Cu-Ti合金原位生成TiB2颗粒时的组织演变
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第10期
论文作者:M. SOBHANI H. ARABI A. MIRHABIBI R. M. D. BRYDSON
文章页码:2994 - 3001
关键词:原位反应;TiB晶须;TiB2颗粒;Cu-Ti合金;复合材料
Key words:in-situ reaction; TiB whiskers; TiB2 particles; Cu-Ti alloy; composite
摘 要:通过原位生成反应,采用Cu-3.4%Ti和Cu-0.7%B中间合金,利用快速凝固技术制备纳米TiB2颗粒增强块体Cu-Ti合金,然后对合金在900 °C进行热处理1~10 h。高分辨透射电镜(HRTEM)观察表明,在铜熔体中,Ti和B通过原位反应生成初始纳米TiB2颗粒和TiB晶须,TiB晶须的生成会导致TiB2颗粒粗化。初始TiB2颗粒沿晶界分布,会阻碍晶粒在高温下的生长。在对合金进行热处理时,晶粒内的Ti和B原子通过扩散反应生成二次TiB2颗粒。对合金热处理前后的导电率和硬度进行测试。结果显示,生成的二次TiB2颗粒能够延缓合金在高温下硬度的下降,合金的电导率和硬度随着热处理时间的延长而增加,在处理8 h时分别为33.5%IACS和HV 158。
Abstract: Bulk Cu-Ti alloy reinforced by TiB2 nano particles was prepared using in-situ reaction between Cu-3.4%Ti and Cu-0.7%B master alloys along with rapid solidification and subsequent heat treatment for 1-10 h at 900 °C. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) characterization showed that primary TiB2 nano particles and TiB whiskers were formed by in-situ reaction between Ti and B in the liquid copper. The formation of TiB whiskers within the melt led to coarsening of TiB2 particles. Primary TiB2 particles were dispersed along the grain boundaries and hindered grain growth at high temperature, while the secondary TiB2 particles were formed during heat treatment of the alloy by diffusion reaction of solute titanium and boron inside the grains. Electrical conductivity and hardness of the composite were evaluated during heat treatment. The results indicated that the formation of secondary TiB2 particles in the matrix caused a delay in hardness reduction at high temperature. The electrical conductivity and hardness increased up to 8 h of heat treatment and reached 33.5% IACS and HV 158, respectively.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 2994-3001
M. SOBHANI1, H. ARABI1, A. MIRHABIBI2,3, R. M. D. BRYDSON3
1. Center of Excellence for Advanced Materials and Processing, School of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran 16845-118, Iran;
2. Center of Excellence for Ceramic Materials in Energy and Environmental Applications, Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran 16845-118, Iran;
3. Institute for Materials Research, University of Leeds, Leeds LS2 9JT, United Kingdom
Received 1 November 2012; accepted 16 April 2013
Abstract: Bulk Cu-Ti alloy reinforced by TiB2 nano particles was prepared using in-situ reaction between Cu-3.4%Ti and Cu-0.7%B master alloys along with rapid solidification and subsequent heat treatment for 1-10 h at 900 °C. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) characterization showed that primary TiB2 nano particles and TiB whiskers were formed by in-situ reaction between Ti and B in the liquid copper. The formation of TiB whiskers within the melt led to coarsening of TiB2 particles. Primary TiB2 particles were dispersed along the grain boundaries and hindered grain growth at high temperature, while the secondary TiB2 particles were formed during heat treatment of the alloy by diffusion reaction of solute titanium and boron inside the grains. Electrical conductivity and hardness of the composite were evaluated during heat treatment. The results indicated that the formation of secondary TiB2 particles in the matrix caused a delay in hardness reduction at high temperature. The electrical conductivity and hardness increased up to 8 h of heat treatment and reached 33.5% IACS and HV 158, respectively.
Key words: in-situ reaction; TiB whiskers; TiB2 particles; Cu-Ti alloy; composite
1 Introduction
Copper and copper based alloys are widely used in numerous applications that require high mechanical properties along with high electrical and thermal conductivities. Mechanical strength of copper can be increased by age hardening or incorporating non-metallic second phase particles such as oxides and boride in its matrix. Adding elements such as Be, Cr, Zr and Ti to copper melt, which have low solubility in copper at lower temperatures, can lead to precipitation of hard secondary phases by age hardening. These precipitates are frequently grown during ageing or working at high temperature, which leads to decrease in electrical conductivity and mechanical properties of alloys. Cu-Ti alloys that are susceptible to age hardening can be a possible substitute for the expensive and toxic age hardened Cu–Be alloys since they have good thermal stability and high temperature strength [1-3]. However, Ti as a partial solute element can reduce electrical conductivity of copper in the case that more than 1% (mass fraction) of this element is added to its chemical content [4]. It has been reported that, by increasing Ti content, the electrical conductivity of copper matrix decreases dramatically as negative effect of Ti on electrical properties of copper alloys is more than that of other common alloying elements such as Zn, Sn and Ni. On the other hand, a low amount of Ti does not lead to precipitation of the required phases for strengthening Cu-Ti alloys [5]. Hence, low mechanical properties of this type of alloys are obtained. In order to compensate for the effects of low amount of Ti in copper, TiB2 particles may be used for reinforcement. TiB2 nano particles can be formed in molten copper by an in-situ reaction between boron and titanium [6]. TiB2 addition to copper alloys greatly increases their stiffness, hardness and wear-resistance and decreases coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE) of this type of alloys [7]. Moreover, harmful effect of the dispersed TiB2 particles on the electrical conductivity of copper is much less than that of other ceramic reinforced particles [8,9]. Previous researches [10] have shown that TiB2 particles can act as a grain growth inhibitor at high temperature, thereby, these particles can preserve high temperature mechanical strength of copper alloy. Moreover, these particles can have a positive effect on precipitating behavior of Cu-Ti alloys [11].
Manufacturing technology of metal matrix composites through casting process is of particular interest due to its lower cost and potential for mass production. Although there are some reports on the effect of TiB2 particles on copper matrix strengthening via various methods such as powder metallurgy [12], melt mixing [13] and mechanical alloying [8], no reports have been published yet about the mechanism of in-situ formation of TiB2 particles in Cu-Ti alloy prepared by cast method. In the current work, Cu-Ti-TiB2 composite was produced via a casting process. The purpose of this work was to study the evolution of in-situ formation of TiB2 particles in rapidly solidified Cu-Ti-TiB2 as well as the hardness and electrical properties of the produced composite.
2 Experimental
In order to prepare Cu-1%Ti-1%TiB2 (mass fraction) in-situ composite, Cu-3.4%Ti and Cu-0.7%B master alloys were prepared from high-purity copper (OFHC), titanium plate (99.99%) and boron powder (99.98%). The master alloys were separately melted in an alumina crucible via high vacuum (3.5×10-2 mbar) induction melting furnace (VIM) and poured in a 50 mm×50 mm×100 mm copper mold. Then, they were degreased in NaOH solution and cleaned in 10% nitric acid. In order to increase their melting rate and mix them simultaneously while avoiding gravity segregation of TiB2 particles in the melt, the surface of two master alloys was coupled and charged in the VIM furnace. The coupled master alloy was melted in a vacuum induction furnace at 1200 °C and, just after melting, the melt mixture was poured in the water-cooled copper die. Heat treatment of the cast ingots was performed in the molten salt bath with equal mass fraction of NaCl and CaCO3 at 900 °C for 1 to 10 h. Thin slices were cut from the heat treated samples using ISOMET low speed cutting machine and polished mechanically up to 15 μm. 3 mm diameter disks were punched out from these samples and then they were electro-polished via a jet electropolisher using solution of 35% nitric acid and 65% methanol at -30 °C at voltage of 12 V. Various samples of as-cast and heat treated composite were investigated by high resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) equipped with electron energy loss spectroscope (EELS) and field emission gun scanning electron microscope (FEG-SEM). Micro hardness tests were performed using Vickers hardness tester under 50 g load. Electrical conductivity in %IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard) of the samples was measured using four-point probe method at room temperature according to ASTM B-193 standard. In order to compare the effect of TiB2 on the microstructure and electrical properties of the composite, a reference sample with Cu-3.4%Ti composition was prepared in the same condition as Cu-Ti-TiB2 composite. All the tests performed in the composite were also performed on this reference sample.
3 Results and discussion
In order to determine the reaction direction and synthesis products in the Cu-Ti-B system, the Gibbs free energy of feasible chemical reactions in molten copper was calculated according to thermodynamic data from Ref. [14] and the results are shown in Fig. 1. Thermodynamic calculation showed that all feasible reactions have a negative change in Gibbs free energy. Nevertheless, due to the lowest Gibbs free energy of TiB2 among the five possible products, the formation of TiB2 in molten copper is more susceptible than that of other components.
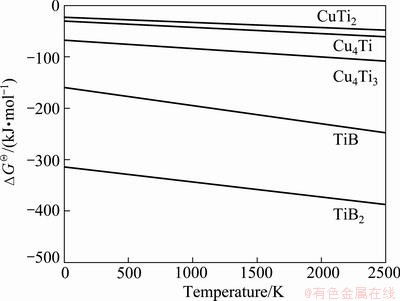
Fig.1 Variation of standard Gibbs free energy of feasible chemical reactions vs temperature in Cu-Ti-B system
Thermodynamically stable TiB2 particles can be formed due to a chemical reaction between elemental boron and titanium at titanium melt micelle interface in molten copper according to GOU et al’s model [15]. Since the melting points of Cu-Ti and Cu-B master alloys are close to each other, they simultaneously begin to melt and mix in the crucible. The diffusion rate of boron element should be higher than that of Ti element due to the higher fluidity of Cu-B alloy melt than that of Cu-Ti at the same temperature. Thus, it can be concluded that boron element could be diffused through Cu-Ti melt micelles interface. At this moment, there is much greater interface between Cu-B and Cu-Ti melt micelles which could lead to the formation of many nano TiB2 particles. Moreover, with the formation of TiB2 particles and the consumption of Ti, the molar ratio of Ti/B is possible to reach 1 at micelle interface. Therefore, under this condition, the diffusion of boron through Cu-Ti melt micelle interface could also lead to the formation of TiB particles.
BS-SEM micrograph of rapidly solidified sample obtained from Cu-Ti-B alloy melt is shown in Fig. 2. As can be seen in this figure, two types of morphology of the reinforced particles were determined within the matrix. The needlelike dark particles (Fig. 2(a)) were identified as TiB whiskers by TEM and selected area diffraction (SAD) pattern, as shown in Fig. 3. It is likely that TiB whiskers were formed in Cu-Ti-B melt by chemical reaction between Ti and B in molten copper due to boron diffusion through the melt micelle interface, as mentioned previously. The second type particles which also have an irregular shape and are especially dispersed along the grain boundaries were identified as TiB2 particles (see Fig. 2(b)).
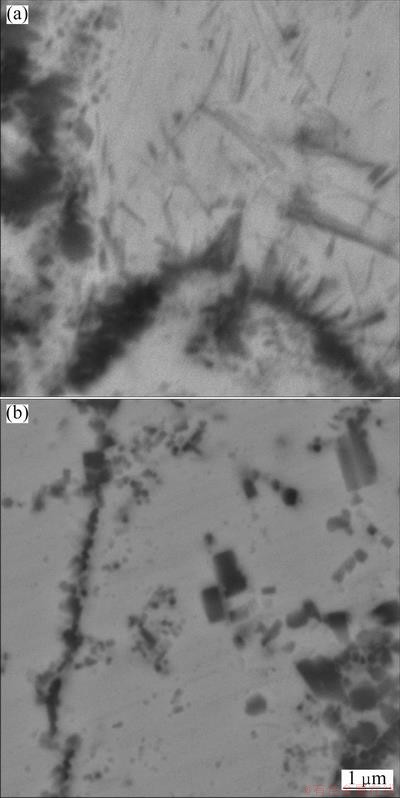
Fig. 2 BS-SEM images of solidified composite showing coarsening of TiB2 particles due to formation of TiB whiskers (a) and TiB2 particles along grain boundary (b)
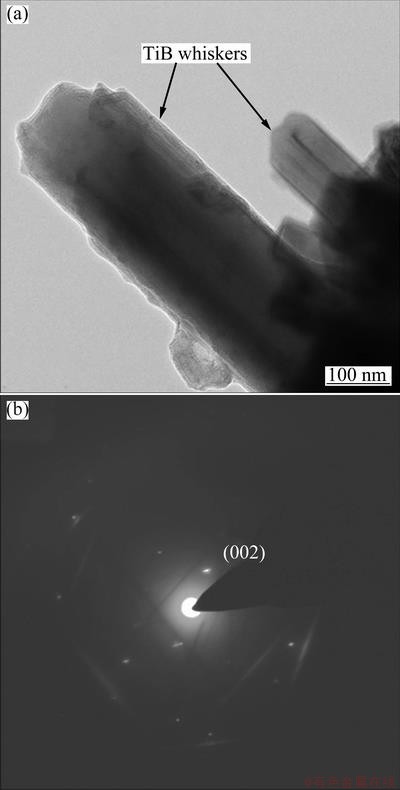
Fig. 3 TEM micrograph of TiB whiskers welded with TiB2 particles (a) and Kikuchi pattern of TiB whiskers (b)
As seen in Fig. 2(a), TiB2 particles which are connected to TiB whiskers have larger size than the separated ones. From this evidence, it can be concluded that the formation of TiB whisker can result in coarsening of TiB2 particles. Increase in the particle size of TiB2 particles by the formation of TiB whiskers can be analyzed by considering the amount of latent heat released due to the formation of TiB whiskers and TiB2 particles in the melt. The formation of TiB2 particles as well as TiB whiskers in the molten copper causes to release latent heat of formation of each particle (i.e. TiB, TiB2) in the melt and leads to increased temperature at reaction interface. The amount of released heat and temperature rising depend on micelle size and mass balance at reaction interface [15,16]. Thermodynamic calculation showed that the latent heat released due to in-situ formation of one mole TiB2 at 1200 °C could increase the temperature of one mole of copper from 1200 °C up to about 8000 °C. This temperature is enough for melting and/or welding TiB2 particles during in-situ reaction. In other words, according to Ti-B phase diagram [17], this temperature is high enough to form new TiB2 particles at congruent temperature (3225 °C) and leads to coarsening of TiB2 particles in molten copper.
The temperature rising at reaction interface also could result in gas generation due to copper evaporation. Figure 4 shows the microstructure of as-cast composite with dot point map of elements. As demonstrated in this figure, the arrangement of TiB2 particles was in the form of burst bubble that can be seen in the region with high concentration of TiB2 particles, which clearly confirmed the gas generation due to the formation of TiB2 particles which could be only observed in the area with a large amount of released heat. This is in agreement with the reported work of DALLAIRE and LEGOUX [18] who stated that the formation of TiB2 particles could lead to copper evaporation.
Microstructure of composite after 10 h of heat treatment is shown in Fig. 5. As shown in this figure, a part of TiB2 particles were dispersed along the grain boundaries. The distribution of TiB2 particles as well as particle size was affected by many factors including in-situ reaction condition and element concentration [15,16]. The density and wetting angle are also two effective factors on distribution of TiB2 particles. Because of the difference between densities of Cu and TiB2, i.e. 8.9 g/cm3 and 4.95 g/cm3 respectively, and low wettability of TiB2 particles by molten copper (i.e. wetting angle is 136°) [19], larger size TiB2 particles were repulsed and redistributed toward the melt freezing interface and finally to grain boundaries while the majority of nano sized particles remained inside the grain according to solid-liquid interface theories for MMCs [20,21]. From Fig. 5, it can be seen that TiB2 particles pinned the grain boundaries and caused significant decrease in grain size of the composite. This decrease in grain size with the presence of TiB2 particles clearly indicated that TiB2 particles could act as grain refinement in α-Cu. This is in accordance with other researchers [7] who also reported that the presence of TiB2 particles in grain boundaries could lead to reduction in grain size and hinder grain growth at high temperature. Figure 6 shows the distribution of TiB whiskers along the grain boundary after deep etching in HNO3, which clearly shows that TiB whiskers along with coarse TiB2 particles also were redistributed by melt freezing interface to grain boundaries.
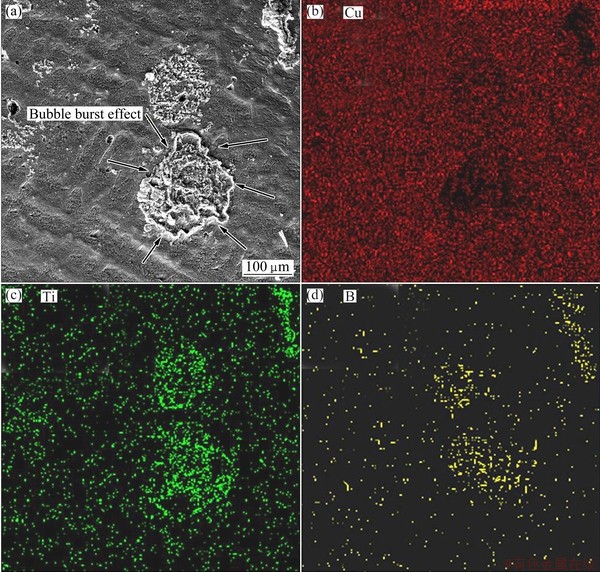
Fig. 4 As-cast micrograph of Cu-Ti-TiB2 with maps of Cu, Ti, B elements
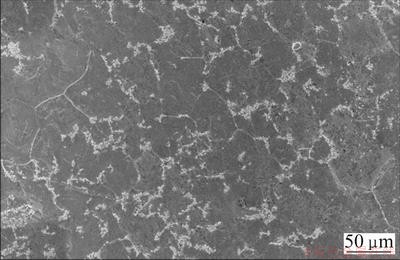
Fig. 5 Distribution of TiB2 particles in grain boundaries

Fig. 6 TiB whiskers along with TiB2 particles in grain boundary after deep etching in HNO3
Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure of composite was evaluated by TEM. Figure 7 shows TEM image of composite with jump ratio map of elements via EELS after 6 h of heat treatment at 900 °C. As seen in this figure, the aggregation of Ti was not completely in alignment with B atoms. This distribution of elements within the matrix indicated that rapid solidification could suppress chemical reaction between boron and titanium atoms and consequently the formation of TiB2 particles in molten copper. In other words, as in-situ formation of TiB2 particles in molten copper is a time-consuming reaction, due to being controlled by the diffusion of boron through melt micelles interfaces, a part of boron may be left within the matrix after rapid solidification. During heat treatment of composite at 900 °C, boron and titanium atoms can react with each other. The result of this reaction is the formation of Ti-B compound at the diffusion reaction interface, as shown with arrow A in Fig. 7(a). Corresponding to TEM image with SAD pattern and chemical analysis results in Fig. 7, it was identified that Ti/B compound consistent with stoichiometry composition of TiB2 particles as their crystal structure is hexagonal with lattice parameters of a=0.303 nm and c=0.323 nm.
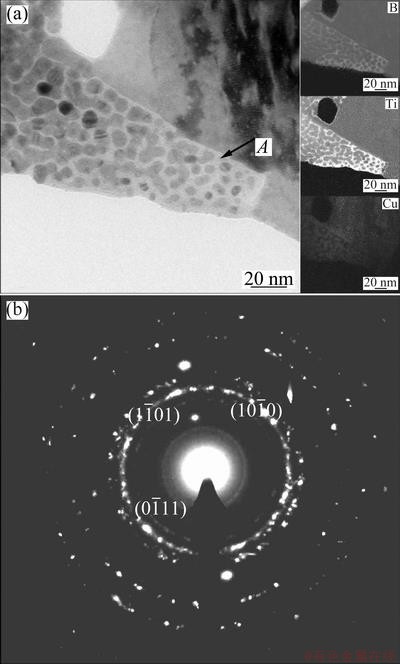
Fig. 7 TEM micrograph showing evolution in formation of secondary TiB2 particles after 6 h of heat treatment with jump ratio elemental map (a) and SAD pattern of TiB2 particles (b)

Fig. 8 HRTEM image showing formation of secondary TiB2 after 8 h of heat treatment at 900 °C
The effect of further heat treatment on the formation of TiB2 particles is shown in Fig. 8. As shown in this figure, the formation of secondary TiB2 is associated with refining of TiB2 particles by driving out of the remained copper from TiB2 structure, as indicated by refining zone in Fig. 8. The final structure of this reaction is TiB2 particles with hexagonal structure, which was confirmed by FFT pattern in Fig. 9.

Fig. 9 FFT pattern of TiB2
Effect of heat treatment on the hardness and grain size of composite in comparison to Cu-3.4%Ti alloy is shown in Fig. 10. The hardness of composite gradually increased as the time of heat treatment increased. The maximum hardness of composite (i.e. HV 158) was achieved after 8 h of heat treatment. This increase in hardness value apparently up to 8 h of heat treatment is most likely due to the formation of the secondary TiB2 particles, as mentioned previously. Based on this result, it could be reasoned that the reinforcing particles can act as a barrier to the movement of dislocation in composite. Thus, more reinforcement particles in the matrix may correspondingly bring greater increase in hardness. After 8 h of heat treatment, decrease of hardness happened and the effect of secondary TiB2 formation was completely revoked. Nevertheless, decrease in hardness after peak value was not remarkable and was attributed to the pinning effects of TiB2 particles at grain boundaries, which hindered the grain growth at high temperature. Figure 10(b) shows the variation of grain size of composite and binary Cu-3.4%Ti alloy versus heat treatment time. The mean grain size of as-cast composite was about 35 μm and gradually increased up to 10 h of heat treatment, while the mean grain size of binary Cu-3.4%Ti sharply increased from 200 μm to about 1 mm after 10 h of heat treatment. The grain growth of binary Cu-Ti followed a relationship with the form of D=Ktn, in which the constant parameters are determined as n=0.51 and k=35.69. This issue indicated that the velocity of grain boundary migration is not a linear function of driving force (i.e. △G), while the rate of grain growth of composite was found to be constant during a period of 10 h of heat treatment. By comparing Figs. 10(a) and (b), it can be concluded that the formation of primary TiB2 particles, which dispersed at grain boundaries, reduces the grain size and hinders the grain growth while the formation of secondary TiB2 particles, which were formed during heat treatment inside the grain, postpones reduction in hardness during high temperature heat treatment.
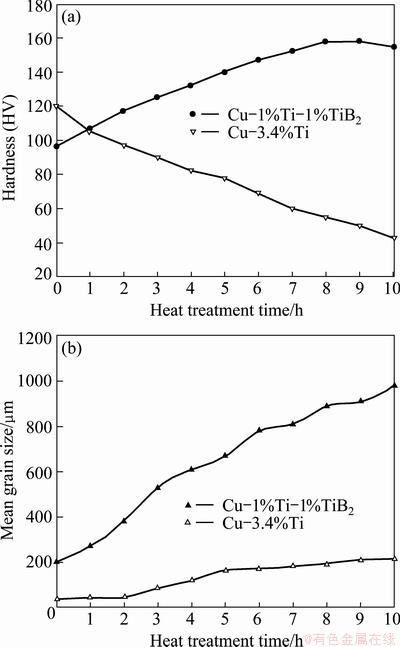
Fig. 10 Variation of harness (a) and grain size (b) as function of heat treatment time for Cu-Ti-TiB2 composite and Cu-3.4%Ti alloy
Electrical conductivity of the composite was evaluated during heat treatment, and the results indicated that electrical conductivity of the as-cast composite was 15% IACS and increased up to 33.5% IACS after 8 h of heat treatment and saturated to about 34% IACS after 10 h of heat treatment. As titanium significantly reduces the electrical conductivity of copper [4], the formation of secondary TiB2 particles within the matrix consumes dissolved titanium in the matrix and results in increased electrical conductivity. In other words, the amount of increase in resistivity due to the increasing volume fraction of TiB2 particles is less than the amount of decrease in resistivity due to the removal of Ti from the matrix, thereby, resulting in an overall increase in electrical conductivity of the composite during heat treatment. This increase in electrical conductivity is mainly due to the reduction of scattering surface of conductive electrons according to Nordheim rule [4]. As shown in Fig. 10(b), the grain size of composite was almost constant during heat treatment, thus it can be concluded that the hardness of composite is almost independent from grain size and mainly affected by the formation of secondary TiB2 particles. This finding along with the fact that electrical conductivity of composite increased during heat treatment exhibited that the rapidly solidified composite can be used for electrical application such as spot welding electrodes, that require high hardness stability at high temperature along with high electrical conductivity.
4 Conclusions
1) Cu-Ti-TiB2 in-situ composite was successfully produced by the reaction of Cu-Ti and Cu-B master alloys.
2) In-situ reaction in Cu-Ti-B system caused the formation of TiB whiskers and TiB2 particles in the matrix.
3) The formation of TiB whiskers resulted in coarsening of TiB2 particles.
4) Primary TiB2 particles formed in molten copper were dispersed along the grain boundaries and acted as an effective grain growth inhibitor. The secondary TiB2 particles were formed in solid-state condition; these particles were formed inside the grains and increased the hardness and electrical conductivity of composite during heat treatment.
5) The maximum values of hardness and electrical conductivity of composite were obtained after 8 h of heat treatment at 900 °C which were HV 158 and 33.5% IACS, respectively.
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the Iranian nanotechnology initiative for financially supporting this project. The authors are grateful to professor. R. M. D. BRYDSON, Department of School of Process, Environmental and Materials Engineering, University of Leeds, for providing TEM facility in Leeds Electron Microscopy and Spectroscopy Centre.
References
[1] TU J P, RONG W, GUO S Y, YANG Y Z. Dry sliding wear behavior of in situ Cu-TiB2 nano-composites against medium carbon steel [J]. Wear, 2003, 255: 832-835.
[2] TJONG S C, LAU K C. Abrasive wear behavior of TiB2 particle- reinforced copper matrix composites [J]. Material Science and Engineer A, 2000, 282: 183-186.
[3] SOFFA W A, LAUGHLIN D E. High-strength age hardening copper–titanium alloys: Redivivus [J]. Progress in Material Science, 2004, 49: 347-366.
[4] NAGARJUNA S, BALASUBRAMANIAN K, SARMA D S. Effect of Ti additions on the electrical resistivity of copper [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 225: 118-124.
[5] NAGARJUNA S, SRINIVAS M, BALASUBRAMANIAN K, SARMA D S. On the variation of mechanical properties with solute content in Cu-Ti alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 259: 34-42.
[6] TU J P, WANG N Y, YANG Y Z, QI W X, LIU F, ZHANG X B. Preparation and properties of TiB2 nanoparticle reinforced copper matrix composites by in situ processing [J]. Materials Letters, 2002, 52: 448-452.
[7] MA Z Y, TJONG S C. High temperature creep behavior of in-situ TiB2 particulate reinforced copper-based composite [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 284: 70-76.
[8] DONG S J, ZHOU Y, SHI Y W, CHANG B H. Formation of a TiB2 reinforced copper-based composite by mechanical alloying and hot pressing [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transaction A, 2002, 33: 1-6.
[9] YID P, CHUNG D D L. Titanium diboride copper matrix composite [J]. Journal of Material Science, 1997, 32: 1703-1709.
[10] BISELLI C, MORRIS D G, RANDALL N. Mechanical alloying of high-strength copper alloys containing TiB2 and Al2O3 dispersed particles [J]. Scripta Materials, 1994, 30(10): 1327-1332.
[11] BOZIC D, STASIC J, RUZIC J, VILOTIJEVIC M, RAJKOVIC V. Synthesis and properties of a Cu-Ti-TiB2 composite hardened by multiple mechanisms [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 8139-8144.
[12] KWON Y S. Microstructure changes in TiB2-Cu nano composite under sintering [J]. Journal of Martial Science, 2004, 39: 5325-5331.
[13] KIM J H, YUN J H, PARK Y H, CHOA K M, CHOI I D, PARK I M. Manufacturing of Cu-TiB2 composites by turbulent in situ mixing process [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 449-451: 1018-1021.
[14] BINNEWIES M, MILKE E. Thermochemical data of elements and compounds [M]. Wienheim: Wiley-VCH, 2002.
[15] GUO M, SHEN K, WANG M. Relationship between microstructure, properties and reaction conditions for Cu-TiB2 alloys prepared by in situ reaction [J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57: 4568-4579.
[16] GUO M X, WANG M P, K SHEN, CAO L F, LI Z, ZHANG Z. Synthesis of nano TiB2 particles in copper matrix by in situ reaction of double-beam melt [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 460: 585-589.
[17] MA Xiao-yan, LI Chang-rong, DU Zhen-min, ZHANG Wei-jing. Thermodynamic assessment of the Ti-B system [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 370: 149-158.
[18] DALLAIRE S, LEGOUX J. Synthesis of TiB2 in liquid copper [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1994, 183: 139-144.
[19] YASINSKAYA G A. The wetting of refractory carbides, borides, and nitrides by molten metals [J]. Soviet Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics, 1966, 5-7: 557-559.
[20] SHANGGUAN D, AHUJA S, STEFANESCU D M. An analytical model for the interaction between an insoluble particle and an advancing solid liquid interface [J]. Metallurgical Transaction A, 1992, 23: 669-680.
[21] STEFANESCU D M, DHINDAW B K, KACAR S A, MOITRA A. Behavior of ceramic particles at the solid-liquid metal interface in metal matrix composites [J]. Metallurgical Transaction A, 1988, 19: 2847-2855.
M. SOBHANI1, H. ARABI1, A. MIRHABIBI2,3, R. M. D. BRYDSON3
1. Center of Excellence for Advanced Materials and Processing, School of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran 16845-118, Iran;
2. Center of Excellence for Ceramic Materials in Energy and Environmental Applications, Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran 16845-118, Iran;
3. Institute for Materials Research, University of Leeds, Leeds LS2 9JT, United Kingdom
摘 要:通过原位生成反应,采用Cu-3.4%Ti和Cu-0.7%B中间合金,利用快速凝固技术制备纳米TiB2颗粒增强块体Cu-Ti合金,然后对合金在900 °C进行热处理1~10 h。高分辨透射电镜(HRTEM)观察表明,在铜熔体中,Ti和B通过原位反应生成初始纳米TiB2颗粒和TiB晶须,TiB晶须的生成会导致TiB2颗粒粗化。初始TiB2颗粒沿晶界分布,会阻碍晶粒在高温下的生长。在对合金进行热处理时,晶粒内的Ti和B原子通过扩散反应生成二次TiB2颗粒。对合金热处理前后的导电率和硬度进行测试。结果显示,生成的二次TiB2颗粒能够延缓合金在高温下硬度的下降,合金的电导率和硬度随着热处理时间的延长而增加,在处理8 h时分别为33.5%IACS和HV 158。
关键词:原位反应;TiB晶须;TiB2颗粒;Cu-Ti合金;复合材料
(Edited by Sai-qian YUAN)
Corresponding author: M. SOBHANI; Tel: +98-21-77459151; Fax: +98-21-77240480; E-mail: m_sobhani@iust.ac.ir
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62826-5

