
Dynamic behavior and fracture mode of TiAl intermetallics with different microstructures at elevated temperatures
ZAN Xiang1, HE Yue-hui2, WANG Yang3, XIA Yuan-ming3
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China;
2. State Key Laboratory for Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. Department of Modern Mechanics, CAS Key Laboratory of Mechanical Behavior and Design of Materials, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230027, China
Received 1 February 2010; accepted 7 June 2010
Abstract: Experimental studies were conducted on the tensile behaviors and fracture modes of TiAl (Ti-46.5Al-2Nb-2Cr) alloys with near gamma (NG) equiaxed and near lamellar (NL) microstructures over a temperature range from room temperature to 840 °C and a strain rate range of 0.001-1 350 s-1. The results indicate that the alloys are both temperature and strain rate dependent and they have a similar dependence. The dynamic strength is higher than the quasi-static strength but almost insensitive to high strain rate range of 320-1 350 s-1. The brittle-to-ductile transition temperature (BDTT) increases with increasing strain rates. NG TiAl yields obviously, while NL TiAl does not. Below BDTT, as the temperature increases, the fracture modes of the two alloys change from planar cleavage fracture to a mixture of transgranular and intergranular fractures, and finally to totally intergranular fracture.
Key words: TiAl intermetallics; high strain rate; elevated temperature character; tensile properties; fracture mode
1 Introduction
With high specific strength, γ-TiAl intermetallic compound is a potential attraction for structural applications at elevated temperatures. However, the poor ductility of TiAl alloy at room temperature (RT) limits its applications[1-3]. Over the past few decades, the effects of the composition, preparing method and microstructure on the mechanical behavior of TiAl alloys have been investigated[4-5], while studies on its dynamic tensile impact behavior at different temperatures are insufficient. SUN et al[6] studied the tensile impact behavior of duplex Ti-45Al-1.6Mn alloy at RT and a strain rate of 300 s-1, and found that the strength increased with increasing strain rate but was not sensitive to high strain rates. WANG et al[7] and ZHOU and XIA[8] investigated the RT tensile properties of two TiAl alloys with lamellar microstructures at high strain rates and the results indicated that the lamellar TiAl broke under impact loadings, exhibiting no plasticity and the fracture strain increased with increasing strain rate. SHAZLY et al[9-10] firstly investigate the tensile mechanical properties of Gamma-Met PX (Ti-45Al-X alloy made by GKSS, in which X refers to Nb, B or C) using the split Hopkinson tensile bar (SHTB) at different temperatures. Unfortunately, there was too much non-constitutive vibration in the stress—strain curves and yet, no further investigations reported the effects of the temperature, strain rate and microstructure on the mechanical behavior of TiAl alloy. ZAN et al[11] made investigations on the tensile impact behavior of duplex Ti-46.5Al-2Nb-2Cr alloy at elevated temperatures under high strain rate loadings and found that the retainable temperature range of strength and the brittle-to-ductile transition temperature (BDTT) were higher than those under quasi-static loadings.
The aim of the present work is to investigate the overall effects of microstructures on the tensile impact behavior and fracture modes of Ti-46.5Al-2Nb-2Cr alloy with near gamma (NG) and near lamellar (NL) microstructures over a temperature range from RT to 840 °C and a strain rate range of 0.001-1 350 s-1.
2 Experimental
The Ti-46.5Al-2Nb-2Cr alloy was produced by casting and then hot isostatically pressed (HIP) at 1 250°C and 125 MPa for 3 h to eliminate casting porosity. The ingot was subsequently heat treated at 1 250 °C for 8 h. Finally, the TiAl alloys with NG and NL microstructures were obtained through the process as shown in Fig.1. The optical photographs of the NG and NL microstructures are shown in Fig.2.
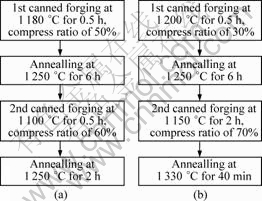
Fig.1 Illustration of canned forging heat treatment for two typical microstructures: (a) NG; (b) NL
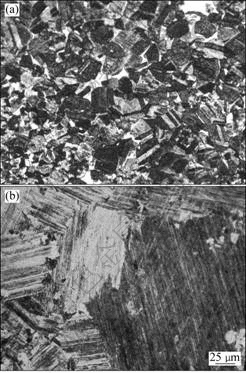
Fig.2 Optical photos of Ti-46.5Al-2Nb-2Cr alloy with two typical microstructures: (a) NG; (b) NL
Tensile impact tests at strain rates of 320, 800 and 1 350 s-1 and temperatures ranging from RT to 840 °C were conducted on a rotating disk indirect bar-bar tensile impact apparatus, with a rapid contact heating technique[12-13]. Quasi-static tensile tests were performed on an MTS 809 servo-hydraulic materials tester at a strain rate of 0.001 s-1. The fractures were observed using a Philips XL 30 ESEM at an accelerating voltage of 15 or 20 kV. Detailed experimental process can be found in Refs.[11-12, 14].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Near gamma microstructure
The true stress—true strain curves of NG TiAl are given in Fig.3, exhibiting obvious yielding. The strength of NG TiAl drops a little after being yielded and then goes into a constant work-hardening stage till the alloy is broken. The effects of temperature and strain rate on the dynamic behavior of NG TiAl are shown in Fig.4. From Figs.3 and 4, it can be concluded that: 1) The dynamic strengths, including yield strength σ0.2, flowing stress under the same strain and ultimate tensile strength (UTS) are obviously higher than those under quasi-static loadings (owing to page limitation, only data of σ0.2 are given); 2) Anomaly yield, though discovered in the high temperature compression of TiAl alloy at a high strain rate[15-17], is not found in the tensile tests; 3) Under quasi-static loadings, the strength value remains stable between 650 and 750 °C, while under dynamic loadings, the temperature range of stable strength extends to 840 °C; 4) Under quasi-static loadings, the BDTT is between 750 and 840 °C (according to the definition, BDTT is the temperature at which the plastic strain attains 7.5%[18-19]) and brittle-to-ductile transition takes place obviously at 840 °C. However, under dynamic loadings, the plastic strain is always less than 4% over the whole testing temperature range (RT -840 °C), which reveals that BDTT under dynamic loadings is higher than that under quasi-static loadings. That is to say, the BDTT increases with increasing strain rate; 5) Below BDTT, the unstable strain εb (the strain corresponding to UTS) under dynamic loadings is slightly higher than that under quasi-static loadings, probably due to the deformation twinning which predominately affects deformation under tensile dynamic loadings[6, 20]; 6) Under dynamic loadings, the work-hardening rate is not sensitive to temperature and strain rate, remaining at about 6 000 MPa. Generally, the comprehensive properties of TiAl alloy under dynamic loadings are better.
SEM images of NG TiAl under quasi-static and dynamic loadings are shown in Figs.5 and 6, respectively. At RT, cleavage planes are found in both loading conditions as shown in Fig.5(a) and Fig.6(a). As the temperature increases, cracks appear between crystalline grains and some planar crystal boundaries also emerge. Here, the fracture mode is a mixture of transgranular and intergranular fracture over the whole strain rate range (Fig.5(b) and Figs.6(b)-(c)). At 840 °C, under quasi-static loading, a small number of dimples appear in addition to planer crystal boundaries (Fig.5(c)), while
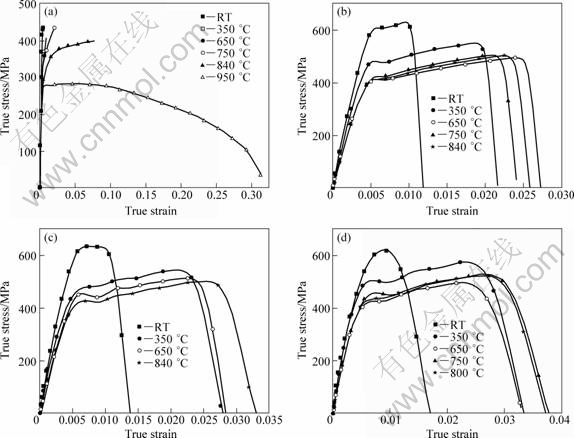
Fig.3 True stress—true strain curves of NG TiAl at different strain rates: (a) 10-3 s-1; (b) 320 s-1; (c) 800 s-1; (d) 1 350 s-1
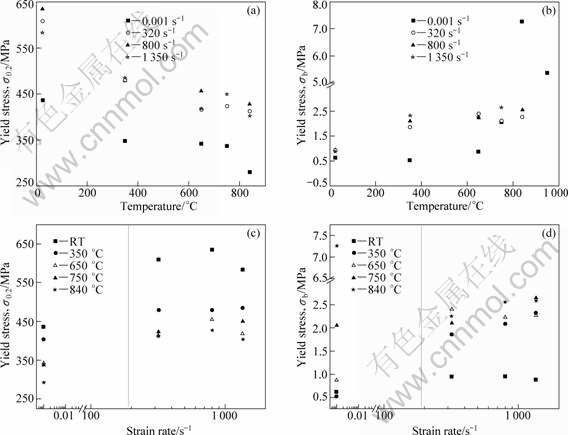
Fig.4 Effects of temperature and strain rate on σ0.2 and σb of NG TiAl
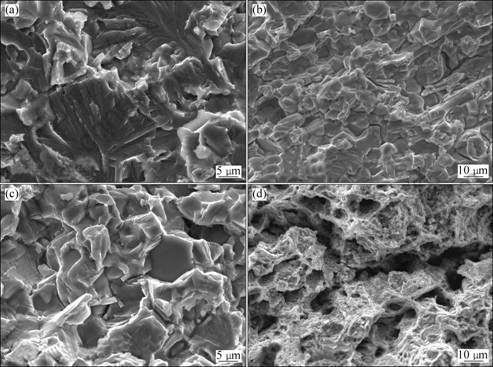
Fig.5 SEM images of NG TiAl alloys under quasi-static loadings at different temperatures: (a) RT; (b) 650 °C; (c) 840 °C; (d) 950 °C
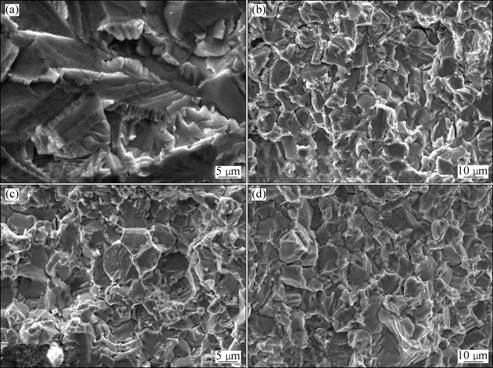
Fig.6 Fractographs of NG TiAl alloy under different dynamic loading conditions: (a) RT, 320 s-1; (b) 350 °C, 1 350 s-1; (c) 650 °C, 800 s-1; (d) 840 °C, 1 350 s-1
under dynamic loadings, the fracture mode is totally intergranular fracture (Fig.6(d)). However, at 950 °C, which is above BDTT, plastic fracture occurs and large number of dimples are found under quasi-static loading (Fig.5(d)).
3.2 Near lamellar microstructure
The stress—strain curves of NL TiAl dependent on temperature and strain rate are similar to those of NG TiAl. Curves at strain rates of 0.001 and 320 s-1 are given in Fig.7 for comparison. No clear yield point can
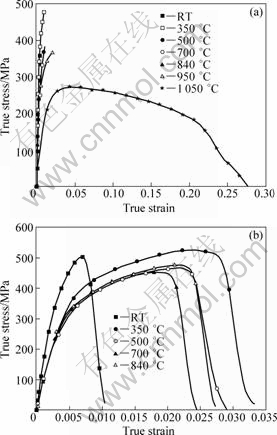
Fig.7 True stress—true strain curves of NL TiAl at different strain rates: (a) 0.001 s-1; (b) 320 s-1
be found and the work-hardening stage is nonlinear. Its BDTT is between 950 and 1 050 °C under quasi-static loadings and the work-hardening rate remains about 6 300 MPa under dynamic loadings.
Also, the fracture mode of NL TiAl is similar to that of NG TiAl (Fig.8). However, intergranular fracture is more common at elevated temperatures. Because of the larger specific surface area of NL TiAl, the effects of crystal boundary movement on its mechanical behavior are greater than those on NG TiAl. In Fig. 8, the fracture surfaces are nearly on the same plane and the fractures are even and flat. At elevated temperatures below BDTT, however, not only planar crystal boundaries but also delamination appear. The higher the temperature is, the more obvious the delamination is. These may probably account for the nonlinearity of the work-hardening stage, but further investigations are needed. At 1 050 °C, plastic fracture also occurs and large number of dimples are found (Fig.8(f)).
3.3 Microstructural effects
From the results in sections 3.1 and 3.2, it is known that the two alloys have similar temperature and strain rate effects on mechanical behaviors. The strength of NL TiAl is less than that of NG TiAl, while the BDTT of the former under quasi-static loadings is higher than that of the latter. No clear yielding point can be found and the work-hardening stage is nonlinear in the true stress—
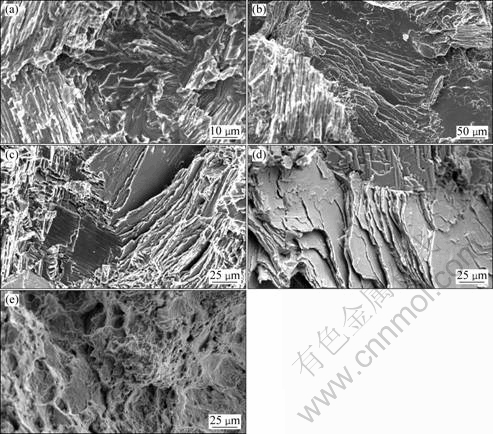
Fig.8 SEM images of NL TiAl at different strain rates and temperatures: (a) RT, 0.001 s-1; (b) 350 °C, 1 350 s-1; (c) 700 °C, 320 s-1; (d) 840 °C, 320 s-1; (e) 1 050 °C, 0.001 s-1
true strain curves of NL TiAl (Fig.9). Additionally, the work- hardening rate of NL TiAl is higher than that of NG TiAl under dynamic loadings. But no obvious patterns can be found in the plastic strains of the two TiAl alloys under the same loading conditions. The two alloys also have similar fracture modes but NL TiAl tends to experience intergranular fracture at elevated temperatures.
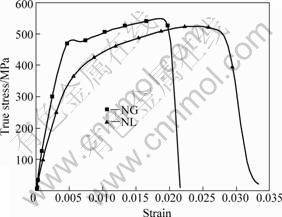
Fig.9 True stress—true strain curves of two TiAl alloys at 350 °C and 320 s-1
4 Conclusions
1) NG TiAl and NL TiAl alloys have similar temperature and strain rate dependences. The dynamic strength is higher than quasi-static strength but almost insensitive to strain rates over the high strain rate range (320-1 350 s-1). Below BDTT, the unstable strain εb under dynamic loadings is slightly higher than that under quasi-static loadings. BDTT increases with increasing strain rate and the work-hardening rates are temperature and strain rate independent under dynamic loadings at elevated temperatures.
2) The strength of NL TiAl alloy is lower than that of NG TiAl alloy, while the BDTT of the former under quasi-static loadings and its work-hardening rate under dynamic loadings are higher than those of the latter. NG TiAl alloy yields obviously, while NL TiAl alloy does not and exhibits nonlinear work-hardening stages in true stress—true strain curves. No patterns can be found in the plastic strains of the two alloys under the same loading conditions.
3) The two alloys experience similar fracture modes. Below BDTT, as the temperature increases, the fracture modes of the two alloys change from planar cleavage fracture to a mixture of transgranular and intergranular fracture, and finally to a totally intergranular fracture. Intergranular fracture tends to occur in NL TiAl at elevated temperatures.
References
[1] KIM Y W. Ordered intermetallic alloy part III: Gamma titanium aluminides [J]. JOM, 1994. 46: 30-39.
[2] APPEL F, WAGNER R. Microstructure and deformation of two-phase γ-titanium aluminides [J]. Materials Science and Engineering R, 1998, 22(5): 187-268.
[3] CLEMENS H, KESTLER H. Processing and applications of intermetallic γ-TiAl-based alloys [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2000, 2(9): 551-570.
[4] LIU C T, MAZIASZ P J. Microstructural control and mechanical properties of dual-phase TiAl alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 1998, 6(7-8): 653-661.
[5] LIU Z C, LIN J P, LI S J, CHEN G L. Effects of Nb and Al on the microstructures and mechanical properties of high Nb containing TiAl base alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2002, 10(7): 653-659.
[6] SUN Z M, KOBAYASHI T, FUKUMASU H, YAMAMOTO I, SHIBUE K. Tensile properties and fracture toughness of a Ti-45Al-1.6Mn alloy at loading velocities of up to 12 m/s [J] Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1998, 29: 263-277.
[7] WANG Y, LIN D, ZHOU Y, XIA Y, LAW C C. Dynamic tensile properties of Ti-47Al-2Mn-2Nb alloy [J] Journal of Materials Science, 1999, 34(3): 509-513.
[8] ZHOU Y, XIA Y. Tensile mechanical behavior of TiAl(FL) at high strain rate [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2000, 35(4): 925-929.
[9] SHAZLY M, PRAKASH V, DRAPER S. Mechanical behavior of Gamma-Met PX under uniaxial loading at elevated temperatures and high strain rates [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2004, 41(22-23): 6485-6503.
[10] SHAZLY M. Dynamic deformation and fracture of gamma-met PX at room and elevated temperatures [D]. Cleveland: Department of Mechanical and Areospace Engineering, Case Western Reserve University, 2005.
[11] ZAN X, WANG Y, XIA Y, HE Y. Strain rate effect on the tensile behavior of Duplex Ti-46.5Al-2Nb-2Cr intermetallics at elevated temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 498(1-2): 296-301.
[12] HUANG W, ZAN X, NIE X, GONG M, WANG Y, XIA Y M. Experimental study on the dynamic tensile behavior of a poly-crystal pure titanium at elevated temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007. 443(1-2): 33-41.
[13] XIA Y M, WANG Y. Dynamic testing of materials with the rotating disk indirect bar-bar tensile impact apparatus [J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 2007, 35(1): 1-5.
[14] ZAN X, CHEN X, HUANG W, XIA Y. Rapid-contact heating technique in tensile impacts at elevated temperatures [J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2005, 20(3): 321-327. (in Chinese)
[15] MALOY S A, GRAY III G T. High strain rate deformation of Ti48Al2Nb2Cr [J]. Acta Materialia, 1996, 44(5): 1741-1756.
[16] VAIDYA R U, JIN Z, CADY C, GRAY III G T, BUTT D P. A comparative study of the strain rate and temperature dependent compression behavior of Ti-46.5Al-3Nb-2Cr-0.2W and Ti-25Al-10Nb-3V-1Mo intermetallic alloys [J]. Scripta Materialia, 1999, 41(6): 569-574.
[17] JIN Z, CADY C, GRAY III G T, KIM Y W. Mechanical behavior of a fine-grained duplex gamma-TiAl alloy [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2000, 31(3): 1007-1016.
[18] WANG Y, LIN D, LAW C C. Brittle-to-ductile transition temperature and its strain rate sensitivity in a two-phase titanium aluminide with near lamellar microstructure [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1999, 34(13): 3155-3159.
[19] WANG Y, LIN D, LAW C C. The effect of boron addition on brittle-to-ductile transition temperature and its strain rate sensitivity in gamma titanium aluminide [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2000. 35(12): 3083-3087.
[20] ZAN X, HE Y, WANG Y, LU Z, XIA Y. Tensile impact behavior and deformation mechanism of duplex TiAl intermetallics at elevated temperatures [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2010, 45(23): 6446-6454.
不同微观组织TiAl金属间化合物高温动态力学行为与断裂特性
昝 祥1,贺跃辉2,汪 洋3,夏源明3
1. 合肥工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,合肥 230009;
2. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083;
3. 中国科学技术大学 近代力学系,中国科学院材料力学行为和设计重点实验室,合肥 230027
摘 要:研究Gamma等轴NG组织和近片层NL组织的Ti-46.5Al-2Nb-2Cr合金在不同温度和应变率下的力学行为和断裂模式,揭示温度和应变率对不同微观组织的力学行为和断裂特性的影响。结果表明,两种微观组织的TiAl合金均与温度和应变率相关,且具有类似的温度和应变相关性:动载下的强度明显高于静载下的强度,但在高应变率范围内(320-1 350 s-1)无明显的应变率相关性;韧脆转变温度(BDTT)随应变率的增加而升高;等轴组织的TiAl合金的真应力—真应变曲线中可以看到明显的屈服现象,而近片层组织的屈服现象不明显。在韧脆转变温度以下,随着温度的上升,两种组织的TiAl的断裂方式均由穿晶解理断裂转变为穿晶断裂与沿晶断裂的混和模式,最后转变为沿晶断裂方式。
关键词: TiAl金属间化合物;高应变率;高温;拉伸特性;断裂方式
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
Foundation item: Projects (10902106, 90505002 ) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: ZAN Xiang; Tel: +86-18605519173; E-mail: zanx@hfut.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60676-6