文章编号:1004-0609(2010)09-1665-06
AZ31B镁合金表面激光熔覆Cu-Ni合金层
崔泽琴1, 2, 吴宏亮1, 王文先1, 2, 许并社1, 2
(1. 太原理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,太原 030024;
2. 太原理工大学 新材料界面科学与工程教育部重点实验室,太原 030024)
摘 要:针对镁合金表面耐磨性和耐蚀性差的问题,利用横流CO2激光器在AZ31B镁合金表面激光熔覆Cu-Ni合金层,并利用光学显微镜(OM)、扫描电镜(SEM)和能谱分析仪(EDS)分析熔覆层与基体的结合界面特征以及显微组织和成分分布情况,测试合金层的显微硬度和耐蚀性。结果表明:合金层与基体结合良好,缺陷较少,但局部存在不均匀的Cu-Ni富集区,且在其边缘区域的枝晶间均匀分布着1~1.5 ?m的十字状Laves相;合金层的硬度分布比较均匀,约为75HV0.05,明显高于基体的显微硬度45HV0.05;Cu-Ni合金层比AZ31B镁合金基体的腐蚀电位正移317 mV,腐蚀电流降低78 mA/cm2,耐蚀性也得到较大改善。
关键词:AZ31B镁合金;Cu-Ni合金层;激光熔覆;耐磨性;耐蚀性
中图分类号:TG 174.44 文献标志码:A
Laser cladding Cu-Ni alloy layer on AZ31B magnesium alloy
CUI Ze-qin1, 2, WU Hong-liang1, WANG Wen-xian1,2, XU Bing-she1,2
(1. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Interface Science and Engineering in Advanced Materials of Ministry of Education,
Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China)
Abstract: To improve the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the surface of magnesium alloy, the laser alloying experiment was carried out on the AZ31B magnesium alloy with pre-placed Cu-Ni powder using transverse flow CO2 laser. The microstructures, interface features and composition distribution of laser cladding layer were studied through OM, SEM and EDS. The results show that the Cu-Ni cladding layer and the substrate achieve a good metallurgical bonding without obvious defects. But there is uneven local Cu-Ni-rich region, and cross-like Laves phases with size of 1-1.5 μm evenly distribute between dendrites and in their edge regions. The microhardness of Cu-Ni cladding layer is more evenly distributed, about 75HV0.05, significantly higher than the matrix hardness (45HV0.05). Compared with AZ31B magnesium alloy, the corrosion potential of Cu-Ni alloy layer is shifted by 317 mV and corrosion current is reduced by 78 mA/cm2.
Key words: AZ31B magnesium alloy; Cu-Ni alloy layer; laser cladding; wear resistance; corrosion resistance
由于轻质高强易回收的优点,镁合金材料被誉为“21世纪最具发展前途的绿色工程结构材料”,因此,其在汽车及航空航天领域得到了广泛的应用[1]。但是,镁合金表面耐磨、耐蚀性能较差,这成为限制镁合金广泛应用的瓶颈[2]。因此,如何提高镁合金的耐磨、耐腐蚀及耐热等综合性能已成为当今镁合金材料研究和发展的重要课题。有效的途径之一是对镁合金表面进行表面改性处理,在基体材料的表面形成相应的保护层[3]。
目前,在镁合金表面改性方面开展的研究工作主要有扩渗合金化、气相沉积涂层、激光处理、金属镀层、阳极氧化和化学转化膜等方法[4-9]。其中,激光处理方法因其独特的优势已开始用于提高镁合金表面性能的研究。该方法包括激光表面重熔、激光合金化和激光熔覆等[10-14]。而关于镁合金表面激光熔覆的研究相对较多。VOLOVITCH等[13]通过激光表面熔覆Al-Si合金粉末,发现腐蚀电位正移了300 mV,腐蚀电流比基材低2个数量级,耐蚀性能有所提高。GAO等[14]利用宽带激光熔覆技术在AZ91HP镁合金表面熔覆Al-Cu粉末,试验发现熔覆层组织主要由Mg17Al12和AlCu4组成,硬度是基体的2.75倍,摩擦体积减少了85%,腐蚀电流降低了2个数量级,腐蚀电压提高了348 mV。这些试验表明,在镁合金表面形成适当的金属间化合物是提高耐腐蚀性的有效方法。
目前的研究报道多集中于Al基强化层、Cu基强化层以及陶瓷粉末强化层,而利用Ni基合金粉末来提高镁合金表面性能的研究还很少见。本研究采用质量比为1?1的Ni基和Cu基混合粉末进行镁合金激光表面熔覆,以求改善镁合金表面的耐磨、耐蚀性。
1 实验
试验基体材料选用变形镁合金AZ31B,其化学成分如表1所示。试样尺寸为180 mm×60 mm×10 mm。熔覆层材料选用具有很好的熔覆性,良好的韧性、耐蚀性、耐磨性和抗氧化性的镍基自熔合金粉末Ni60和纯度为99.9%的Cu粉的混合粉末,其质量比为1?1。Ni60粉末的成分如表2所列。
表 1 AZ31B镁合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of AZ31B (mass fraction, %)

表2 Ni60合金粉末的化学成分
Table 2 Chemical composition of Ni60 alloy powder(mass fraction, %)

试验前,用粗砂纸去除镁合金板表面氧化膜,之后用丙酮清洗,去除油污。试验采用预置粉末法,熔覆层厚度约为1 mm。激光熔覆利用5 kW横流CO2激光器进行,光斑直径为3 mm,焦距为+10 mm,试验过程中采用氩气保护,与激光束成45?,保护气流量为15 L/min。为使熔覆层表面成型良好,每道熔覆保持30%的搭接率,在下一次激光处理时,要冷却足够的时间使前一道的温度降至室温。试验所用工艺参数:激光功率1 500 W,扫描速度360 mm/min。激光熔覆层与基体结合界面特征及微观组织形貌通过CMM-20E型光学显微镜、JSM-6700F冷场发射电子显微镜 (SEM)及能谱仪(EDS)进行观察;通过HVS-1000A显微硬度计测试其硬度,所加载荷为0.49N,加载时间为15 s;采用PS-168A型电化学测量系统进行Cu-Ni熔覆层和AZ31B母材的电化学腐蚀性能试验,腐蚀介质为3.5%(质量分数)的NaCl(pH=7)溶液,测试面积为1 cm2,极化试验扫描速度为2 mV/s。
2 结果与分析
2.1 显微组织分析
图1所示为熔覆层的低倍扫描电镜像。由图1可以看出,合金层厚度约为0.6 mm,合金层分布较均匀。
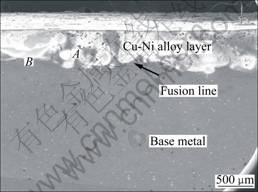
图1 激光熔覆Cu-Ni合金层的SEM像
Fig.1 SEM image of laser cladding Cu-Ni layer
对合金层各区域进行放大后,其显微组织形貌如图2所示。图2(a)、(b)、(c)所示分别为熔覆层上部、中部和基体结合界面的显微组织。由图2(a)可看出,合金层上部形成了细小的等轴晶和部分短小的树枝晶。这主要是由于激光能量集中,加热速度快,合金层表面冷却凝固速度快而形成的。由于成分过冷度的增大,界面上凸起部分能够伸入液体内部较长的距离,并向周围排溶质,于是在横向也产生了成分过冷,就从主干上长出了短小的二次横枝,但由于主干间距较小,就形成了定向生长很强烈的胞状树枝晶(见图2(b))。
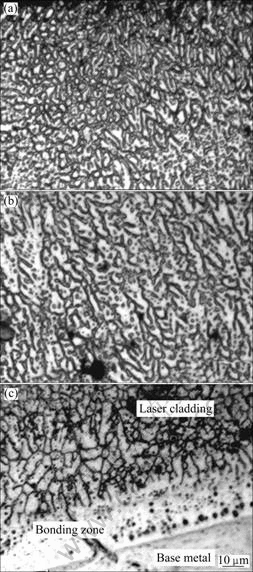
图2 Cu-Ni合金层的显微组织
Fig.2 Microstructures of Cu-Ni layer: (a) Top; (b) Middle; (c) Bonding interface
由图2(c)可看出,界面处形成了一层厚约25 ?m的熔合区,以平面晶态形式生长,熔合区上部以胞状晶为主,主要是由于镁合金导热快,熔合区位置与基体之间温度梯度大,而结晶速度小,成分过冷接近于零。所以,平面晶得到发展,随着远离熔化边界,温度梯度变小,结晶速度逐渐增大,产生了较小的成分过冷,便出现了胞状结晶。
在扫描电镜下还观察到合金层局部区域出现了Cu-Ni富集区,如图1中的A区,对其放大后的SEM像如图3所示。并对1区进行EDS分析,其主要成分如表3所列。分析出现Cu-Ni富集区的原因主要是因为镁合金基体与合金粉末的密度和熔点等物理性能差异太大。由图3可看出,沿着富集区的边界,枝晶比较明显,并且离富集区越远,枝晶间距相对增大。主要是因为在富集区边界处,Ni、Cu等元素较充裕,在冷却凝固过程中先形成富含Ni、Cu的枝晶,枝晶间被少量的镁元素填充;随着枝晶的进一步伸入,Ni、Cu等元素被大量的镁基体稀释,枝晶则被充裕的镁基体包围,使其得不到发展,甚至出现了断续,如图3中2区所示。
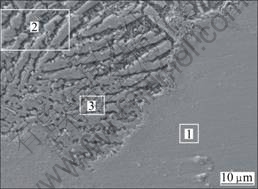
图3 Cu-Ni富集区的SEM像
Fig.3 SEM image of Cu-Ni-rich region
表3 图3中区1成分
Table 3 Composition of region 1 in Fig.3
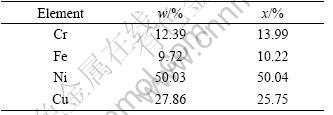
在图3中还发现在枝晶区域内分布着大量的十字状的浅白色物质,对图3的区3放大,其放大图如图4所示。由图4可见,这种浅白色的十字状相特别细小,尺寸较大的也只有1.5 ?m左右,较小的不到1 ?m,对其做EDS能谱分析,主要成分如表4所列。
由Mg-Ni二元相图[15]可知,当温度比较高(在147 ℃左右)时,在Ni元素含量充足的氛围中会生成金属间化合物MgNi2,因而由相图及EDS能谱分析推断浅白色相为Laves相MgNi2。随着枝晶间距的增大,Laves相MgNi2的数量减少,主要是因为随着枝晶间距的增大,Mg基体对Ni的稀释率增大,减少了形成MgNi2的物质条件。

图4 图3中区3的放大图
Fig.4 Enlarged view of region 3 in Fig.3
表4 十字状物质相的成分表
Table 4 Composition of cross-structure phase
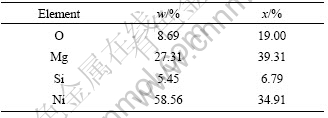
为了进一步深入分析,对合金层与基体的结合区域(图1的B区)进行放大,如图5(a)的所示,并对图5(a)的 1、2区域进行能谱分析,分析结果如图5(b)和(c)所示。
由图5可见,熔合区附近组织为网状结构,突出的亮白区域成分主要是由O、Mg、Ni、Cu等元素组成,而Ni、Cu元素在镁基体中的溶解度极小,极易在晶界处形成耐蚀的Mg2Ni和Mg2Cu等金属间化合物,经腐蚀液的浸蚀,形成突出的网状结构;凹下的灰色区域成分主要由O、Mg元素组成,确定其为Mg基体。
2.2 显微硬度分析
从熔覆层表层到基体每隔0.05 mm取一点熔覆层的纵向显微硬度分布如图6所示。由图6(a)可以看出,从合金表层到基体,显微硬度依次降低。合金层的显微硬度达到75HV0.05~110HV0.05,明显高于基体的显微硬度45HV0.05。分析其原因是合金表层生成的细小晶粒造成细晶强化;合金层中部则是由于生成了Laves相MgNi2;越接近熔合线,则随着稀释率的增大,硬度值逐渐减小。图6(b)所示为距熔覆层表面0.2 mm处的横向显微硬度分布图,从左到右每隔1 mm取一点,以下每点读数3次,取其平均值得出。
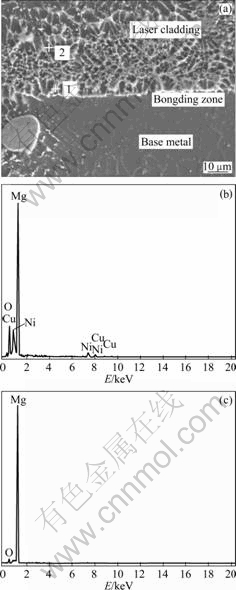
图5 图1 B区的SEM像和EDS能谱
Fig.5 SEM image of region B in Fig.1 (a) and EDS spectra of zones 1 (b) and 2 (c)
从图6(b)可以看出,合金层的横向显微硬度分布均匀,基本都在75HV0.05左右,这和合金层纵向显微硬度图在0.2 mm位置的硬度值基本一致,但在14 mm位置,硬度值却达到280HV0.05,分析其原因是由于局部分布不均匀的Cu-Ni富集相造成的。
2.3 耐蚀性分析
电化学腐蚀性能结果如图7所示,其中曲线1和2分别是Cu-Ni合金层和原始镁合金的极化曲线。根据Tafel直线外推法计算得出动态极化腐蚀电位(φcorr)和腐蚀电流密度(Jcorr),如图7所示。可见,Cu-Ni合金层的腐蚀电势比AZ31B母材的正移了316 mV,而腐蚀电流密度比AZ31B母材的低78 mA/cm2。与基材相比,在AZ31B镁合金表面激光Cu-Ni合金化后,其表面耐蚀性得到了明显改善。对于具有Cu-Ni合金层的镁合金,分析其耐蚀性提高的原因为:1) Cu-Ni合金层晶粒明显细化(见图1(a)),这就减少了组成电偶腐蚀的α-Mg和β-Mg17Al12的有效接触面积,从而抑制了腐蚀电流的增大;2) 合金层中形成金属间化合物,这些化合物相对于α-Mg均呈高的电势,从整体上来说提高了合金层的腐蚀电势,这是使具有Cu-Ni合金层的AZ31B镁合金在Cl-环境中耐蚀性增加的重要原因。而对于原始镁合金,其组织晶粒粗大,骨骼状β-Mg17Al12呈不连续分布在晶界,在3.5%的NaCl溶液介质中由α-Mg和β-Mg17Al12组成电偶腐蚀,不连续分布的β-Mg17Al12相使之反应剧烈[16]。
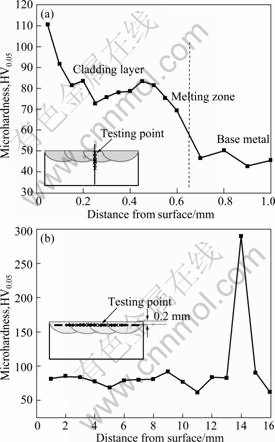
图6 Cu-Ni合金层显微硬度图
Fig.6 Microhardness of Cu-Ni alloy layer: (a) Longitudinal distribution; (b) Transverse distribution
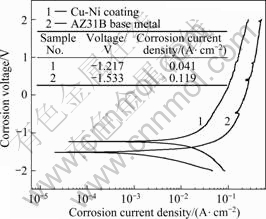
图7 Cu-Ni合金层和AZ31B母材的极化曲线图
Fig.7 Polarization curves of Cu-Ni alloy layer and AZ31B magnesium
3 结论
1) 在AZ31B镁合金表面激光熔覆Cu-Ni合金粉末后,Cu-Ni合金层与基体形成良好的冶金结合,且晶粒明显细化,但在局部区域出现了Cu-Ni富集区,在富集区边缘区域的枝晶间形成了十字状的Laves相。
2) Cu-Ni合金层的纵向显微硬度从表层的110HV0.05降低到基体的45HV0.05,横向显微硬度分布均匀,基本在75HV0.05左右。
3) 与原始AZ31B镁合金相比,Cu-Ni合金层的腐蚀电位正移了317 mV,腐蚀电流密度降低了78 mA/cm2,其耐蚀性得到明显改善。
REFERENCES
[1] 丁文江. 镁合金科学与技术[M]. 北京: 科学技术社, 2007.
DING Wen-jiang. Magnesium alloy science and technology[M]. Beijing: Scientific Technology Press, 2007.
[2] 姚美意, 周邦新. 镁合金耐蚀表面处理的研究进展[J] .材料保护, 2001, 34(10): 19-21.
YAO Mei-yi, ZHOU Bang-xin. Review of the progress in surface treatments for magnesium alloys[J]. Materials Protection, 2001, 34(10): 19-21.
[3] 陈 愚, 肖泽辉, 谭香玲. 镁合金表面熔覆改性技术的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2008, 22(3): 90-93.
CHEN Yu, XIAO Ze-hui, TAN Xiang-ling. Research development of surface overlaying modification technology of magnesium alloys[J]. Materials Review, 2008, 22(3): 90-93.
[4] 马幼平, 徐可为, 潘希德, 温维新, 刘鹏飞. 表面扩渗Al、Zn处理对ZM5镁合金的性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2005, 34(3): 433-435.
MA You-ping, XU Ke-wei, PAN Xi-de, WEN Wei-xin, LIU Peng-fei. Effect of solid diffusion metallic cementation on properties of ZM5 magnesium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005, 34(3): 433-435.
[5] 郭洪飞, 安茂忠, 刘荣娟. 镁及其合金表面化学转化处理技术[J]. 轻合金加工技术, 2003, 31(8): 35-38.
GUO Hong-fei, AN Mao-zhong, LIU Rong-juan. Conversion coating technology of magnesium and its alloys[J]. Light Alloy Fabrication Technology, 2003, 31(8): 35-38.
[6] TAN A L K, SOUTAR A M, ANNERGREN I F, LIU Y N. Multilayer sol-gel coatings for corrosion protection of magnesium [J] Surface and Coatings Technology, 2005, 198: 478-482.
[7] HOCHE H, SCHEERER H, PROBST D, BROSZEIT E, BERGER C. Development of a plasma surface treatment for magnesium alloys to ensure sufficient wear and corrosion resistance [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2003, 174/175: 1018-1023.
[8] STIPPICH F, VERA E, WOLF G K, BERG G, FRIEDRICH C. Enhanced corrosion protection of magnesium oxide coatings on magnesium deposited by ion beam assisted evaporation[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 1998, 103/104: 29-35.
[9] 余 刚, 刘跃龙, 李 瑛, 叶立元, 郭小华, 赵 亮. Mg 合金的腐蚀与防护[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(6): 1087-1095.
YU Gang, LIU Yue-long, LI Ying, YE Li-yuan, GUO Xiao-hua, ZHAO Liang. Corrosion and protection of magnesium alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(6): 1087-1095.
[10] 陈长军, 王东生, 郭文渊, 王茂才. 镁合金激光表面改性研究进展[J]. 材料保护, 2003, 36(1): 25-26.
CHEN Chang-jun, WANG Dong-sheng, GUO Wen-yuan, WANG Mao-cai. Laser surface modification of Mg-base alloy[J]. Material Protection, 2003, 36(1): 25-26.
[11] 陈菊芳, 张永康, 李仁兴, 秦海永. AM50A 镁合金激光表面熔凝层的强化效果与机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(8): 1426-1431.
CHEN Ju-fang, ZHANG Yong-kang, LI Ren-xing, QIN Hai-yong. Strengthening effect and mechanism of laser surface melted AM50A magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(8): 1426-1431.
[12] 陈长军, 常庆明, 张 敏, 王茂才. ZM5 镁合金表面激光Al合金化行为的研究[J]. 应用激光, 2007, 27(4): 261-268.
CHEN Chang-jun, CHANG Qing-ming , ZHANG Min , WANG Mao-cai. Study of the behavior of laser alloying Al powder on ZM5 Mg alloy[J]. Applied Laser, 2007, 27(4): 261-268.
[13] VOLOVITCH P, MASSE J E, FABRE A, BARRALLIER L, SAIKALY W. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy ZE41 with laser surface cladding by Al-Si powder[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2008, 202: 4901-4914.
[14] GAO Ya-li, WANG Cun-shan, PANG Hong-jie, LIU Hong-bin, YAO Man. Broad-beam laser cladding of Al-Cu alloy coating on AZ91HP magnesium alloy[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2007, 253: 4917-4922.
[15] 刘楚明, 朱秀荣, 周海涛. 镁合金相图集[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2006.
LIU Chu-ming, ZHU Xiu-rong, ZHOU Hai-tao. Phase diagrams for magnesium alloys[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2006.
[16] 徐锦锋, 翟秋亚, 袁 森. AZ91D镁合金的快速凝固特征[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(6): 939-944.
XU Jin-feng, ZHAI Qiu-ya, YUAN Sen. Rapid solidification characteristics of melt-spun AZ91D magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(6): 939-944.
(编辑 杨 华)
基金项目:山西省自然科学基金资助项目(2008011044)
收稿日期:2009-11-15;修订日期:2010-02-06
通信作者:王文先,教授;电话/传真:0351-6010076;E-mail:wwx960@126.com