


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 442-446
Experimental measurements of short-term adsorption of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans onto chalcopyrite
WANG Zhao-hui1, XIE Xue-hui1, LIU Jian-she1, 2
1. College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China;
2. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 16 March 2011; accepted 30 May 2011
Abstract: The influencing factors in adsorption such as adsorption time, pulp concentration, bacterial concentration, pH as well as ionic strength were investigated to explore the relationship among them and bacterial adsorption. The adsorption was a rapid process for bacterial adhesion to chalcopyrite. The extent of adsorption increased with increasing initial bacterial concentration and pulp concentration. The optimal pH for Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans adsorption onto chalcopyrite surfaces was in the range of pH 1-3. The increase of ionic strength led to decrease in bacterial adsorption, which can be well explained by electric double layer theory. The adsorption behavior appeared to be controlled by both hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions at the interface of bacteria and mineral.
Key words: bacterial adsorption; chalcopyrite; ionic strength; hydrophobicity; Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
1 Introduction
In the last years, the application of bioleaching methods to the extraction of metals from minerals gained a prominent role in hydrometallurgy processes over the world [1,2]. Bacterial adsorption on sulfide minerals surface and its role in sulfide bioleaching have been extensively investigated [3-6]. Almost the researchers tried to bridge the amounts of bacteria adsorbed with the bioleaching rate [7-9], although as approved in experiments, the amounts adsorbed and the leaching rate did not present direct linear relationship [10,11]. However, it was commonly convinced that bacterial adsorption on mineral surface was prerequisite for direct bacterial oxidation [12,13]. To elucidate the roles of bacterial adsorption on mineral leaching, long-term adsorption processes with sulfide dissolution were investigated by many authors [5,13-16]. For example, RODRIGUEZ et al [5] studied the relationship between the degree of bacterial attachment and their influence on the dissolution rate in 32 days of bioleaching processes. The bacterial attachment to chalcopyrite was characterized by three distinct stages. The maximum attachment was reached in an initial stage (first 24 h). PISAPIA et al [13] measured the total bacteria coverage rates in the process of pyrite corrosion after 22 months of incubation. They found bacteria adhered mainly to corrosion pitting walls with a higher affinity.
However, the mineral surface property often changed in the long-term adsorption experiments owing to the destruction of surface crystal lattice during the leaching process [6]. Besides, the biomass increased rapidly with the energy acquired in oxidizing mineral [5]. In this case, it is difficult to calculate the amounts of bacteria adsorbed according to the difference between the initial inoculated concentrations of cells and the concentration of cells remaining in the liquid phase after adhesion. Therefore, the experiment phenomenon could not be well explained in the long-term adsorption since every experiment condition changed with the bacterial oxidation. In this context, the research on short-term adsorption seems more important and has more clear significance, since the properties of mineral and bacteria do not change during the short-term adsorption.
Experimental studies demonstrated that bacterial species, mineralogy and ionic strength strongly affect the extent of bacteria adsorption onto mineral surface [17]. Chemical composition of different mineral surface, pulp concentration, nutrition condition, temperature, pH value and poisonous elements were suggested as the main factors controlling the initial deposition of bacteria onto mineral surfaces. However, the underlying mechanism involved in the short-term bacterial adsorption onto sulfide minerals surface has not been fully considered yet. In this study, the adsorption time, pulp concentration, bacterial concentration, pH and ionic strength are chosen as influencing factors in short-term bacteria-chalcopyrite adsorption experiments.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
Chalcopyrite used in the experiment was well-crystallized mineral from a domestic geological museum. The mineral particles were transferred to agate mortar and well polished (<74 μm). The powder was sealed and reserved in wide-mouth bottle.
Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans (A.f) strain used in the experiment was isolated and purified from drain water in Qixiashan, Nanjing, China, which was identified and used for bacterial adsorption in our previous study [4]. Element sulfur was chosen as energy source just because of its advantage of less precipitate and higher biomass. The cultivation of A.f strain was identical to Refs. [4,18]. As the growth of bacteria was in the logarithmic phase, the bacteria culture was first passed through Waterman No. 44 filter paper to remove residual element sulfur. The filtrate was then centrifuged at 5000 r/min for 30 min. The residual pellet was rinsed by double-distilled water and then centrifuged as described earlier. This procedure was repeated three times to make sure of the removal of all the precipitate. The cell pellet was finally suspended in distilled water and stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C.
Sodium chloride (chromatographically grade) was used as supporting electrolyte in the measurement. Double distilled water was used throughout the experiments.
2.2 Experimental method
Batch experiments were conducted to measure A.f adhesion to chalcopyrite as a function of adsorption time, pulp concentration, bacterial content, pH and ionic strength at 30 °C and 105 Pa, following a procedure similar to these used by YEE et al [17] and AMS et al [19]. A known concentration of bacteria was suspended in 10 mL aqueous solution, and placed in contact with a known mass of chalcopyrite. The pH of each batch experiment was adjusted using small aliquots of diluted HCl or NaOH. In the ionic strength experiments, varying amount of NaCl electrolyte was added to each reaction vessel, and then diluted to a total volume of 10 mL. In each type of batch experiment, the bacteria-mineral mixture was allowed to equilibrate for 2.5 h (or for different times for the kinetic experiments). Inflator equipment was used to ensure the thorough contact between bacteria and mineral. At given time intervals, the inflator was paused and the test tubes were allowed to set for 20 min. The supernatant fluid was withdrawn and counted with microscope. The amounts adsorbed can be calculated by the differences in bacterial concentration before and after adsorption, assuming that any decrease in unattached bacterial concentration was caused by bacterial adhesion to mineral surface.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of adsorption time
1 mL bacterial suspension with a known concentration (1.8×108 cell/mL) was added in a test tube, and then 0.1 g chalcopyrite powder was added. The bacterial concentration in the liquid was observed at regular intervals. The results of the adsorption kinetic experiments are shown in Fig. 1. Given the experimental uncertainty associated with each measurement, Fig. 1 indicates that bacterial adsorption proceeds rapidly with equilibrium reached in 150 min, and with no subsequent significant changes to the extent of adsorption. Therefore, it is reasonable to fix adsorption equilibrium time as 150 min in the following experiments.

Fig. 1 Effect of adsorption time on amount of bacteria adsorbed on mineral
3.2 Effect of pulp concentration
The chalcopyrite powder with the mass of 0.05, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 1.0, 1.2 and 1.5 g was put into each test tube and the same volume bacterial suspension (1 mL, 1.8×108 cell/mL) was added. The change of bacterial concentration in the liquid as a function of the pulp concentration is shown in Fig. 2. The bacterial concentration in liquid declined exponentially and nearly approached to zero when the pulp concentration reached 0.15 g/mL. When the pulp concentration was within the range of 0.005-0.03 g/mL, the amount of residual bacteria in solution sharply decreased. This indicated that the initial inoculated concentration of cells was relatively in excess at this stage corresponding to the surface sites available for bacterial adsorption. In addition, the lower the pulp concentration was, the less the shearing force of the suspension, which also favored the bacterial adhesion to minerals. When the pulp concentration was up to 0.05-0.15 g/mL, the bacterial concentration in the liquid hardly changed. Under this condition, almost all of bacteria have adhered to chalcopyrite surfaces. However, it does not mean that increasing pulp concentration favors the bacterial attachment, because the excessive high shearing force at high concentration of mineral dosage maybe damage the cell, which would cause a decrease of the amount of bacteria adsorbed.

Fig. 2 Effect of pulp concentration on bacterial concentration in fluid
3.3 Effect of bacterial concentration
Different volume of cell suspension was added in each test tube containing 0.1 g of chalcopyrite powder to obtain different bacterial concentration. Figure 3 illustrates that the extent of bacterial adsorption onto the chalcopyrite changed with the initial inoculated concentration of bacteria. In experiments that were conducted with identical amount of chalcopyrite, the amount of bacteria adsorbed onto the mineral surface directly corresponded to the concentration of bacteria present (R=0.995). The monotonic increase in adsorption with increasing concentration indicates that, the mineral surface is not saturated with respect to adsorbed bacteria under these experimental conditions.

Fig. 3 Effect of initial bacterial concentration on amount of bacteria adsorbed on mineral
3.4 Effect of pH
Since pH has great effect on the activity and surface property of both bacterial and mineral, it is always regarded as an essential parameter on the mineral adsorption. The concentrations of mineral and bacteria were 0.01 g/mL and 1.8×107 cell/mL, respectively. Figure 4 depicts the pH-dependent adsorption behavior in the bacteria-chalcopyrite system. The curve of bacterial adhesion appears as “n” in shape, and the maximum of bacteria adsorbed onto mineral was as much as about 3.2×108 cell/g at pH 1-3. pH can greatly influence the surface potential of bacteria and chalcopyrite and therefore the electrostatic force of interaction. A.f cells cultivated by element sulfur are charged negatively above approximately pH 3.8, whereas the minerals are charged positively in the entire pH range studied [20-22]. This suggests that a repulsive electrostatic force may operate at lower acidic pH values (pH < 3.8), which does bring negative effect on bacterial adhesion. However, it seems from Fig. 4 that the optimal pH for A.f adsorption is just below pH 3.8. Therefore, our results indicate that electrostatic interactions alone cannot successfully account for the adsorption behavior.
According to the chemical driving force for adsorption, the Gibbs free energy of adsorption can be represented as the sum of hydrophobic and electrostatic components such that [17]:
ΔG=ΔGhydrophobic+ΔGelectrostatic (1)
The ΔGhydrophobic term is directly related to the concentration of neutral sites on the bacterial surface, favoring increased adsorption as the concentration of these sites increases. At low pH, the bacterial surface is dominated by R—COOH sites, which behaves hydro- phobically and therefore bacteria more readily adsorb onto mineral surface. With the increase in pH, the bacteria become progressively more negatively-charged, thus increasing its ability to remain in suspension. The decreasing hydrophobic nature of the bacteria would offset the increasing electrostatic attraction between the mineral and bacterial surfaces. Therefore, a marked decrease in adsorption was observed with increasing pH (pH>3.0).

Fig. 4 Effect of pH value on amount of bacteria adsorbed on mineral
3.5 Effect of ionic strength
Bacterial adsorption in bioleaching process took place not in a pure water system but in a complicated condition containing inorganic salt that bacterial growth required and metal ions that were extracted by bacterial oxidation. All those ions resulted in the increase of ionic strength of solution, so ionic strength should be one of the most important factors in bacterial adsorption. Figure 5 presents the effect of ionic strength on bacterial adsorption. Basically, the extent of bacterial adsorption onto chalcopyrite declined with the increase of ionic strength.
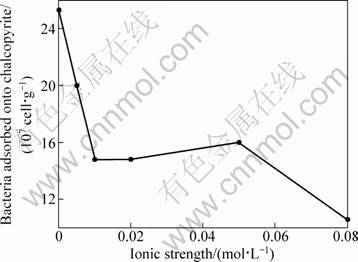
Fig. 5 Effect of ionic strength on amount of bacteria adsorbed on mineral
Both pH and the ratio of bacteria to mineral are held constant in ionic strength experiments, and thus ΔGhydrophobic is also constant. The observed changes in bacteria adsorption should be ascribed to the changes in ΔGelectrostatic. ΔGelectrostatic as a function of distance H between mineral and bacteria could be expressed as [21]:
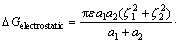
 (2)
(2)
where a1, a2 are radii of mineral and bacteria particles, respectively; κ is the reciprocal of double-layer thickness; and ζ is the zeta potential.
At low ionic strength, the double layers associated with both surfaces are relatively thick, and the attractive electric fields extend further into solution, thus increasing the potential for adsorption. With the increase of ionic strength I,κ in Eq. (2) increases, which implies that the electrical double layer of both mineral and bacteria particles is compressed. The higher concentration of electrolyte ions limits the interaction between the two surfaces, and the adsorption is reduced though they remain oppositely charged.
4 Conclusions
1) Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans adsorption onto chalcopyrite surfaces is a rapid process. The amount adsorbed reaches 2.5×108 cell/g at 5 min and the adsorption process comes to equilibrium after 150 min.
2) Increasing the initial bacterial concentration and pulp concentration leads to an increase in extent of adsorption. The optimal pH for Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans adsorption onto chalcopyrite surfaces is in the range of pH 1-3. With increasing ionic strength, the bacterial adsorption is reduced due to the electrical double layer compression of both mineral and bacteria particles.
3) The bacterial adsorption of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans onto chalcopyrite is driven by hydrophobicity, but electrostatic interactions also play an important role.
References
[1] SUZUKI I. Microbial leaching of metals from sulfide minerals [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2001, 19: 119-132.
[2] WATLING H R. The bioleaching of sulphide minerals with emphasis on copper sulphides—A review [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 84: 81-108.
[3] HARNEIT K, G?KSEL A, KOCK D, KLOCK J H, GEHRKE T, SAND W. Adhesion to metal sulfide surfaces by cells of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 83: 245-254.
[4] LIU Jian-she, XIE Xue-hui, LI Bang-mei, DONG Qing-hai. Adsorption characteristics of thiobacillus ferrooxidans on surface of sulfide minerals [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2005, 12: 671-676.
[5] RODR?GUEZ Y, BALLESTER A, BL?ZQUEZ M L, GONZ?LEZ F, MU?OZ J A. Study of bacterial attachment during the bioleaching of pyrite, chalcopyrite, and sphalerite [J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2003, 20: 131-141.
[6] OHMURA N, KITAMURA K, SAIKI H. Selective Adhesion of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans to Pyrite [J]. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 1993, 59: 4044-4050.
[7] AFRICA C J, van HILLE R P, HARRISON S T L. Investigation and visualization of microbial attachment trends to sulphide minerals in a bioleach environment [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2009, 71-73: 345-348.
[8] WANG Xiu-mei, LIU Jian-she, LI Bang-mei, ZHU Jian-yu,WANG Hua-tai, YAN Yin, QIU Guan-zhou. Study on the enthalpy variation during adsorption processes of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC23270 on the surface of minerals and its metabolic thermogenesis under different conditions [J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2009, 15(2): 256-262. (in Chinese)
[9] XIE Xue-hui, XIAO Sheng-mu, LIU Jian-she. Microbial communities in acid mine drainage and their interaction with pyrite surface [J]. Current Microbiology, 2009, 59: 71-77.
[10] PORRO S, RAM?REZ S, RECHE C, CURUTCHET G, ALONSO-ROMANOWSKI S, DONATI E. Bacterial attachment: Its role in bioleaching processes [J]. Process Biochemistry, 1997, 32(7): 573-578.
[11] SAMPSON M I, PHILLIPS C V, BLAKE R C. Influence of the attachment of acidophilic bacteria during the oxidation of mineral sulfides [J]. Mineral Engineering, 2000, 13: 373-389.
[12] JIA Chun-yun, WEI De-zhou, LIU Wen-gang, HAN Cong, GAO Shu-ling, WANG Yu-juan. Selective adsorption of bacteria on sulfide minerals surface [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(5): 1247-1252.
[13] PISAPIA C, HUMBERT B, CHAUSSIDON M, MUSTIN C. Perforative corrosion of pyrite enhanced by direct attachment of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2008, 25: 261-273.
[14] VILINSKA A, RAO K H. Surface thermodynamics and extended DLVO theory of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans cells adhesion on pyrite and chalcopyrite [J]. The Open Colloid Science Journal, 2009, 2: 1-14.
[15] FLORIAN B M, NO?L N, BELLENBERG S, HUERGO J, ROHWERDER T, SAND W. Attachment behavior of leaching bacteria to metal sulfides elucidated by combined atomic force and epifluorescence microscopy [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2009, 71-73: 337-340.
[16] MANGOLD S, HARNEIT K, ROHWERDER T, CLAUS G, SAND W. Novel combination of atomic force microscopy and epifluorescence microscopy for visualization of leaching bacteria on pyrite [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(2): 410-415.
[17] YEE N, FEIN J B, DAUGHNEY C J. Experimental study of the pH, ionic strength, and reversibility behavior of bacteria-mineral adsorption [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochinica Acta, 2000, 64: 609-617.
[18] ZHOU Ji-kui, NIU Yin-jian, QIU Guan-zhou, QIN Wen-qing. Protein content of mineral-adhered bacterium by ninhydrin colorimetric method [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2003, 34: 128-130. (in Chinese)
[19] AMS D, FEIN J, DONG H, MAURICE P. Experimental measurements of the adsorption of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas mendocina onto Fe-oxyhydroxide-coated and uncoated quartz grains [J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2004, 21: 511-519.
[20] LIU Jian-she, WANG Zhao-hui, CHEN Hong, ZHANG Yan-hua. Study on interfacial electrokinetic characteristics before and after bioleaching microorganism adhesion to pyrite [J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metal Society of China, 2006, 16: 676-680.
[21] SHARMA P K, RAO K H. Adhesion of Paenibacillus polymyxa on chalcopyrite and pyrite: Surface thermodynamics and extended DLVO theory [J]. Colloids and Surface B: Biointerface, 2003, 29: 21-38.
[22] XIA Le-xian, LIU Xin-xing, ZENG Jia, YIN Chu, GAO Jian, LIU Jian-she, QIU Guan-zhou. Mechanism of enhanced bioleaching efficiency of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans after adaptation with chalcopyrite [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 92: 95-101.
嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌在黄铜矿表面的短期吸附实验研究
王兆慧1,谢学辉1,柳建设1,2
1. 东华大学 环境科学与工程学院,上海 201620;
2. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:为了探明细菌在黄铜矿表面的吸附机制,采取短期吸附的实验方法,研究吸附时间、矿浆浓度、细菌浓度、pH值和离子强度等因素对吸附行为的影响。结果表明,细菌吸附量随初始细菌浓度和矿浆浓度的增加而增大。Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans在黄铜矿表面的最佳吸附pH范围为1-3。离子强度的增大会抑制细菌吸附,这一现象可以通过双电层理论得到很好的解释。细菌与黄铜矿的吸附行为受疏水性和静电作用力共同影响。
关键词:细菌吸附;黄铜矿;离子强度;疏水性;Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
(Edited by YUAN Sai-qian)
Foundation item: Projects (41073060, 21007009, 50874032) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (B604) supported by Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project, China; Project (10CG34) supported by Shanghai Municipal Education Commission and Shanghai Education Development Foundation, China
Corresponding author: LIU Jian-she; Tel: +86-21-67792523; E-mail: liujianshe@dhu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61196-5