文章编号:1004-0609(2015)04-0938-07
层错能对电沉积纳米晶Ni-Fe合金显微组织与力学性能的影响
温建程1,戴品强1, 2
(1. 福州大学 材料科学与工程学院,福州 350108;
2. 福建工程学院 材料科学与工程学院,福州 350108)
摘 要:采用脉冲电沉积方法,通过改变Fe含量获得不同层错能的纳米晶Ni-Fe合金。采用X射线衍射(XRD)、透射电镜(TEM) 与拉伸试验研究纳米晶Ni-Fe合金的显微组织和力学性能。结果表明:制备的Ni-Fe合金均为面心立方结构的单相固溶体,平均晶粒尺寸为12~25 nm,且平均晶粒尺寸随层错能的减小而减小。纳米晶Ni-Fe合金抗拉强度为1361~1978 MPa,断裂伸长率为9.3%~13.2%,纳米晶Ni-Fe合金的抗拉强度和断裂伸长率均随层错能的减小而增加。合金抗拉强度的增加是细晶强化作用的结果。随着Ni-Fe合金层错能的降低,加工硬化率提高,塑性失稳被推迟,从而获得较高的塑性。
关键词:Ni-Fe合金;纳米晶;力学性能;层错能
中图分类号:TG174.4 文献标志码:A
Effect of stacking fault energy on microstructures and mechanical properties of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni-Fe alloy
WEN Jian-cheng1, DAI Pin-qiang1, 2
(1. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou 350108, China;
2. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Fujian University of Technology, Fuzhou 350108, China)
Abstract: Nanocrystalline Ni-Fe alloys with different stacking fault energies were prepared by changing Fe content using pulse electrodeposition method. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the nanocrystalline Ni-Fe alloys were characterized by XRD, TEM and tensile testing. The results indicate that all the prepared Ni-Fe alloys are face-centered cubic structure, single-phase solid solution with the average grain size in the range of 12-25 nm, and the average grain size decreases with decreasing the stacking fault energy. The ultimate tension strength of the nanocrystalline Ni-Fe alloys is in the range of 1361-1978 MPa and the elongation to failure is in the range of 9.3%-13.2%. Both the ultimate tension strength and the elongation to failure increase with decreasing stacking fault energy. The increase of tensile strength is due to the fine-grain strengthening. For Ni-Fe alloy, with decreasing the stacking fault energy, the work hardening rate increases, and the plastic instability is delayed, consequently higher plasticity is gained.
Key words: Ni-Fe alloy; nanocrystalline; mechanical property; stacking fault energy
纳米晶金属材料由于具有很高的强度,在过去的20年里受到大量研究者的关注。根据Hall-Petch关系,普遍认为纳米晶金属材料强度和硬度的提高来源于晶粒尺寸的减小(小于100 nm)[1]。然而,这往往以塑性的降低为代价。以往的研究结果表明,由于占有较大体积分数的纳米结构晶界会约束晶粒内部位错的产生和存储,使得纳米晶金属材料的塑性比同类粗晶材料的低得多,甚至低于5%[2],这严重制约了纳米晶金属材料的实际应用。因此,提高纳米晶金属材料的塑性一直是纳米材料研究的热点问题。目前已经发现一些提高纳米晶金属材料塑性的途径,如双峰晶粒尺寸分布的纳米晶材料[3]、引入纳米孪晶[4]和宽晶粒尺寸分布纳米晶材料[5]等。而近期有研究指出,塑性差并不是纳米晶金属材料的本质特征[6],纳米晶金属材料在保持高强度(约2 GPa)的同时也可能获得高塑性(大于10%)[7-8]。这些高塑性的纳米晶合金的共同特点是具有高的加工硬化率,塑性失稳被推迟,从而提高了纳米晶金属材料的塑性[9-10]。提高纳米晶合金的加工硬化率是提高合金塑性的一条有效途径。
层错能是影响金属材料变形行为的一个非常重要的参数[11]。近几年来,有学者研究层错能对纳米晶Cu-Zn合金和Cu-Al合金力学性能的影响,结果表明层错能的降低能同时提高强度和塑性[12-16]。被广泛认可的原因是层错能的降低能够提高位错密度和孪晶密度,促使晶界产生不全位错,并且提高位错的存储能力,从而提高加工硬化能力和塑性[17-19]。但上述研究都只局限于纳米晶Cu合金(Cu-Zn、Cu-Al、Cu-Ge),同时Cu与Zn、Al原子半径相差较大,难以区分固溶强化对于合金强度的影响。并且其纳米晶材料的制备方法也都只局限在剧烈塑性变形(SPD),包括高压扭转(HPT)[20]、等径角挤压(ECAP)[21]、冷轧[14]等。因此,层错能与强度、塑性关系的规律在其他合金体系中(如传统的Ni基合金系)是否一致是一个值得探索的问题。SUN等[22]通过高压扭转(HPT)制备了不同层错能的纳米晶Ni-40%Co和Ni-65%Co(质量分数),研究层错能对其力学性能的影响,得到了类似的结论,即层错能的降低同时提高了纳米晶的强度和塑性。然而,SUN等采用的剧烈塑性变形制备方法是一种自上而下的制备方法,会不可避免地造成纳米晶金属材料位错密度的极大增加,和真实的纳米晶金属材料有一定差距。由于电沉积方法能够制备全致密无缺陷的纳米晶块体材料[10],同时Ni和Fe原子半径相差较小,能最大程度地减小固溶强化作用的影响[18]。因此,本文作者采用脉冲电沉积方法制备一系列不同成分的纳米晶Ni-Fe合金,获得不同层错能的合金,研究层错能对纳米晶Ni-Fe合金组织结构和力学性能的影响。
1 实验
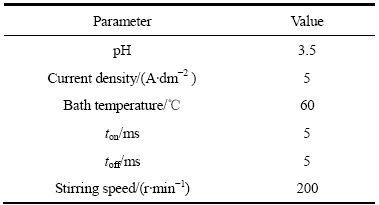
采用脉冲电沉积方法制备晶粒尺寸为纳米尺度的Ni-Fe合金。镀液的基本组成为氨基磺酸镍、硫酸亚铁、氯化镍、硼酸、柠檬酸钠、抗坏血酸、十二烷基硫酸钠和糖精。通过调整镀液中Ni2+与Fe2+的摩尔比改变Ni-Fe合金中的Fe含量。电沉积工艺参数如表1所列。阳极选用高纯低硫镍板(纯度>99.9%),阴极选用经SiC砂纸打磨的不锈钢片,浸液阴阳极面积比为1:4。电沉积过程中使用氨基磺酸溶液和碱式碳酸镍溶液稳定镀液的pH值。沉积5 h后,采用机械法剥离镀层,镀层厚度约为200 μm。
表1 电沉积纳米晶Ni-Fe合金工艺参数
Table 1 Technological parameters for electrodeposited nano- crystalline Ni-Fe alloys
采用扫描电子显微镜(日立S-3400Ⅱ)附带的能谱仪测量Ni-Fe合金的成分。采用X射线衍射仪(D8-ADVANCE)分析Ni-Fe合金镀层的显微组织,衍射条件为铜靶,扣除仪器宽化后,根据谢乐公式计算平均晶粒尺寸。不同成分的Ni-Fe合金层错能数值可由文献[23]中成分与层错能关系曲线得到。采用线切割机从Ni-Fe合金镀层上切割拉伸试样,试样标距尺寸为10 mm×6 mm,厚200 μm。在微机控制的电子万能试验机(CMT-6104)上进行室温下的单向拉伸试验,应变速率为1×10-3 s-1。采用上述扫描电子显微镜观察拉伸断口形貌。采用透射电子显微镜(JEOL,JEM2100)对Ni-Fe合金的显微组织进行观察,电子加速电压为200 kV。透镜样品采用双喷电解仪进行减薄,所用的电解液为15 mL高氯酸+285 mL乙醇溶液,电解电压为50 V,电解温度为-20~-30 ℃。采用透射电子显微镜暗场像统计晶粒尺寸分布。
2 实验结果
2.1 纳米晶Ni-Fe合金的显微组织
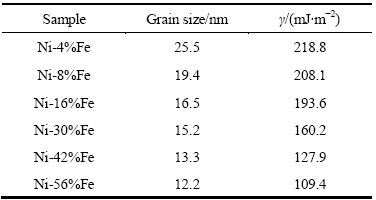
图1所示为所制备的电沉积Ni-Fe合金的XRD谱。由图1可看出,所制备的电沉积Ni-Fe合金都为单相面心立方结构,表明Fe原子固溶进入Ni原子的晶格点阵中,形成(γ-Fe, Ni)置换固溶体。表2所列为电沉积Ni-Fe合金的晶粒尺寸和层错能数值。由表2可见,随合金Fe含量的增加,层错能降低。随着层错能的减小,(111)晶面的衍射峰相对强度逐渐增强,同时(200)晶面的衍射峰相对强度逐渐减弱。同时,对应晶面的衍射峰峰位朝低角端逐步漂移,可能是因为随着合金中Fe原子的增加,γ相发生了晶格膨胀。由表2还可知,电沉积Ni-Fe合金的平均晶粒尺寸均为纳米尺度,为12~25 nm,并且随着合金层错能的减小,晶粒尺寸也随之减小。因为6种成分试样的制备工艺完全一致,只改变了Fe2+的浓度变化,所以可以排除工艺参数对合金晶粒尺寸的影响,可以认为晶粒尺寸的变化完全由合金层错能变化(成分变化)所引起。LI等[24]在研究电沉积Ni-Fe合金工艺时也发现了类似的规律,即晶粒尺寸随着层错能的变化而强烈变化。这个规律也存在于其他电沉积合金体系中,如Ni-Co合金[25]和Ni-W合金[26]等。由层错能引起的晶粒尺寸变化得到了许多研究的证实[11-16],但其变化的机理还不是很清楚,需要作进一步的探索。
图2(a),(c),(e)所示分别为纳米晶Ni-8%Fe、Ni-16%Fe、Ni-42%Fe的TEM明场像。可以观察到,随着合金中铁含量的增加,层错能的减小,晶粒尺寸也减小,这与XRD测量结果一致。图2(a),(c),(e)右上角所示为同成分合金的选区电子衍射花样,其呈现连续的环状,进一步表明电沉积Ni-Fe合金的晶粒为纳米级。图2(b),(d),(f)所示分别为对应纳米晶Ni-Fe合金的晶粒尺寸统计分布。由晶粒尺寸统计结果计算出的Ni-8%Fe、Ni-16%Fe、Ni-42%Fe的平均晶粒尺寸分别为22.9、18.1、13.9 nm,此数值都稍大于同成分下采用XRD方法所测量的晶粒尺寸(1~3 nm)。
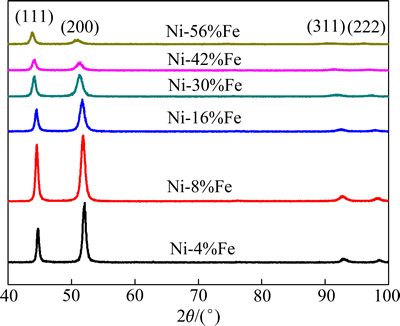
图1 纳米晶Ni-Fe合金的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of nanocrystalline Ni-Fe alloys
表2 纳米晶Ni-Fe合金试样的晶粒尺寸和层错能
Table 2 Stacking fault energies (γ) and grain sizes of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni-Fe alloys
2.2 纳米晶Ni-Fe合金的力学性能
图3(a)所示为合金的工程应力-应变曲线。从图3(a)中可见,所制备的纳米晶Ni-Fe合金表现出高强度和良好的塑性,强度为1361~1978 MPa,断裂伸长率均在9%以上。各成分纳米晶Ni-Fe合金均呈现典型无制备缺陷纳米晶塑性拉伸曲线,即存在拉伸曲线的3个特征阶段:1) 塑性变形初期表现出的应变硬化阶段;2) 应变硬化后出现总应变量为1%~2%的恒流变应力下的塑性变形阶段;3) 塑性变形阶段后发生塑性失稳断裂。图3(b)所示为纳米晶Ni-Fe合金抗拉强度随层错能变化曲线,从图3(b)中可看出,抗拉强度随着层错能的减小而增加。由于Fe和Ni原子半径相差较小,固溶强化作用较小[18],强度的提高主要来自层错能的减小引起的细晶强化作用。图3(c)所示为纳米晶Ni-Fe合金断裂伸长率随层错能变化的曲线。从图3(c)可见,断裂伸长率整体上随层错能的增加而增大,断裂伸长率从9%增加到13%。在纳米晶Ni-Co合金中也发现了同样的现象,强度和塑性随着层错能的减小而增加[7]。通过剧烈塑性变形制备的纳米晶Cu-Al、Cu-Zn合金体系中,其层错能的降低引起强度和塑性的同时提高[11-16, 20-22]。本研究结果表明在电沉积纳米晶Ni-Fe合金中也存在类似的强度、塑性与层错能的关系。
2.3 纳米晶Ni-Fe合金的拉伸断口形貌
图4所示为纳米晶Ni-Fe合金拉伸断口的SEM像,由于各成分Ni-Fe合金拉伸断口形貌较为相似,这里只选择纳米晶Ni-4%Fe、Ni-16%Fe、Ni-30%Fe、Ni-42%Fe合金断口为代表。由图4中可见,纳米晶Ni-Fe合金断口表面均呈现韧性断裂的韧窝特征,且存在不同程度的颈缩和剪切带。事实上,颈缩和剪切带是局部变形失稳的特征。由图4(a)和(e)可看出,层错能较低的纳米晶Ni-Fe合金,其颈缩量比层错能高的合金的小,表明其塑性失稳较后者轻微。从图4(b)~(d)和(f)可看出,随着合金中层错能降低、晶粒尺寸减小,其韧窝尺寸也由大变小,由深变浅。这也证实了文献[27]中韧窝尺寸与晶粒大小的关系,韧窝尺寸随晶粒尺寸的减小而减小。
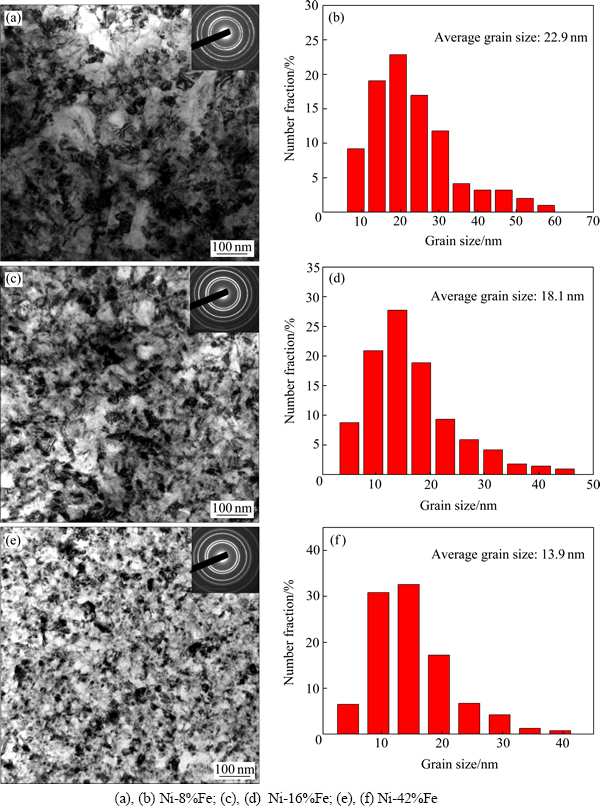
图2 纳米晶Ni-Fe合金的TEM明场像和对应晶粒尺寸统计分布
Fig. 2 Bright field TEM images and statistical distribution of grain size for nanocrystalline Ni-Fe alloys
3 分析与讨论
由以上的实验结果可知,制备的纳米晶Ni-Fe合金,由于其合金化程度不同,其层错能也不同,层错能随Fe含量的增加而减小。图5所示为对应含4%Fe和42%Fe合金的加工硬化率曲线,由图5中可看出,含42%Fe合金的加工硬化率明显大于含4%Fe合金的,塑性失稳被大大推迟。断口形貌观察结果(见图4(a)和(e))也证实,含42%Fe合金的断口形貌颈缩量和剪切带明显小于含4%Fe合金的,即低层错能合金的塑性失稳和非均匀变形明显小于高层错能的纳米晶Ni-Fe合金的,从而具有较高的塑性。
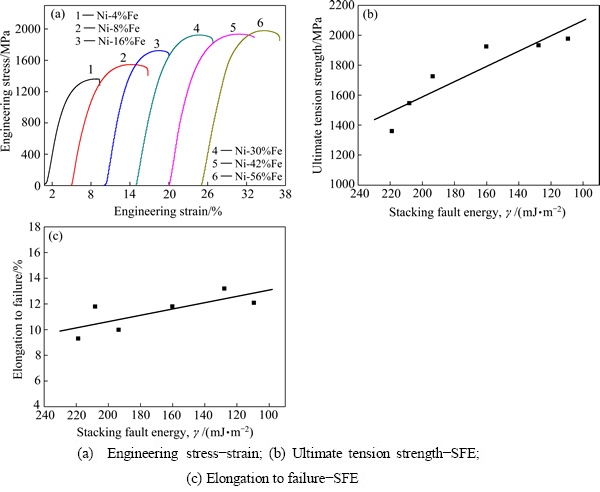
图3 电沉积纳米晶Ni-Fe合金的工程应力-应变曲线及其强度、伸长率与层错能的关系
Fig. 3 Engineering stress-strain curves of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni-Fe alloys and relationships among strength, elongation and stacking fault energy(SFE)
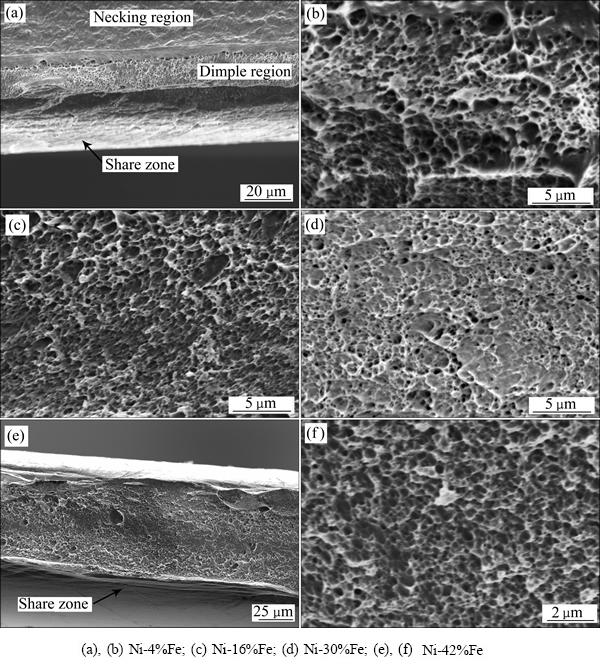
图4 纳米晶Ni-Fe合金拉伸断口的SEM像
Fig. 4 SEM images of tension fracture of nanocrystalline Ni-Fe alloys
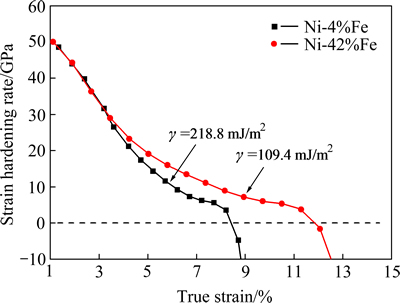
图5 纳米晶Ni-Fe合金加工硬化率图
Fig. 5 Work hardening rates of nanocrystalline Ni-Fe alloys
层错能的降低,使得高Fe合金加工硬化率高于低Fe合金,具有较好的塑性。在传统的粗晶金属材料中,合金化能够降低金属材料的层错能,并在塑性变形中阻碍螺型位错的交滑移,从而导致高的加工硬化率,最终影响材料的性能。EDALATI等[28]、WANG等[19]和ZHAO等[12]研究表明在纳米晶材料中也不例外,即合金化会导致层错能的降低,并改变材料塑性变形机制,提高加工硬化率。对于晶粒尺寸约为20 nm的纳米晶材料,晶界发射不全位错是其塑性变形的主要形式,这已经得到了分子动力学模拟[29]和TEM观察[30]的证实。但SWYGENHOVEN等[17]和YIP等[31]通过分子动力学模拟也发现,材料层错能的变化会导致纳米晶内位错运动的增加。层错能对于纳米晶材料内位错的产生有重要影响,由于位错分裂距离依赖于层错能的变化。对于低层错能的材料,具有更大的位错分裂距离,所以由不全位错主导了晶粒活动[29]。而WANG等[19]更进一步通过实验证明层错能的降低能够促进晶界发射不全位错和提高位错的存储能力,并最终提高塑性。ZHAO等[12]通过剧烈塑性变形(SPD) 制备了不同层错能的纳米晶铜锌合金(Cu, Cu-10%Zn, Cu-30%Zn),结果表明低的层错能能提高合金塑性,且存在最佳的层错能达到最优的塑性和强度。秦丽元等[32]研究了不同层错能的Ni-Co合金力学性能,也得出了类似结果,其通过电沉积制备了纳米晶Ni-49.2%Co和Ni-66.7%Co合金,研究发现Co元素的引入降低了层错能,提高其加工硬化能力,使塑性明显提高。通过合金化降低层错能,能够提高加工硬化率[18-19, 22]。而高的加工硬化率能够推迟塑性失稳和减少非均匀变形,从而有利于提高塑性[33]。
综上所述,纳米晶Ni-Fe合金层错能的降低,能够提高加工硬化率。加工硬化率的提高大大推迟了塑性失稳,从而获得了较高的塑性,即随着层错能的降低,塑性随之提高。
4 结论
1) 通过脉冲电沉积制备了不同Fe含量(4%~56%)的纳米晶Ni-Fe合金,其层错能随Fe含量的增加而降低。纳米晶Ni-Fe合金的平均晶粒尺寸随着层错能的降低而减小。
2) 纳米晶Ni-Fe合金的强度和塑性均随层错能的降低而增加,抗拉强度为1361~1978 MPa,断裂伸长率为9.3%~13.2%。
3) 随着层错能的降低,纳米晶Ni-Fe合金强度的增加是由于细晶强化作用的结果。同时层错能的降低使得加工硬化率提高,塑性失稳被推迟,从而具有较高的塑性。
REFERENCES
[1] Gleiter H. Nanocrystalline materials[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 1989, 33(4): 223-315.
[2] LI H, Jiang F, Ni S, LI L, SHA G, LIAO X. Mechanical behaviors of as-deposited and annealed nanostructured Ni-Fe alloys[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 65(1): 1-4.
[3] WANG Y, CHEN M, ZHOU F, MA E. High tensile ductility in a nanostructured metal[J]. Nature, 2002, 419(6910): 912-915.
[4] SHEN Y F, LU L, LU Q H, JIN Z H, LU K. Tensile properties of copper with nano-scale twins[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 52(10): 989-994.
[5] XU W C, DAI P Q. Microstructures and mechanical properties of electro-deposited nanocrystalline Ni with broad grain size distribution[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(12): 2075-2079.
[6] LI H, LIAW P K, CHOO H, TABACHNIKOVA E D, PODOLSKIY A V, SMIRNOV S N. Temperature-dependent mechanical behavior of a nanostructured Ni-Fe alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 493(1): 93-96.
[7] XU W, DAI P, WU X. Effect of stress-induced grain growth during room temperature tensile deformation on ductility in nanocrystalline metals[J]. Bulletin of Materials Science, 2010, 33(5): 561-568.
[8] MATSUI I, TAKIGAWA Y, UESUGI T, HIGASHI K. Effect of orientation on tensile ductility of electrodeposited bulk nanocrystalline Ni-W alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 578: 318-322.
[9] WANG Y M, MA E. Strain hardening, strain rate sensitivity, and ductility of nanostructured metals[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 375: 46-52.
[10] MEYERS M A, MISHRA A, BENSON D J. Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2006, 51(4): 427-556.
[11] ZHANG Y, TAO N R, LU K. Effects of stacking fault energy, strain rate and temperature on microstructure and strength of nanostructured Cu-Al alloys subjected to plastic deformation[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(15): 6048-6058.
[12] ZHAO Y H, LIAO X Z, HORITA Z, LANGDON T G, ZHU Y T. Determining the optimal stacking fault energy for achieving high ductility in ultrafine-grained Cu-Zn alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 493: 123-129.
[13] JAMAATI R, TOROGHINEJAD M R. Effect of stacking fault energy on mechanical properties of nanostructured FCC materials processed by the ARB process[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 606: 443-450.
[14] SAN X Y, LIANG X G, CHEN L P, XIA Z L, ZHU X K. Influence of stacking fault energy on the mechanical properties in cold-rolling Cu and Cu-Ge alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 7867-7870.
[15] GONG Y L, WEN C E, LI Y C, REN S Y, CHENG L P, ZHU X K. Simultaneously enhanced strength and ductility of Cu-xGe alloys through manipulating the stacking fault energy (SFE)[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 569: 144-149.
[16] SAN Xing-yuan, LIANG Xiao-guang, CHENG Lian-pin, SHEN Li, ZHU Xin-kun. Effect of stacking fault energy on mechanical properties of ultrafine-grain Cu and Cu-Al alloy processed by cold-rolling[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(4): 819-824.
[17] SWYGENHOVEN H, DERLET P M,  . Stacking fault energies and slip in nanocrystalline metals[J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3(6): 399-403.
. Stacking fault energies and slip in nanocrystalline metals[J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3(6): 399-403.
[18] LI H, EBRAHIMI F, CHOO H, LIAW P K. Grain size dependence of tensile behavior in nanocrystalline Ni-Fe alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2006, 41(22): 7636-7642.
[19] WANG Z W, WANG Y B, LIAO X Z, ZHAO Y H, LAVERNIA E J, ZHU Y H, HORITA Z, LANGDON T G. Influence of stacking fault energy on deformation mechanism and dislocation storage capacity in ultrafine-grained materials[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2009, 60(1): 52-55.
[20] AN X H, LIN Q Y, WU S D, ZHANG Z F, FIGUEIREDO R B, GAO N, LANGDON T G. The influence of stacking fault energy on the mechanical properties of nanostructured Cu and Cu-Al alloys processed by high-pressure torsion[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 64(10): 954-957.
[21] HUANG C X, HU W, YANG G, ZHANG Z F, WU S D, WANG Q Y, GOTTSTEIN G. The effect of stacking fault energy on equilibrium grain size and tensile properties of nanostructured copper and copper-aluminum alloys processed by equal channel angular pressing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 556: 638-647.
[22] SUN P L, ZHAO Y H, COOLEY J C, KASSNER M E, HORITA Z, LANGDON T G, LAVERNIA E J, ZHU Y T. Effect of stacking fault energy on strength and ductility of nanostructured alloys: An evaluation with minimum solution hardening[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 525: 83-86.
[23] SCHRAMM R E, REED R P. Stacking fault energies of FCC Fe-Ni alloys by X-ray diffraction line profile analysis[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1976, 7(3): 359-363.
[24] LI H, EBRAHIMI F. Synthesis and characterization of electrodeposited nanocrystalline nickel-iron alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 347: 93-101.
[25] 许伟长, 戴品强, 郑耀东. 钴含量对电沉积纳米晶镍钴合金组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(1): 92-99.
XU Wei-chang, DAI Pin-qiang, ZHENG Yao-dong. Effect of Co content on structures and mechanical properties of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni-Co alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(1): 92-99.
[26] DETOR A J, SCHUH C A. Tailoring and patterning the grain size of nanocrystalline alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(1): 371-379.
[27] KUMAR K S, SURESH S, CHISHOLM M F, HORTON J A, WANG P. Deformation of electrodeposited nanocrystalline nickel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(2): 387-405.
[28] EDALATI K, AKAMA D, NISHIO A, LEE S, YONENAGA Y, CUBERO J, HORIYA Z. Influence of dislocation-solute atom interactions and stacking fault energy on grain size of single-phase alloys after severe plastic deformation using high-pressure torsion[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 69: 68-77.
[29] YAMAKOV V, WOLF D, PHILLPOT S R, MUKHERJEE A K, GLRITER H. Deformation-mechanism map for nanocrystalline metals by molecular-dynamics simulation[J]. Nature Materials, 2003, 3(1): 43-47.
[30] ZHANG X Y, WU X L, ZHU A W. Growth of deformation twins in room-temperature rolled nanocrystalline nickel[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 94(12): 121907.
[31] YIP S. Nanocrystalline metals: Mapping plasticity[J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3(1): 11-12.
[32] 秦丽元, 连建设, 蒋恩臣, 刘中原. 不同结构纳米晶镍钴合金的力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(10): 2846-2850.
QIN Li-yuan, LIAN Jian-she, JIANG En-chen, LIU Zhong-yuan. Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline Ni-Co alloy with different microstructures[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(10): 2846-2850.
[33] ZHU Y T, LIAO X. Nanostructured metals: Retaining ductility[J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3(6): 351-352.
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:福建省自然科学基金资助项目(2012J01202);福建省教育厅重点项目(JA11179)
收稿日期:2014-08-11;修订日期:2014-11-30
通信作者:戴品强,教授,博士;电话:13860693956;E-mail: pqdai@126.com