DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.07.07
冷却速率对TC16钛合金显微组织和力学性能的影响
张志强1,董利民1,胡 明1, 2,雷晓飞1,杨 洋3,杨 锐1
(1. 中国科学院 金属研究所,沈阳 110016;
2. 东北大学 材料科学与工程学院,沈阳 110819;
3. 中国科学院 福建物质结构研究所,福州 350002)
摘 要:利用XRD、SEM、TEM和力学试验机等手段分析不同冷却速率的TC16钛合金试样的相组成、显微组织和力学性能,并分析冷却速率对TC16钛合金显微组织和力学性能的影响。结果表明:TC16钛合金经800 ℃保温处理后,水淬和空冷试样均由α相、α″马氏体、ω相和β相组成,炉冷试样仅由α相和b相组成;水淬和空冷试样中的初生α相体积分数和晶粒尺寸都相近,均比炉冷试样的小。水淬和空冷试样的单向拉伸曲线上,出现双屈服现象;随着冷却速率的降低,TC16钛合金的屈服强度提高;水淬和空冷试样的抗拉强度相近,高于炉冷试样的;3种冷却速度试样的伸长率和断面收缩率相近,都具有优异的室温塑性。
关键词:TC16钛合金;冷却速率;显微组织;力学性能;循环拉伸
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-07-1391-08 中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
α+β钛合金具有高的比强度、优异的疲劳性能和抗腐蚀性能,被广泛用于航空、航天、海洋、化工等工业领域[1-3]。目前,通过采用热加工变形和后续热处理工艺相结合的方式,可以制备出组织均匀一致且性能满足使役条件的钛合金产品。在热加工变形后或热处理时,钛合金产品的冷却速率会造成初生α相的体积分数和晶粒尺寸、次生α相的形貌以及相组成的差异,进而直接影响合金的力学性能。因此,掌握冷却速率对α+β钛合金显微组织和力学性能的影响具有重要意义[2, 4]。
在关于冷却速率对α+β钛合金显微组织和力学性能影响研究中,基本选用β相稳定元素相对较少的α+β钛合金(Mo质量分数小于5%)[4-18]。现有研究结果表明,随着冷却速率的降低,初生α相体积分数和晶粒尺寸均增加,次生α相的形成温度降低,层片状次生α相体积分数和尺寸减小,初生α相的生长速度高于次生α相,在β相晶界处容易形成晶界α相;Ti-6Al-4V合金中初生α相中所含的稳定元素含量变化不大,其生长受β相中V元素扩散控制,Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo- 0.1Si合金和TA15合金中初生α相中所含的稳定元素含量变化较小,其生长受β相中Mo元素扩散控制。随着冷却速率的降低,β相中β相稳定元素含量越高,导致β相依次转变为α″马氏体、α′马氏体、α相。随着冷却速率的降低,屈服强度和抗拉强度逐渐降低,塑性逐渐提高。从上可知,β相稳定元素含量,特别是熔点较高金属,极大影响着冷却时初生α相的生长速度和体积分数,以及快速冷却时高温β相产生的非扩散型相变,从而导致材料性能发生较大差异,因此,深入研究冷却速率对更高Mo含量的α-β钛合金的影响具有重要的理论意义和工程价值,但是目前相关研究较少。
TC16钛合金是一种马氏体型a+β钛合金,名义成分为Ti-3Al-4.5V-5Mo(质量分数,%),该合金的β相稳定元素含量较高,Mo含量为8%,是俄罗斯和我国航空航天领域用来制备钛合金紧固件的主要材料[19-20]。由于TC16合金具有较高β相稳定元素含量,所以在热加工或热处理时,不同的冷却速率可能会导致β相发生b→α、β→α″和b→w等相变,这些会形成不同的显微组织,进而影响其力学性能。因此,本文将TC16钛合金在800 ℃保温处理后,采用水淬、空冷和炉冷等手段冷却,进而研究冷却速率对TC16合金的相组成、显微组织以及力学性能的影响规律,分析相组成、显微组织变化及力学性能变化的控制因素,以期为TC16钛合金的工艺优化和工业生产提供理论指导。
1 实验
采用3次真空自耗熔炼制备出TC16钛合金铸锭,然后铸锭经开坯、锻造、轧制、拉丝等工艺,制备出直径为8 mm的丝材。经过金相法测定,该合金的相变点为860~865 ℃。当空气加热炉升温至800 ℃后,将TC16合金试样放入,升温;当炉温再次升至800 ℃后,保温2 h,随后采用水淬、空冷和炉冷等冷却方式进行冷却,水淬和空冷试样直接冷却至室温,炉冷试样随炉冷却至550 ℃后出炉,再空冷至室温。用于物相分析、显微组织分析的水淬、空冷和炉冷试样,均车削至直径6 mm,以消除热处理时高温氧化对试验结果的影响。用于单向拉伸试验和循环拉伸试验的水淬、空冷和炉冷试样,直接加工成拉伸试样,其工作直径均为4 mm,标距均为27 mm。物相分析采用D/max-2400PC X射线衍射仪(XRD)Cu Ka进行。显微组织分析采用SSX-550 扫描电镜(SEM)和配置了能谱(EDS)的Tecnai G2 20透射电镜(TEM)。TEM样品先机械研磨厚度至50 μm,随后采用Tenupol-5型双喷电解减薄仪减薄,双喷液为6%高氯酸+35%正丁醇+59%甲醇(体积分数)。双喷时,采用液氮冷却双喷液,工作温度为-20~-30 ℃,电压10~20 V。单向拉伸实验在Shimadzu AG-100kN万能力学试验机上进行,丝杠移动速度为1mm/min。循环拉伸在Instron 8872力学试验机上进行,应变速率为2.2×10-4 s-1,应变循环增幅为1%,直到6%为止。
2 实验结果
TC16合金800 ℃保温处理后经由水淬、空冷和炉冷等方式冷却,不同冷却速率试样的相组成如图1所示。可以看出,水淬和空冷试样都由α相、α″马氏体和β相组成,而炉冷试样中仅有α相和β相,这说明了水淬和空冷的冷却速率较大,容易发生β→α″转变,而炉冷的冷却速率较低,只能发生β→α相转变。通过对比水淬和空冷试样中β相的{110}衍射峰、α″马氏体的{020}和{021}衍射峰发现,水淬试样的β相衍射强度要比空冷试样的低,α″马氏体的衍射强度比空冷试样的高,这说明水淬试样中β相转变为α″马氏体的体积分数比空冷试样的高,保留的亚稳β相体积分数比空冷试样的低。

图1 不同冷却速率的TC16钛合金试样XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD pattterns of TC16 titanium alloy at different cooling rates
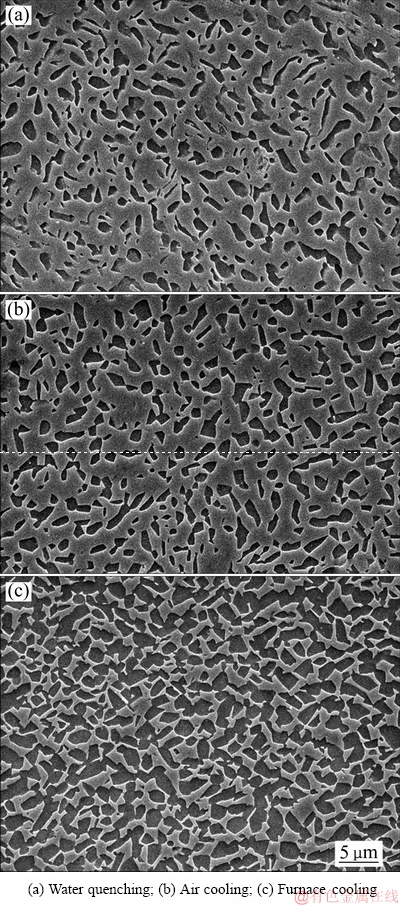
图2 不同冷却速率的TC16合金试样SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM images of TC16 titanium alloy at different cooling rates
图2所示为800 ℃保温处理后不同冷却速率试样的SEM像。图2中黑色的等轴或短片状相为α相,而灰色的相为β相。可以看出,水淬试样中初生α相的体积分数最小,炉冷试样的最大;水淬与空冷试样中初生α相的晶粒大小相近,均比炉冷试样的小;依据SEM像,对初生α相的体积分数进行了统计,结果显示,水淬试样中初生α相的体积分数为27%,空冷试样的约为29%,炉冷试样的为62%。在水淬和空冷试样中,未能观察到针状或层片状α″马氏体,这可能是因为两种冷却方式的冷却速率较快,形成的α″马氏体尺寸细小和体积分数有限,且为了突出合金热处理后的宏观形貌,所选SEM像倍数偏低,降低了α″马氏体被观察到的概率;另外,α″马氏体与亚稳β相的成分相近,难以腐蚀出明显衬度。
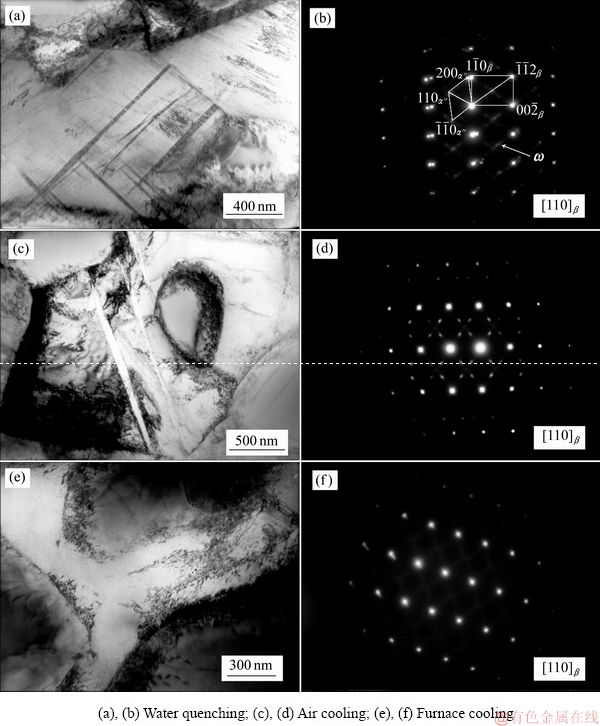
图3 不同冷却速率的TC16合金试样的TEM像和转变β组织的选区电子衍射斑点
Fig. 3 TEM images((a), (c), (e)) and corresponding b phase SAED((b), (d), (f)) of TC16 titanium alloy treated at different cooling rates
为了进一步分辨不同冷却速率下转变β相中的组织形貌,对水淬、空冷和炉冷试样进行了TEM观察和SAED分析,如图3所示。在水淬试样中(见图3(a)和(b)),转变β相中观察到了针状相,厚度约为50~80 nm,经晶带轴为[110]b的选区电子衍射标定,该针状相为α″马氏体,这与XRD结果一致。另外,在该晶带轴的选区衍射斑点上,在1/3<112>*β与2/3<112>*β中发现强度较高的衍射斑点,该斑点可标定为ω相的特征斑点[19-23],这说明TC16合金在水淬时部分β相转变为ω相。在空冷试样的转变β相中也发现了针状的α″马氏体和ω相,α″马氏体的厚度约为100 nm,如图3(c)和(d)所示。空冷试样上的ω相特征斑点的衍射强度比水淬试样高,如图3(b)和(d)所示,这说明空冷试样中快冷形成的ω相体积分数相对偏高。但是,在水淬和空冷试样的XRD结果中,均未能观察到ω相衍射峰,说明这两种冷却试样中淬火ω相体积分数较小,可以不考虑它对力学性能的影响。在炉冷试样的β相中,仅观察到少量位错,未观察到其他显微组织特征(见图3(e));在其选区电子衍射斑点,也仅能标定出中β相(见图3(f))。
通过TEM的EDAX设备,还测定了不同冷却速率试样的转变β相中Al、Mo和V元素的含量,并利 用[Mo]eq=[Mo]+0.2[Ta]+0.28[Nb]+0.4[W]+0.67[V]+ 1.25[Cr]+1.25[Ni]+1.7[Mn]+1.7[Co]+2.5[Fe][2]计算了转变β相的等效Mo含量,具体结果见表1。从表1中可以看出,在水淬、空冷和炉冷等3种冷却试样中,水淬试样的转变β相中Al元素含量相对较高,空冷试样的次之,炉冷试样的最低;水淬试样中Mo和V元素含量相对较低,炉冷试样最高,3种冷却试样中转变β相的等效Mo含量分别为8.01%、10.17%和16.35%(质量分数)。这些结果表明,随着冷却速率的降低,TC16合金β转变组织中Al元素含量降低,Mo和V元素含量增高。
表1 不同冷却速率的TC16合金试样的EDS结果
Table 1 EDS results of TC16 titanium alloy at different cooling rates
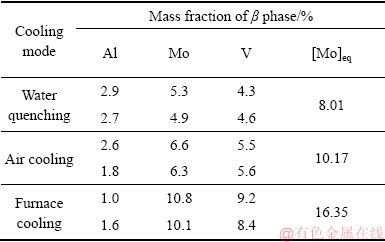
图4所示为TC16合金800 ℃保温处理后不同冷却速率试样单向拉伸试验的工程应力-应变曲线。水淬和空冷试样的拉伸曲线上出现了“双屈服现象”,而炉冷试样的未出现双屈服。
水淬和空冷试样中出现双屈服现象有两种可能的解释,一种是由于这两种冷却试样中的亚稳β相可以在较低应力作用下发生应力诱发α″马氏体相变[24-26];另一种可能是这两种冷却试样中存在的淬火多变体α″马氏体,在较低应力下发生去孪晶过程而转变为单变体[27-29]。相比之下,炉冷试样的中α相体积分数高达62%,晶间β相的等效Mo含量为16.35%,大量的β稳定元素偏聚在β相中,提高了其稳定性,因此,淬火与外加应力均无法诱发α″马氏体的生成,炉冷试样的曲线上未出现双屈服现象。
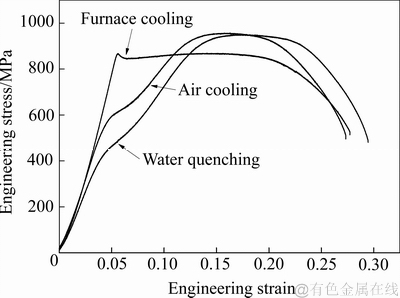
图4 不同冷却速率的TC16合金试样的工程应力-应变曲线
Fig. 4 Engineering stress-strain curves of TC16 titanium alloy cooled at different cooling rates
表2所列为TC16合金800 ℃保温处理后不同冷却速率试样的室温拉伸性能,水淬和空冷试样选取了应变0.2%时的强度值作为其屈服强度,炉冷试样由于出现了屈服点,选取了屈服点的强度值作为其屈服强度。水淬和空冷试样的抗拉强度相近,均高于炉冷试样的,其原因可能是,水淬和空冷试样中初生α相体积分数低,而转变β相的体积分数高,β相中存在一定量的淬火α″马氏体和ω相,使试样中相界面较多,能够有效阻碍滑移位错,致使其抗拉强度相对较高。水淬试样的屈服强度最低,炉冷试样的屈服强度最高,该结果与现有α+β钛合金冷却速率对力学性能的影响研究中得出的规律不同[8-9, 18]。因为与低Mo含量钛合金相比,TC16合金中β相稳定元素含量高,水淬和空冷试样的β相中Mo含量适当;当这两种试样进行单向拉伸试验时,可以在较低载荷作用下,发生应力诱发α″马氏体,或者多变体的淬火α″马氏体转变为单变体,从而有效降低了合金的屈服强度;而炉冷试样中β相趋于稳定且浓度高,难以发生应力诱发马氏体相变,且因其转变β相中无淬火α″马氏体,不能发生多变体α″马氏体向单变体转变,只能位错滑移,这极大提高了其屈服强度。从表2中可以看出,3种冷却试样的伸长率和断面收缩率相近,都具有优异的塑性。
表2 不同冷却速率的TC16钛合金试样的室温拉伸性能
Table 2 Room temperature tensile properties of TC16 titanium alloy at different cooling rates

为了进一步揭示800 ℃保温处理后水淬和空冷的TC16合金试样的力学行为差异,开展了这两种冷却速率试样的循环拉伸试验,其曲线如见图5所示,并按照文献[27]的方法分别在曲线上对两种冷却试样的初始屈服应力进行测量。在水淬试样的循环拉伸曲线上,初始屈服应力为403 MPa,出现了明显的滞回环;随着循环应变的增加,拉伸应力不断提高。空冷试样的初始屈服应力为738 MPa,曲线上也出现了滞回环,但滞回面积明显高于水淬试样,当变形增加到4%时,滞回环幅度减小;随着循环应变的提高,应力的增幅明显比水淬试样低。循环拉伸曲线的初始屈服应力与正常拉伸试验结果之间的差异,可能是由于两种拉伸试验中的拉伸速度不同和取值方法不同。循环曲线上的滞回环与α″马氏体有关,水淬试样的滞回面积小,而空冷试样的滞回面积大,这说明水淬试样中α″马氏体可回复性较差,而空冷试样的可回复性较好。此外,水淬试样的循环拉伸初始屈服应力较低,而空冷试样的较高,这与不同试样的显微组织中的马氏体片层取向有关,如图3所示。由图3(a)可见,水冷试样显微组织中马氏体片层的取向较多,且存在交叉,由图3(b)可见,空冷试样中马氏体变体取向单一,这归根结底与两种冷却方式所形成的亚稳β相的稳定性,即等效Mo含量有关。考虑到多变体马氏体转变为单变体马氏体所需要的临界应力值较低[27-29],且变体单一化后的应力卸载无法即时应变回复,可以认为水淬试样初始屈服点对应着α″马氏体由多变体到单变体的转变,随着应变增加,会逐次发生单变体马氏体的弹性变形;继续拉伸,单变体的α″马氏体则会出现第二个屈服点。空冷试样的循环拉伸初始屈服应力高,这与其在初始屈服点时发生的应力诱发α″马氏体有关,该条件下所需要的应力临界值较大。
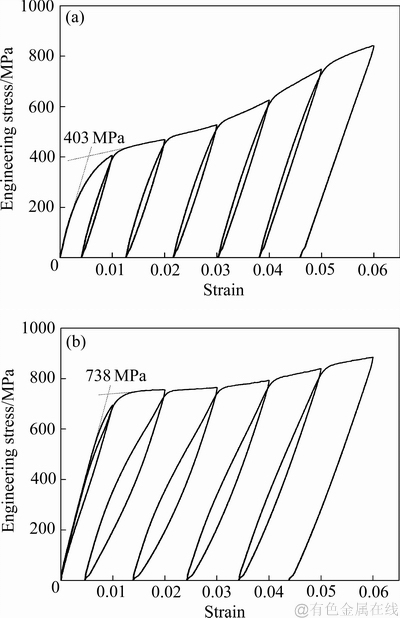
图5 不同冷却速率的TC16合金试样的循环拉伸应力-应变曲线
Fig. 5 Cyclic tensile stress-strain curve of TC16 titanium alloy in water quenching sample(a) and air cooling sample(b)
3 分析与讨论
TC16合金经过800 ℃保温处理后,采用水淬、空冷和炉冷的方式进行冷却。不同冷却试样中β相的化学成分分析结果(见表1)表明,在冷却过程中,随着冷却速率的降低,转变β相中Al元素含量减少,Mo和V元素含量增加,这说明了在800 ℃保温处理时,较多的α相稳定元素Al固溶在高温β相。在冷却过程中,随着试样温度降低,转变β相中的Al元素固溶度降低,过量的Al元素将从转变β相中排出,扩散到α/β相界面;β相稳定元素Mo和V向远离α/β相界面方向在β相中扩散,导致α/β界面附近的β相在初生α相上直接转变成α相,结果就是初生α相晶粒尺寸增大。尽管水淬和空冷时TC16合金具有较高的过冷度,初生α相可以具有较高的生长速率,但是,β→α同素异构相变是扩散型相变,较高的冷却速率导致合金在高温段停留时间过短,致使转变β相中Al、Mo和V元素扩散有限,从而初生α相长大有限。而炉冷时尽管TC16合金的过冷度偏低,但其高温区停留时间较长,Al、Mo和V元素扩散较为充分,初生α相得到充分长大,从而体积分数也得到较大提高。尽管水淬试样比空冷试样的冷却速率大,但是Mo元素在β相中扩散速率较低,大幅减弱了水淬和空冷之间的冷却速率差异影响,从而导致两种冷却试样中初生α相的体积分数和晶粒尺寸相近。
通常,转变β相的Mo含量为4%~6%(质量分数)为水淬时形成α′马氏体和α″马氏体的分界线,Mo含量为10%~13.6%且水淬时,α″马氏体和亚稳β相的分界线[30-32]形成。在TC16钛合金冷却过程中,转变β相中Mo和V元素含量富集,水淬试样中转变β相的Mo含量为8.01%,处于α′/α″分界线与α″/β分界线之间,肯定也处于淬火ω相形成的区域,因此,水淬时,高温β相转变为α″马氏体、淬火ω相和亚稳β相,如图3(a)和(b)所示。空冷试样的Mo含量为10.17%,处于α′/α″分界线与α″/β分界线之间,同时也处于淬火ω相形成的区域,因此,冷却时合金中组成相与水淬试样一致的(见图3(c)和(d)),但是,由于空冷试样中Mo和V元素含量比水淬试样的高,其马氏体转变温度低,导致转变成的α″马氏体体积分数相对较小,亚稳β相得到较多保留;也因其Mo含量较高,导致其形成的淬火ω相体积分数偏高。炉冷试样中转变β相的等效Mo含量为16.35%,远离α″马氏体和亚稳β相的分界线,此时,马氏体相变的开始温度已经低于室温,因此,在炉冷过程中,仅有β相保留。
水淬、空冷和炉冷试样中转变β相的等效Mo含量分别为8.01%、10.17%和16.35%(见表1)。水淬试样的等效Mo含量比空冷试样低,这就造成冷却后水淬试样中α″马氏体体积分数高,保留的β相体积分数低;而空冷试样中保留的β相体积分数高,α″马氏体体积分数低。水淬试样的Mo含量接近易发生多变体马氏体转变为单变体所需β相稳定元素浓度。在单向拉伸和循环拉伸试验时,较低应力下,转变β相中的α″马氏体由多变体转变为单变体,形成第一个屈服点;而空冷试样中Mo含量接近应力诱发α″马氏体的所需β相稳定元素浓度。在单向拉伸和循环拉伸试验时,较低应力下的β相中发生应力诱发α″马氏体,形成第一个屈服点。另外,炉冷试样中晶间β相的Mo含量高,大量的β稳定元素偏聚在β相中,提高了其稳定性,所以淬火与外加应力均无法诱发α″马氏体的生成,因此,炉冷试样的曲线上未出现双屈服现象。
4 结论
1) TC16合金800 ℃保温处理后,水淬和空冷试样均由α相、α″马氏体、ω相和β相组成,炉冷试样仅由α相和β相组成;水淬和空冷试样中,初生α相的晶粒尺寸和体积分数都相近,均比炉冷试样小。
2) 在单向拉伸实验中,水淬和空冷试样出现了双屈服现象,水淬试样屈服强度最低,炉冷试样屈服强度最高;水淬和空冷试样的抗拉强度相近,均高于炉冷试样的;3种冷却速率的TC16合金试样的伸长率和断面收缩率相近,均具有优异的室温塑性。
3) 在循环拉伸实验中,水淬试样的初始屈服应力低,曲线上出现了明显的滞回环;随着循环应变的提高,应力不断提高。空冷试样的初始屈服应力高,曲线上也出现了明显的滞回环,滞回面积比水淬试样高;随着循环应变的提高,应力的增幅较低。
REFERENCES
[1] BANERJEE D, WILLIAMS J C. Perspectives on titanium science and technology[J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61: 844-879.
[2] LUETJERING G, WILLIAMS J C. Titanium[M]. 2nd ed. Heidelberg: Springer, 2007.
[3] MOISEYEV V N. Titanium alloys—Russian aircraft and aerospace applications[M]. New York: CRC Press, 2006.
[4] SEMIATIN S L, KNISLEY S L, FAGIN P N, ZHANG F, BARKER D R. Microstructure evolution during alpha-beta heat treatment of Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2003, 34: 2377-2386.
[5] SEMIATIN S L, LEHNER T M, MILLER J D, DOHERTY R D, FURRER D U. Alpha/beta heat treatment of a nonuniform microstructure[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transaction A, 2007, 38: 910-921.
[6] AHMED T, RACK H J. Phase transformations during cooling in a+b titanium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 243: 206-211.
[7] KUBIAK K, SIENIAWSKI J. Development of the microstructure and fatigue strength of two phase titanium alloys in the processes of forging and heat treatment[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1998, 78(1/3): 117-121.
[8] GIL F J, GINEBRA M P, MANERO J M, PLANELL J A. Formation of a-widmanstaetten structure: Effect of grain size and cooling rate on the widmanstaetten morphologies and on the mechanical properties in Ti6Al4V alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2001, 329(1/2): 142-152.
[9] JOVANOVIC M T, TADIC S, ZEC S, MISKOVIC Z, BOBIC I. The effect of annealing temperatures and cooling rates on microstructure and mechanical properties of investment cast Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Materials and Design, 2006, 27: 192-199.
[10] AFONSO C R M, ALEIXO G T, RAMIREZ A J, CARAM R. Influence of cooling rate on microstructure of Ti-Nb alloy for orthopedic implants[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2007, 27(4): 908-913.
[11] HED, ZHUJ C, ZAEFFERER S, RAABE D, LIU Y, LAI Z L, YANG X W. Influences of deformation strain, strain rate and cooling rate on the Burgers orientation relationship and variants morphology during b→a phase transformation in a near a titanium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 549: 20-29.
[12] GAO X X, ZENG W D, ZHANGD F, WANG Q J. A study of epitaxial growth behaviors of equiaxed alpha phase at different cooling rates in near alpha titanium alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 122: 298-309.
[13] 曾卫东, 周义刚. 冷速对TC11合金b加工显微组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2002, 38(12): 1273-1276.
ZENG Wei-dong, ZHOU Yi-gang. Influence of cooling rate on microstructure and mechanical properties of beta processed TC11 alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2001, 38(12): 1273-1276.
[14] ZHU S, YANG H, GUO L G, FAN X G. Effect of cooling rate on microstructure evolution during a/b heat treatment of TA15 titanium alloy[J]. Materials Characterization, 2012, 70: 101-110.
[15] 彭 聪, 张书源, 任 玲, 杨 柯. 冷速对含铜钛合金显微组织和性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2017, 53(10): 1377-1384.
PENG Cong, ZHANG Shu-yuan, REN Leng, YANG Ke. Effect of cooling rate on microstructure and properties of a Cu-containing titanium alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2017, 53(10): 1377-1384
[16] 崔 霞, 贾鹏程, 杜海明, 欧阳德来. 冷却速率对TA15钛合金显微组织和性能的影响[J]. 失效分析与预防, 2016, 11(4): 208-211.
CUI Xia, JIA Peng-cheng, DU Hai-ming, OUYANG De-lai. Effect of cooling rate on microstructure and property of TA15 titanium alloy[J]. Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2016, 11(4): 208-211.
[17] 宋 淼, 马英杰, 邬 军, 李玉兰, 刘羽寅, 雷家峰. 冷却速率对Ti-5.8Al-3Mo-1Cr-2Sn-2Zr-1V-0.15Si合金组织及性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): 565-569.
SONG Miao, MA Ying-jie, WU Jun, LI Yu-lan, LIU Yu-yin, LEI Jia-feng. Effect of cooling rate on microstructure and properties of Ti-5.8Al-3Mo-1Cr-2Sn-2Zr-1V-0.15Si titanium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): 565-569
[18] 徐戊矫, 谭玉全, 龚利华, 章 磊. 退火温度和冷却速率对TC4钛合金组织及性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2016, 45(11): 2932-2936.
XU Wu-jiao, TAN Yu-quan, GONG Li-hua, ZHANG Lei. Effect of annealing temperature and cooling rate on microstructure and properties of TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016, 45(11): 2932-2936.
[19] 张庆玲, 王庆如, 李兴无. 航空用钛合金紧固件选材分 析[J]. 材料工程, 2007, 284: 11-14.
ZHANG Qing-ling, WANG Qing-ru, LI Xing-wu. Materials selection analysis for titanium alloy fasteners in aviation industry[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2007, 284: 11-14.
[20] 张青来, 匡雁锐, 韩寅奔, 韩伟东, 冯甜甜. 冷镦紧固件用Ti-3Al-4Mo-4.5V钛合金的微观组织及性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(10): 2756-2761.
ZHANG Qing-lai, KUANG Yan-rui, HAN Yin-ben, HAN Wei-dong, FENG Tian-tian. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Ti-3Al-5Mo-4.5V titanium alloy for cold upsetting fasteners[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(10): 2756-2761.
[21] SASSS L. The structure and decoposition of Zr and Ti b.c.c solid solutions[J]. Journal of the Less Common Metals, 1972, 28: 157-173.
[22] JONES N G, DASHWOOD R J, JACKSON M, DYE D.b phase decomposition in Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr[J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57(13): 3830-3839.
[23] DEVARAJ A, NAG S, SRINIVASAN R,WILLIAMS R E A, BANERJEE S, BANERJEE R, FRASER H L. Experimental evidence of concurrent compositional and structural instablilities leading to w precipitation in titanium- molybdenum alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(2): 596-609.
[24] DUERIG T W, ALBRECHT J, RICHTER D, FISCHER P. Formation and reversion of stress induced martensite in Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al[J]. Acta Materialia, 1982, 30(12): 2161-2172.
[25] DUERIG T W, TERLINDE G T, WILLIAMS J C. Phase transformations and tensile properties of Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1980, 11(12): 1987-1998.
[26] GROSDIDIER T, PHILIPPE M J. Deformation induced martensite and superelasticity in a b-metastable titanium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 291: 218-223.
[27] RAMAROLAHY, A, CASTANY P, PRIMA F, LAHEURTE P, PERON I, GLORIANT. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of superelastic Ti-24Nb-0.5O and Ti-24Nb-0.5Nb biomedical alloys[J]. Journal of Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2012, 9: 83-90.
[28] HAGIHARA K, NAKANO T. Experimental clarification of the cyclic deformation mechanisms of β-type Ti-Nb-Ta- Zr-alloy single crystals developed for the single-crystalline implant[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2017, 98: 27-44.
[29] YANG Y, CASTANY P, BERTRAND E, CORNEN M, LIN J X, GLORIANT T. Stress release-induced interfacial twin boundary ω phase formation in a β-type Ti-based single crystal displaying stress-induced α′′ martensitic transformation[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 149: 97-107.
[30] HOW F, JU C P, LINJ H C. Structure and properties of cast binary Ti-Mo alloys[J]. Biomaterials, 1999, 20(22): 2115-2122.
[31] DAVIS R, FLOWER H M, WEST D R F. Martensitic transformations in Ti-Mo alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1979, 14(3): 712-722.
[32] COLLINGS E W. The physical metallurgy of titanium alloys[M]. OH: ASM International, 1988: 83-84.
Effect of cooling rate on microstructure and mechanical properties of TC16 titanium alloy
ZHANG Zhi-qiang1, DONG Li-min1, HU Ming1, 2, LEI Xiao-fei1, YANG Yang3, YANG Rui1
(1. Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China;
3. Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Fuzhou 350002, China)
Abstract: The microstructure evolutions of the TC16 titanium alloy corresponding to different cooling rates at 800 ℃ were investigated by techniques of XRD, SEM and TEM. The tensile properties of each sample were finally evaluated. The results show that TC16 titanium alloy consists of primary a phase, α″ martensite, thermal w phase and metastable b phase in both water quenching and air cooling samples, but only primary α phase and metastable b phase are identified in furnace cooled sample. The volume fraction and grain size of primary α phase in both water quenching and air cooling samples are nearly the same, which are smaller than that of furnace cooling one. The dual yielding phenomenon was observed on the engineering stress-strain curves of both water quenching and air cooling samples. With decreasing the cooling rate, the yield strength of TC16 titanium alloy increases. The ultimate tensile strength of water quenching and air cooling samples exhibits the same value which is larger than that of furnace cooling one. Although the slight difference on the tensile strength for three kinds of samples, the elongation and area reduction representing the ductility are nearly the same.
Key words: TC16 titanium alloy; cooling rate; microstructure; mechanic property; cyclic tensile deformation
Foundation item: Project(2015-PY05) supported by the Innovative foundation of the Institute for Metal Research, China
Received date: 2018-07-12; Accepted date: 2019-03-11
Corresponding author: DONG Li-min; Tel: +86-24-23971942; E-mail: lmdong@imr.ac.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:中国科学院金属研究所创新基金资助项目(2015-PY05)
收稿日期:2018-07-12;修订日期:2019-03-11
通信作者:董利民,研究员,博士;电话:024-23971942;E-mail:lmdong@imr.ac.cn