氧含量对TiAl合金等温氧化行为的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第3期
论文作者:赵堃 欧阳思慧 刘咏 刘彬 梁霄鹏 李慧中 王宇
文章页码:526 - 533
关键词:TiAl金属间化合物;氧含量;等温氧化;氧化动力学
Key words:TiAl intermetallics; oxygen content; isothermal oxidation; oxidation kinetic
摘 要:研究不同氧含量Ti-45Al-2Fe-2Mo-1Cr合金在空气中950 °C下热处理100 h的等温氧化行为,并计算其氧化动力学参数。实验结果表明,随着氧含量的增加,该合金的高温抗氧化性能下降,氧化质量增加和氧化膜的厚度增加。随着基体氧含量的变化,近氧化膜表面的合金显微组织呈现不同的形貌:在低氧含量的合金中,可见Z相;在中高氧含量的的合金中,可见τ2 (Al2FeTi)相。随着氧含量增加,TiAl合金的内氧化现象加剧,其抗氧化性能降低。控制TiAl合金中的氧含量是提高其抗氧化性能的可行方式。
Abstract: Isothermal oxidation behaviors of Ti-45Al-2Fe-2Mo-1Cr intermetallics with different oxygen contents were studied under the condition of 950 °C, 100 h in air, and the oxidation kinetic parameters were also evaluated. The results show that the oxidation resistance of the TiAl intermetallics is negatively related to the oxygen content, and both the mass gain and thickness of oxide scale increase with the oxygen content. The sub-surface microstructure of the oxide scales varies with the oxygen content. Z phase is observed in the sub-surface area of the low-oxygen-content alloy, while the τ2(Al2FeTi) phase is found in the medium-oxygen-content and the high-oxygen-content alloys. The deterioration of oxidation resistance is due to the enhanced internal oxidation with the increase of oxygen content. It is possible to improve the oxidation resistance by controlling the oxygen content.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 526-533
Kun ZHAO1, Si-hui OUYANG1, Yong LIU1, Bin LIU1, Xiao-peng LIANG2, Hui-zhong LI2, Yu WANG3
1. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. Department of Modern Mechanics, University of Science & Technology of China, Hefei 230027, China
Received 5 February 2018; accepted 7 May 2018
Abstract: Isothermal oxidation behaviors of Ti-45Al-2Fe-2Mo-1Cr intermetallics with different oxygen contents were studied under the condition of 950 °C, 100 h in air, and the oxidation kinetic parameters were also evaluated. The results show that the oxidation resistance of the TiAl intermetallics is negatively related to the oxygen content, and both the mass gain and thickness of oxide scale increase with the oxygen content. The sub-surface microstructure of the oxide scales varies with the oxygen content. Z phase is observed in the sub-surface area of the low-oxygen-content alloy, while the τ2(Al2FeTi) phase is found in the medium-oxygen-content and the high-oxygen-content alloys. The deterioration of oxidation resistance is due to the enhanced internal oxidation with the increase of oxygen content. It is possible to improve the oxidation resistance by controlling the oxygen content.
Key words: TiAl intermetallics; oxygen content; isothermal oxidation; oxidation kinetic
1 Introduction
TiAl intermetallics are promising high temperature structural materials due to their good high temperature strength, creep resistance and low density [1-5]. However, the application of TiAl intermetallics is limited by its brittleness [1,6], poor workability at elevated temperature [1,4] and their inadequate oxidation resistance above 850 °C [7]. The high temperature oxidation behavior of TiAl intermetallics has been extensively investigated, especially with respect to the influence of alloying elements, for example, Nb [8,9], W [10], Mo [9,10] and Si [10] elements were reported to improve the high temperature oxidation resistance, due to the presence of a continuous Al2O3 layer and the relatively massive precipitation of Al2O3 in the vicinity of the scale-metal interface. The growth of the rutile scale is remarkably suppressed when Ti is substituted by 1at.%-l0 at.% of Nb [8,9]. Compared with the elements W and Mo, Si appears to be relatively more beneficial at low temperatures (<700 °C) [10]. Mn is detrimental to the oxidation resistance of TiAl intermetallics, because TiO2 doped with low valence cations (Mn2+) results in an increase of defect concentrations and promotes inward diffusion of oxygen atoms [11].
The effects of interstitial atoms on high temperature oxidation behavior of TiAl intermetallics were also investigated. Oxygen and nitrogen are common interstitial atoms, which take up octahedral sites in γ phase (L10 structure). Nitrogen has both positive and negative effects on the high temperature oxidation resistance [12]. On one hand, a continuous TiN layer at oxide-matrix interface is a barrier impeding the ingress of oxygen into TiAl intermetallics and preventing the internal oxidation [12]. On the other hand, TiN and Ti2AlN particles in protective Al2O3 layer disrupt its continuity and promote the formation of a rapidly growing mixture of TiO2 and Al2O3.
The published data of oxygen are limited and scattered. SHIDA and MIURA [10] found that oxygen is a neutral element for TiAl intermetallics, and the mass gain doesn’t vary with the amount of oxygen addition. KEKARE and ASWATH [13] found that after being oxidized at 704 °C and 815 °C for 100 h, the alloys with the oxygen content of 400×10-6 and 600×10-6 show no apparent difference in the oxidation behavior. When the oxidation temperature increases to 982 °C, the increase of oxygen content (from 400×10-6 to 600×10-6) results in an obvious increase of mass gain. The apparent difference in the oxidation behavior is attributed to the presence of a larger number of cracks in oxides, which provide easy paths for the penetration of oxygen. For both studies, the oxygen contents are in a small range, and the effect of dissolved oxygen on the oxidation mechanism also has not been clarified.
In this work, the oxidation behavior of TiAl intermetallics with different amounts of oxygen (between 900×10-6 and 1100×10-6) was investigated. The effects of oxygen content on the oxidation behavior and microstructural evolution were discussed.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials preparation
Pre-alloyed Ti-45Al-2Fe-2Mo-1Cr (at.%) powder was fabricated by electrode induction gas atomization (EIGA) method. The oxygen content of the pre-alloyed power was about 780×10-6. The powder size (D50) was around 75 μm. Three TiAl intermetallics with different oxygen contents were prepared by powder metallurgy (PM) method under the atmospheres with different oxygen contents. The oxygen content was measured by LECO-TCH 600 using the inert gas fusion technique. The alloys with oxygen contents of 900×10-6, 980×10-6 and 1100×10-6 were called as low-oxygen- content (LOC) alloy, medium-oxygen-content (MOC) alloy and high-oxygen-content (HOC) alloy in the following, respectively.
2.2 Isothermal oxidation
Isothermal oxidation specimens with the dimensions of 10 mm×5 mm×1 mm were cut from the TiAl samples with different oxygen contents. The surfaces were ground down to 2000 SiC paper and then cleaned ultrasonically in ethanol. During the oxidation process, each specimen was placed in corundum crucible. The experiments were performed in static air at 950 °C for 100 h. The specimens were put in a muffle furnace and pre-heated to the test temperature. After being oxidized for a certain time, the crucibles with the specimens were taken out from the furnace, cooled in air for 15 min and weighed using a balance with a resolution of 0.01 mg. Then, the specimens were placed to the furnace again for further oxidation. The mass gain was measured including spalled oxide scales.
2.3 Microstructural characterization
After oxidation, the specimens were prepared by conventional grinding and polishing techniques for microstructural analyses. Microstructural observations were carried out on a scanning electron microscope (SEM: FEI Helios NanoLab G3 UC). Microchemical information was obtained by electron probe micro analysis (EPMA: JXA-8530F). X-ray diffraction was used to identify oxidation products (XRD: Rigaku D/max 2500 18 kW). The volume fraction of phases in SEM images was calculated through Image Proplus software.
3 Results
3.1 Initial materials
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns of the LOC, MOC and HOC alloys. All the alloys contain γ phase and β phase, and the γ phase is the major phase, and the β phase is the minor phase. Figure 2 shows the SEM images of the LOC, MOC and HOC alloys. In these images, the γ phase shows dark contrast, while the β phase shows bright contrast. It is shown that all the alloys are nearly fully dense, no apparent pores can be found. The volume fractions of β phase in the LOC, MOC and HOC alloys are 11%, 10% and 12%, respectively.
3.2 Oxidation behavior
3.2.1 Oxidation kinetics
Figure 3 shows the mass gain during the oxidation test at 950 °C for 100 h. It can be found that the LOC alloy shows much less mass gain than other two alloys. The mass gains of the LOC, MOC and HOC alloys oxidized for 100 h are 4.42, 8.13 and 9.97 mg/cm2, respectively. This clearly indicates that the oxidation mass gain increases with the oxygen content. The mass gain of the HOC alloy is about twice that of the LOC alloy. For all the three alloys, a rapid oxidation was observed during the initial exposure of 14 h. Then, the oxidation kinetics curve of the LOC alloy shows a nearly parabolic behavior during the whole testing process. No delamination or spallation is observed in the whole oxidation process of the LOC alloy. The mass gain of the MOC alloy increases slowly from 14 to 38 h and sharply after 38 h. There is a slight increase of mass gain for the HOC alloy from 14 to 24 h and a rapid increase after 24 h. When rapid increase of mass gain happens, severe delamination and spallation are found in the MOC alloy and the HOC alloy.
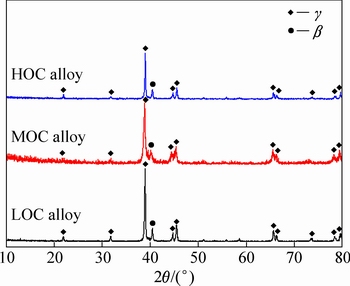
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of as-received LOC, MOC and HOC alloys
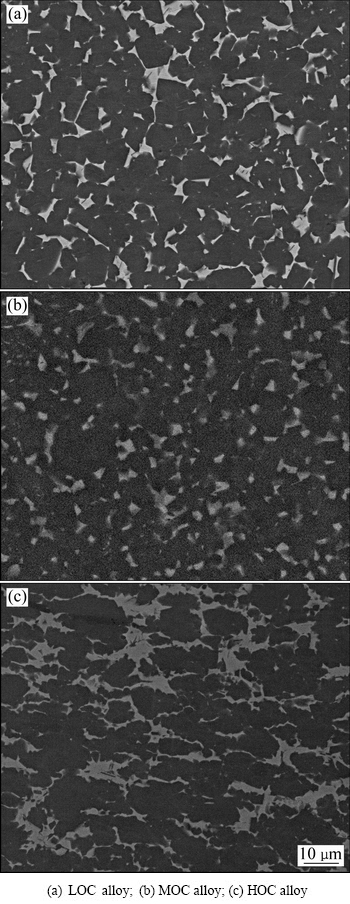
Fig. 2 SEM images of as-received materials
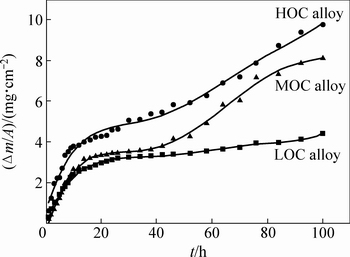
Fig. 3 Oxidation kinetics curves of LOC, MOC and HOC alloys treated at 950 °C for 100 h
The velocity of mass gain can be calculated by the following equation:
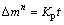 (1)
(1)
where Δm is the mass gain per unit area (mg/cm2), n is the power exponent, Kp is the oxidation rate constant (mg2/(cm4·h)) and t is the time.
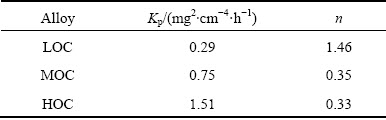
The kinetic parameters for the oxidation of the LOC, MOC and HOC alloys at 950 °C are summarized in Table 1. It is shown that the rate constants of the LOC, MOC and HOC alloys are 0.29, 0.75 and 1.51 mg2/(cm4·h), respectively. The power exponents of the LOC, MOC and HOC alloys are 1.46, 0.35 and 0.33, respectively. It is widely accepted that the smaller the rate constant is, the better the oxidation resistance is. Also, the larger the power exponent is, the better the oxidation resistance is. When the power exponent is lower than 1, the oxidation kinetics curve is linear, which means that the alloy exhibits low oxidation resistance. When the oxidation kinetics is linear, the oxidation reaction rate is controlled by surface reaction or the diffusion of oxygen [14]. The LOC alloy exhibits the best oxidation resistance, while the HOC alloy exhibits the worst oxidation resistance. It can be found that oxidation resistance decreases with the oxygen content.
Table 1 Kinetic parameters for oxidation of LOC, MOC and HOC alloys at 950 °C
3.2.2 Microstructure of oxidized alloys
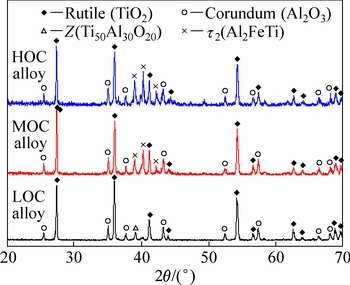
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of oxide scales of oxidized LOC, MOC and HOC alloys
Figure 4 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns of the LOC, MOC and HOC alloys after oxidation at 950 °C for 100 h. For all the specimens, peaks of rutile (TiO2) and corundum (Al2O3) can be identified. Rutile is the major oxide and the corundum is the minor phase. In the LOC alloy, Z phase could also be identified. Z phase is an oxygen-rich phase with the stoichiometry of Ti50Al30O20 [15]. The products of the MOC alloy and the HOC alloy are similar, in which no Z phase but a small amount of τ2 phase is found. τ2 phase is a ternary phase in Ti-Al-Fe system, whose stoichiometry is Al2FeTi [16].
Figure 5 shows the cross-sectional microstructures of the oxidized LOC, MOC and HOC alloys. The thickness of each layer in the oxidation scales of the three TiAl alloys is summarized in Table 2. It is shown that the thickness of oxide scales increases with the oxygen content. The oxide thicknesses of the LOC, MOC and HOC alloys are 16.2, 25.4 and 47.7 μm, respectively. Four layers can be observed in the oxide scales of the alloys (Figs. 5(a), (c) and (e)). The top layer I is rich in TiO2, the layer II is rich in Al2O3, the layer III is a mixture of TiO2 and Al2O3, while the layer IV is rich in Al2O3. It is found that the layer II in the MOC and HOC alloys are not as continuous as the LOC alloy.
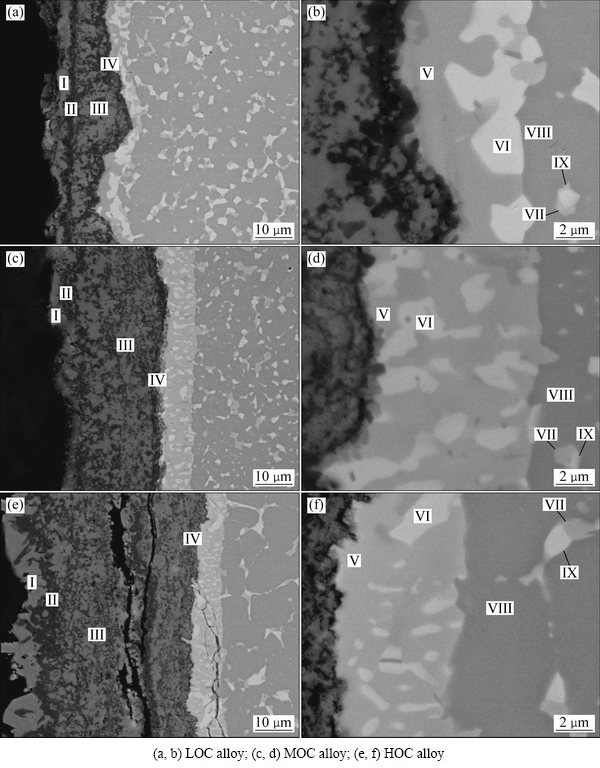
Fig. 5 Cross-sectional microstructures of oxidized samples
Table 2 Thickness of each layer in oxidation scales of LOC, MOC and HOC alloys after oxidation tests
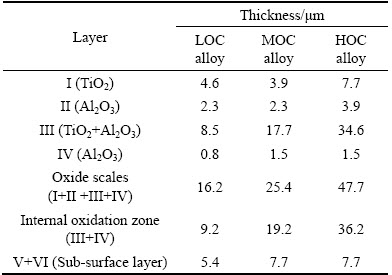
Layer II is the boundary of internal oxidation and external oxidation. The mixture of TiO2 and Al2O3 in layer III is the product of internal oxidation. Since the thickness of layer III in the LOC alloy is lower than that of the other alloys (Table 2). It is deduced that the LOC alloy experiences less internal oxidation than the other alloys. As shown in Fig. 5(b), the layer IV in the LOC alloy is much thicker and more compact than that of the other alloys, indicating a better protection for the substrate. In addition, cracks can be found between the TiO2 and Al2O3 interfaces in the HOC alloy (Fig. 5(e)).
As shown in Table 2, the thickness of sub-surface layers of the LOC, MOC and HOC alloys are 5.4, 7.7 and 7.7 μm, respectively. The sub-surface layers have a two-phase microstructure (Figs. 5(b), (d) and (f)). In the LOC alloy, the EDS result of the dark grey phase (area V, Fig. 5(b)) shows that the stoichiometric ratio of Ti:Al:O is 5:3:2, which may correspond to Z-Ti50Al30O20 phase [15]. The results are in agreement with the XRD results in Fig. 4. Area VI (Fig. 5(b)) showing bright contrast can be identified as β phase, due to its high content of Fe. In the MOC and HOC alloys, the Z phase is not found in the sub-surface zone according to the EDS results. In the dark phases, which is marked by V in Figs. 5(d) and (f), the stoichiometric ratio of Ti to Al is almost 1:1 and Fe element is more than 15 at.%. According to Fe-Al-Ti ternary phase diagram (Fig. 6) [17], it can be identified as τ2 phase. The τ2 phase is a ternary phase with Mn23Th6 type (D8a) structure [18]. The bright phase, marked as VI in Figs. 5(d) and (f), is β phase. Therefore, the sub-surface areas of the MOC and HOC alloys are composed of τ2 phase and β phase, while that of the LOC alloy is composed of Z and β phases.
High magnification images show that medium grey phase forms in the substrate during oxidation, which is marked by VII in Figs. 5(b), (d) and (f). EDS results show that the VII areas are rich in Fe and Cr (Table 3), which is similar with the area V in the MOC and the HOC alloys. Fe content in the VII area is more than 10 at.%, which is much higher than its solubility in β and γ phases [16], therefore, it can be identified as τ2 phase. The τ2 phase is located in the triple junction of the β and γ phases.
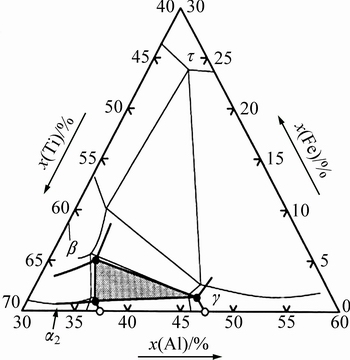
Fig. 6 Fe-Ti-Al isothermal section at 1000 °C [19]
Surface analysis results of the oxidized LOC, MOC and HOC alloys are shown in Fig. 7. Known from Fig. 7, the surfaces of all the alloys are covered with a mixture of randomly oriented TiO2 grains. The shape and size of TiO2 grain on the three alloys vary with the oxygen content. The morphology of TiO2 grains on the LOC and MOC alloys are pillar and platy (Figs. 7(a) and (b)). However, the TiO2 grains on the HOC specimen grow and connect with each other, so that the shape of a certain number of grains cannot be recognized (Fig. 7(c)). The average grain sizes of the TiO2 on the oxidized LOC, MOC and HOC alloys are 1.3, 2.0 and 2.5 μm, respectively. The grain size of the HOC alloy is bigger than the other alloys, which means that both internal and external oxidation of the HOC alloy is more severe than the other alloys, which is in agreement with the results of mass gain.
4 Discussion
There are five steps in the process of high temperature oxidation of TiAl alloys [14]. The first one is the contact of oxygen molecule and metal surface, and the second step is the physical adsorption of oxygen caused by van-der-Waals force. In the third step, the decomposition of oxygen molecule and chemical adsorption of oxygen atoms are involved, and then, the oxygen atoms dissolve in the TiAl substrate, and TiO2 nucleates in the area where oxygen is over-saturated. Simultaneously, mixture of Al2O3 and TiO2 precipitates as the product of internal oxidation. In the fourth step, crystal whiskers of TiO2 grow and connect with each other, thus an oxide film forms. At the same time, Al2O3 and TiO2 grow in island mode. Finally, oxides grow by mass transfer through oxygen vacancy and Ti ions.
Table 3 Chemical compositions of each layer in oxidation scales of LOC, MOC and HOC alloys after oxidation tests
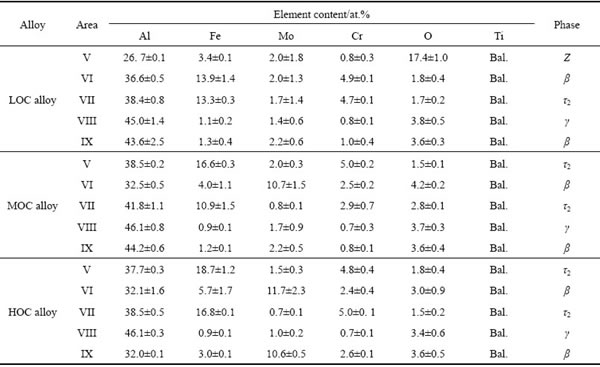

Fig. 7 Surface morphologies of oxidized samples
For the present Ti-45Al-2Fe-2Mo-1Cr alloy with low oxygen content (LOC alloy), oxide scales grow homogeneously, and dense continuous Al2O3 film (layers II and IV) forms below and above the mixture of Al2O3 and TiO2 (layer III). In this case, the Al2O3 layer is protective, serving as a barrier for internal and external diffusion of atoms. For the alloys with higher oxygen content of 980×10-6 (MOC alloy) and 1046×10-6 (HOC alloy), the Al2O3 films are less compact and continuous, which don’t show good protective effect. Also, the oxide scale cracks and oxygen atoms enter through the oxide scales of the HOC alloy. Thus, severe spallation of the oxide scales occurs.
Diffusion is involved in the high temperature oxidation of the TiAl alloys: one is the internal diffusion of oxygen atoms, and the other is the external diffusion of metal atoms simultaneously. It is deduced that the outer scale of TiO2 results from external diffusion of the metal atoms, especially the Ti atoms. Similarly, the inner scale of mixed Al2O3 and TiO2 is the product of internal diffusion. When dissolved oxygen content increases from 980×10-6 to 1100×10-6, mass gain increases from 8.13 to 9.97 mg/cm2. The internal oxidation zone consists of layer III (mixture of TiO2 and Al2O3) and layer IV (Al2O3). The thickness of the internal oxidation zone increases with the dissolved oxygen content. Known from Table 2, the internal oxidation zones of the oxidized LOC, MOC and HOC alloys are as deep as 9.23, 19.23 and 36.16 μm, respectively. Internal oxidation usually proceeds according to a parabolic rate law expressed in the equation below [19]:
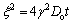 (2)
(2)
where ξ is the thickness of the internal oxidation zone (layer III) at time t, Do is the diffusion coefficient of oxygen in the TiAl alloy, and γ is a dimensionless kinetics parameter. The value of γ is inversely related to the atomic concentration of Al in the bulk alloy, 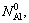 and the interdiffusion coefficient in the TiAl alloy, DTiAl, but it is directly related to the solubility of oxygen on the alloy surface,
and the interdiffusion coefficient in the TiAl alloy, DTiAl, but it is directly related to the solubility of oxygen on the alloy surface,  . Thus, ξ tends to decrease with increasing
. Thus, ξ tends to decrease with increasing  and decreasing
and decreasing  . Supposing that the diffusion coefficients of oxygen are all the same for the three alloys, the higher the initial oxygen content of TiAl alloy is, the higher the final oxygen content of TiAl alloy is. Thus, the varying thickness of internal oxidation zone with oxygen contents could be explained.
. Supposing that the diffusion coefficients of oxygen are all the same for the three alloys, the higher the initial oxygen content of TiAl alloy is, the higher the final oxygen content of TiAl alloy is. Thus, the varying thickness of internal oxidation zone with oxygen contents could be explained.
It is reported that the oxidation of the TiAl alloys is related to the microstructure, especially for the multi-phase alloy. In the present work, the Ti-45Al-2Fe-2Mo-1Cr alloys contain mostly the γ phase and a small amount of β phase. The solubility of Fe is approximately 2.5 at.% in γ phase and varies little with temperature [16]. The β and γ phases are not thermo-dynamically stable due to phase transformation at 950 °C. According to RAGHAVAN [16], τ2 forms from the reaction between γ and β phases. Known from Fig. 6, there is a (τ2+β+TiAl) three-phase field at 1000 °C. τ2 phase with chemical composition of Al2FeTi has the Mn23Th6 type (D8a) cubic structure. PALM et al [17] made a detailed study of the homogeneity range and the lattice parameter variations of the τ2 phase. At 1000 °C, two separate composition islands with Ti ranges of 21-31.5 at.% and 37.5-44 at.% exist [17]. The composition of τ2 in this work is in agreement with the latter range. The formation of τ2 phase may have an effect on the oxidation behavior of the present TiAl alloy; however, further study needs to be done to clarify the mechanism.
In conclusion, the mass gain of the TiAl alloys increases with the oxygen content. The dense protective Al2O3 layer at scale-alloy interface is beneficial for the oxidation resistance of the LOC alloy. The increase of oxygen content promotes the internal oxidation. It is possible to improve the oxidation resistance of the TiAl alloys by controlling dissolved oxygen content.
5 Conclusions
(1) The oxidation resistance of the TiAl alloys is negatively related to the oxygen content, both the mass gain and thickness of oxide scale increase with the oxygen content. The oxidation rate constant increases with the oxygen content, while the power exponent decreases with the oxygen content.
(2) The sub-surface microstructure of the oxide scales varies with the oxygen content. Z phase is observed in the sub-surface area of in the LOC alloy, while the τ2 (Al2FeTi) phase is found in the MOC and the HOC alloys.
(3) The deterioration of oxidation resistance is due to the enhanced internal oxidation with increase of oxygen content. It is possible to improve the oxidation resistance of the TiAl alloys by controlling dissolved oxygen content.
References
[1] XU Wen-chen, HUANG Kai, WU Shi-feng, ZONG Ying-ying, SHAN De-bin. Influence of Mo content on microstructure and mechanical properties of β-containing TiAl alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 820-828.
[2] LIU Yong, LIANG Xiao-oeng, LIU Bin, HE Wei-wei, LI Jian-bo, GAN Ziyang, HE Yue-hui. Investigations on processing powder metallurgical high-Nb TiAl alloy sheets [J]. Intermetallics, 2014, 55: 80-89.
[3] ZHENG De-shuang, CHEN Rui-run, MA Teng-fei, DING Hong-sheng, SU Yan-qing, GUO Jing-jie, FU Heng-zhi. Microstructure modification and mechanical performances enhancement of Ti44Al6Nb1Cr alloy by ultrasound treatment [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 710: 409-417.
[4] ZHOU Can-xu, LIU Bin, LIU Yong, QIU Cong-zhang, LI Hui-zhong, HE Yue-hui. Effect of carbon on high temperature compressive and creep properties of beta-stablized TiAl alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 2400-2405.
[5] CHEN Guang, PENG Ying-bo, ZHENG Gong, QI Zhi-xiang, WANG Min-zhi, YU Hui-chen, DONG Cheng-li, LIU C T. Polysynthetic twinned TiAl single crystals for high-temperature applications [J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(8): 876-881.
[6] STOLOFF N S, LIU C T, DEEVI S C. Emerging applications of intermetallics [J]. Intermetallics, 2000, 8: 1313-1320.
[7] ZHANG Tie-bang, DING Hao, DENG Zhi-hai, ZHONG Hong, HU Rui, Xue Xiang-yi, LI Jin-shan. Synergistic effect of Nb and Mo on oxidation behavior of TiAl based alloys [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41(1): 33-37. (in Chinese).
[8] YOSHIHARA M, MIURA K. Effects of Nb addition on oxidation behavior of TiAl [J]. Intermetallics, 1995, 3: 351-363.
[9] KIM B G, KIM G M, KIM C J. Oxidation behavior of TiAl-X (X=Cr, V, Si, Mo or Nb) intermetallics at elevated temperature [J]. Scripta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1995, 33(7): 1117-1125.
[10] SHIDA Y, ANADA H. The effect of various ternary additives on the oxidation behavior of TiAl in high-temperature air [J]. Oxidation of Metals, 1996, 45(1-2): 197-219.
[11] WU Y, HWANG S K, HAGIHARA K, UMAKOSHI Y. Isothermal oxidation behavior of two-phase TiAl-Mn-Mo-C-Y alloys fabricated by different processes [J]. Intermetallics, 2006, 14(1): 9-23.
[12] SCHAAF P, QUADAKKERS W J, ZHENG N, WALLURA E, GIL A. Beneficial and detrimental effects of nitrogen on the oxidation behaviour of TiAl-based intermetallics [J]. Materials Corrosion, 1997, 48(1): 28-34.
[13] KEKARE S A, ASWATH P B. Oxidation of TiAl based intermetallics [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1997, 32(9): 2485-2499.
[14] BIRKS N, MEIER G H. Introduction to high temperature oxidation of metals [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006.
[15] COPLAND E H, GLEESON B, YOUNG D J. Formation of Z-Ti50Al30O20 in the sub-oxide zones of γ-TiAl based alloys during oxidation at 1000 oC [J]. Acta Materialia, 1999, 47(10): 2937-2949.
[16] RAGHAVAN V. Al-Fe-Ti (aluminum-iron-titanium) [J]. Journal of Phase Equilibria, 2002, 23(4): 367-374.
[17] PALM F, INDEN G, THOMAS M. The Fe-Al-Ti system [J]. Journal of Phase Equilibria, 1995, 16(3): 209-222.
[18] KAINUMA R, FUJITA Y, MITSUI H, OHNUMA I, ISHIDA K. Phase equilibria among α (hcp), β (bcc) and γ (L10) phases in Ti-Al base ternary alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2000, 8: 855-867.
[19] RAPP R A. Kinetics, Microstructures and mechanism of internal oxidation-its effect and prevention in high temperature alloy oxidation [J]. Corrosion, 1965, 21(12): 382-401.
赵 堃1,欧阳思慧1,刘 咏1,刘 彬1,梁霄鹏2,李慧中2,王 宇3
1. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
3. 中国科学技术大学 近代力学系,合肥 230027
摘 要:研究不同氧含量Ti-45Al-2Fe-2Mo-1Cr合金在空气中950 °C下热处理100 h的等温氧化行为,并计算其氧化动力学参数。实验结果表明,随着氧含量的增加,该合金的高温抗氧化性能下降,氧化质量增加和氧化膜的厚度增加。随着基体氧含量的变化,近氧化膜表面的合金显微组织呈现不同的形貌:在低氧含量的合金中,可见Z相;在中高氧含量的的合金中,可见τ2 (Al2FeTi)相。随着氧含量增加,TiAl合金的内氧化现象加剧,其抗氧化性能降低。控制TiAl合金中的氧含量是提高其抗氧化性能的可行方式。
关键词:TiAl金属间化合物;氧含量;等温氧化;氧化动力学
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (2014CB644002) supported by the National Key Fundamental Research and Development of China; Project (2017JJ2311) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China; Project (KFJJ11-7M) supported by the State Key Laboratory of Explosion Science and Technology, China
Corresponding author: Bin LIU; Tel: +86-731-88877669; Fax: +86-731-88710855; E-mail: binliu@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)64961-7

