文章编号:1004-0609(2016)02-0317-11
硅元素对超细晶黄铜力学性能及退火行为的影响
张祥凯1,杨续跃1, 2
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属先进结构材料与制造协同创新中心,长沙 410083)
摘 要:通过XRD、TEM、EBSD以及拉伸试验研究硅元素对超细晶黄铜力学性能和退火行为的影响。将Cu-20Zn和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金在液氮温度(约-196 ℃)下进行轧制并进行退火处理。结果表明:与液氮轧制后Cu-20Zn合金相比,液氮轧制后Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的强度显著提升,这是因为加入的硅元素使得层错能降低,使其变形后具有细小的晶粒以及较高的位错和孪晶密度。Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金热稳定性的提升源自层错能(SFE)的降低以及硅原子与位错的相互作用,使得其内部位错运动受阻。退火后的Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金优异的强度和塑性的综合力学性能源自其组织内部细小的晶粒、形变孪晶以及大量的退火孪晶和HAGBs的共同作用。
关键词:铜合金;层错能;力学性能;孪晶;退火行为
中图分类号:TG146.1 文献标志码:A
Cu-Zn系合金因其优异的力学性能、良好的电导率以及较高的耐腐蚀性被广泛应用于电子和机械等领域[1]。对于结构材料来说,强度和塑性是尤为重要的两个性能指标[2]。细化晶粒通常能够提高金属材料的强度。剧烈塑性变形(Severe plastic deformation, SPD)作为一种能够制备超细晶材料而受到了广泛关注[3-4]。利用SPD方法不仅可以制备出较大尺寸的样品,同时还可以避免在制备过程中引入空隙和污染源[5-6]。室温下SPD过程中的晶粒细化主要通过位错的运动来实现的。晶粒尺寸随着变形量的增加而减小。当位错的累积和湮灭达到一个动态平衡状态时,晶粒不能再通过这种机制被细化而达到一个饱和值[7]。变形温度是影响材料晶粒细化机制以及变形机制的一个重要参数。对于大多数面心立方金属来说,降低变形温度能够促使晶粒进一步细化。因为变形温度的降低有利于形变孪晶形成。低温变形时形变孪晶与位错相互作用使得晶粒进一步细化[8-10]。因此相比于其他SPD方法[11-13],低温变形不需要很大的变形量就可以获得超细晶。
经过SPD方法获得的超细晶材料通常强度很高、塑性很低,这极大地限制了它们的实际工程应用[14-15]。超细晶材料的塑性低是因为其内部位错密度几乎达到饱和以及细小的晶粒尺寸导致其加工硬化率低[16]。有研究表明[17-19],通过降低材料的层错能使得材料的强度和塑性得到同步提升。层错能的降低有利于孪晶和层错的形成,孪晶和层错能够有效地阻碍位错的运动并且孪晶能够为位错累积提供存储空间。尽管降低层错能能够使得材料的强度和塑性得到同步提升,但是塑性提升的非常有限[14, 20]。变形后的退火处理是提升材料塑性的有效方法。材料经过剧烈塑性变形后的强度很高,随后的退火处理在提升塑性的同时虽然会降低材料的强度,但是材料的强度仍然较高[21-22]。因此,通过剧烈塑性变形以及适当的退火处理能够使得材料获得较好的综合力学性能。
因此,本文作者通过向Cu-20Zn中加入硅元素来降低其层错能,使得其在液氮轧制后的性能得到提升,并且通过变形后的退火处理使得其综合力学性能得到进一步提升。同时,研究硅元素的添加对其力学性能和组织以及退火行为的影响。
1 实验
实验所用材料Cu-20%Zn和Cu-20%Zn-1.2%Si(质量分数)。将配料在GW-10型无芯中频感应炉中进行熔炼,经热轧、冷轧和中间退火后,得到实验所需的合金板材。添加的硅元素能够使得合金的层错能大大降低[23]。三元合金的层错能可由式(1)以及相关的二元合金层错能计算得到[24-25]:
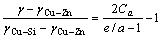 (1)
(1)
式中:e/a为合金中价电子浓度即每个原子平均的价电子数;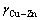 和
和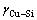 分别是与三元合金具有相同价电子浓度的二元合金的层错能;Ca是溶质总的摩尔分数。计算Cu-20Zn-1.2Si的层错能时,e/a为1.287,
分别是与三元合金具有相同价电子浓度的二元合金的层错能;Ca是溶质总的摩尔分数。计算Cu-20Zn-1.2Si的层错能时,e/a为1.287,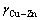 和
和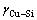 分别为13和6 mJ/m2[23]。由此得出Cu-20Zn-1.2Si的层错能为9 mJ/m2。Cu-20Zn合金e/a为1.198,其层错能为18 mJ/m2[23]。
分别为13和6 mJ/m2[23]。由此得出Cu-20Zn-1.2Si的层错能为9 mJ/m2。Cu-20Zn合金e/a为1.198,其层错能为18 mJ/m2[23]。
将厚度为15 mm Cu-20Zn 和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金铸锭在830 ℃保温1 h进行均匀化处理,然后热轧到5.5 mm厚。将这些轧板在490 ℃保温50 min进行中间退火并水淬。图1所示为铜合金原始组织(490 ℃, 50 min),可以看出,Si元素的加入使得铜合金的组织得到了很大的细化。再将这些板材进行液氮冷轧至不同的变形量。液氮轧制时,先将板材放在液氮中浸泡10~20 min,道次压下率为10%~15%。轧制完成后,所有样品在SG-3-10型盐浴炉中进行不同温度(180~380 ℃)退火,退火完成后立即出炉水淬。拉伸试样采用线切割机制备,拉伸方向与轧制方向平行。为了确保数据可靠性,每个状态的样品至少制备两个拉伸样品进行拉伸试验然后取平均值。试样标距尺寸宽度为1.5 mm,标距长度为6 mm。拉伸实验采用DWD-100A型微机控制电子万能试验机在室温进行,初始拉伸应变速率3×10-3 s-1。在HV-2型维氏硬度计上进行硬度测试。每个试样均匀取9个不同的点进行硬度测试取平均值。加载载荷为9.8 N,保载时间为30 s。采用Rigaku D/max 2500型X射线衍射仪对变形后样品进行定量的分析位错和孪晶密度。在室温下以4(°)/min的速度进行扫描。采用在氩气保护条件下400 ℃退火纯铜样品作为标样来扣除仪器宽化的影响。使用MDI Jade 6 选择Pearson VII函数拟合确定峰的强度、位置以及半高宽等参数,从而得到晶粒尺寸和微观应变。采用Tecnai G2 20型透射电子显微镜(Transmission electron microscope, TEM)对轧后样品的板面和纵截面进行了显微组织的观察,样品在Tenupol-3型双喷电解仪中进行双喷穿孔,双喷液采用体积比为1:2的硝酸与甲醇溶液。采用Sirion 200型场发射扫描电镜(SEM)对退火后的样品的板面进行显微组织观察。为了使数据更加可靠,分析晶粒取向差时去除了所有取向差低于2°的低角度晶界。并且以15°取向差来区分低角度晶界(Low angle grain boundaries, LAGBs)和高角度晶界(High angle grain boundaries, HAGBs)。

图1 铜合金的原始组织形貌
Fig. 1 Optical micrographs of Cu alloys annealed at 490 ℃ for 50 min
2 结果与讨论
2.1 变形后的显微组织和力学性能
图2所示为经过90%变形量后的Cu-20Zn和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的TEM像。可以看到Cu-20Zn合金内部累积了大量的位错和位错胞以及一些孪晶(见图2(a)中白色箭头所示),孪晶间距从10nm到40nm不等,如图2(a)所示。从Cu-20Zn合金纵截面组织可以看到大部分晶粒沿着轧制方向被拉长呈层片状,如图2(b)所示。与Cu-20Zn合金相比,可以看到Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金内部累积了大量的位错和位错胞以及更多的孪晶,孪晶间距从5 nm到20 nm不等,如图2(c)所示。图2(d)所示为Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金纵截面组织,与Cu-20Zn合金相比,可以看到Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金纵截面几乎所有晶粒都沿着轧制方向被拉长呈层片状并且层片间距更加细小。通过XRD技术分析了Cu-20Zn和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的位错和孪晶密度。图3所示为铜合金XRD谱,可以看出层错能的降低使得衍射峰向小角度偏移。剧烈塑性变形材料的位错密度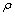 可由式(2)计算得出[25]:
可由式(2)计算得出[25]:
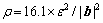 (2)
(2)
式中: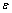 为微观应变;b为柏氏矢量。在面心立方中
为微观应变;b为柏氏矢量。在面心立方中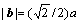 ,a为点阵常数。孪晶密度
,a为点阵常数。孪晶密度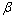 定义为在任何两个相邻{111}面出现孪晶界的几率并且可由式(3)计算得到[26-27]:
定义为在任何两个相邻{111}面出现孪晶界的几率并且可由式(3)计算得到[26-27]:
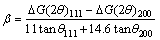 (3)
(3)
式中: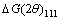 和
和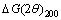 分别为{111}和{200}衍射峰重心对应的衍射角与峰值对应的衍射角的差值。表1所列为铜合金的位错和孪晶密度计算结果。可以看出,层错能对材料变形后的显微组织有着重要影响,Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金组织中的位错和孪晶密度都要高于Cu-20Zn合金的。众所周知,层错能与材料的变形机制密切相关。一方面,硅元素的加入使得Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金层错能降低,这有利于全位错分裂成两个不全位错以及一个位于它们之间的层错。层错能越低,层错越宽[28],因此Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中层错宽度大于Cu-20Zn合金的。Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中较宽的层错能够更有效地阻碍全位错的交滑移或攀移,从而抑制动态回复[29],使得变形后Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中的位错密度较高。另一方面,硅元素的加入使得合金的层错能降低,此时位错滑移所需的应力要高于孪生的,使得孪晶更容易形成[30]。此外,孪晶可以为位错积累提供场所[31]。因此,硅元素的加入使得Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金层错能降低有利于位错和孪晶密度的增加。这与TEM和XRD分析结果一致。
分别为{111}和{200}衍射峰重心对应的衍射角与峰值对应的衍射角的差值。表1所列为铜合金的位错和孪晶密度计算结果。可以看出,层错能对材料变形后的显微组织有着重要影响,Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金组织中的位错和孪晶密度都要高于Cu-20Zn合金的。众所周知,层错能与材料的变形机制密切相关。一方面,硅元素的加入使得Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金层错能降低,这有利于全位错分裂成两个不全位错以及一个位于它们之间的层错。层错能越低,层错越宽[28],因此Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中层错宽度大于Cu-20Zn合金的。Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中较宽的层错能够更有效地阻碍全位错的交滑移或攀移,从而抑制动态回复[29],使得变形后Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中的位错密度较高。另一方面,硅元素的加入使得合金的层错能降低,此时位错滑移所需的应力要高于孪生的,使得孪晶更容易形成[30]。此外,孪晶可以为位错积累提供场所[31]。因此,硅元素的加入使得Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金层错能降低有利于位错和孪晶密度的增加。这与TEM和XRD分析结果一致。

图2 Cu-20Zn合金和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的TEM像
Fig. 2 TEM images of Cu-20Zn alloy((a), (b)) and Cu-20Zn-1.2Si((c), (d))
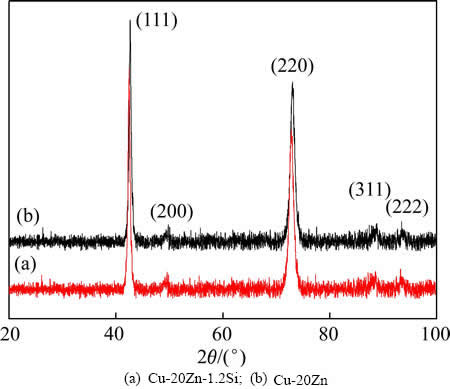
图3 铜合金XRD谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of Cu alloys
表1 铜合金位错和孪晶密度
Table 1 Dislocation density ρ and twin density β of Cu alloys

图4所示为经过不同变形量的Cu-20Zn 和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金工程应力-应变曲线以及拉伸性能曲线。为了方便比较,图4也列出了490 ℃退火50 min的粗晶粒(Coarse-grained,CG) Cu-20Zn和Cu-20Zn- 1.2Si合金的拉伸曲线。两种合金的拉伸曲线都是在很小的应变量达到应力峰值然后迅速的下降。两种合金经过90%变形量的样品的屈服强度(Yield strength, YS)和抗拉强度(Ultimate tensile strength,UTS)相比于粗晶粒的样品都得到了显著的提升,但是总的伸长率都显著的下降了。在真应变为2.3时,Cu-20Zn合金的YS和UTS分别为728和790 MPa。相比之下,Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金在真应变为2.3时具有更高的YS(886 MPa)和UTS(940 MPa)。式(4)可以用来计算材料的屈服强度[32]:
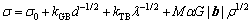 (4)
(4)
式中: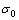 为摩擦应力;kGB为常数;d为晶粒尺寸;kTB为常数;
为摩擦应力;kGB为常数;d为晶粒尺寸;kTB为常数;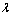 为孪晶厚度;M为泰勒因子;
为孪晶厚度;M为泰勒因子;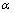 为常数;G为剪切模量;b为柏氏矢量;
为常数;G为剪切模量;b为柏氏矢量;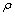 为位错密度。从式(4)中可以看出,晶粒尺寸以及位错和孪晶密度对材料的强度有显著的影响。尽管Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中的硅元素会产生固溶强化,但其强化作用相对于其他强化机制来说可以忽略不计[19]。由TEM和XRD分析可知,层错能较低的Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金变形后具有较小的晶粒尺寸和较高的位错及孪晶密度,这些高密度的晶格缺陷之间的相互作用使得Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金具有更高的强度。
为位错密度。从式(4)中可以看出,晶粒尺寸以及位错和孪晶密度对材料的强度有显著的影响。尽管Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中的硅元素会产生固溶强化,但其强化作用相对于其他强化机制来说可以忽略不计[19]。由TEM和XRD分析可知,层错能较低的Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金变形后具有较小的晶粒尺寸和较高的位错及孪晶密度,这些高密度的晶格缺陷之间的相互作用使得Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金具有更高的强度。

图4 经过不同应变量后铜合金工程应力-应变曲线
Fig. 4 Engineering stress-strain curves of Cu alloys with different rolling strains
2.2 退火后的显微组织和力学性能
图5所示为Cu-20Zn 和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金在不同温度退火1 h的硬度曲线。两种合金的退火曲线可以分为3个阶段。在退火阶段1,随着退火温度的升高,Cu-20Zn合金的硬度略微下降。这表明Cu-20Zn合金在200 ℃以下温度退火合金只发生回复。相比之下,Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金在退火阶段1的硬度随着退火温度的升高不降反增,在240 ℃达到硬度最大值,表现出明显的退火硬化现象。这是因为Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金在低温退火时,由于原子扩散,硅原子容易在堆垛层错处偏析形成铃木气团[33-34]。在退火阶段2,当退火温度分别超过220和260 ℃时,Cu-20Zn和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的硬度都显著地下降。这与再结晶过程开始有关。可以看到,Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金再结晶开始的温度更高,这意味着它的热稳定性因硅元素的加入而得到了提高。一方面,添加的硅原子与位错相互作用能够阻碍位错运动和晶界迁移;另一方面,硅元素的加入使得Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的层错能降低,层错宽度变宽,不利于位错的运动[35-36]。从而层错能较低的Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的热稳定性得到提高。在退火最终阶段3,Cu-20Zn合金的硬度随着退火温度的升高略有下降。然而随着退火温度的升高,Cu-20Zn-1.9Si合金的硬度基本保持不变。这表明Cu-20Zn-1.9Si合金晶粒长大被抑制了。晶粒长大与晶界的迁移有关。添加的硅元素会钉扎晶界,这会阻碍Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金晶粒再结晶之后的进一步长大[37],因此,Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金晶粒尺寸在退火阶段3比较稳定,其硬度值也保持在一个稳定值。

图5 铜合金不同温度退火1 h硬度曲线
Fig. 5 Hardness curves of Cu alloys annealed at different temperatures for 1 h
图6所示为Cu-20Zn和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金分别在300和340 ℃退火1 h的独特晶粒彩色(Unique grain color, UGC)图及其对应的晶粒尺寸分布图。每一种颜色代表一个晶粒。Cu-20Zn合金中的晶粒大部分为等轴的,绝大部分晶粒尺寸处于0.5到2.5 μm的范围内,平均晶粒尺寸为1.4 μm。同时,其内部出现了少量的异常长大的晶粒(3~4 μm),如图6(a)和(c)所示。这与图5中Cu-20Zn合金在退火的第3个阶段硬度略有下降的结果是一致的。相比之下,Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中的等轴晶粒分布的更加均匀细小且没有显著长大的晶粒,其平均晶粒尺寸为1.1 μm,如图6(b)和(d)所示。图7所示为Cu-20Zn和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金分别在300和340 ℃退火1 h的取向差分布图。Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中HAGBs分数(96.6%)要高于Cu-20Zn合金的(91.1%)。说明Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的再结晶过程进行的更加充分。同时可以看到两种合金取向差均在60°出现了峰值。这与大量的Σ3退火孪晶界出现有关。图8所示为Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金300 ℃退火1 h 的TEM像。晶粒内部出现了细长板条状相互平行的退火孪晶。Cu-20Zn和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中Σ3退火孪晶界分数分别为31.8% 和42.6%。退火孪晶形成的驱动力为分离新形成晶粒晶界总过剩能的降低。同时,层错能够为退火孪晶形成提供形核场所[38]。因此,层错能较低的Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金退火后组织中出现了更多的退火孪晶,从而其退火孪晶界分数要高于Cu-20Zn合金的。

图6 Cu-20Zn合金和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金300 ℃和340 ℃退火1 h UGC图和晶粒尺寸分布图
Fig. 6 Unique grain color map((a), (b)) and grain size distributions((c), (d)) of different alloys

图7 Cu-20Zn合金和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金300 ℃和340 ℃退火1 h取向差分布图
Fig. 7 Misorientation angles distributions of different alloys
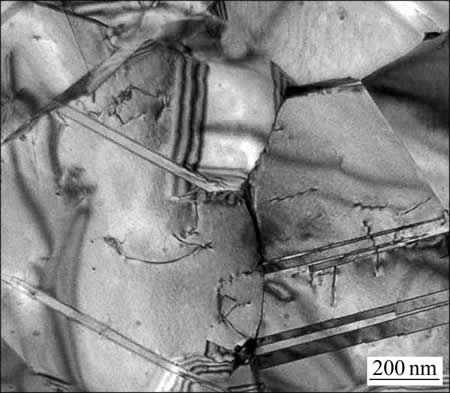
图8 Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金300 ℃退火1 h的TEM像
Fig. 8 TEM image of Cu-20Zn-1.2Si alloy annealed at 300 ℃ for 1 h
材料退火后的组织与其内部储能密切相关[37]。内核平均取向差(Kernel average misorientation, KAM)图能够反应出局部几何必须位错密度和局部储能。KAM图是基于计算图中任意一个给定点与其周围邻近点的平均取向差而得到的图[39],晶粒内部KAM值越高表示局部储能越高,反之亦然[40]。图9所示为Cu-20Zn和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金分别在300和340 ℃退火1 h的KAM图。可以看出Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金退火后的内部储能低于Cu-20Zn合金。表2列出了两种合金退火后的KAM分数、平均KAM值、位错密度以及单位体积内的储能。位错密度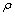 可由式(5)计算得到[41]:
可由式(5)计算得到[41]:
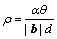 (5)
(5)
式中: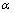 为与位错排列形状有关的常数,这里取
为与位错排列形状有关的常数,这里取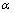 =3是由于其介于完全倾斜和完全扭曲之间。
=3是由于其介于完全倾斜和完全扭曲之间。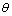 、b和d分别为平均KAM值、柏氏矢量和扫描步长。单位体积的储能可由式(6)计算得到:
、b和d分别为平均KAM值、柏氏矢量和扫描步长。单位体积的储能可由式(6)计算得到:
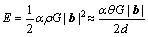 (6)
(6)
式中:G为剪切模量。这里G和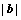 分别取为39 GPa和0.26 nm[42]。实验中所采用的扫描步长d=80 nm。从表2中可以看出:Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金内部的位错密度以及储能均低于Cu-20Zn合金的。层错能的降低使得变形后的Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金内部累积了更高的位错和孪晶密度,这使得Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的再结晶驱动力增大和形核场所增多,使得其再结晶晶粒尺寸更加细小[43]。同时已经形成的退火孪晶也会阻碍晶粒的长大[37-38]。退火孪晶界的界面能比传统的HAGBs界面能低一个数量级,因此退火孪晶界热稳定性更好。它们能够阻碍晶界的迁移从而阻碍晶粒的长大[37]。此外,因为Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金具有更大的再结晶驱动力,大部分储能在再结晶阶段释放了[43],其晶粒长大阶段的储能低于Cu-20Zn合金的,使得晶粒长大阶段的驱动力较小。此外,硅原子也会阻碍晶界迁移[36]。因此层错能较低的Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金再结晶晶粒尺寸更加细小均匀。
分别取为39 GPa和0.26 nm[42]。实验中所采用的扫描步长d=80 nm。从表2中可以看出:Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金内部的位错密度以及储能均低于Cu-20Zn合金的。层错能的降低使得变形后的Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金内部累积了更高的位错和孪晶密度,这使得Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的再结晶驱动力增大和形核场所增多,使得其再结晶晶粒尺寸更加细小[43]。同时已经形成的退火孪晶也会阻碍晶粒的长大[37-38]。退火孪晶界的界面能比传统的HAGBs界面能低一个数量级,因此退火孪晶界热稳定性更好。它们能够阻碍晶界的迁移从而阻碍晶粒的长大[37]。此外,因为Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金具有更大的再结晶驱动力,大部分储能在再结晶阶段释放了[43],其晶粒长大阶段的储能低于Cu-20Zn合金的,使得晶粒长大阶段的驱动力较小。此外,硅原子也会阻碍晶界迁移[36]。因此层错能较低的Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金再结晶晶粒尺寸更加细小均匀。

图9 Cu-20Zn合金300 ℃和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金340 ℃退火1 h的KAM图
Fig. 9 Kernel average misorientation map of Cu-20Zn alloy annealed at 300 ℃ for 1 h(a) and Cu-20Zn-1.2Si alloy annealed at 340 ℃ for 1 h(b)
表2 铜合金退火后的KAM分布、平均KAM、位错密度以及储能
Table 2 Kernel average misorientation distributions, dislocation density and stored energy of Cu alloys

图10(a)所示为Cu-20Zn和Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金在不同退火条件下的应力-应变曲线。从图10(a)中可以看出,在塑性差不多相等的情况下,层错能较低的Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的抗拉强度要比Cu-20Zn合金的高出100~300 MPa。图10(b)所示为两种合金的均匀伸长率(Uniform elongation, UE)与抗拉强度(Ultimate tensile strength, UTS)关系曲线。可以看出:在抗拉强度相同的情况下,Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的UE要比Cu-20Zn合金的高出2%~15%。Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金强度和塑性的综合力学性能要优于Cu-20Zn合金的。Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金优异的强度和塑性的综合力学性能原因可以归结为以下几点。就强度而言,强度的提升源于以下两点:1)退火后Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的晶粒尺寸(1.1 μm)比Cu-20Zn合金的晶粒尺寸(1.4 μm)细小。从经典的Hall-Petch公式可知晶粒尺寸越小,材料的强度越高[44-45];2) 层错能降低使得材料内部的形变和退火孪晶密度增加,它们会阻碍位错的运动,Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金需要在更大的外力作用下才能继续发生塑性变形[8,19,46]。众所周知,材料的UE是由材料加工硬化率决定的[35]。塑性的提升可归结为以下4点:1)层错能的降低使得作为动态回复机制的交滑移显著地受到抑制,从而Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的加工硬化率得到提高[35]。2)层错能的降低使得Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金组织中形成了大量的退火孪晶,它们能够为位错积累提供场所。此外,层错也能够与滑移的位错相互作用,因此提高了Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的加工硬化率[47-48]。3)Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中较高的HAGBs分数对塑性也有重要影响。HAGBs能够阻碍位错运动,使得位错在晶界处缠结和积累,从而提高Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的加工硬化率[49]。4)拉伸试验时,再结晶晶粒内部容易产生形变孪晶。这些形变孪晶不仅能够为位错累积提供充足的空间而且也能够提高加工硬化率,从而使得材料的塑性得到进一步提升[50-51]。因此,再结晶程度较高的Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金塑性要优于Cu-20Zn合金的。

图10 铜合金不同退火条件的工程应力-应变曲线以及均匀伸长率与抗拉强度之间的关系
Fig. 10 Typical engineering stress-strain curves of Cu alloys at different annealing conditions(a) and relationship between uniform elongation and ultimate tensile strength of Cu alloys at different annealing conditions(b)
3 结论
1) 经过不同程度的变形后,Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金强度均要高于Cu-20Zn合金的。这是因为加入的硅原子使得Cu-20Zn合金层错能降低,在塑性变形过程中,Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金中能够累积更多的位错以及孪晶。
2) 硅元素的加入使得Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的热稳定性得到提高。一方面,添加的硅原子与位错相互作用能够阻碍位错运动和晶界迁移;另一方面,硅元素的加入使得Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金的层错能降低,层错宽度变宽,不利于位错的运动。
3) 经过适当的退火处理后,Cu-20Zn-1.2Si合金表现出更加优异的强度和塑性的综合力学性能。这是其组织内部更加细小的晶粒,形变孪晶以及大量的退火孪晶和HAGBs的共同作用的结果。
REFERENCES
[1] WEN Hai-ming, TOPPING T D, ISHEIM D, SEIDMAN D N, LAVERNIA E J. Strengthening mechanisms in a high-strength bulk nanostructured Cu-Zn-Al alloy processed via cryomilling and spark plasma sintering[J]. Acta Mater, 2013, 61: 2769-2782.
[2] ZHAO Yong-hao, ZHU Yun-tian, LAVERNIA E J. Strategies for improving tensile ductility of bulk nanostructured materials[J]. Adv Eng Mater, 2010, 12: 769-778.
[3] VALIEV R Z, ISLAMGALIEV R K, ALEXANDROV I V. Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation[J]. Prog Mater Sci, 2000, 45: 103-189.
[4] 康志新, 彭勇辉, 赖晓明, 李元元, 赵海东, 张卫文. 剧塑性变形制备超细晶/纳米晶结构金属材料的研究现状和应用展望[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(4): 587-598.
KANG Zhi-xin, PENG Yong-hui, LAI Xiao-ming, LI Yuan-yuan, ZHAO Hai-dong, ZHANG Wei-wen. Researches status and application prospect of ultrafine grained and/or nano-crystalline metallic materials processed by severe plastic deformation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(4): 587-598.
[5] ZHU Yun-tian, LIAO Xiao-zhou. Nanostructured metals: Retaining ductility[J]. Nat Mater, 2004, 3: 351-352.
[6] 安祥海, 吴世丁, 张哲峰. 层错能对纳米晶Cu-Al合金微观结构、拉伸及疲劳性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2014, 50: 191-201.
AN Xiang-hai, WU Shi-ding, ZHANG Zhe-feng. Influence of stacking fault energy on the microstructures tensileand fatigue properties of nanostructured Cu-Al alloys[J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2014, 50: 191-201.
[7] GONG Yu-lan, WEN Cen-e, WU Xiao-xiang, REN Shi-ying, CHENG Lian-ping, ZHU Xin-kun. The influence of strain rate, deformation temperature and stacking fault energy on the mechanical properties of Cu alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2013, 583: 199-204.
[8] CHRISTIAN J W, MAHAJAN S. Deformation twinning[J]. Prog Mater Sci, 1995, 39: 1-157.
[9] 刘满平, 王 俊, 蒋婷慧, 吴振杰, 谢学峰, 刘 强. 高压扭转大塑性变形Al-Mg铝合金中的层错和形变孪晶[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(6): 1383-1392.
LIU Man-ping, WANG Jun, JIANG Ting-hui, WU Zheng-jie, XIE Xue-feng, LIU Qiang. Stacking faults and deformation twins in Al-Mg alloys subjected to high pressure torsion[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(6): 1383-1392.
[10] SAN Xing-yuan, LIANG Xiao-guang, CHENG Lian-ping, SHEN Li, ZHU Xin-kun. Effect of stacking fault energy on mechanical properties of ultrafine-grain Cu and Cu-Al alloy process by cold-rolling[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(4): 819-824.
[11] KANG D H, KIM T W. Mechanical behavior and microstructural evolution of commercially pure titanium in enhanced multi-pass equal channel angular pressing and cold extrusion[J]. Mater Des, 2010, 31: S54-S60.
[12] KAWASAKI M, AHN B, LANGDON T G. Effect of strain reversals on the processing of high-purity aluminum by high-pressure torsion[J]. J Mater Sci, 2010, 45: 4583-4893.
[13] JAMAATI R, TOROGHINEJAD M R. Effect of friction, annealing conditions and hardness on the bond strength of Al/Al strips produced by cold roll bonding process[J]. Mater Des, 2010, 31: 4508-4513.
[14] GONG Yu-lan, WEN Cen-e, LI Yun-cang, WU Xiao-xiang, CHENG Lian-ping, HAN X C, ZHU Xin-kun. Simultaneously enhanced strength and ductility of Cu-xGe alloys through manipulating the stacking fault energy (SFE)[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2013, 569: 144-149.
[15] 秦丽元, 连建设, 蒋恩臣, 刘中原. 不同结构纳米晶镍钴合金的力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(10): 2846-2850.
QIN Li-yuan, LIAN Jian-she, JIANG En-chen, LIU Zhong-yuan. Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline Ni-Co alloy with different microstructures[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(10): 2846-2850.
[16] ZHAO Yong-hao, LIAO Xiao-zhou, HORITA Z, LANGDON T G, ZHU Yun-tian. Determining the optimal stacking fault energy for achieving high ductility in ultrafine-grained Cu-Zn alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 493: 123-129.
[17] ZHAO Yong-hao, ZHU Yun-tian, LIAO Xiao-zhou, HORITA Z, LANGDON T G. Tailoring stacking fault energy for high ductility and high strength in ultrafine grained Cu and its alloy[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89: 121906-1-121906-3.
[18] AN Xiang-hai, LIN Q Y, WU Shi-ding, ZHANG Zhe-feng, FIGUEIREDO R B, GAO N, LANGDON T G. The influence of stacking fault energy on the mechanical properties of nanostructured Cu and Cu-Al alloys processed by high-pressure torsion[J]. Scr Mater, 2011, 64: 954-957.
[19] QU Shen, AN Xiang-hai, YANG Hua-Jie, HUANG C X, YANG G, ZANG Q S, WANG Z G, WU Shi-ding, ZHANG Zhe-feng. Microstructural evolutioin and mechanical properties of Cu-Al alloys subjected to equal channel angular pressing[J]. Acta Mater, 2009, 57: 1586-1601.
[20] SUN Pei-ling, ZHAO Yong-hao, COOLEY J C, KASSNER M E, HORITA Z, LANGDON T G, LAVERNIA E J, ZHU Yun-tian. Effect of stacking fault energy on strength and ductility of nanostructured alloys: An evaluation with minimum solution hardening[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2009, 525: 83-86.
[21] WANG Yin-min, CHEN Ming-wei, ZHOU Feng-hua, MA E. High tensile ductility in a nanostructured metal[J]. Nature, 2002, 419: 912-914.
[22] HUANG Xiao-xu, HANSEN N, TSUJI N. Hardening by annealing and softening by deformation in nanostructured metals[J]. Science, 2006, 312: 249-251.
[23] OISHI K, SASAKI I, OTANI J. Effect of silicon addition on grain refinement of copper alloys[J]. Mater Lett, 2003, 57: 2280-2286.
[24] DENANOT M F, VILLAIN J P. The stacking fault energy in Cu-Al-Zn alloys[J]. Phys Status Solid (a), 1971, 8: K125-K127.
[25] ZHANG Ye-xin, TAO Nai-rong, LU Ke. Mechanical properties and rolling behaviors of nano-grained copper with embedded nano-twin bundles[J]. Acta Mater, 2008, 56: 2429-2440.
[26] WAGNER C N J. Stacking faults by low-temperature cold work in copper and alpha brass[J]. Acta Metall, 1957, 5: 427-434.
[27] COHEN J B, WAGNER C N J. Determination of twin fault probabilities from the diffraction patterns of fcc metals and alloys[J]. J Appl Phys, 1962, 33: 2073-2077.
[28] ROHATGI A, VECCHIO K S, GRAY III G T. The influence of stacking fault energy on the mechanical behavior of Cu and Cu-Al alloys: Deformation twinning, work hardening, and dynamic recovery[J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2001, 32: 135-145.
[29]  , WEERTMAN J R. Dislocations, grain size and planar faults in nanostructured copper determined by high resolution X-ray diffraction and a new procedure of peak profile analysis[J]. Acta Mater, 1998, 46: 3693-3699.
, WEERTMAN J R. Dislocations, grain size and planar faults in nanostructured copper determined by high resolution X-ray diffraction and a new procedure of peak profile analysis[J]. Acta Mater, 1998, 46: 3693-3699.
[30] MEYERS M A,  , LUBARDA V A. The onset of twinning in metals: A constitutive description[J]. Acta Mater, 2001, 49: 4025-4039.
, LUBARDA V A. The onset of twinning in metals: A constitutive description[J]. Acta Mater, 2001, 49: 4025-4039.
[31] CUBICZA J, CHINH N Q, LABAR L J, HEGEDUS Z, LANGDON T G. Principles of self-annealing in silver processed by equal-channel angular pressing: The significance of a very low stacking fault energy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 527: 752-760.
[32] ZHANG Xiang-kai, YANG Xu-yue, CHEN Wei, QIN Jia, FOUSE J. Effects of rolling temperature and subsequent annealing on mechanical properties of ultra fine-grained Cu-Zn-Si alloy[J]. Mater Charact, 2015, 106: 100-107.
[33] NESTOROVIC S, MARKOVIC D. Influence of alloying on the annealing hardening effect in sintered copper alloys[J]. Mater Trans, 1999, 40: 222-224.
[34] HAMATANI D, MATSUDA K, KAWABATA T, UETANI Y, IKENO S. HRTEM study of α-phase in Cu-Zn-Si alloy[J]. Adv Mater Res, 2007, 15/17: 667-671.
[35] AN Xiang-hai, WU Shi-ding, ZHANG Zhe-feng, FIGUEIREDO R B, GAO N, LANGDON T G. Enhanced strength-ductility synergy in nanostructured Cu and Cu-Al alloys processed by high-pressure torsion and subsequent annealing[J]. Scr Mater, 2012, 66: 227-230.
[36] ZHANG Hong-wen, LU Ke, PIPPAN R, HUANG Xiao-xu, HANSEN N. Enhancement of strength and stability of nanostructured Ni by small amounts of solutes[J]. Scr Mater, 2011, 65: 481-484.
[37] HUMPHREYS F J, HATHERLY M. Recrystallization and related annealing phenomena[M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 2004: 1-658.
[38] XUE Peng, XIAO Bo-lü, MA Zong-yi. Enhanced strength and ductility of friction stir processed Cu-Al alloys with abundant twin boundaries[J]. Scr Mater, 2013, 68: 751-754.
[39] WRONSKI S, TARASIUK J, BACROIX B, WIERZBANOWSKI K, PAUL H. Microstructure heterogeneity after the ECAP process and its influence on recrystallization in aluminium[J]. Mater Charact, 2013, 78: 60-68.
[40] YI S B, SCHESTAKOW I, ZAEFFERER S. Twinning-related microstructural evolution during hot rolling and subsequent annealing of pure magnesium[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2009, 516: 58-64.
[41] TAKAYAMA Y, SZPUNAR J A. Stored energy and Taylor factor relation in an Al-Mg-Mn alloy sheet worked by continuous cyclic bending[J]. Mater Trans, 2004, 45: 2316-2325.
[42] KUMAR N K, ROY B, DAS J. Effect of twin spacing, dislocation density and crystallite size on the strength of nanostructured α-brass[J]. J Alloy Compd, 2015, 618: 139-145.
[43] AN Xiang-hai, QU Shen, WU Shi-ding, ZHANG Zhe-feng. Effects of stacking fault energy on the thermal stability and mechanical properties of nanostructured Cu-Al alloys during thermal annealing[J]. J Mater Res, 2011, 26: 407-415.
[44] HALL E O. The deformation and ageing of mild steel: Ⅲ. Discussion of results[J]. Proc Phys Soc B, 1951, 64: 747-753.
[45] PETCH N J. The cleavage strength of polycrystals[J]. J Iron Steel Inst, 1953, 174: 25-28.
[46] PANDE C S, RATH B B, IMAN M A. Effect of annealing twins on Hall-Petch relation in polycrystalline materials[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 367: 171-175.
[47] CHEN Xian-hua, LU Lei, LU Ke. Grain size dependence of tensile properties in ultrafine-grained Cu with nanoscale twins[J]. Scr Mater, 2011, 64: 311-314.
[48] LU Ke, LU Lei, SURESH S. Strengthening materials by engineering coherent internal boundaries at the nanoscale[J]. Science, 2009, 324: 349-352.
[49] YANG Deng-ke, HODSON P D, WEN Cen-e. Simultaneously enhanced strength and ductility of titanium via multimodal grain structure[J]. Scr Mater, 2010, 63: 941-944.
[50] WANG Z W, WANG Y B, LIAO Xiao-zhou, ZHAO Yong-hao, LAVERNIA E J, ZHU Yun-tian, HORITA Z, LANGDON T G. Influence of stacking fault energy on deformation mechanism and dislocation storage capacity in ultrafine-grained materials[J]. Scr Mater, 2009, 60: 52-55.
[51] BOUAZIZ O, ALLAIN S, SCOTT C. Effect of grain and twin boundaries on the hardening mechanisms of twinning-induced plasticity steels[J]. Scr Mater, 2008, 58: 484-487.
Effect of silicon on mechanical properties and annealing behavior of ultrafine grained brasses
ZHANG Xiang-kai1, YANG Xu-yue1, 2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Nonferrous Metal Oriented Advanced Structural Materials and Manufacturing Cooperative Innovation Center,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The effect of silicon on mechanical properties and annealing behavior of ultrafine-grained (UFG) brasses was investigated in Cu-20Zn and Cu-20Zn-1.2Si alloys by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), electron back scattered diffraction (EBSD) and tensile tests. These two brasses were rolled at cryogenic temperature (about -196 ℃) up to different rolling strains. The results show that the significant improvement of strength in Cu-20Zn-1.2Si alloy is attributed to the formation of fine grains and high densities of dislocations and deformation twins by decreasing the stacking fault energy (SFE). Thermal stability of Cu-20Zn-1.2Si alloy is enhanced due to the reductions of dislocation mobility and grain boundaries migration during annealing by decreasing of SFE and addition of Si. Fine grains, deformation twins and abundant annealing twins are introduced into Cu-20Zn-1.2Si alloy by decreasing the SFE, resulting in a superior strength and ductility combination.
Key words: Cu alloy; stack fault energy; mechanical property; twins; annealing behavior
Foundation item: Project(51174234) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2015-07-30; Accepted date: 2015-10-26
Corresponding author: YANG Xu-yue; Tel: +86-13873133470; E-mail: yangxuyue@csu.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51174234)
收稿日期:2015-02-09;修订日期:2015-11-02
通信作者:杨续跃,教授,博士;电话:13873133470;E-mail: yangxuyue@csu.edu.cn