基于不等间隔接收机钟差组合预报模型的辅助定位方法
占建伟1, 2,吴鹏1,龚航1,彭竞1,欧钢1
(1. 国防科技大学 电子科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410073;
2. 第二炮兵工程大学 四系,陕西 西安,710025)
摘要:在典型城市或室内应用等情况下,卫星导航信号由于被频繁遮挡变而变得微弱甚至不可用,使得传统的定位模式难以满足连续定位的要求。针对此问题,分析接收机钟差辅助定位的可行性,建立原点插值条件下使残差平方和最小的多项式钟差预报模型和改进的非等间距灰色系统钟差预报模型,并提出一种基于不等间隔接收机钟差解算值序列的动态加权组合预测模型及相应的钟差辅助定位算法。该模型通过权值的合理选取可实现单一模型的最优组合,具有更高的预测精度和稳健性。实测结果表明:该组合模型对钟差解算值序列的预测是可行和有效的; 对于50 s内的短时钟差辅助定位,定位误差与连续正常定位接近,仅降低2.76%,可有效提高可见卫星不足4颗时的定位连续性。
关键词:卫星导航;接收机钟差;钟差辅助; 组合模型;不等间隔
中图分类号:TN96 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2014)02-0457-07
A clock-aided positioning algorithm using combination prediction model based on unequal interval receiver clock bias data
ZHAN Jianwei1, 2, WU Peng1, GONG Hang1, PENG Jing1, OU Gang1
(1. College of Electronic Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China;
2. The 4th Department, The Second Artillery Engineering University, Xi’an 710025, China)
Abstract: In the typical urban or indoor environment, the satellite navigation signals are degraded because of obstruction to receiver-to-satellite line of sights, making in conventional four-satellite positioning method is very hard to satisfy the requirement of continuous positioning. To solve the problem, the feasibility of the clock-aided positioning method was analyzed, and then an improved polynomial model based on the generalized extended interpolation method and an improved grey model were established. Finally, a combination prediction model and the corresponding assisted positioning algorithm were proposed, based on unequal interval receiver clock bias (RCB) data. The model can provide an optimal combination by solving the weighting factor so as to obtain a higher prediction accuracy and improve robustness. The experimental results based on BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) observation data show that the RCB prediction is feasible and effective. Moreover, for 50 s RCB prediction in the urban environment, the three-dimensional (3D) position error using the clock-aided position algorithm is about 2.76% larger than four-satellite 3D position error, and the availability of positioning can be efficiently improved.
Key words: satellite navigation; receiver clock bias; clock-aided; combination model; unequal interval
在卫星信号受遮挡严重地区,例如城市高楼、停车场、隧道、室内,可能出现部分信号中断或全部信号中断情况。定义可见卫星仅有3颗的情况为“3-D不完备条件”,可见卫星数大于4颗的情况为“完备条件”[1]。统计表明,“3-D不完备条件”以大于10%的概率频繁出现,每次出现平均持续约为50 s[2],这导致接收机首次定位时间和失锁重捕时间大大增加,采用完备条件下的定位方法可能无法给出定位结果或者定位精度很差,严重影响BDS,GPS和Galileo等各类接收机的定位可用性和可靠性,使其应用范围受到了极大限制。针对这一问题,往往通过集成传感器引入外部测量信息辅助的方法降低对可见卫星数的依赖,以实现三维定位,如气压高度表、RFID,伪卫星、INS或者电子地图匹配等方法[3-6]。但是,以上方法需借助外部设备,往往成本较大,作用范围具有一定的局限性。不借助任何外部信息、完全利用接收机在非辅助条件下解算得到钟差解算值,通过建立钟差预测模型,预测未来所需某时刻的钟差用于辅助定位的方法,实现简单、灵活、性价比高。目前,已有若干文献对接收机钟差辅助建模及辅助定位算法进行了一定的研究[7-10],但不够成熟和全面。归纳起来,上述文献所提出的方法主要有以下几个特点:(1) 以往的研究往往集中于廉价原子钟、恒温晶振,缺少对廉价温补晶体振荡器(TCXO)的相关分析,而后者在许多接收机里很普及,尽管其长稳不如原子钟理想,但是其50 s以内的短期稳定度一般可以达到10-9以上[1];(2) 钟差模型的建立采用的是等间隔的观测数据,而城市典型环境下的信号中断往往呈现间歇性的特点,用户定位的连续性得不到保证,解算得到的钟差解算值序列往往是不等间隔的;(3) 单一的钟差预测模型有其自身的特点和适用范围,对于不同的环境,单一模型的可靠性得不到保证,在实用上存在一定的局限性和缺陷。为了解决上述问题,本文作者利用非等间距接收机钟差解算值序列,基于传统的多项式模型和灰色模型,分别提出广义延拓逼近法的改进多项式模型和改进非等间距灰色模型;并在此基础上提出了一种动态加权组合预测模型及其相应的辅助定位算法。
1 钟差预报模型建模
1.1 改进的多项式钟差模型
设在城市遮挡环境中得到预处理后的不等间隔健康钟差序列为x(t1),x(t2),…,x(tm),其中ti-ti-1≠常数。根据钟差的物理意义,一般采用多项式模型对接收机钟差进行建模[11]。

 (1)
(1)
其中,α0,α1,α2,…,αn为待定的多项式模型参数,分别表示钟偏、钟速、频率漂移等;n为模型的阶数,可通过残差确定,针对大多数接收机晶振,n=2时可满足模型精度要求;t0为参考时刻,一般进行归一化处理,即令t0=0;w(ti)由多种噪声组成,主要包括相位噪声和测量噪声。
考虑到原点tn及附近的钟差解算值对预测值影响最大,因此选择约束在原点误差最小的条件下,通过使残差平方和达到最小值来确定α中各参数α0,α1,α2,…,αn,具体如式(2)所示。
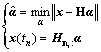 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
其中:Hn为H矩阵的第n行构成的行向量。
式(2)可以采用拉格朗日乘子法进行解算[12]。
1.2 改进的不等间隔灰色模型
灰色GM(1,1)模型广泛应用于少数据、贫信息、不确定性问题的预测,在卫星钟差的长期预报中具有一定的实用性[13]。而接收机钟差与卫星钟差一样,受多种噪声的影响,有些噪声特性已经明确,有些噪声特性未知或者不确定,符合灰色系统的特点,因此,本文尝试将接收机钟差序列视为灰色系统。
传统的GM(1,1)模型都是基于等间隔观测数据建立的,并不能直接应用于非等间隔钟差数据的预报, 必须进行适当改进。相似问题在其他领域已经有一定研究,考虑到典型城市3-D不完备条件下接收机观测数据少,线性化的特点,本文采用文献[13]。中提出的改进模型AMUGM(1,1)。该模型的特点是通过优化背景值,扩大了模型的实用性,使其同时适用于具有线性变化和指数变化规律的数据序列预测,其钟差预测值的表达式为
 (6)
(6)
其中,待定参数灰系数 和灰作用量
和灰作用量 分别反映序列的增长速度和数据变化的关系,而
分别反映序列的增长速度和数据变化的关系,而
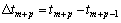 ,p≥1 (7)
,p≥1 (7)
当m>4时,利用最小二乘原理,可求得参数估计值为:
 (8)
(8)
 (9)
(9)
 (10)
(10)
 (11)
(11)
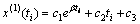 (12)
(12)
式中,x(1)(ti) 表示原始序列与时间间隔相乘后的一次累加序列,其累加关系如(13)所示;β,c1,c2,c3依据平均值和最小二乘原理求取。待确定各参数后,可以依据式(6)预测钟差值。
 (13)
(13)
1.3 动态加权组合模型
任何单一的预报模型都有自身的特点和适用性。如多项式模型物理意义明确,短期预报效果好,而灰色模型在只有少量观测数据情况下,长期预报也能保证预报的精度[11]。因此,应用组合方式是实现2种模型优势互补的一种有效途径。在各种组合模型中,加权线性组合模型被广泛应用,该模型具有优化目标函数和优化准则建立及求解简单、计算量小的优点。
设 和
和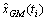 分别为基于改进多项式模型和改进AMUGM(1, 1)模型得到的ti时刻钟差模拟值,εp(ti)和εGM(ti)为对应的模拟误差。则可利用加权线性组合模型得到组合模拟值
分别为基于改进多项式模型和改进AMUGM(1, 1)模型得到的ti时刻钟差模拟值,εp(ti)和εGM(ti)为对应的模拟误差。则可利用加权线性组合模型得到组合模拟值 和误差ε (ti),如式(14)和式(15)所示。
和误差ε (ti),如式(14)和式(15)所示。
 (14)
(14)
 (15)
(15)
权值wp和wGM通过求解组合模拟误差平方和最小值来确定,对应的优化目标函数如式(16)所示。同时定义ε,εp 和εGM分别为对应观测值组成的列向量,如式(17)~(19)所示。
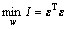 (16)
(16)
 (17)
(17)
 (18)
(18)
 (19)
(19)
利用消元法和并将I对w求微分,易得到最优权值为wp。如式(20)所示。而wGM可依据式(14)的约束方程解算得到。
 (20)
(20)
以上建立的模型可以用来预测短时内的钟差,但是由于参数固定,其预测误差会随着时间增长而逐渐积累。因此,提出采用“滑动窗”来锁定最新的钟差解算值,同时剔除“最旧钟差解算值”,然后重新估计模型参数。这样,每次计算就只需要固定长度的最新观测值,大大减小了存储量,提高了运算速度。
1.4 模型短期预测能力评价标
建立组合模型后,选用的预测性能评价标准主要包括残差平方s和平均相对误差△,计算公式如下:
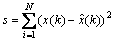 (21)
(21)
 (22)
(22)
其中:x(k)和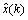 分别为实际钟差值与模型预测值。
分别为实际钟差值与模型预测值。
2 钟差辅助定位算法
2.1 钟差辅助的原理
依据钟差组合预测模型外推预测得到接收机钟差预报值,可建立如下约束方程用于辅助定位:
 (23)
(23)
其中,ωx为伪距测量误差标准差和钟差误差标准差的归一化参数,用于调整约束方程(23)的误差分量,使得调整后的误差分量具有相同的方差。
 (24)
(24)
将式(23)并入无任何辅助的基本定位方程组(25),从而可完成3-D不完备条件下的辅助定位。
 (25)
(25)
其中:△ρ为测量伪距值与伪距估计值之间的偏差;ε为伪距测量误差矢量;G为n×4的观测矩阵;n为可视有效卫星数。可以看出,基于钟差辅助的定位算法实际上相当于增加了1颗观测卫星,是解决3-D不完备条件下定位连续性和可用性的有效方法之一。
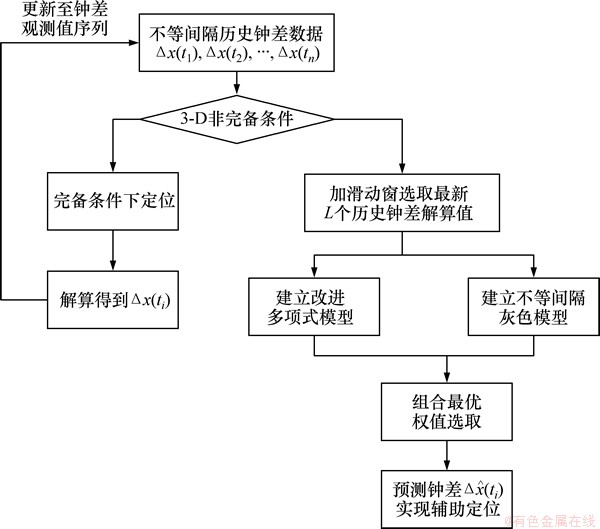
图1 短时预报钟差辅助定位算法
Fig. 1 Flow of clock-aided positioning algorithm for short-term prediction
值得注意的是:针对短时预报得到钟差预测值,在滑动过程中,不宜作为新息引入模型。原因是与正常解算钟差值相比,钟差预测值多了1项预测误差。由式(26)可知,该预测误差将引起额外的定位误差。
2.2 接收机钟差辅助的定位精度
在钟差辅助定位中,钟差预测模型的精度将直接影响最终的三维定位精度,其影响可采用式(26)进行评估[10]。而式(27)进一步表明,当钟差预测值和实际钟差之间的误差σb大于时间精度因子(DTDOP)和卫星基准伪距测量均方差σs的乘积时,钟差辅助定位的误差比完备定位条件下的定位误差大。
 (26)
(26)
 (27)
(27)
 (28)
(28)
其中,H3为3×3的几何观测矩阵。
而在钟差辅助定位中,σb应由2部分组成,模型预测值与实际钟差解算值间误差σp,以及实际钟差解算值与真实钟差间误差σc。当预测模型为改进二次多项式模型时[8],三者的关系可以表示为
 (29)
(29)
根据式(29)可知,σp作为钟差σb的主要组成部分,将是影响辅助定位精度的主要误差因素。因此,高精度的钟差预报模型有利于提高定位精度。
3 试验结果及讨论
3.1 钟差预报性能评估
3.1.1 钟差数据合理性验证
为了验证钟差预测模型辅助接收机定位解算的性能,于2013-03-20在长沙某固定点采用北斗接收机进行静态数据采集,采样频率为1 Hz,接收机记录了各可视卫星的坐标、伪距、精度因子和接收机钟差等观测数据,时间起点对应的周内时间为265 151 s。其中,定位解算时采用的卫星伪距均方根误差分别为:σGEO=6.5 m,σIGSO=4.5 m,σs=σGEO。
晶振的频率稳定度在一定的程度上反映了钟差的可预测性[1]。利用上述连续的钟差解算值计算得到频率稳定度,如图2所示。 由图2可见:实验所得北斗接收机TCVCXO(CFPT-XXX)晶振50 s的频率稳定度约为2.5×10-9,钟差预测可以达到纳秒级。

图2 实验所用北斗接收机晶振的频率稳定度
Fig. 2 Frequency stability of BDS receiver’oscillator
3.1.2 3-D不完备条件下不连续定位场景
实际测试统计表明,在城市、峡谷等信号遮挡严重的区域,3-D不完备条件的平均维持时间约为50 s。因此,从上述连续的历史观测数据中分段选择连续的钟差解算值,对典型的城市定位场景进行建模,如图3所示。由图3可见:整个观测时段内接收机经历了3次3-D不完备条件,分别为图中A,B,C段,其余为完备时段,可以得到钟差解算值。定义△tA,△tB和△tC的信号中断时长分别为:△tA=54 s,△tB=14 s,△tC=14 s。

图3 典型城市环境下的辅助定位场景
Fig. 3 Experimental scenario in typical urban environment
3.1.3 3-D不完备条件下组合预测模型性能
(1) 组合预测模型与一般多项式模型比较。2种模型利用上述不等间隔钟差解算值数据连续外推155 ~ 205 s,结果如图4所示。从图4可见:随着预测时间的延长,2种模型的预测误差都逐渐积累;当预测时为55 s时,组合预测模型的预测误差达到-0.279 m,一般二次多项式模型达到-0.343 m;当预测时长达到80 s时,组合预测模型的预测误差达到-1.096 m,一般二次多项式模型达到-1.187 m。而从变化趋势来讲,2种模型是一致的,差异仅表现在预测起点。这是组合预测模型采用加权和广义延拓逼近优化的结果。总体来看,与一般二次多项式模型相比,组合预测模型预测精度提高1.764 m, 但都能满足3-D不完备条件下信号中断时长最大50 s时的精度要求。

图4 典型城市环境下组合模型与传统二次模型钟差预测结果对比(△t=30 s)
Fig. 4 Comparison of RCB predictions using combination and second-order polynomial model in typical urban environment
(2) 信号遮挡时长对组合预测模型精度的影响。图5所示为信号受遮挡时长△tA,△tB,△tC不同取值对预测精度的影响。考虑到典型城市环境的特点,各参数的取值范围满足式(30)。从图5可见:从总的趋势上讲,钟差预测误差随着△ti 的延长而积累,导致定位精度降低。经计算,当△tA=23 s时,钟差预测误差达到最大值,emax=-2.010 m。
 (30)
(30)
(3) 新息对组合预测模型精度的影响。为了验证“滑动窗”对预测精度的影响,针对不同的新息类型和滑动方式,采用表1所示的4种方式进行预测精度对比分析,其仿真结果如图6和图7所示。
从图4、图6、图7和表1可见:(1) 将钟差预测值引入模型观测值序列动态更新模型参数后,将导致模型精度下降;(2) 组合预测模型2的精度略低于非滑动模型1。这与滑动窗选取的观测值长度有关,在观测数据充足的情况下,可以避免此影响。

图5 信号遮挡时长对模型预测精度的影响(i=A,B,C)
Fig. 5 Duration of signal blockage effect on prediction accuracy
表1 不同新息对模型预测精度的影响
Table 1 Effect of different types of new information on prediction accuracy
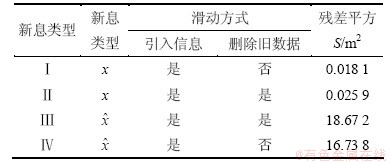

图6 将钟差解算值作为新息时模型预测精度
Fig. 6 Prediction accuracy of models using RCB as new information

图7 将健康钟差预测值作为信息时模型的预测精度
Fig. 7 Prediction accuracy of models using predicted RCB as new information
3.2 钟辅助定位性能评估
为了验证组合预测模型辅助定位算法的性能,采用受△tA,△tB和△tC等信号受遮挡影响的20个不等间隔历史钟差解算值作为历史观测数据, 进行辅助定位性能仿真,并与完备条件下的4星定位结果进行比较。其中钟差辅助定位所用3颗星为SV01,SV 04和SV07,完备条件下的定位所用4颗星为SV01,SV 04,SV07和SV08,定位频率为1 Hz。
图8和图9所示为2种定位方法的三维定位误差及其累积分布。从图8可见:4星定位的定位误差为10.960 m;而辅助定位的定位误差为11.263 m,比正常定位略微增大2.76%。这是受钟差预报误差影响而导致的,但仍然可以满足短时3-D不完备条件下北斗接收机辅助定位精度需求。

图8 钟差辅助定位和四星定位解算结果
Fig. 8 Positioning results of clock-aided algorithm and four-satellite method

图9 钟差辅助定位和四星定位解算结果累积概率分布对比
Fig. 9 Cumulative distribution function of positioning errors of clock-aided algorithm and four-satellite method
通过以上的对比分析可以看出:采用预测钟差解算值进行辅助定位,在短时期内可以继续为用户提供与完备条件下性能相当的定位、导航和授时服务,有效地提高了定位的连续性和可用性。
4 结论
(1) 广义严拓逼近法通过优化预测模型在原点的误差,使得模型具有更高的短期外推精度和可靠性。
(2) 采用“滑动窗”的方式,可以将健康的钟差解算值引入模型,建立参数动态更新的钟差预测模型,使模型更好地符合实时变化规律,以保持更高的预测精度。
(3) 线性组合模型通过最优加权组合,实现了单一的改进多项式模型和改进不等间隔灰色模型的优势互补,有效提高了模型的适用性和可靠性。
(4) 通过北斗接收机的实测数据验证分析表明,该算法解决了一定外推时间内3-D不完备条件下的定位连续性问题,针对不同类型的不等间隔序列,都能保证满足导航定位精度要求,有效提高了定位的连续性和可靠性。且该新方法无需增加额外的设备,辅助方式灵活、简单、经济。
参考文献:
[1] Misra P N. The role of the clock in a GPS receiver[J]. GPS World, 1996, 7(4): 60-66.
[2] 郑睿, 陈杰. 信号短暂缺失下的不完备条件GPS定位算法研究[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2009, 38(4): 496-500.
ZHENG Rui, CHEN Jie. New algorithm of GPS positioning in incomplete condition of temporal insufficient signal[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2009, 38(4): 496-500.
[3] 陈宇波, 宋迎春. 非高斯噪声下的车载GPS信号定位算法[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 41(4): 1462-1466.
CHEN Yubo, SONG Yingchun. A Bays filter algorithm with non-Gaussian noises based on location of vehicular[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology (Science and Technology), 2010, 41(4): 1462-1466.
[4] TANG Hui, Kim D. RFID indoor positioning and navigation using a regularized particle filter integrated with a probability model[C]//Proceedings of the 24th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division (ION GNSS 2011). Portland: Oregon Convention Center, 2011: 3470-3479.
[5] GUO Yao, WU Wenqi, TANG Kanghua. A new inertial aid method for high dynamic Compass signal tracking based on a nonlinear tracking differentiator[J]. Sensors, 2012, 12(6): 7634-7647.
[6] TONG Xiaohua, WU Songchun, WU Shuqing, et al. A novel vehicle navigation map matching algorithm based on fuzzy logic and its application[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2005, 12(2): 214-219.
[7] TENG Yunlong, SHI Yibing. Clock-based RAIM method and its application in GPS receiver positioning[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2012, 19(6): 1558-1563.
[8] 王永超, 黄智刚. 时钟改进模型辅助RAIM算法研究[J]. 电子学报, 2007, 35(6): 1084-1088.
WANG Yongchao, HUANG Zhigang. Research on receiver autonomous integrity monitoring augmented with improved clock bias model[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2007, 35(6): 1084-1088.
[9] Bednarz S, Misra P. Receiver clock-based integrity monitoring for GPS precision approaches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(2): 636-643.
[10] Ramlall R, Streeter J, Schnecker J F. Three satellite navigation in an urban canyon using a chip-scale atomic clock[C]// Proceedings of the 24th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division (ION GNSS 2011), Portland: Oregon Convention Center, 2011: 2937-2945.
[11] Kaplan, E D, Hegarty C J. Understanding GPS Principles and Applications[M]. Norwood: Artech House Inc, 2006: 304-305.
[12] SHI Huli, YAN Yihua. Extended interpolation method and its applications in piecewise approximations[C]//Computational and Applied Mathematics, Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers, 1992: 229-236.
[13] 朱祥维, 肖华, 雍少为, 等. 卫星钟差预报的Kalman算法及其性能分析[J]. 宇航学报, 2008, 29(3): 966-970.
ZHU Xiangwei, XIAO Hua, YONG Shaowei, et al. The Kalman algorithm used for satellite clock offset prediction and its performance analysis[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2008, 29(3): 966-970.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2013-05-20;修回日期:2013-09-05
基金项目:教育部新世纪优秀人才支持计划项目(NCET-08-0144)
通信作者:占建伟(1983-),男,江西乐安人,博士研究生,从事卫星导航测试仿真技术的研究;电话:0731-84576543;E-mail:sophy_zjw@nudt.edu.cn