膜的质量和生长速率随微通道深度的增加而急剧下降,单个金刚石晶粒由发育完善、刻面清晰的晶粒逐渐转变为微米团簇,最后转变为球状纳米晶。为改善金刚石膜质量和提高生长速率,设计出一种气源强制输送热丝化学气相沉积装置。此外,对比分析无气源强制输送条件下金刚石的生长,并讨论气源强制输送的增强机理。
Abstract: Deposition of diamond inside the trenches or microchannels by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is limited by the diffusion efficiency of important radical species for diamond growth (H, CH3·) and the pore depth of the substrate template. By ultrasonic seeding with nanodiamond suspension, three-dimensional (3D) penetration structure diamond was successfully deposited in cylindrical microchannels of Cu template by hot-filament chemical vapor deposition. Micro-Raman spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were used to characterize diamond film and the effects of microchannel depth on the morphology, grain size and growth rate of diamond film were comprehensively investigated. The results show that diamond quality and growth rate sharply decrease with the increase of the depth of cylindrical microchannel. Individual diamond grain develops gradually from faceted crystals into micrometer cluster, and finally to ballas-type nanocrystalline one. In order to modify the rapid decrease of diamond quality and growth rate, a new hot filament apparatus with a forced gas flow through Cu microchannels was designed. Furthermore, the growth of diamond film by new apparatus was compared with that without a forced gas flow, and the enhancement mechanism was discussed.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 2009-2017
Xue-zhang LIU1, Xiong-wei ZHANG2, Zhi-ming YU2
1. School of Materials and Mechanical Engineering, Jiangxi Science and Technology Normal University, Nanchang 330013, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 10 March 2014; accepted 26 June 2014
Abstract: Deposition of diamond inside the trenches or microchannels by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is limited by the diffusion efficiency of important radical species for diamond growth (H, CH3·) and the pore depth of the substrate template. By ultrasonic seeding with nanodiamond suspension, three-dimensional (3D) penetration structure diamond was successfully deposited in cylindrical microchannels of Cu template by hot-filament chemical vapor deposition. Micro-Raman spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were used to characterize diamond film and the effects of microchannel depth on the morphology, grain size and growth rate of diamond film were comprehensively investigated. The results show that diamond quality and growth rate sharply decrease with the increase of the depth of cylindrical microchannel. Individual diamond grain develops gradually from faceted crystals into micrometer cluster, and finally to ballas-type nanocrystalline one. In order to modify the rapid decrease of diamond quality and growth rate, a new hot filament apparatus with a forced gas flow through Cu microchannels was designed. Furthermore, the growth of diamond film by new apparatus was compared with that without a forced gas flow, and the enhancement mechanism was discussed.
Key words: chemical vapor deposition; diamond; template; Cu substrate; microchannel
1 Introduction
Due to its extreme hardness, high electrical resistivity, wide band gap and the highest thermal conductivity, diamond is considered as an excellent candidate for micro- or nano-electromechanical systems (MEMS/NEMS) [1]. The development of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) technique for diamond widens its applications. Prototypes of MEMS/NEMS made of CVD diamond have been used for certain application areas such as gears, motors, burrs, electron emission tips and scanning probe microscopy (SPM) tips [2-4]. MALAVE et al [5] prepared diamond cantilevers for scanning probe microscopy measurements by using a silicon template. Their radius of curvature is about 20 nm. Diamond tips doped with about 1% boron (carrier concentrations ≥1021 cm-3) show a resistivity of 10-3 Ω/cm. ADAMSCHIK et al [6] presented a diamond micro reactor system. It consists of reaction chambers with removable bottom and integrates micro dosage elements allowing the ejection and mixture of two different fluids onto the removable bottom substrate. CVD diamond which is chemically inert ensures the reactions with superior precision and reliability. In their experiments, the diamond micro reactor system combined with a specifically designed chemistry for the DNA-synthesis enables the parallel production of DNA-chain-clusters with individual sequence arranged in an array (DNA-chip).
However, three-dimensional (3D) diamond devices prepared by using molding technique require deposition of diamond from the vapor phase inside the trenches or microchannels. Under those conditions, diamond growth is limited by the diffusion efficiency of the important radical species (H, CH3·) for diamond growth. For the same composition of feed gas, gas chemistry will vary along with the depth due to surface recombination and the different transport of gas-phase radical species inside microchannels, which finally affect the growth of crystalline diamond films compared with non-diamond carbon. Preliminary results of our pertinent studies show that the process window for diamond deposition in microchannels is very narrow [7]. The adjustment of the process parameters including pressure, flow, composition of the feed gas and the substrate temperature is not very effective. For example, gas pressure serves as opposite effects by influencing the concentrations and the mean free paths of radical species, simultaneously.
Then, in this work, Cu templates with an open pored structure were used as substrates. Micro-Raman spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy were used to characterize the diamond film and the effects of infiltration depths on the morphology, grain size and growth rate of diamond film were comprehensively investigated. Furthermore, a new hot filament apparatus with a forced transport of radical species through Cu microchannels was designed to overcome the dilemma of the narrow process window. The growth of diamond film was compared with that without a forced gas flow.
2 Experimental
2.1 Diamond deposition and substrate pretreatment
Cu templates full of cylindrical microchannels with 1 mm in diameter were used as substrates. Those microchannels are vertical to template surfaces, which allow neglecting tortuosity. Prior to deposition, Cu templates were first dipped in 0.5% hydrochloric acid (HCl) for 5 min to remove surface oxide layer and machining burr, and then rinsed in de-ionized water to remove residual HCl. As a seeding pretreatment, the substrates were ultrasonically treated in an aqueous suspension of detonation nanodiamond powders (particle size ~10 nm) for 30 min, followed by a rinsing in acetone for 5 min.
A standard hot-filament chemical vapor deposition (HF-CVD) system was used to deposit diamond films. Details of the experimental set-up can be found elsewhere [8]. The process gas was activated by using a spiral coil filament (tungsten wire, diameter 0.38 mm), suspended between two molybdenum rods. Filament temperatures (Tf) were measured by optical pyrometer. Substrate temperatures (Ts) were controlled by Tf and filament-substrate distance (df), and measured by K-type thermocouples attached to the substrate surface. Table 1 shows the process parameters in detail. For realizing a forced gas flow through template microchannels, we built a special substrate holder with integrated vacuum connection (Fig. 1).
Table 1 Experimental parameters used for diamond deposition

2.2 Characterization
The morphologies of the deposited diamond were characterized by field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM, FEI Sirion 200). Microstructural analyses of diamond film were performed by micro-Raman spectroscopy (Lab Raman RH800) in room temperature using an Ar+ ion laser (488 nm) at the range of 800-2200 cm-1. Prior to Raman characterization of the deposited film, Raman system was calibrated by using a Si sample.
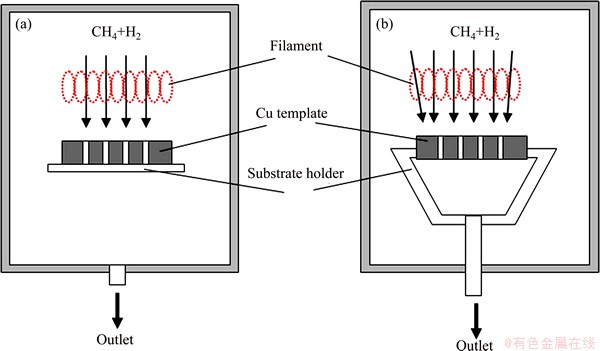
Fig. 1 Schematic drawing of experimental setup without (a) and with (b) forced gas flow through substrate microchannels
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Diamond nucleation with nanodiamond seeding
Copper, like diamond, has a cubic crystal structure, and its lattice mismatch with diamond is only 1.14%. However, diamond cannot nucleate on copper through forming carbide, nor can it be dissolved in copper. A thin graphite layer must be produced as an intermediate at the early stage, which results in low density of diamond nucleation (5×104-1×106 cm-2) and long induction time (>10 h) [9]. Low nucleation density produces discontinuous diamond film. In order to enhance diamond nucleation on Cu substrate, a number of surface pretreatment methods have been developed, including diamond scratching, carbon implanting and biased- enhanced nucleation [10]. But those methods are practical for plane substrate instead of cylindrical microchannels.
As Cu templates were ultrasonically treated in an aqueous suspension of detonation nanodiamond powders, a large number of nanodiamonds could adhere to the inner wall of cylindrical microchannels via van der Waals interactions [11]. These induced seeds will act as starting points for the nucleation of diamond from the gas phase. Figures 2(a) and (b) show the cross-sectional SEM micrographs of 3D penetration structure of diamond deposited in cylindrical microchannels without or with a forced gas flow through substrate microchannels, respectively. It is visible that both of diamond films develop continuously from the upper surface of cylindrical microchannels to the bottom. The thicknesses are approximately 1.06 μm. Those SEM results give evidences of the successful enhancement nucleation by nanodiamond seeding. While, in our experiments, the nucleation density by nanoseeding is at least boosted to the order of 1011 cm-2 since the value is the lower limit for the growth of continuous diamond film [12].
Because of the non-carbon affinity of copper, diamond film directly depositing on Cu substrates always suffers from poor adhesion. Therefore, continuous films would catastrophically fail (crack and delaminate) when taking them out from the depositing chamber, although continuous films could grow on Cu substrates. The debonding phenomenon is also obvious in both SEM images.
3.2 Diamond growth without forced gas flow through substrate microchannels
Figure 3 shows the morphologies of diamond film deposited in cylindrical microchannels without a forced gas flow through substrate microchannels. The surface SEM micrographs were collected in steps of 200 μm starting from the top to the bottom. It can be seen that diamond grains deposited at the microchannel mouth are well-faceted and the average size of those crystals is 13.7 μm (Fg. 3(a)). No preferred orientation is observed. While, a large number of smaller diamond grains appear at the neighborhood of larger ones. The grain size of the small grains is ranged from 2 to 4 μm. Previous work shows that smaller grains are formed as a consequence of the enhanced secondary nucleation effect [7]. The morphology of diamond film in cylindrical microchannels shows that the amount of big grains decreases and that of secondarily nucleated crystals adequately develops (Fig. 3(b)). The size distribution becomes uniform. It is widely accepted that secondary nucleation is correlated with deposition temperature [13]. When the substrate is closer to the hot filament, the higher temperature causes excessively fast growth of some diamond crystals, and eventually immerses the others. A large number of grain boundaries among big crystals are generated and ultimately induce secondary nucleation.
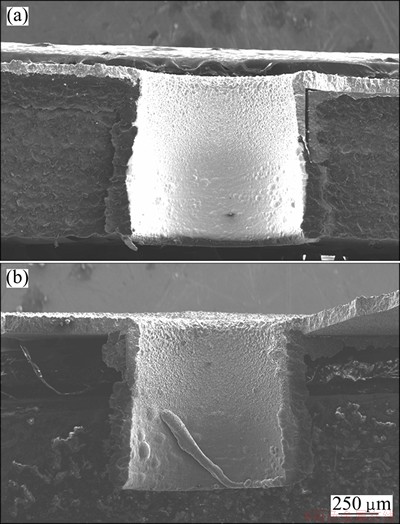
Fig. 2 3D penetration structures of diamond deposited in CVD system by adopting without (a) and with (b) forced gas flow through substrate microchannels
Figure 3(c) shows the morphology of diamond film at deeper position. Compared with Fig. 3(a), the secondary nucleation is lower and its grain size is more uniform. The average size of diamond crystals deceases to 6.8 μm. As the SEM image apparently illustrated, the quality of diamond crystal decreases. There are outstanding reentrant grooves at crystal edges.  and PRIOR et al [14] demonstrated that those defect generation depended on the growth parameter α (
and PRIOR et al [14] demonstrated that those defect generation depended on the growth parameter α (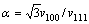 , where v100 and v111 are the growth velocities of the (100) surface and the (111) surface, respectively). Those reentrant grooves between twin boundaries will develop between the (111) facets for α<1.5 and the (100) facets for α>1.5.
, where v100 and v111 are the growth velocities of the (100) surface and the (111) surface, respectively). Those reentrant grooves between twin boundaries will develop between the (111) facets for α<1.5 and the (100) facets for α>1.5.
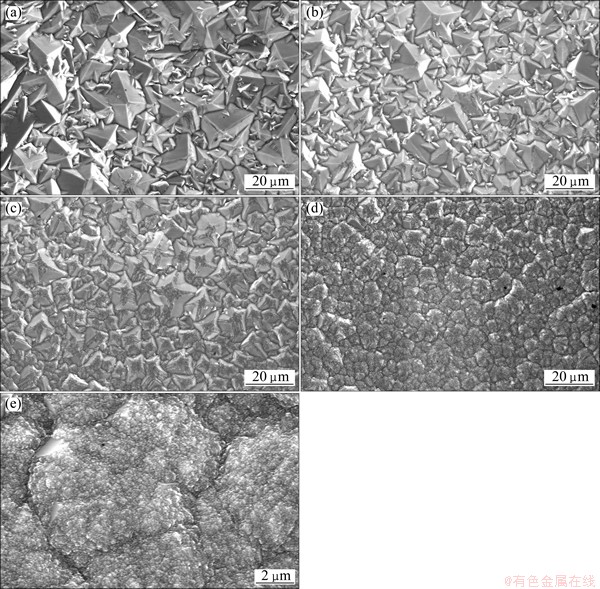
Fig. 3 Morphologies of diamond films deposited in Cu microchannels without forced gas flow along depth of 0 μm (a), 200 μm (b), 400 μm (c), 600 μm (d) and 800 μm (e)
When the depth of cylindrical microchannels further increases, the diamond film is still continuous (Fig. 3(d)). No cave defect is observed. However, the facets of diamond grains disappear obviously. The crystalline grains are entirely refined. Individual diamond crystal develops into micrometer cluster. Those deviations show a larger degree of decline of diamond quality. Figure 3(e) presents the morphology of diamond film at the greatest depth of cylindrical microchannels, which is close to the bottom. Diamond crystals now completely become ballas-type nanocrystalline diamond.
Putting together the morphologies of diamond films along the depth of cylindrical microchannels in Fig. 3, we are able to find out that 1) 3D penetration structure of diamond has developed continuously from the top surface of cylindrical microchannels to the bottom, and 2) diamond quality gradually reduces with the increase of the depth of cylindrical microchannels. Faceted diamond crystals gradually develop into micrometer cluster, and finally into ballas-type nanocrystalline diamond. Figure 3(d) presents a transition state from micrometer crystals to the nanometers ones.
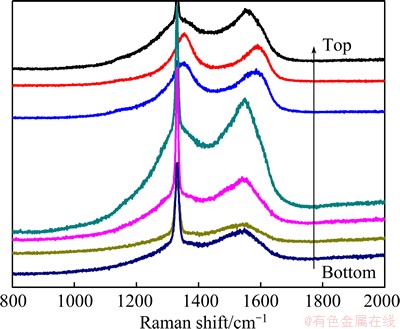
Fig. 4 Raman spectra of diamond films deposited in Cu microchannel without forced gas flow through substrate microchannels
Figure 4 shows the Raman spectra collected in steps of 150 μm from the microchannel top to the bottom. As the results shown in Fig. 4, the diamond peaks are centered at 1333 cm-1, while the Raman peak at 1365 cm-1 and 1570 cm-1 are corresponding to the so-called D-band and G-band of graphite, respectively. When the microchannel depth is less than 500 μm, the diamond peaks are all stronger than non-diamond peaks. Since the Raman signal is 50 times more sensitive to non-diamond carbon than that to crystalline diamond for the laser wavelength used in our experiments [15], the Raman results show that diamond film deposited in the microchannel still has high percentage of sp3 carbon which corresponds to diamond phase to maximum depth of 500 μm. While intensity of non-diamond phase peaks becomes stronger with the increase of microchannel depth, and it achieves the maxima at the depth of 500 μm. At depth greater than 500 μm, the peaks referring to diamond phase and non-diamond phase both become very weak, which indicates that the deposited film is of poor quality in this depth range. It is noted that the thickness of diamond film has certain influence on its Raman scattering intensity [16]. Apparently, the change of diamond quality along the depth is in agreement with the results of SEM.
3.3 Diamond growth with forced gas flow through substrate microchannels
Figure 5 shows the morphologies of diamond films deposited in cylindrical microchannels with a forced gas flow through template microchannels. We collected the surface SEM micrographs starting from the microchannel top to the bottom with the same interval in Fig. 3. Figure 5(a) shows the closest point to the hot filament. The SEM image shows that diamond grains are adequately developed. All of the diamond grains present their thermal equilibrium shapes, such as octahedron, rhombic-dodecahedron and truncated octahedron. Those well-faceted crystals are averagely 11.7 μm in size. Compared with Fig. 3(a), diamond grains in Fig. 5(a) have higher crystallinity and their size distribution is more uniform. Additionally, there are some twin crystals (indicated with white arrow), which is in agreement with the results obtained by other investigatiors [17]. The growth characteristics may originate from the special property of Cu substrate. Because it neither forms carbide with diamond nor dissolves carbon. The morphology of diamond film in cylindrical microchannels shows that twin crystals decrease and the grains size becomes more uniform (Fig. 5(b)). Diamond crystals are still well-faceted, but the average size decreases to 9.5 μm.
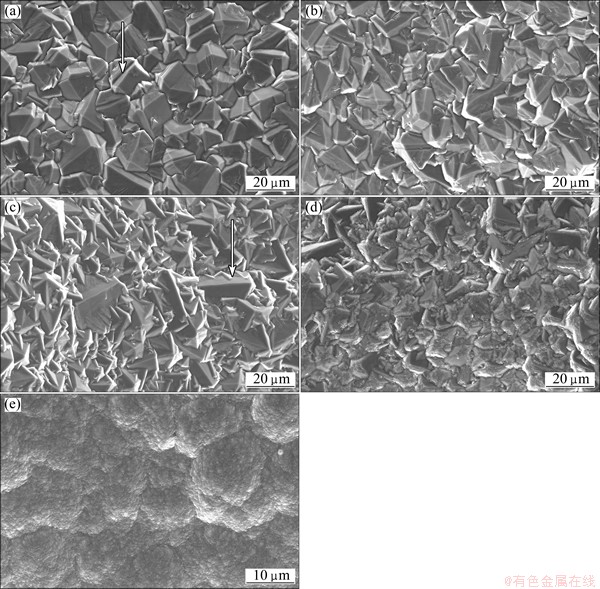
Fig. 5 Morphologies of diamond films deposited in Cu microchannels with forced gas flow along depth of 0 μm (a), 200 μm (b), 400 μm (c), 600 μm (d) and 800 μm (e)
With the increase of microchannel depth, diamond crystals are mostly refined except for few big ones (Fig. 5(c)). The average size of all crystal grains is 7.5 μm. Secondary nucleation is less obvious. Interestingly, a new growth defect is presented in Fig. 5(c) (indicated with white arrow). Excrescences are found on the {100} in-faces. According to a growth model proposed by SCHWARZ et al [18], the observed growth defect is primarily caused by the gas phase conditions during the CVD process. This result implies that the change of gas chemistry in cylindrical microchannels is caused by a forced gas flow.
When the depth of cylindrical microchannel further increases, faceted faces become indistinct, which reveals that the crystallinity decreases (Fig. 5(d)). But the grain size shows minor difference compared with Fig. 5(c). Figure 5(e) shows the morphology of diamond film deposited at the deeper position of cylindrical microchannel. As the SEM image demonstrated, diamond film is still continuous. However, crystal grains now completely change into ballas-type nanocrystalline ones.
As like to diamond film deposited in cylindrical microchannels without a forced gas flow (Fig. 3), we are also able to find out the same reduction of diamond quality with increasing the depth of cylindrical microchannels from the SEM micrographs in Fig. 5. Faceted crystals gradually develop into defect ones, and finally into ballas-type nanocrystalline diamond. Figure 5(d) presents a transition state developing from micrometer crystals to nanometers ones.
Figure 6 shows the Raman spectra collected in steps of 150 μm from the microchannel top to the bottom. As shown in Fig. 6, the sharp peaks at 1331 cm-1 and the broad peaks at approximately 1580 cm-1 are assigned to the characteristic peaks of crystalline diamond and the G-band of graphite, respectively. When the microchannel depth is less than 650 μm, the diamond peaks are all stronger than the non-diamond peaks. Regarding that the sp2-bonded graphite has much higher Raman scattering efficiency than sp3-bonded diamond [15], diamond film deposited in cylindrical microchannel with the depth less than 650 μm obviously has high percentage of diamond phases.
With the increase of microchannel depth, the peak heights (intensity) of crystalline diamond have no apparent decrease, but its full-width-half-maximum (FWHM) of diamond peak gradually broadens. The width of characteristic peak indicates that diamond quality decreases and its crystalline grains are refined, which is in agreement with SEM results (Fig. 5). Besides, the peak intensities of non-diamond phases become stronger with the increase of microchannel depth. Finally, once the depth is larger than 650 μm, the peaks of diamond phases and non-diamond phases both become very weak. Compared with Fig. 4, the relationship between diamond quality and microchannel depth is fairly regular in Fig. 6.
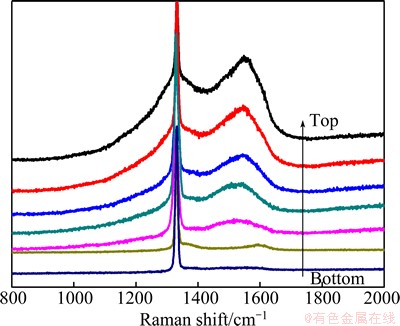
Fig. 6 Raman spectra of diamond films deposited in Cu microchannel with forced gas flow through substrate microchannels
3.4 Influence of forced flow through Cu microchannel
In a hot filament apparatus, atomic H created by thermal dissociation of H2 plays an important role in CVD diamond process. On the one hand, atomic hydrogen drives the inter-conversion between C1 (CHx) and C2 (C2Hy) species both via the families of radical forming (so-called H-shifting) abstraction reactions and, in the cooler regions, by a sequence of third-body stabilized H addition reactions that culminate in the conversion of C2Hy species to members of the CHx family [19]. On the other hand, atomic hydrogen can effectively etch the sp2 carbon [20]. Recently, laser probing measurements have verified that atomic hydrogen dissociated on the HF surface diffuses throughout the reactor volume. The loss of atomic hydrogen is not efficient in dilute CH4/H2 gas mixtures [21]. Then, in the present work, atomic hydrogen densities in the cooler periphery of the reactor are far more excessive than those expected on the basis of local thermodynamic equilibrium.
However, diamond deposition inside a hole/ microchannel is more complex than that on a plane substrate because the probability of reaction between radical species and the wall surface of cylindrical microchannels becomes much higher than that with other gas species. For the same composition of feed gas, radical species concentrations will vary along the depth [7].
In view of the surface recombination and the different transport rates of gas-phase radicals participating in the growth processes, the concentration of radical species Ck inside a cylindrical microchannel can be described by the following one-dimensional, reaction– diffusion equation [22]:
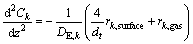 (1)
(1)
where rk represents the reaction rates on the surface and at the gas phase, dt is the effective microchannel diameter and DE,k is the effective diffusion coefficient for radical species k through the stagnant gas phase.
Regarding of each individual elemental reaction with the appropriate rates, EATON et al [22] have resolved the concentration of the main species presented in diamond deposition by Eq. (1). Their results prove that radical species concentration is a function of the depth. Atomic hydrogen concentration decreases along the depth because of faster recombination on wall surfaces, while the concentration of activated species like CH3· decreases along the depth because of shorter mean free path. Compared with other major radical species (e.g., CHx and C2Hy), the concentration of atomic hydrogen decreases faster. Therefore, this would favor fast growth of non-diamond phases at the greater depth. Actually, we did observe a gradual reduction of diamond quality and crystal size with the increase of the depth of cylindrical microchannels whether a forced gas flow through substrate microchannels was used. For an individual crystal, it gradually develops from faceted diamond to micrometer cluster, and finally to ballas-type nanocrystalline one. Those results verify that the decline of radical specie concentration along the depth exists in both growth conditions.
Comparing Fig. 5 and Fig. 6 with Fig. 3 and Fig. 4, respectively, we can find out two prominent effects brought by a forced gas flow through substrate microchannels. 1) Diamond film with medium crystallinity can be deposited at depth of up to approximately 600 μm. While, the diamond crystallinity drastically decreases only at the depth of 400 μm once a forced flow is not used, and 2) the reduction trend of diamond quality distinctly becomes slower.
Recently, kinetic Monte Carlo research found that the growth process of CVD diamond is mainly dominated by only two species (H· and CH3·) in a hot filament deposition system [23]. The flux of CH3· to the surface governs the growth rate while the flux of atomic H· controls the rate of all surface reactions, including etch rate and mobility of adsorbed CH2 species, and hence surface roughness. The role of all other hydrocarbon-bond radicals (C, CH, CH2, C2, etc.) in the overall growth process is minimal due to their negligible concentrations at the surface compared to that of CH3·. An equation is proposed to predict the growth rate G [23]:
G=0.285×10-14Ts0.5c(CHx)/[1+0.3exp(3430/Ts)+0.1exp(-4420/Ts)c(H2)/c(H)], x = 0-3 (2)
where Ts is the substrate temperature, c(CHx), c(H2) and c(H) are the corresponding concentrations of radical species. As described in Eq. (2), the growth rates are proportional to the concentration of CH3· when the concentration of H· is stable.
According to Eqs. (1) and (2), the decline of major radical species (e.g., CH3·) concentrations with the increase of the depth will result in the same decrease of growth rate.
Figure 7 gives the relationship between growth rates of diamond film and the depth of cylindrical microchannels. Because diamond films delaminate naturally from Cu substrate, we can get an exact calculation of the growth rate. As shown in Fig. 7, both curves decrease with the increase of depth. This change law is anticipated by Eq. (1) and Eq. (2). For diamond growth without a forced gas flow through substrate microchannels, growth rate decreases from 1.6 μm/h at the top to 0.09 μm/h at the bottom. When a forced gas flow is used, the corresponding values are 1.6 μm/h and 0.46 μm/h, respectively. The decrease trend of growth rate from the mouth to increasing depth is much lower. In other word, we are able to achieve a more uniform depositing thickness in microchannels with a forced gas flow through substrate microchannels.
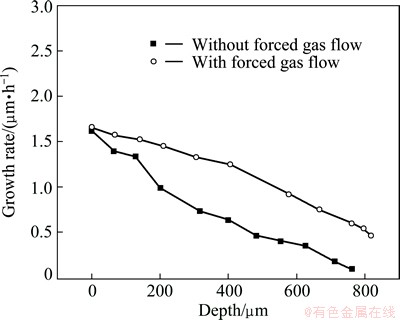
Fig. 7 Growth rates of diamond films along depths deposited in CVD system without or with forced gas flow through substrate microchannels
Besides, we can find that the decrease of growth rate near the microchannel mouth is more intense than that at greater depth without a forced gas flow. A bottleneck problem is resulted by a overgrowing of diamond film at the mouth because of the decrease of hydrogen and important radical species at greater depths. As a consequence, the mouth will close before the cylindrical microchannel is completely infiltrated with diamond. It is disadvantageous for the preparation of diamond/metal or diamond/ceramics by chemical vapor infiltration [24]. This effect can be alleviated by using a forced gas flow through substrate microchannels (Fig. 7).
The enhancement mechanism of diamond quality and growth rate by a forced transport of radical species through cylindrical microchannels can be attributed to two effects. On one hand, atomic hydrogen is not obviously influenced by the forced gas flow because of its high diffusion rates. While, CH3· radicals have shorter mean free path, therefore, their concentration in cylindrical microchannels is much more boosted by the forced gas flow, and finally causes the increase of growth rate [21] (Fig. 7). On the other hand, by decreasing dwell time of the growth species in the microchannels by a force gas flow, a reaction to higher carbon molecules was suppressed [16]. This can also cause a higher amount of sp3-bonds in the diamond deposition (Fig. 6). Besides, a forced gas flow affords to provide atomic hydrogen with very high gas velocities. High kinetic energy results in enhanced surface mobility of these reactive species, which promotes an aggregation of the precursors and diamond growth [25]. Therefore, diamond grains are more adequately developed than those without a forced gas flow (Fig. 5).
GLASER et al [24] induced oxygen gas with a n(C)/n(O) ratio of 0.7 in a hot filament system. Because the decrease of the concentration of oxygenated radicals is not as intense as that of atomic hydrogen, oxygenated radicals etch graphite at higher rates than atomic hydrogen. They deposited diamond with medium quality at greater depths. But the addition of oxygen caused rapid decrease of growth rates. While, in our experiments, a forced gas flow through substrate microchannels does promote diamond deposition at greater depths and increase of the growth rate.
4 Conclusions
1) By an ultrasonic seeding with nanodiamond suspension, three-dimensional (3D) penetration structure diamond was successfully deposited in cylindrical microchannels of Cu template by hot-filament chemical vapor deposition (HF-CVD).
2) Diamond quality and crystal size both gradually decrease with the increase of cylindrical microchannels depth whether a forced gas flow through substrate microchannels is adopted. For an individual crystal, it gradually develops from faceted diamond into micrometer cluster, and finally into ballas-type nanocrystalline one.
3) A forced gas flow is beneficial to higher diamond qualities at greater depths. Diamond film with medium crystallinity can be deposited on microchannels at depth of up to approximately 600 μm. While, the diamond crystallinity decreased drastically when the depth was larger than 400 μm once a forced flow was not used.
4) The enhancement of diamond quality and growth rate by adopting a forced gas flow through substrate microchannels can be attributed to the boosted concentration of CH3· radicals, decreased dwell time of the growth species and high gas velocities of atomic hydrogen.
References
[1] LIAO M Y, KOIDE Y. Carbon-based materials: Growth, properties, MEMS/NEMS technologies, and MEM/NEM switches [J]. Critical Reviews in Solid State and Materials Sciences, 2011, 36(2): 66-101.
[2] BALDWIN J W, ZALALUTDINOV M K, FEYGELSON T, PATE B B, BUTLER J E. Nanocrystalline diamond resonator array for R-F signal processing [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2006, 15(11-12): 2061-2067.
[3] UEDA K, KASU M, YAMAUCHI Y, MAKIMOTO T, SCHWITTERS M, TWITCHEN D J. Diamond FET using high-quality polycrystalline diamond with f(T) of 45 GHz and f(max) of 120 GHz [J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2006, 27(7): 570-572.
[4] ZHU X W, ASLARN D M. CVD diamond thin film technology for MEMS packaging [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2006, 15(2-3): 254-258.
[5] MALAVE A, OESTERSCHULZE E, KULISCH W, TRENKLER T. Diamond tips and cantilevers for the characterization of semiconductor devices [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 1999, 8(2-5): 283-287.
[6] ADAMSCHIK M, HINZ M, MAIER C, SCHMID P. Diamond micro system for bio-chemistry [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2001, 10(3-7): 722-730.
[7] YU Z M, LIU X X, WEI Q P, YANG T M, ZHAI H. Nanocrystalline diamond matrix deposited on copper substrate by radical species restricted diffusion [J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2013, 13(7): 6910-6916.
[8] LIU X X, WEI Q P, YU Z M, YANG T M, ZHAI H. Adherent diamond film deposited on Cu substrate by carbon transport from nanodiamond buried under Pt interlayer [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 265: 714-719.
[9] CONSTANT L, SPEISSER C, NORMAND F L. HFCVD diamond growth on Cu(111): Evidence for carbon phase transformations by in situ AES and XPS [J]. Surface Science, 1997, 387(1-3): 28-43.
[10] LIU Xue-zhang, WEI Qiu-ping, ZHAI Hao, YU Zhi-ming. Enhancement of nucleation of diamond films deposited on copper substrate by nickel modification layer [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(3): 667-673.
[11] LIU X Z, YU T, WEI Q P, YU Z M, XU X X. Enhanced diamond nucleation on copper substrates by employing an electrostatic self-assembly seeding process with modified nanodiamond particles [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2012, 412: 82-89.
[12] BUIJNSTERS J G, VAZQUEZ L, van DREUMEL G W G, ter MEULEN J J. Enhancement of the nucleation of smooth and dense nanocrystalline diamond films by using molybdenum seed layers [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 108(10): 103514-103519.
[13] WEI Q P, ASHFOLD M N R, MANKELEVICH Y A, YU Z M. Diamond growth on WC-Co substrates by hot filament chemical vapor deposition: Effect of filament–substrate separation [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2011, 20(5-6): 641-650.
[14]  J, PRIOR Y. Study of morphological behavior of single diamond crystals [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2000, 209(4): 779-788.
J, PRIOR Y. Study of morphological behavior of single diamond crystals [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2000, 209(4): 779-788.
[15] KNIGHT D S. Characterization of diamond films by Raman spectroscopy [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 1989, 4(2): 385-393.
[16] LEE S T, LIN Z, JING X. CVD diamond films: Nucleation and growth [J]. Materials Science and Engineering R: Reports, 1999, 25(4): 123-154.
[17] FAN Q H, PEREIRA E,  J. Diamond deposition on copper: Studies on nucleation, growth, and adhesion behaviours [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1999, 34(6): 1353-1365.
J. Diamond deposition on copper: Studies on nucleation, growth, and adhesion behaviours [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1999, 34(6): 1353-1365.
[18] SCHWARZ S, ROTTMAIR C, HIRMKE J, ROSIWAL S, SINGER R F. CVD-diamond single-crystal growth [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2004, 271(3-4): 425-434.
[19] BUTLER J E, MANKELEVICH Y A, CHEESMAN A, MA J, ASHFOLD M N R. Understanding the chemical vapor deposition of diamond: Recent progress [J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2009, 21(36): 364201.
[20] MONTEIRO O R, LIU H B. Nucleation and growth of CVD diamond films on patterned substrates [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2003, 12(8): 1357-1361.
[21] COMERFORD D W, D’HAENENS-JOHANSSON U F S, SMITH J A, ASHFOLD M N R, MANKELEVICH Y A. Filament seasoning and its effect on the chemistry prevailing in hot filament activated gas mixtures used in diamond chemical vapour deposition [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2008, 516(5): 521-525.
[22] EATON S C, SUNKARA M K, UENO M, WALSH K M. Modeling the effect of oxygen on vapor phase diamond deposition inside micro-trenches [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2001, 10(12): 2212-2219.
[23] MAY P W, HARVEY J N, ALLAN N L, RICHLEY J C, MANKELEVICH Y A. Simulations of chemical vapor deposition diamond film growth using a kinetic Monte Carlo model [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 108(1): 014905.
[24] GLASER A, ROSIWAL S M, FREELS B, SINGER R F. Chemical vapor infiltration (CVI)—Part I: A new technique to achieve diamond composites [J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2004, 13(4-8): 834-838.
[25] LIANG X, WANG L, ZHU H, YANG D. Effect of pressure on nanocrystalline diamond films deposition by hot filament CVD technique from CH4/H2 gas mixture [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2007, 202(2): 261-267.
刘学璋1,张雄伟2,余志明2
1. 江西科技师范大学 材料与机电学院,南昌 330013;
2. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:主要活性基团(H, CH3·)的有效扩散与基体模板孔的深度限制了沟道或通道内金刚石的沉积。通过纳米金刚石悬浮液超声震荡加载籽晶,随后热丝化学气相沉积,在铜模板圆柱型微通道内成功制备出三维结构的金刚石膜。分别采用微区激光拉曼光谱和扫描电子显微镜表征金刚石膜,考察微通道深度对金刚石形貌、晶粒尺寸与膜生长速率的影响。结果显示:金刚石膜的质量和生长速率随微通道深度的增加而急剧下降,单个金刚石晶粒由发育完善、刻面清晰的晶粒逐渐转变为微米团簇,最后转变为球状纳米晶。为改善金刚石膜质量和提高生长速率,设计出一种气源强制输送热丝化学气相沉积装置。此外,对比分析无气源强制输送条件下金刚石的生长,并讨论气源强制输送的增强机理。
关键词:化学气相沉积;金刚石;模板;铜基体;微通道
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (21271188) supported by the Nature Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Zhi-ming YU; Tel: +86-731-88830335; Fax: +86-731-88876692; E-mail: Zhiming@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63810-9

