碱度对低钛型钒钛磁铁矿烧结成矿行为的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第6期
论文作者:杨松陶 周密 姜涛 王艳军 薛向欣
文章页码:2087 - 2094
Key words:low-titanium vanadium-titanium magnetite; sinter; basicity; mineralogy; TiO2; CaO
摘 要:碱度对低钛型钒钛烧结矿的质量有着重要的影响。通过烧结杯试验、矿相分析、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和能谱(EDS)分析研究碱度对低钛型钒钛磁铁矿烧结成矿过程的影响和元素在烧结过程中的分布及迁移变化规律。结果表明:在烧结过程中同等接触条件下,CaO优先与TiO2反应生成钙钛矿,导致烧结矿的液相总含量较少;在碱度为1.9~2.7的范围内,随着碱度的提高,烧结矿中的钙钛矿含量提高,铁酸钙含量先小幅增加后快速升高,硅酸盐含量降低,烧结矿的冶金性能得到改善;元素分布情况为Ti主要赋存于钙钛矿中,V主要赋存于硅酸盐中,Fe主要赋存于磁铁矿和赤铁矿中,Ca、Si在硅酸盐和钙钛矿中的赋存量最多,随着碱度的提高,铁酸钙中Al、Mg含量增加,而在其他矿物中Al、Mg含量降低。
Abstract: Basicity has an important effect on the sinter quality, especially for low-titanium vanadium-titanium sinter. The effect of basicity on sintering behavior of low-titanium vanadium-titanium mixture, and the transference and distribution of element in sintering process were researched by sinter pot test, mineralogical analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis. The results show that CaO preferentially reacts with TiO2, generating pervoskite, so that the total liquid phase content of the sinter is low. There is an increase in the perovskite concentration of the sinter with the basicity ranging from 1.9:1 to 2.7:1. With increasing the basicity, the calcium ferrite content increases slightly and then rises rapidly, while the silicate content decreases and the metallurgical property of the sinter is improved. As for the distribution of these elements in the sinter, Ti occurs mainly in perovskite, V occurs mainly in silicate, and Fe occurs mainly in magnetite and hematite. The most abundant occurrence of Ca and Si occurs in silicate and perovskite. With increasing the basicity, the contents of Al and Mg increase in calcium ferrite, while they decrease in other minerals.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 2087-2094
Song-tao YANG1, Mi ZHOU1, Tao JIANG1,2, Yan-jun WANG1, Xiang-xin XUE1,2
1. School of Materials and Metallurgy, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China;
2. Liaoning Key Laboratory for Metallurgical Resources Recycling Science, Shenyang 110819, China
Received 13 July 2014; accepted 20 October 2014
Abstract: Basicity has an important effect on the sinter quality, especially for low-titanium vanadium-titanium sinter. The effect of basicity on sintering behavior of low-titanium vanadium-titanium mixture, and the transference and distribution of element in sintering process were researched by sinter pot test, mineralogical analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis. The results show that CaO preferentially reacts with TiO2, generating pervoskite, so that the total liquid phase content of the sinter is low. There is an increase in the perovskite concentration of the sinter with the basicity ranging from 1.9:1 to 2.7:1. With increasing the basicity, the calcium ferrite content increases slightly and then rises rapidly, while the silicate content decreases and the metallurgical property of the sinter is improved. As for the distribution of these elements in the sinter, Ti occurs mainly in perovskite, V occurs mainly in silicate, and Fe occurs mainly in magnetite and hematite. The most abundant occurrence of Ca and Si occurs in silicate and perovskite. With increasing the basicity, the contents of Al and Mg increase in calcium ferrite, while they decrease in other minerals.
Key words: low-titanium vanadium-titanium magnetite; sinter; basicity; mineralogy; TiO2; CaO
1 Introduction
Low-titanium vanadium-titanium magnetite (LVT) has a very high comprehensive utilization value due to its high contents of V, Ti and Cr [1-3]. Currently, the optimal smelting route of LVT in industrial production is blast furnace (BF). In the smelting process, it is found that LVT sinter with poor intensity and reduction degradation index (RDI) was affected seriously by the blast furnace, for the produced sinter is characterized with insufficient bonding phase. Sinter is mainly dependent on the liquid phase consolidation, which is generated in the sintering process, and the basicity (R=n(CaO)/ n(SiO2)) has an important effect on the quality of the bonding phase, mineral composition, formation mechanism and various physicochemical properties [4-9]. The action of CaO in the sintering process is affected by many factors including the types of ores and raw materials. Perovskite and calcium ferrite have great effect on the metallurgical property especially perovskite. Perovskite usually disperses between the slag phase, calcium ferrite and the iron minerals, and it weakens the role of bonding phase and iron minerals, and produces cracks easily when there is an external force.
But up to now, the effect of basicity on LVT sinter has not been clear. In this study, LVT ores in Chengde, China, were used as the main raw materials and the effect of basicity on the sintering of LVT was researched by sintering pot test. First, the sintering rate and the yield were calculated, then, the sinter tumbler strength index (TI), reduction degradation index (RDI) and the reduction index (RI) were tested. Furthermore, the effect of basicity on the mineralogy of LVT sinter and the mechanism were clarified by metallographic microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). Finally, the transference and distribution of elements in the sintering process of LVT were revealed.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
Four kinds of low-titanium vanadium-titanium ores were supplied by Chengde Jianlong Iron and Steel Group Company, China. The chemical compositions of raw materials and coke breeze for experiment are listed in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. The basic sintering characteristics of LVT are shown in Table 3. It can be seen from Table 1 that the total content of Fe of LVT (A, B, C, D) is much higher than that of ores E and F, and the TiO2 content of LVT varies from 1.45% to 3.15% along with the V2O5 content of LVT varies from 0.37% to 0.59%. Therefore, it will have a significant effect on the iron grade of the sinter, and the content of TiO2 has a negative influence on the quality of the sinter to a certain extent.
The basic sintering characteristics of iron ores exhibit some physical and chemical characters, which are reflected by the changes of ores at high temperature during the sintering process [10-12]. The characteristics are as follows: assimilation ability, liquid phase fluidity, self-strength of binding phase, and crystal intensity. It is found that there is great significance in mastering the sintering characteristics of iron ores at high temperatures [13,14]. Table 3 shows that LVT(A, B, C, D) has a high assimilation temperature (1513.15-1543.15 K), a high strength of binding phase (3547-5484 N), and a high crystal stock strength (4554-8074 N) but a weak liquidity index (0.04-0.12).
2.2 Experimental procedure
On the basis of the basic characteristics of LVT above, the sinter pot test scheme is designed and shown in Table 4. LVT is the mixture of LVT A, B, C, and D. The basicity (R=n(CaO)/n(SiO2)) was adjusted by quicklime to1.9:1, 2.1:1, 2.3:1, 2.5:1, 2.7:1, respectively.
The flow chart of sintering test is shown in Fig. 1.
Table 1 Chemical compositions of raw materials
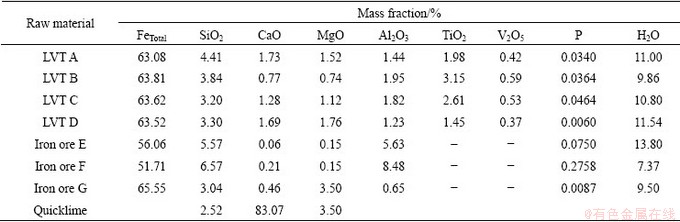
Table 2 Industrial analyses of coke breeze and chemical compositions of ash (mass fraction, %)
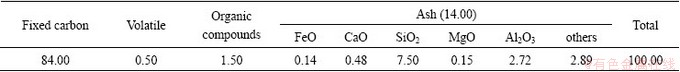
Table 3 Experimental results of iron ore powders with basic characteristics
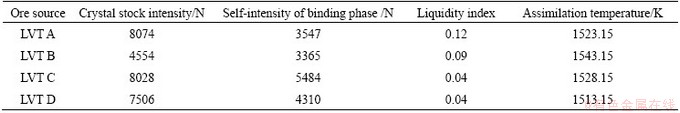
Table 4 Ore-matching schemes of sinter test
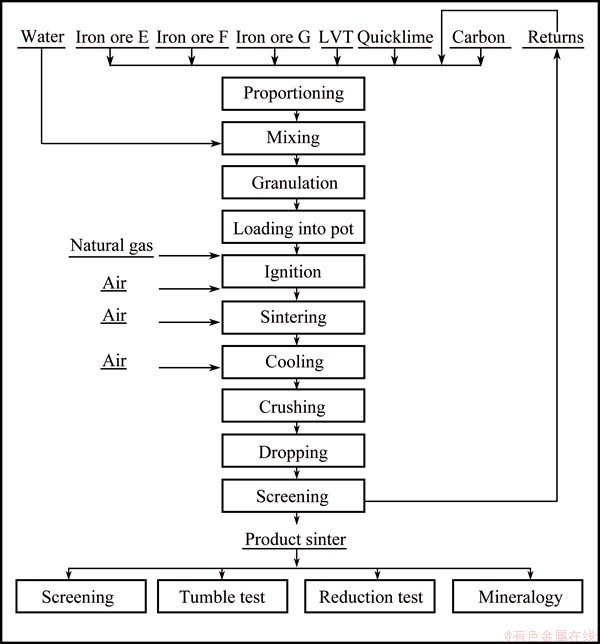
Fig. 1 Sinter pot test flow-sheet of LVT sintering
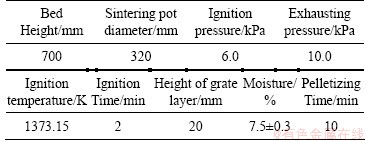
The sintering test covered proportioning, mixing, granulation, ignition, sintering, cooling, crushing and the treatment of cooled sinter. The sinter mixtures were loaded into the sinter pot after granulation, and then ignited at 1373.15 K for 2 min. The sintering proceeded until the temperature of the flue gas reached the peak value, and was followed by cooling for 10 min in ambient air, and then the sinter cake was dislodged. The sintering test parameters, which were kept fixed and listed in Table 5.
Table 5 Parameters of sintering test
2.3 Metallurgical test and micro-analysis
The metallurgical properties of LVT sinters including TI, RDI and RI were tested according to the standard GB 8209-87, GB/T 13242-91 and GB/T 13241-91, respectively. The LVT sinter samples with different basicities were treated with a coarse sandpaper after being encapsulated by resin, and then treated with a relatively smooth frosted glass panel for further processing. Finally, the samples were polished in a polishing machine. Mineralogical analysis of samples was performed by a Leica DM1750M metallographic microscope and a JEOL S-3400N scanning electron microscope.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Experimental results
The sintering indexes of LVT sinter are shown in Table 6. It shows that with increasing the basicity, the vertical sintering speed of the sinter increases, the large-grained sinter decreases and the fine-grained sinter increases, and the finished product ratio shows a declining trend. With increasing the basicity, more quicklime improves the granulation condition of the mixture, increases the pelletization of the mixture, and improves the permeability of the LVT mixture, so, the vertical sintering speed rises. As the burning loss increases with increasing the quicklime, the yield has a little drop.
Figure 2 shows the effect of basicity on the metallurgical properties of LVT sinter. As can be seen from Fig. 2, with increasing the basicity, the RDI rises form 53.35% to 75.09%, along with the TI increasing from 58.23% to 63.53%. Although the RI of LVT sinter has a little drop, it still gets to 74.57% when the basicity is 2.7:1. These results clearly indicate that the basicity has a positive impact on the metallurgical properties of LVT sinter.
3.2 Thermo-mechanical analysis
The effect of basicity (addition in the form of quicklime) on the minerals of LVT sinter was dicussed according to the following reactions:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
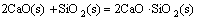 (3)
(3)
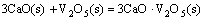 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
 (7)
(7)
 (8)
(8)
Figure 3 shows the relationships between the Gibbs free energy change and the temperature of Reactions (1)-(8). As can be seen from Fig. 3, the reaction that CaO involved is complex. The thermodynamic feasibility of CaO reacting with SiO2 to generate calcium silicate is higher than that of other reactions, but SiO2 is insufficient in the ore powder and mostly exists in the form of the complex silicate minerals such as pyroxene and feldspar. CaO can react with gangue minerals and FeO (reductive product), generating the low-melting-point liquid phase minerals. Ti-bearing minerals can also react with CaO to generate the liquid phase with lower melting point. Under the same condition, the Gibbs free energy change of reaction between TiO2 and CaO is far lower than that of reaction between CaO and Fe2O3, thus CaO prefers to react with TiO2 to generate perovskite, which is the reason that the content of liquid phases in LVT sinter is less than that in ordinary sinter.
Table 6 Effect of basicity on parameters of LVT sintering
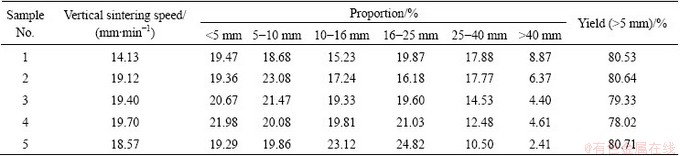
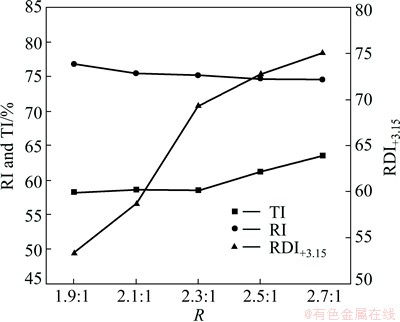
Fig. 2 Effect of basicity on metallurgical properties of LVT sinter
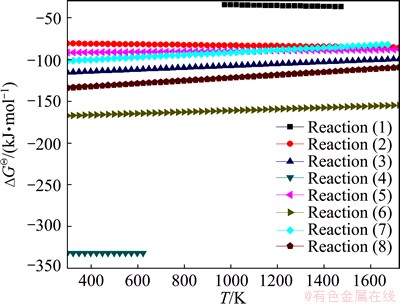
Fig. 3 Relationships between Gibbs free energy change and temperature of Reactions (1)-(8)
3.3 Mineral compositions and mechanism of LVT sinter
Table 7 shows the mineral compositions of LVT sinter. It can be found that the increase of basicity changes the mineral compositions of the sinter significantly. As increasing the basicity, the volume fraction of perovskite increases and then levels off, whereas the calcium ferrite content only increases a little at first and then rises rapidly. The bonding phase mainly consists of silicate and calcium ferrite at R=1.9:1, and mainly consists of calcium ferrite along with a small amount of silicate at R=2.3:1. As the basicity increases, the amount of generated calcium ferrite also increases. This may be attributed to the fact that when the CaO content increases, CaO has more opportunities to contact with Fe2O3, and more likely to generate calcium ferrite and increases the calcium ferrite content subsequently. When the basicity extends to 2.5:1, the magnetite decreases while the concentration of calcium ferrite continues to rise by about 25%. Then, the bonding phase mainly consists of calcium ferrite.
With increasing the basicity, the content of calcium ferrite increases and the TI of sinter rises. Generally, the bonding phase accounts for 30%-45% of the total mineral volume, which is condensed after the liquid phase [15]. The bonding phase quantity, mineral composition, formation mechanism, and various physicochemical properties have important effects on the quality of the sinter. Due to the occurrence of TiO2 in LVT sinter and the complicated formation mechanism of the minerals, there is a large quantity of perovskite generated with fewer bonding phases during the sintering process. Calcium ferrite only accounts for 10%-20% in the final product at R=1.9:1, which is extremely low, as 35% calcium ferrite can be found in ordinary sinter. This is the main reason for the poor TI of LVT sinter. The bonding phases and minerals of LVT sinter mainly consist of calcium ferrite. The sequence of main minerals that decrease the strength of the final product can be shown as calcium ferrite > magnetite > hematite > silicate. Calcium ferrite and silicate are the most important bonding phases in sinter. With increasing the basicity, the content of high-strength calcium ferrite increases sharply with the decline of other minerals with low-strength. This is beneficial to the improvement of TI of the sinter.
With increasing the basicity, the content of calcium ferrite increases, the content of silicate decreases, and the RDI property improves. Due to the crystal transition of Fe2O3 to Fe3O4 as the sinter reduced, there are expansion and pulverization [16,17]. The content of silicate slag as a bonding phase is lower for the SiO2 content is lower in LVT sinter. Moreover, due to the effect of TiO2, there is a large amount of perovskite that fails to bond and with a poor resistance to expansion and pulverization, and the brittleness of perovskite hinders the joined crystal effect between hematite and magnetite. This is another reason that causes LVT with poor TI and RDI. The internal stress of LVT sinter is greater than that of ordinary sinter due to its mineral diversity and the differences in thermal expansibility. This results in the formation of a multitude of micro cracks during the low-temperature reduction stage (≤773.15 K), which provides the favorable condition for forming macro cracks and for intensifying the fragmentation within higher temperature range. Therefore, the low-temperature reduction disintegration property of vanadium-titanium sinter is worse than that of ordinary ore. Thus, with increasing the basicity, the content of calcium ferrite and the bonding phases of the sinter increase, which inhibits the volume expansion in the reduction process and improves the low-temperature reduction disintegration accordingly.
3.4 Element distribution and migration
Figures 4-6 show the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images and the energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) mappings of the sintering samples with different basicities (R=1.9:1, 2.3:1, 2.7:1). Table 8 shows the EDS analysis results of the detected points in these samples. Figures 4-6 show that, as the basicity increases, the granular and the lath-shaped structures in the sinter decrease and the needle interlaced structures increase. According to the mineralogical analysis and the distribution of the elements in Figs. 4-6, there are Fe, O and Mg which mainly exist in the magnetite and hematite zone, and there are Ti, Ca and O which mainly exist in the perovskite zone.
According to Table 8, point A in Figs. 4-6 mainly contains O and Fe. Through mineralogical analysis on samples using metallographic microscope, and considering the comparative analysis of the typical structural formula, point A corresponds to magnetite. With increasing the basicity, the contents of Al and Mg decrease in magnetite that is generated during the sintering process, but the content of Ca rises slightly. This shows that, along with the increase of CaO, the solid solubility of Al2O3 and MgO decreases, while the content of Fe rises accordingly. Point B in Figs. 4-6 mainly contains O and Fe. Through mineralogical analysis on samples using metallographic microscope, and considering the comparative analysis of the typical structural formula, point B is hematite. Increasing the basicity has little impact on the content of Ti in hematite generated during the sintering process, though the solid solubility of Al and Mg in the sinter does decrease and the content of Fe rises accordingly. So, the solid solution rule of hematite is similar to that of magnetite. Point C in Figs. 4-6 mainly contains Ca, Ti, and O. Considering the comparative analysis of the typical structural formula, point C is perovskite. With the increase of CaO, the contents of Al and Fe in perovskite generated during the sintering process decrease and the content of Ti increases accordingly; however, the content changes of Ca and Si have no obvious rule. Point D in Figs. 4-6 mainly contains Fe, Ca, and O. Considering the comparative analysis of the typical structural formula, point D is calcium ferrite. With increasing the basicity, the contents of Al, Mg, Ca, and Si increase, but the contents of Fe and Ti decrease, which shows that more acicular calcium ferrite SFCA generated. Point E in Figs. 4-6 mainly contains Si, Ca, and O. Considering the comparative analysis of the typical structural formula, point E is silicate. The increased basicity causes no obvious changes in the contents of Al, Ca, and Si in silicate generated during the sintering process, and there is a slight decrease in the content of Ti and an increase in the contents of V and Fe.
Table 7 Mineral compositions of vanadium-titanium magnetite sinter
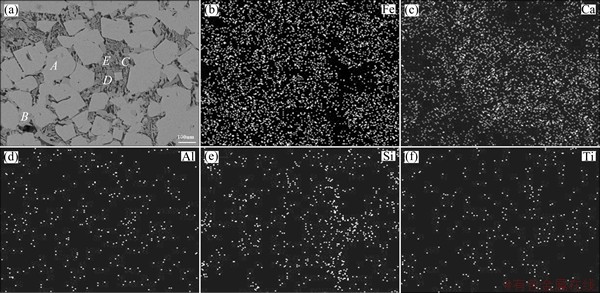
Fig. 4 SEM image (a) and EDS mapping (b-f) of sample with R=1.9:1
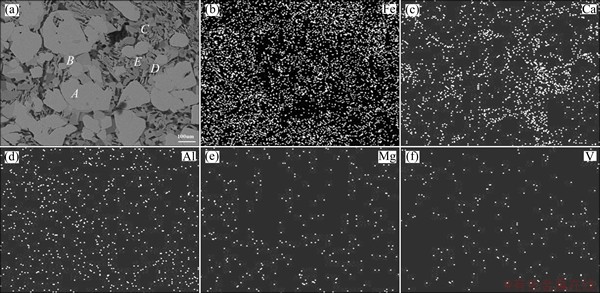
Fig. 5 SEM image (a) and EDS mapping (b-f) of sample with R=2.3:1
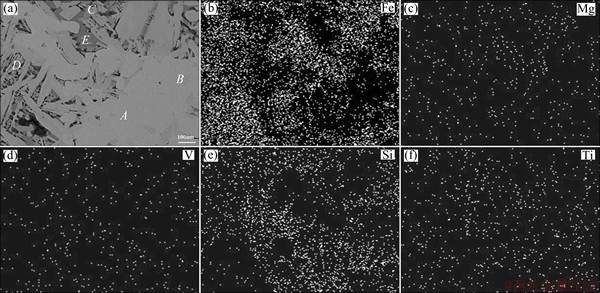
Fig. 6 SEM image (a) and EDS mapping (b-f) of sample with R=2.7:1
Table 8 EDS analysis of samples
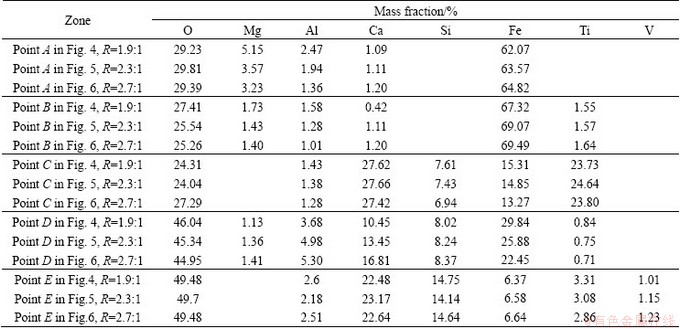
With increasing the basicity, the CaO content of the sinter increases, but the contents of other elements decrease. V mainly occurs in silicate; Ti mainly occurs in perovskite, but also in silicate and other minerals; Fe mainly occurs in hematite and magnetite, but also in calcium ferrite, silicate and perovskite. The solid solubility of Al in hematite, magnetite, perovskite, and silicate decreases slightly, but increases in calcium ferrite. With increasing the basicity, Al mostly enters into calcium ferrite, and the Al content is among the main factors affecting the form of calcium ferrite. A large amount of Ca, some Fe and Si, and a small amount of Al occur in perovskite. The decrease of Mg is mainly reflected in magnetite and hematite, but Mg slightly increases in calcium ferrite with increasing the basicity. Obviously, the occurrence of Ca and Si in silicate and perovskite is higher than that in calcium ferrite, magnetite, and hematite. With increasing the basicity, the Ca content increases in calcium ferrite, but the change is insignificant in other minerals.
4 Conclusions
1) With the basicity of sinter ranging from 1.9:1 to 2.7:1, the metallurgical properties including the TI and the RDI of LVT sinter are significantly improved, and with no significant change in the RI.
2) In the sintering process of LVT sinter, CaO preferentially reacts with TiO2 in its liquid form, generating pervoskite, so that the total liquid phase concentration of the sinter is low.
3) As increasing the basicity of LVT sinter, the volume fraction of perovskite increases and then levels off, the volume fraction of calcium ferrite increases slightly at first and then rises rapidly and the content of silicate decreases. The bonding phase of the sinter with a basicity of 1.9:1 mainly consists of silicate and calcium ferrite. With increasing the basicity, the calcium ferrite content increases and the silicate content decreases. When the basicity is 2.7:1, the bonding phase of the sinter mainly consists of calcium ferrite.
4) Ti in LVT sinter mainly occurs in perovskite, V mainly occurs in silicate, and Fe mainly occurs in magnetite and hematite. The occurrence of Ca and Si is most abundant in silicate and calcium ferrite. With increasing the basicity, the content of Al and Mg increases in calcium ferrite but decreases in other minerals.
References
[1] DENG Zhi-gan, WEI Chang, LI Xing-bin, XU Hong-sheng, LI Min-ting, LI Cun-xiong, FAN Gang. Leaching vanadium from extracted vanadium residue of vanadium titanomagnetite [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(6): 1770-1777. (in Chinese)
[2] YU Yong-fu. Advance in iron ore dressing technology at home and abroad and their influence on iron-smelting [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(1): 47-51. (in Chinese)
[3] MA Jian-ming, CHEN Cong-xi. The development and utilization of new type iron in china-super lean magnetite of Chengde [J]. Metal Bulletin of China, 2007, (20): 31-34. (in Chinese)
[4] DIDEVICH A V, KHLAPONIN N S, VASKEVICH M Y, ZOTOV A V. Producing high-basicity sinter from low-silica ore [J]. Steel in Translation, 2008, 38(7): 546-549.
[5] UMADEVI T, SAH R, MAHAPATRA P C. Influence of sinter basicity (CaO/SiO2) on low and high alumina iron ore sinter quality [J]. Transactions of the Institutions of Mining and Metallurgy, Section C: Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 2014, 123(2): 75-85.
[6] ZHANG Q J, LIU J J, JIANG L M, MO W L, LI Y L, ZHANG Y Z. Multi-fractional research on pore distribution in the sinter ore with different basicity [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 268-270: 321-325.
[7] DETKOVA T V, MALYSHEVA T Y, PAVLOV R M. Sinter at cherepovets metallurgical works (basicity 1.0-3.0) [J]. Steel in Translation, 2013, 43(7): 409-414.
[8] SUN Yan-qin, YANG Song-tao, LU Qing, LI Fu-ming. Influence of basicity on separated granulating sintering of vanadium titanium magnetite [J]. Journal of Northeastern University: Natural Science, 2011, 32(9): 1269-1273. (in Chinese)
[9] MALYSHEVA T Y, YUSFIN Y S, MANSUROVA N R, GIBADULIN M F, LEKIN V P. Mechanism of mineral formation and metallurgical properties of sinter of basicity 1.1-3.1 at OAO MMK [J]. Steel in Translation, 2007, 37(2): 126-130.
[10] MACHIDA S, NUSHIRO K, ICHIKAWA K, NODA H, SAKAI H. Experimental evaluation of chemical composition and viscosity of melts during iron ore sintering [J]. ISIJ International, 2005, 45(4): 513-521.
[11] LONG F Y, WU S L, ZHU J, DU Y, ZHANG G L. Experimental research on bonding intensity of iron ores in the sintering process [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 391-392: 60-64.
[12] WU Sheng-li, PEI Yuan-dong, CHEN Hui, PENG Peng, YANG Fan. Evaluation on liquid phase fluidity of iron ore in sintering [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2008, 30(10): 1095-1100. (in Chinese)
[13] WU S L, ZHANG G L, CHEN S G, SU B. Influencing factors and effects of assimilation characteristic of iron ores in sintering process [J]. ISIJ International, 2014, 54(3): 582-588.
[14] DU Y, WU S L, ZHANG G L, LONG F Y, ZHU J. The influence of iron ore quality degradation on the assimilability of sinter ore [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 391-392: 71-74.
[15] FROHLICHOVA M, FINDORAK R, LEGEMZA J. Structural analysis of sinter with titanium addition [J]. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials, 2013, 58(1): 179-185.
[16] GUO Y F, ZHOU J F, JIANG T, CHEN F, SONG X L, TANG M J, QING L J. Study on the improvements of reduction swellability and low temperature reduction disintegration of vanadium-titanium magnetite oxidized pellets [C]//Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing-held During the TMS 2013 Annual Meeting and Exhibition. San Antonio, USA: John Wiley & Sons, 2013: 509-516.
[17] MURAKAMI, KAMIYA Y, KODAIRA T, KASAI E. Reduction disintegration behavior of iron ore sinter under high H2 and H2O conditions [J]. ISIJ International, 2012, 52(8): 1447-1453.
杨松陶1,周 密1,姜 涛1,2,王艳军1,薛向欣1,2
1. 东北大学 材料与冶金学院,沈阳 110819;
2. 东北大学 辽宁省冶金资源循环科学重点实验室,沈阳 110819
摘 要:碱度对低钛型钒钛烧结矿的质量有着重要的影响。通过烧结杯试验、矿相分析、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和能谱(EDS)分析研究碱度对低钛型钒钛磁铁矿烧结成矿过程的影响和元素在烧结过程中的分布及迁移变化规律。结果表明:在烧结过程中同等接触条件下,CaO优先与TiO2反应生成钙钛矿,导致烧结矿的液相总含量较少;在碱度为1.9~2.7的范围内,随着碱度的提高,烧结矿中的钙钛矿含量提高,铁酸钙含量先小幅增加后快速升高,硅酸盐含量降低,烧结矿的冶金性能得到改善;元素分布情况为Ti主要赋存于钙钛矿中,V主要赋存于硅酸盐中,Fe主要赋存于磁铁矿和赤铁矿中,Ca、Si在硅酸盐和钙钛矿中的赋存量最多,随着碱度的提高,铁酸钙中Al、Mg含量增加,而在其他矿物中Al、Mg含量降低。
关键词:低钛型钒钛磁铁矿;烧结矿;碱度;矿相;TiO2;CaO
(Edited by Mu-lan QIN)
Foundation item: Projects (2012AA062302, 2012AA062304) supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program); Projects (51090384, 51174051) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2012DFR60210) supported by the International Cooperation of Ministry of China
Corresponding author: Xiang-xin XUE; Tel: +24-83681711; E-mail: xuexx@mail.neu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63819-5

