
Electrochemical behavior of chalcopyrite in presence of
Thiobacillus ferrooxidans
LI Hong-xu(李宏煦)1,2, QIU Guan-zhou(邱冠周)3, HU Yue-hua(胡岳华)3,
CANG Da-qiang(苍大强)1,2, WANG Dian-zuo(王淀佐)3
1. School of Metallurgy and Ecology Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing,
Beijing 100083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Ecological and Recycling Metallurgy, Ministry of Education, Beijing 100083, China;
3. School of Resources Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 23 December 2005; accepted 17 April 2006
Abstract: The chalcopyrite anode dissolution behavior in the presence or absence of bacteria in 9 K media using bacteria modified powder microelectrode at 30 ℃ was studied. It is found that during the anode dissolution, many intermediate transient reactions occur accompanying with the production of chalcocite and covellite at potential between -0.075 V and -0.025 V (vs SCE). At low scanning potential between -0.1 and -0.250 V, the iron ion is released in ferrous form, but at the relative high potential up to 0.7 V, it is the ferric one. The presence of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans makes peak current increase and the initial peak potential negatively move, hinting the decomposed oxidation reaction easily occurred and especially the iron ion released and ferrous oxidation reaction enhanced. The characteristic at potential between -0.75 and -0.5 V demonstrates the Thiobacillus ferrooxidans also contributes to the element sulfur formed on the oxidation surface and removed during anode process. The added ferric in the cell could enhance the dissolution reaction, while the increased acid under pH=2 might slightly hamper the process. The anode dissolution kinetics studies show that the presence of bacteria could decease corrosion potential from 0.238 V to 0.184 V and increase the corrosion current density from 1.632 14×10-8 A/cm2 to 2.374 11×10-7A/cm2.
Key words: biohydrometallurgy; bioleaching; anode oxidation; bacteria modification; powder microelectrode; chalcopyrite; kinetics
1 Introduction
The bioleaching research has a great progress in metallurgy industry. A significant number of commercial applications have emerged and are able to compete with conventional processing, especially the application for the copper recovery. Furthermore, bioleaching treatments have the advantage of being friendly to environment [1,2]. However bioleaching applications for copper extraction are mainly concentrated on the treatment of secondary copper minerals. Chalcopyrite is the most abound ore of the sulfide minerals of copper[3], but it shows very slow kinetics and limited recovery, so it needs to elucidate the oxidation mechanism. We know that the microorganism can catalyze the copper dissolution. It is demonstrated that chalcopyrite and most other metallic sulfides are semiconductor and dissolved by the electrochemistry mechanism, so using the electrochemistry methods to elucidate their oxidation mechanism is reasonable[4-13]. Furthermore, there are lots of studies on the anode dissolving mechanism of chalcopyrite in different media including culture media[14,15], however there is little information on the experiments with microorganism at present. One of the most important reasons is that it is difficult to guarantee the effective attachment of microorganism on the chalcopyrite surface when the quick electrochemical scanning is carried on, with the conventional polished natural massive specimen used as work electrode and the microorganism added in the media solution[16]. For this reason, a new method of bacteria modified powder microelectrode is used as the working electrode to overcome the difficulties above. Based on the characteristic of the powder microelectrodes, apart from the full attachment of leaching bacteria on the chalcopy- rite powder surface, more information about transient intermediate reaction and other useful information during electrochemistry scanning could be obtained[17-19]. Although it is reported that some microorganisms like sulfulobus are more effective on the chalcopyrite resolution, at ambient temperature, Thiobacillus ferrooxidans is still the main microorganism for bioleaching[20,21], so in this work, we use Thiobacillus ferrooxidans as bioleaching microorganism.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Mineral
The natural chalcopyrite was got from Hunan Museum, with high quality and showing few foreign inclusions under the microscope. The massive specimen was crushed and milled under N2 atmosphere in order to prevent the surface oxidation. The size of particle was less than 50 μm. The component of the mineral is Cu31.78 %, Fe32. 05 % and S34.56 %.
2.2 Bacterial culture
The mixed cultures of acidophilic bacteria were obtained from Guangdong Dabaoshan Copper Mine. The Thiobacillus ferrooxidans was isolated from mixed cultured in laboratory. The standard composition of the nutritive media was 9 K media: (NH)4SO4 3.0 g/L; KCl 0.1 g/L; K2HPO4 0.5 g/L; MgSO4?7H2O 5 g/L and Ca(NO3)2 0.01 g/L. The water used in the experiment was ferrous ion free.
2.3 Electrode
A micro plate electrode using platinum wire with the diameter of 50 μm was prepared normally. On the micro electrode surface, a small 100 μm deep pitch was corroded. The chalcopyrite powder was washed with acetone prior to usage, and mineral powder was saturated by the bacteria culture medium with bio-cells sufficiently, then enough time was kept for bacteria attaching on the powder surface fully and absolutely, so the bacteria modified sulfide powder was prepared. The powder was compressed into the electrode pitch using a glass plate to make the powder electrode surface flawless[17,22]. The powder micro-electrode is composed of a micro plate electrode and a thin layer electrode. The structure of the electrode is shown in Fig 1.
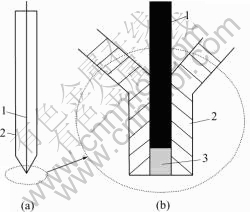
Fig.1 Scheme of bacteria modified powder microelectrode ((b) is tip of (a)): 1 Platinum wire; 2 Glass jacket; 3 Chalcopyrite powder 2.4 Electrochemical experiment
The electrochemical measurements were performed in a typical electrochemical cell (500 mL), as shown in Fig.2, with three electrodes: the working electrode (bacteria modified chalcopyrite powder microelectrode), the counter electrode (Pt plate), and the reference electrode (KCl-saturated calomel electrode). The cell temperature was kept constant by connecting thermo- statically a controlled water loop. The electrolyte used in the experiment was standard 9 K media without ferrous ions. The used water was ion removed. The electro- chemical experiments were carried out using Solartron 1287 with analyzing software. In the paper, all the potential values are versus SCE.

Fig.2 Scheme of electrochemical measurement system
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Influence of bacteria
Fig.3 and Fig.4 show the cyclic voltammograms of the chalcopyrite powder microelectrode in the absence or presence of bacteria. The initial sweep potential is the rest potential. By comparing different sweep cycle, we can see that the oxidation of chalcopyrite includes multi intermediate steps like peaks A, B, C and I. From Fig.3 and Fig.4, we know that the shape of the anode prewave of the first cycle is different from the second and third ones. By comparing the anode oxidation reaction and cathode reduction reaction, it is demonstrated that there is a thin layer product covered on the chalcopyrite surface after oxidation reactions, and the anode oxidation process is controlled by diffusion step.
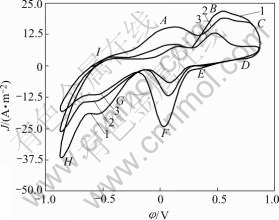
Fig.3 Cyclic voltammograms of chalcopyrite in absence of bacteria (r0=5×10-5m, 5 mV/s, θ=25 ℃, pH=2, initial sweep direction: anode): 1 First cycle; 2 Second cycle; 3 Third cycle
The above result is similar to the results described in Refs.[13, 23-28] using massive chalcopyrite electrode in acid medium. It is possible that the layer is composed of element sulfur or other intermediate phases created during oxidation on the chalcopyrite surface. The initial potential of peak A has a small negative movement during second and third cycle sweep in anode direction. It possibly contributes to the deformation of crystal lattice of chalcopyrite after first cycle polarized and the formation of intermediate production after first cathode reduction sweeping.

Fig.4 Cyclic voltammograms of chalcopyrite in presence of bacteria (r0=5×10-5m, 5 mV/s, θ=25 ℃, pH=2, initial sweep direction: anode): 1 First cycle; 2 Second cycle; 3 Third cycle
In Fig.3 and Fig.4, the peaks A, B represent the oxidation process of chalcopyrite. From the beginning to the peak, at different potentials there exist different oxidation steps. At low potential approximating -0.075 V, the chalcopyrite is transformed to an intermediate phase (Cu1-xFe1-yS2-z), and precarious chalcosite CuS2 is formed with Fe2+ being released. The possible oxidation reaction happens as follows:
CuFeS2→CuS2+Fe2+ (1)
As potential increases approximately up to -0.021 V, CuS2 transfers to another precarious intermediate one, CuS, by oxidation reaction:
CuS2→2CuS+S0 (2)
With the scanning carrying on, the intermediate covelite CuS is oxidized and Cu2+ is released and element sulfur S0 is formed at potential of 0.230 V represented by the following reaction:
CuS→Cu2++S0 (3)
At the potential between -0.1 and 0.250 V, the overall oxidation reactions of chalcopyrite could be represented by
CuFeS2→Cu2++Fe2++2S0+4e (4)
When the potential moves more positively, the more chalcopyrites change to Cu2+, Fe2+ and S0. After then, the S0 would be oxidized to 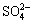 at the potential range of 0.3-0.7 V represented by peak B. The results are consistent to other works by using massive electrode [25,26]. As the potentials become more positive than 0.7 V, Fe2+ begins to be oxidized to Fe3+ as well as the S0 is further oxidized to
at the potential range of 0.3-0.7 V represented by peak B. The results are consistent to other works by using massive electrode [25,26]. As the potentials become more positive than 0.7 V, Fe2+ begins to be oxidized to Fe3+ as well as the S0 is further oxidized to  at peak C according to reactions (5) and (6):
at peak C according to reactions (5) and (6):
Fe2+→Fe3+ (5)
2S0+2H2O+3O2→4H2++2 (6)
(6)
During chalcopyrite oxidation, reactions (2), (3), (5) and (6) are the main process, and reactions (3) and (6) is the confining steps in overall process. The overall dissolution of chalcopyrite in aquatic medium takes place through the following reaction:
CuFeS2+2H2O+3O2→Cu2++Fe3++2 +4H+ (7)
+4H+ (7)
In the reverse scanning, the oxidation ranges of peak D and E may represent the reduction of Fe3+ and Cu2+ produced in anode direction, respectively. The peak F may represent the reverse reaction of (3), like the results of BIEGLER et al[26,27]. We know that during the cathode scanning there would form a reduction layer on the chalcopyrite surface. At the acid solution the peak G and H represent series of reaction as follows:
2CuS+2H++2e→Cu2S+H2S (8)
S0+2H++2e→H2S (9)
By comparing Fig.3 and Fig.4, we know that in the presence of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, at the anode sweep direction the peak current density increases, and the oxidation potential moves negatively, especially at peaks B and C. That means the presence of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans could enhance the chalcopyrite oxidation, especially the ferrous and element sulfur oxidation process are accelerated. The peak current density of peak D during cathode sweeping is also increased, which demonstrates that the more ferric ions are produced during anode process. The shape of peak I of Fig.4 is more flat than that of Fig.3. It shows that the less element sulfur is formed on the mineral surface after anode bio oxidation, which means more element sulfur was removed by bacteria.
Data in Table 1 are the anode sweep results of every peak currents and prewave initial potentials of first cycle in absence of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans during anode oxidation and cathode reduction process. The results show that the attachment of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans on the surface could accelerate oxidation speed of chalcopyrite, apart from enhancing the copper ion extraction and ferrous oxidation release. It also has effective contribution to the oxidation of element sulfur formed on the surface.
Table 1 Scanning results of peak current density and initial potential (first cycle)

3.2 Influence of pH
Fig.5 shows the cyclic voltammograms of the chalcopyrite in the presence of bacteria under different acid conditions. From it we know that when the pH decreases from 2 to 1.5, the potentials of every oxidation steps of chalcopyrite (especially peaks B and C represented reactions) in anode direction become more electropositive, the current density decreases simultane- ously, and the oxidation reaction speed is hampered slightly. This result is similar to other works[14,26,29] In cathode sweep, the shifts of at least 0.15 V in the initial potential of F and G reactions towards more electropositive zone because of the decrease of pH from 2.0 to 1.5 are observed. This shows there is a clear influence of pH on the cathode process through reactions (8) and (9). The increase of H+ concentration would make two reactions move towards right hand direction, H2S would be generated more easily, and the reverse oxidation reaction would become more difficult.
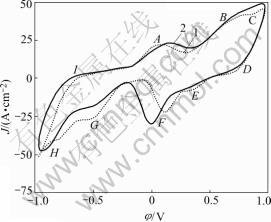
Fig.5 Cyclic voltammograms of chalcopyrite at different pH values (r0=5×10-5m, 5 mV/s, θ=25 ℃, pH=2, initial sweep direction: anode; in presence of bacteria): 1 pH=2; 2 pH=1.5
3.2 Influence of Fe3+
Fig.6 shows the cyclic voltammograms of chalcopyrite when Fe3+ is the presence or absence. At the anode scanning, the current densities of peaks A, B, C and I increase and the initial potentials of prewave negatively move. From this we know that the addition of Fe3+ enhances chalcopyrite decomposition rates apparently, and Fe3+ contributes to the oxidation of intermediate phases such as CuS or Cu2S. On the other hand, peak I shows that by the increase of oxidation rates there are more element sulfur formed on the chalcopyrite surface, although the element sulfur is diminished by Thiobacillus ferrooxidation.
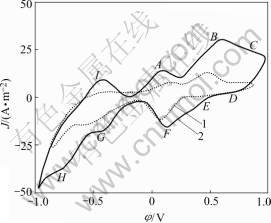
Fig.6 Cyclic voltammograms of chalcopyrite at different ferric concentrations (r0=5×10-5m, 5 mV/s, θ=25 ℃, pH=2, initial sweep direction: anode; in the presence of bacteria): 1 [Fe3+]= 0.000 mol/dm3; 2 [Fe3+]=0.179 mol/dm3
In the reverse scanning, the peak current densities of the relative reduction reactions corresponding to the oxidation reactions increase and the initial potentials move positively. Compared with the scanning results with and without ferric, the Fe3+ reduction process of reaction (10) represented by peak D in Fig.6 is more obvious after ferric addition. On the other hand there is almost no reduction reaction peak observed in the absence of ferric and Thiobacillus ferrooxidans shown in Fig.1.
Fe3++e→Fe2+ (10)
When ferric and bacteria are in absence, they give a very slow oxidation process on the fresh surface of chalcopyrite in acid solution, which is in accordance with the results of WARREN and SOHN[29]. On the contrary it is demonstrated that the Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and ferric positively enhance the dissolution of chalcopyrite. Collaboratively the current densities of other reduction reactions in cathode scanning are increased relatively.
3.4 Corrosion kinetics
Fig.7 shows the Tafel curve of chalcopyrite powder electrode. The relationship between over potential and corrosion current density could be expressed by Tafel equation as follows:
 (11)
(11)
If formula (11) is ameliorated by Allen-Hikling equation, we can get
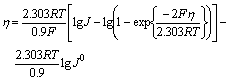 (12)
(12)
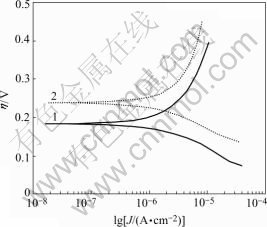
Fig.7 Tafel curve of chalcopyrite powder electrode (r0=5×10-5m, 5 mV/s, 5 mV/s, pH=2, T=298 K, 9K medium): 1 In absence of bacteria; 2 In presence of bacteria
Based on the data of polarization curve shown in Fig.7 and using Eqn.(12), the value of equilibrium potential of corrosion reaction and the corrosion current density would be obtained under solution pH value of 2. If bacteria is in the presence, the Ecorr is 0.184 V and the  would climb up to 2.374 11×10-7A/cm2. However when bacteria is in the absence, the Ecorr is up to 0.238 V and the
would climb up to 2.374 11×10-7A/cm2. However when bacteria is in the absence, the Ecorr is up to 0.238 V and the 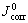 is only 1.632 14×10-8A/cm2. By comparing different results we know that the presence of bacteria could decrease the corrosion potential and increase the corrosion current of chalcopyrite, which means that the presence of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans could improve chalcopyrite corrosion kinetics and make it give more easy dissolution. That is one of the reasons why the bacteria could accelerate the oxidation and dissolution of chalcopyrite in acid solution.
is only 1.632 14×10-8A/cm2. By comparing different results we know that the presence of bacteria could decrease the corrosion potential and increase the corrosion current of chalcopyrite, which means that the presence of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans could improve chalcopyrite corrosion kinetics and make it give more easy dissolution. That is one of the reasons why the bacteria could accelerate the oxidation and dissolution of chalcopyrite in acid solution.
4 Conclusions
1) The anode oxidation process and dissolution of chalcopyrite have many intermediate transient reactions including producing intermediate compounds of chalcocite and covellite companying with metal ion released and element sulfur formed on the mineral surface. At lower scanning potentials the iron is extracted from chalcopyrite by ferrous, but at the relative high potential it is by the ferric owing to the fact that the released ferrous would be oxidized to ferric, and the element sulfur would be oxidized to sulfuric partially in the further steps.
2) In the presence of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, the peak current density of the reaction increases with scanning carrying on, and the initial potential negatively moves especially in oxidation direction. This demonstrates that apart from enhancing the metallic ion extracted from chalcopyrite, Thiobacillus ferrooxidans also contributes to the oxidation of element sulfur formed on the chalcopyrite surface during the intermediate process.
3) The decrease of pH value from 2.0 to 1.5 gives slight prohibition to the dissolution of chalcopyrite. The Fe3+ added in the medium can enhance the anode oxidation of chalcopyrite.
4) Corrosion kinetics studies show that the bacteria could decrease chalcopyrite corrosion potential and increase the corrosion current, resulting in the corrosion kinetics improved and more easy dissolution of the bacteria in acid solution.
References
[1] EHRLICH H L. Past, present and future of biohydrometallurgy [A]. BALLESTER A, AMILS R, Eds. International Biohydrometallurgy Symposium [C]. Elsevier, Amsterdam. 1999. 3-12.
[2] BRIERLEY J A, BRIERLEY C L. Present and future commercial applications of biohydrometallurgy [A]. BALLESTER A, AMILS R, Eds. International Bio-hydrometallurgy Symposium [C]. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1999. 3-12.
[3] ROMANO P, BLAZQUEZ M L, ALGUACIL F J, MUNOZ J A, BALLESTER M A, GONZALEZ F. Comparative study on the selective chalcopyrite bioleaching of a molybdenite concentrate with mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria [J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2001, 196: 71-75.
[4] HANSFORD G S, VARGAS T. Chemical and electrochemical basis of bioleaching processes [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 59: 135-145.
[5] LI Hong-xu, WANG Dian-zuo. The electrochemistry aspect of bioleaching(Ⅰ) [J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2002, 11(4): 49-53. (in Chinese)
[6] LI Hong-xu, WANG Dian-zuo. The electrochemistry aspect of bioleaching(Ⅱ) [J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2003, 12(2): 45-48. (in Chinese)
[7] LI Hong-xu, WANG Dian-zuo. The progress of electrochemistry investigation in bioleaching [J]. Nonferrous Metals (Chinese, quarterly). 2003, 55(1): 81-85. (in Chinese)
[8] WOLFGANG SAND, TILMAN GEHRKE, PETER-GEORG JOZSA, AXEL SCHIPPERS. Biochemistry of bacterial leaching— direct vs indirect bioleaching [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 59: 159-175.
[9] MICHAEL J NICOL, ISABEL LA?ZARO. The role of Eh measurements in the interpretation of the kinetics and mechanisms of the oxidation and leaching of sulphide minerals [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2002, 63:15-22.
[10] ADIBAH YAHYA, D BARRIE JOHNSON. Bioleaching of pyrite at low pH and low redox potentials by novel mesophilic Gram-positive bacteria [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2002, 63: 181-188.
[11] ABHA KUMARI, NATARAJAN K A. Electrobioleaching of polymetallic ocean nodules [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 62: 125-134.
[12] GIANNETTI B F, BONILLA S H, ZINOLA C F, RABOCZKAY T. A study of the main oxidation products of natural pyrite by voltammetric and photoelectrochemical responses [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 60: 41-53.
[13] MISHRA K K, OSSEO-ASURE. Aspect of the interface electrochemistry of semiconductor [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1988, 135: 2502-2508.
[14] C?MEZ C, FIGUEROA M, MU?OZ J, BL?ZQUEZ M L. Electrochemistry of chalcopyrite [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1996, 43: 331-344.
[15] LARAZO I, MARTINEZ-MEDINA N, RODIRGUEZ I. The use of carbon paste electrode with non conducting binder for the study of minerals-chalcopyrite [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1995, 38: 277-287.
[16] PALENCIA I, WAN R Y, MILLER I D. The electrochemical behavior of semiconductor natural pyrite in the presence of bacteria [J]. Metal Mater Trans B, 1991, 22: 765-773.
[17] CHA C S, LI C M. Powder microelectrodes [J]. J Electroanalytical Chem, 1994, 368: 47-54.
[18] LI Hong-xu, WANG Dian-zuo, HU Yue-hua, QIU Guan-zhou. The electrochemical study on the oxidation of Fe2+ on the Thiobacillus ferroxidans modified powder microelectrode [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12: 1263. (in Chinese)
[19] LI Hong-xu, HU Yue-hua, QIU Guan-zhou, WANG Dian-zuo. The influence of Cu2+ to the oxidation of Fe2+ on the Thiobacillus ferroxidans modified powder microelectrode [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13: 229. (in Chinese)
[20] JOSE’ PIZARRO, EUGENIA JEDLICKI, OMAR ORELLANA, JAIME ROMERO. Bacterial populations in samples of bioleached copper ore as revealed by analysis of DNA obtained before and after cultivation [J]. Appl Enviro Microbio, 1996, 62: 1323-1328.
[21] LI Hong-xu, WANG Dian-zuo. The microorganism and their behavior in bio-leaching [J]. Nonferrous Metals (Chinese, quarterly), 2003, 55(2): 58. (in Chinese)
[22] LI Hong-xu. Studies on the Electrochemical Mechanism and Technology of Sulfide Bioleaching [D]. Changsha, China, 2001, 17-20. (in Chinese)
[23] PARKER A J, PAUL R L, POWER G P. Electrochemistry of the oxidative leaching of copper from chalcopyrite [J]. J Electroanal Chem, 1981, 118: 305-316.
[24] STANKOVIC Z D. The anodic dissolution reaction of chalcopyrite [J]. Erzmetall, 1986, 39: 623-628.
[25] WARREN G W, WADSWORTH M E, EL-RAGHY S H. Passive and transpassive anodic behavior of chalcopyrite in acid solutions [J]. Metall Trans B, 1982, 13: 571-579.
[26] BIEGLER T, SWIFT D A. Anodic electrochemistry of chalcopyrite [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 1979, 9: 545-554.
[27] BIEGLER T, HOME M D. The electrochemistry or surface oxidation of chalcopyrite [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1985, 132: 1363-1369.
[28] HOLLIDAY R I, RICHMOND W R. An electrochemical study of the oxidation of chalcopyrite in acidic solution [J]. J Electronal Chem, 1990, 288: 83-98.
[29] WARREN G W, SOHN H J. The effect of electrolyte composition on the cathodic reduction of CuFeS2 [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1985, 15: 133-149.
Foundation item: Project(2004CB619205) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project(50204001) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: LI Hong-xu; Tel/Fax: +86-10-62332786; E-mail: lihongxu2001@126.com
(Edited by YANG Bing)