
EPS-contact-leaching mechanism of chalcopyrite concentrates by
A. ferrooxidans
YU Run-lan(余润兰), TAN Jian-xi(谭建锡), YANG Peng(杨 鹏),
SUN Jing(孙 静), OU Yang(欧 阳), XIONG Jing(熊 晶), DAI Yun-jie(戴云杰)
Key Laboratory of Biometallurgy of Ministry of Education, School of Minerals Processing and
Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
Received 20 September 2008; accepted 5 November 2008
Abstract: The effect of extracelluar polymeric substances(EPS) on the bioleaching chalcopyrite concentrates in the presence of iron- and sulphur-oxidizing bacteria (A. ferrooxidans) was studied. The bacterial number, pH, redox potential, and the concentrations of Fe2+and Cu2+ ions were investigated. The leached residues were analyzed by the X-ray diffraction and FT-IR. The results indicate that the EPS makes the bacteria adhere to the chalcopyrite surface easily and it is helpful for bacteria in disadvantageous environment. At the same time, EPS film layer with Fe3+ deposits on the surface of chalcopyrite and becomes a barrier of oxygen transfer to chalcopyrite to passivate chalcopyrite, and creates the high redox potential space through concentrating Fe3+ ions to accelerate bioleaching pyrite in chalcopyrite concentrates. The results suggest that EPS formation promotes bioleaching pyrite and inhibits bioleaching chalcopyrite, especially under high potential condition.
Key words: EPS-contact-leaching mechanism; chalcopyrite concentrate; bioleaching; passivation
1 Introduction
Many studies have shown that bacterial leaching of metal sulphides, including secondary copper sulphides, is possible[1-3]. Chalcopyrite is the most abundant and commercial interest copper mineral. However, there is still uncertainty about bioleaching of chalcopyrite as its slow kinetics results in low copper extraction[4].
Many researches have dealt with the subject of the slow kinetics of chalcopyrite leaching and its passivation [5-7]. These studies all agree that the precipitation of jarosite, a common product in bioleached residues, is linked to the passivation of chalcopyrite. The biological mechanisms and the reactions that come into play during the oxidative dissolution of metal sulphides are controversial and still poorly understood[1,2,4,8]. Two mechanisms are known to be responsible for the bioleaching of sulphides, namely indirect and direct mechanisms. The direct mechanism involves the enzymatic attack of the mineral by the bacterium, for which intimate contact and adhesion are required. The indirect mechanism, on the other hand, operates with the chemical action of acidic ferric sulphate solutions produced by bacterial oxidation of ferrous iron or pyrite (FeS2), normally presenting in these environments. In this mechanism, previous researchers thought that adhesion of the bacteria to the mineral surface was supposed to be not required[9-10]. But in recent studies, majority researchers thought that the adhesion of the bacteria to the mineral surface is also not neglected because the oxidation of iron is thought to exist not only in the solution but also at the adsorption interface. Recently, some studies suggested that extracellular polymeric substances(EPS) present in cell envelope [11-12] might play a very important role at the initial stages of adhesion. Other studies[12-13] have observed EPS of T. f and iron ion in the EPS by the method of electronic microscope and cellular chemistry.
Although the fact that EPS plays a very important role in adhesion of the bacteria to the mineral surface[11-13] has been accepted by many researchers, there is poor research about the relationship of EPS, bioleaching chalcopyrite and its passivation.
The aim of this work is to further understand the role and mechanism of EPS during bioleaching chalcopyrite concentrates.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Preparation of chalcopyrite sample
A flotation chalcopyrite concentrate with a mean particle size of about 75 ?m obtained from Dexing Copper Mine (Jiangxi Province, China) was washed by 1 mol/L HCl and 2 mol/L H2SO4 in turn for three times, then washed with acetone to remove the flotation reagent. The chalcopyrite concentrate was put in air for 4 h, then, dried for 24 h at 100 ℃. Finally, the mineral was sterilized for 24 h by UV in asepsis room.
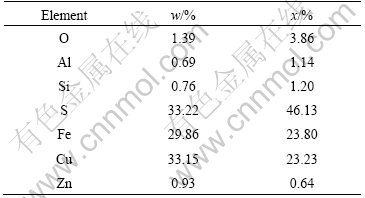
The chemical and mineralogical analyses of chalcopyrite concentrate are listed in Table 1 by X-ray diffraction. The sample contains 33.15% Cu, 29.86% Fe, 33.22% S, and minor amounts of quartz, pyrite and covellite as accessory minerals.
Table 1 Main compositions of chalcopyrite concentrate
2.2 Microorganisms and culture medium
The leaching solution contains 3.00 g/L (NH4)2SO4, 0.10 g/L KCl, 0.50 g/L K2HPO4, 0.50 g/L MgSO4·7H2O and 0.01 g/L Ca(NO3)2. The leaching solution was sterilized in steam at 121 ℃ for 15 min before being used. An EPS solution was prepared according to the analysis results of EPS from previous research [11-12,14]. Its main components were as follows (w/v): rhamnose 10.8%, fucose 17.1%, mannose 0.7%, glucose 15.2%, C18 21.6%, and adjusted pH to 2.0 with sulphuric acid.
A. ferrooxidans used in this study was initially adapted to grow with chalcopyrite through several subcultures in liquid medium through successive replacement of Fe2+ with chalcopyrite. The supernatant solution from the culture was used as inoculum.
All leaching experiments were performed in 250 mL shake flasks containing 200 mL leaching solution mentioned above with 1% chalcopyrite concentrates as the sole substrate. Flasks were placed on an orbital Shaker and incubated at 30 ℃, shaking at the rate of 180 r/min. Leaching experiments were carried out as follows: abiotic controls, abiotic controls with 1% (v/v) EPS solution mentioned above, bioleaching without the EPS solution and bioleaching with 1% (v/v) the EPS solution.
2.3 Analytical procedures
Bacteria were observed and counted by blood cell counting chambers with an optical microscope, the pH was measured by PHS-3C pH meter, and the solution potential(φ) by Pt and silver-silver chloride double electrodes at the interval of two days during bioleaching. All the solution potentials have been converted to standard hydrogen electrode (vs SHE). Soluble copper was determined by Atomic Absorption Spectro- photometry(AAS), and ferrous ion was determined by titration with potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7 ), after centrifugation to separate the solid material and bacteria. Finally, the residues of leached samples were dried in vacuum desiccator, and characterized by X-ray diffraction(XRD) and FT-IR.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Bacteria concentration with bacteria and with bacteria and EPS experiments
Fig.1 shows the change of the bacterial number in the experiments with bacteria and with bacteria and EPS during bioleaching chalcopyrite, respectively. An adaptive phase occurs in 5 d, and the logarithmic growth phase of bacteria is about from 5-15 d. Then, the bacteria concentration begins to decrease, and a second growth peak appears again. It seems to be the change of the living circumstance for bacterial. It can be seen from Fig.2, the redox potential of the solution rapidly rises over 750 mV (vs SHE), so it can be inferred that high redox potential results in the suppression of bacterial activity. Subsequently, bacteria gradually adapt the environment of high redox potential of solution again.
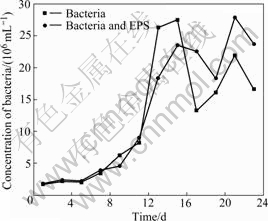
Fig.1 Change of bacterial concentration with time in bioleaching solution
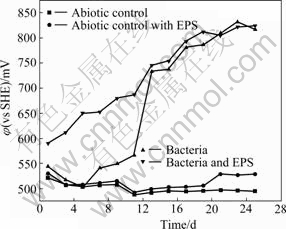
Fig.2 Change of redox potential of bioleaching solutions with time
Seen from Fig.3 and Fig.4, the drop of the pH and the increase of Fe2+ concentration in the solutions with bacteria and with bacteria and EPS may be explained according to the following reaction:
CuFeS2+16Fe3++8H2O→Cu2++2SO42-+17Fe2++16H+
(1)
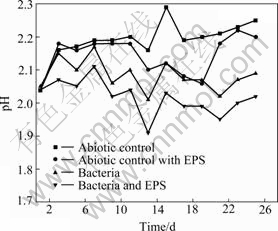
Fig.3 pH change of leaching solutions with time
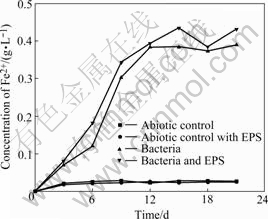
Fig.4 Change of Fe2+ concentration in bioleaching solutions with time
The enough concentration of Fe2+ makes bacteria second adaptive phase shorter.
EPS mediates the contact between the bacterial cell and the sulfide energy source, having a pivotal role in organic film formation and bacterium-substrate interaction[11]. The amount of attaching cells was decreased significantly when cells were depleted of their EPS[12]. Seen from Fig.1, the bacterial concentration in the experiment with simulative EPS is lower than that in experiment without simulative EPS from the 7th day to the 15th day, but opposite appearance occurs at the end stage. As our bacterial count is based on free bacteria in solution, the results can be explained as follows: 1) EPS makes bacteria adherent to chalcopyrite surface and bacteria enter into the EPS environment easily at the logarithmic growth stage of bacteria under low potential condition; 2) EPS plays an important role in protecting bacteria at the end stage[15-16] when solution potential is over 750 mV.
3.2 Change of pH values of bioleaching solutions
The variety of solution pH is shown in Fig.3. The total trend of pH change in abiotic control rises persistently, because there is only chemical leaching. Therefore, the pH increase of the solution cannot be avoided according to the following reaction:
CuFeS2+O2+4H+→Cu2++Fe2++2S0+2H2O (2)
The total trend of pH change in abiotic control with EPS experiment first rises, then drops, and rises again. Because abiotic control with EPS is also an abiotic control, the initial variety of solution pH is similar to abiotic control. Then, the drop of the pH is due to the chelating action of EPS which contains —OH and —COOH to release H+ into the solution according to the Reaction (3). Finally, the chelating action of EPS is up to saturation, and the chemical leaching appearance similar to abiotic control occurs again:
Fe2++2EPS-H→Fe(EPS)2+2H+ (3)
The pH values of solution with bacteria and with bacteria and EPS inoculated with 5% cultures are lower than those of solution with abiotic control and with abiotic control with EPS due to the bioleaching chalcopyrite concentrates.
The total trend of pH change in experiments with bacteria and with bacteria and EPS is gradually decreased except initial stage. Bacterial metabolizing consumes H+ according to Reactions (4)-(5) during the initial period of bioleaching, then, the dissolution of chalcopyrite by bacteria produces sulfuric acid, iron deposits and jarosites, consequently, resulting in the gradual drop of solution pH, according to the Reactions (6)-(8):
Fe2+-e→Fe3+ (bacteria) (4)
4H++O2+4e→2H2O (bacteria) (5)
2S0+3O2+2H2O→2SO42-+4H+ (6)
Fe3++nH2O→Fe(OH)n+nH+ (1≤n≤3) (7)
K++2SO42-+3Fe3++6H2O→KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6+6H+ (8)
A little rise of pH at the end stage should be as a consequence that high potential and a lot of jarosits inhibite bioleaching chalcopyrite.
The fact that the pH value of the solution with bacteria and EPS is lower compared with the solution with bacteria and EPS-free demonstrates that EPS is helpful for bioleaching and Fe2+ oxidation, which also can be seen from Figs.2 and 4. The potential increases significantly by the adherence of EPS-contained bacteria from the beginning of bioleaching to the 11th day. It may be hypothesized that[17-19] this EPS layer constitutes a special, enlarged reaction space. The role of EPS layer is to increase the concentration of Fe3+ close to the chalcopyrite surface by complexing iron(Ⅲ) ions, thereby causing an acceleration of chemical or electrochemical dissolution of sulfide[14].
Consequently, it can be concluded that simulative EPS solution increases the redox potential of solution by maintaining the high concentration of Fe3+ ions, which is favor for precipitation as jarosite and hydrolyzation resulting in the drop of pH.
3.3 Evolution and analysis of redox potential in bioleaching solutions
Redox potentials in non-inoculated experiments with abiotic control and with abiotic control and EPS show slight change of fluctuation and maintain the value around 500 mV (vs SHE), as shown in Fig.2. This indicates that chemical dissolution is very poor. The redox potential in experiments with bacteria and with bacteria and EPS shows upwards in whole time, then tends towards equilibrium around 800 mV (vs SHE). The redox potential in the experiment with bacteria and EPS is always higher compared with the experiment with bacteria before the 15th day. Obviously, EPS not only reduces the adaption period of bacteria but also concentrates Fe3+ ions. After 15 d, nearly the same appearance occurs in experiments with bacteria and with bacteria and EPS because EPS film layer is also gradually formed in experiment with bacteria according to FU et al[13].
3.4 Discussion on iron(Ⅱ) and copper concentrations in bioleaching solutions
Seen from Fig.4, the Fe2+concentrations of the solutions with abiotic control and with abiotic control and EPS always maintain at a very low level, while the evolution trend of the solutions with bacteria and with bacteria and EPS shows gradually upwards to an equilibrium. Seen from Fig.5, the copper dissolution rate decreases and copper concentration increases with increasing time. Dissolution of chalcopyrite in the non-inoculated experiments with abiotic control and with abiotic control with EPS is mainly due to the chemical leaching with low copper extraction. Yet, the dissolution rates of chalcopyrite in the experiments with bacteria and with bacteria and EPS slow down when the redox potentials are higher than 650 mV (vs SHE), and the rate of copper dissolution almost decreases over the 15th day, here, the redox potential is around 750 mV (vs SHE). This coincides with the study that maximum dissolution of chalcopyrite occurs at about 650 mV (vs SHE)[20].
It is interesting to find that the Fe2+concentration of solution with bacteria and EPS is higher than that of solution with bacteria, while the change of copper concentration is on the contrary, as shown in Fig.5. The previous study noted that high Fe(Ⅲ) concentration inhibits the bacterial activity and is favored for passivation of chalcopyrite and dissolution of pyrite and sphalerite[21]. Moreover, some studies pointed out that in the case of pyrite, this sulfide chiefly dissolves when chalcopyrite has already been passivated[22]. Considering chalcopyrite concentrate used in this study contains a few pyrites and the fact that the Fe2+ concentration of the solution with bacteria and EPS is higher than that of the solution with bacteria while their change of copper concentration are on the contrary. The conclusion can be inferred that this EPS is helpful for bioleaching pyrite but inhibits bioleaching chalcopyrite in some extent.
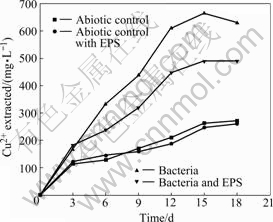
Fig.5 Change of copper concentrations in bioleaching solutions with time
Fig.6 reveals that the bioleached residues include CuFeS2, jarosites, sulfur and FeOOH, etc, and the amount of residues such as jarosites and FeOOH of bacteria solution is higher than that of bacteria and EPS solution. This indicates that EPS inhibits the formation of jarosite. At the same time, the FT-IR spectra presented in Fig.7 can be inferred that the adsorption of EPS on the surface of residues and the dissolution of chalcopyrite concentrate. In addition, the redox potential in experiment with bacteria and EPS is also higher than that with bacteria during the bioleaching chalcopyrite concentrate, as shown in Fig.2[23-25].
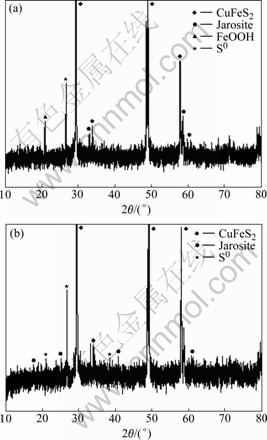
Fig.6 XRD patterns of bioleached residues: (a) Bacteria; (b) Bacteria and EPS
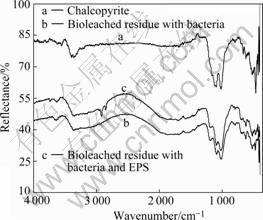
Fig.7 FT-IR spectra of chalcopyrite and bioleached residues
Consequently, EPS film layer with Fe3+ and its deposits on the surface of chalcopyrite may create the high redox potential space to reduce oxygen transfer and to passivate chalcopyrite, at the same time, accelerates the bioleaching pyrite.
4 Conclusions
1) EPS makes bacteria adhere to chalcopyrite surface easily and plays an important role in protecting bacteria against disadvantage environment.
2) EPS film layer can concentrate Fe3+ ions and H+ ions.
3) EPS film layer with Fe3+ and its deposits on the surface of chalcopyrite reduce oxygen transfer and passivate chalcopyrite, at the same time, can create the high redox potential space through concentrating Fe3+ ions, especially more than 750 mV, to accelerate bioleaching the pyrite in chalcopyrite concentrates.
References
[1] WATLING H R. The bioleaching of sulfide minerals with emphasis on copper sulphides—A review [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 84: 81-108.
[2] SAND W, GEHRKE H. Extracellular polymeric substances mediate bioleaching/biocorrosion via interfacial processes involving iorn(Ⅲ) ions and acidophilic bacteria [J]. Research in Microbiology, 2006, 157: 49-56.
[3] OLSON G J, BRIERLEY J A, BRIERLEY C L. Bioleaching review (part B): Progress in bioleaching: applications of microbial processes by the minerals industries [J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2003, 63: 249-257.
[4] C?RDOBA E M, MU?OZ J A, BL?ZQUEZ M L, GONZ?LEZ F, BALLESTER A. Leaching of chalcopyrite with ferric ion (Part IV): The role of redox potential in the presence of mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 93: 106-115.
[5] STOTT M B, WATLING H R, FRANZMANN P D, SUTTON D. The role of iron-hydroxy precipitates in the passivation of chalcopyrite during bioleaching [J]. Miner Eng, 2000, 13(10/11): 1117-1127.
[6] BEVILAQUA D, LEITE A L L C, GARC?A O, TUOVINEN O H. Oxidation of chalcopyrite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans in shake flasks [J]. Process Biochem, 2002, 38: 587-592.
[7] DEVECI H, AKCIL A, ALP I. Bioleaching of complex zinc sulphide using mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria: Comparative importance of pH and iron [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 73: 293-303.
[8] BOON M. The mechanism of ‘direct’ and ‘indirect’ bacterial oxidation of sulphide minerals [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 62: 67-70.
[9] CURUTCHET G, DONATI E. Iron-oxidizing and leaching activities of sulphur-grown Thiobacillus ferrooxidans cell on other substrates: Effect of culture pH [J]. J Biosci Bioeng, 2000, 90: 54-58.
[10] SAMPSON M I, PHILLIPS C V, BLAKE II R C. Influence of the attachment of acidophilic bacteria during the oxidation of mineral sulfides [J]. Miner Eng, 2000, 13: 373-389.
[11] GEHRKE T, TELEGDI J, THIERRY D, SAND W. Importance of extracellular polymeric substances from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans for bioleaching [J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1998, 64(7): 2743-2747.
[12] HARNEIT K, G?KSEL A, KOCK D, KLOCK J H, GEHRKE T, SAND W. Adhesion to metal sulfide surfaces by cells of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 83: 245-254.
[13] FU Jian-hua, QIU Guan-zhou, HU Yue-hua, XU Jing. The role of EPS of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans during bioleaching [J]. Acta Laser Biology Sinica, 2004, 13(1): 62-66. (in Chinese)
[14] KINZLERA K, GEHRKEA T, TELEGDIB J, SANDA W. Bioleaching—A result of interfacial processes caused by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 71: 83-88.
[15] HUNG Chin-chang, SANTSCHIA P H, GILLOW J B. Isolation and characterization of extracellular polysaccharides produced by pseudomonas fluorescens Biovar II [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2005, 61: 141-147.
[16] GUIBAUD G, COMTE S, BORDAS F, DUPUY S, BAUDU M. Comparison of the complexation potential of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), extracted from activated sludges and produced by pure bacteria strains, for cadmium, lead and nickel [J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 59: 629-638.
[17] SAND W, GEHRKE T, JOZSA P G, SCHIPPERS A. Direct versus indirect bioleaching [C]// Biohydrometallurgy and the Environment Toward the Mining of the 21st Century (Part A). Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1999: 27-49.
[18] FOWLER T A, HOLMES P R, CRUNDWELL F K. Mechanism of pyrite dissolution in the presence of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1999, 65(7): 2987-2993.
[19] TRIBUTSCH H. Direct versus indirect bioleaching [C]// Biohydrometallurgy and the Environment Toward the Mining of the 21st Century (Part A). Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1999: 51-60.
[20] HIROYOSHI N, KITAGAWA H, TSUNEKAWA M. Effect of solution composition on the optimum redox potential for chalcopyrite leaching in sulfuric acid solutions [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 91: 144-149.
[21] CANCHO L, BL?ZQUEZ M L, BALLESTER A, GONZ?LEZ F, MU?OZ J A. Bioleaching of a chalcopyrite concentrate with moderate thermophilic microorganisms in a continuous reactor system [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2007, 87: 100-111.
[22] C?RDOBA E M, MU?OZ J A, BL?ZQUEZ M L, GONZ?LEZ F, BALLESTER A. Leaching of chalcopyrite with ferric ion (Part II): Effect of redox potential [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 93: 88-96.
[23] THIRD K A, CORD-RUWISCH R, WATLING H R. The role of iron-oxidizing bacteria in stimulation or inhibition of chalcopyrite bioleaching [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 57: 225-233.
[24] THIRD K A, CORD-RUWISCH R, WATLING H R. Control of the redox potential by oxygen limitation improves bacterial leaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Biotechnol Bioeng, 2002, 78(4): 433-441.
[25] SANDSTROM A, SHCHUKAREV A, PAUL J. XPS characterisation of chalcopyrite chemically and bio-leached at high and low redox potential [J]. Miner Eng, 2005, 18: 505-515.
Foundation item: Project(2004CB619204) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project(50621063) supported by the Chinese Science Foundation for Distinguished Group
Corresponding author: YU Run-lan; Tel: +86-731-8836943; E-mail: YRL715@sina.com.cn
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)