


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 1594-1598
Roles of Zr and Y in cast microstructure of M951 nickel-based superalloy
ZHOU Peng-jie1,2, YU Jin-jiang2, SUN Xiao-feng2, GUAN Heng-rong2, HU Zhuang-qi2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology,Zhenjiang 212003, China;
2. Department of Superalloys, Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China
Received 14 August 2011; accepted 21 November 2011
Abstract: The influence of Zr and Y on the cast microstructure of a nickel-based superalloy was investigated by optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy(SEM), electron probe micro-analysis (EPMA) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The γ+γ′ eutectic volume in the superalloy rises notably with the increase of Zr or Y content. Meanwhile, the morphologies of primary MC carbides change from needle and platelet-like to blocky shape with increasing Zr and Y doped. The XRD results show that the primary MC carbide lattice constant increases with Zr and Y additions, and EPMA investigation shows that the platelet-like MC carbides contain primarily Nb and C, while those carbides in blocky shape have 39.2% Zr and 39.6% Nb in average,. These influences on the cast microstructure can be attributed to the atomic size effects of Zr and Y.
Key words: yttrium; zirconium; carbides; nickel based superalloys; microstructure; solidification
1 Introduction
The creep and stress-rupture properties of conventionally-cast nickel-based superalloys can be notably improved by adding an appropriate amount of trace element [1-3]. The improvement primarily results from the enhanced grain boundary cohesive strength by alloying with minor element [4-6]. Other mechanisms reported include counteracting detrimental elements by forming stable compound [7-9], stabilizing the MC carbides [10]. With the application of vacuum induction melting (VIM) and the decreasing content of impurities in raw materials, minor alloying method has been greatly restricted within the past decade. Recently, trace elements have been reintroduced into the fourth and fifth generation single crystal superalloys because of their certain roles.
Although tremendous work has been carried out since the 1960’s, and good agreement has been made on the effects of Zr and B, a clear understanding of the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Because of the complexity of superalloy constitution and the difficulty of direct investigation of minor alloying behavior, some results are controversial and often contradictory. One of the reasons for the confusion is the lack of systematic study on the effect of minor alloying elements, linking their role with the elements character. Specifically, little attention has been paid specifically to the general characters of the trace elements. Studying the relationship between common effect of minor alloying and its common elements characters is important. This provides a thought that gives insight into the mechanisms of minor alloying based on their common characters. This is a new approach, and will help us to understand the underlying mechanism of minor alloying. This study focuses on the influence of trace elements having large atomic radii. These elements are Zr, Y and Hf. The role of minor alloying is discussed in detail with respect to the as-cast microstructure changes.
2 Experimental
The experimental alloy was M951, and its nominal chemistry compositions, except the minor elements studied here, were 0.05C, 0.023B, 9Cr, 5Co, 6Al, 2.2Nb, 3Mo, 3.5W, and balanced Ni. The mother alloy was first prepared on a 500 kg vacuum induction melting(VIM) and cast into 30 kg alloy rods. Then the alloys were remelted in a 10 kg laboratory VIM furnace, where the minor elements were introduced into just before pouring to prepare alloys with various contents of trace elements. The real Y contents were (mass fraction, %) 0, 0.002, 0.006, 0.013, 0.014, 0.017, and the real Zr contents were (mass fraction, %) 0, 0.005, 0.013, 0.04, 0.049, 0.11. Each ingot was about 4.5 kg, and the diameters of the specimens were 10 mm. The pour temperature was approximately 1450 ℃ and the cooling rates were believed to be identical with an estimation of 100 ℃/min.
For optical examination, the specimens were polished, etched in a solution of 100 mL HCl + 80 mL H2O + 20 g CuSO4, and observed on a LEICA MEF4M optical microscope (OM) and JSM6480 scanning electron microscope (SEM). A zone with 5 mm in diameter was randomly picked to count the eutectic volume. In this zone, all images with eutectic colonies were selected with a magnification of 500, which were counted by SISC IAS V8.0 image analysis system. The minor phases in the alloys were extracted by using the electrolyte of 50 mL hydrochloric acid + 100 mL glycerol + 1000 mL methanol. The extraction temperature was placed between -3 ℃ and 2 ℃ and the current density was 0.07 A/mm2. Then the extracted powder was observed by SEM and the compositions of these minor phases were investigated via an electron probe micro analyzer (EPMA) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscope (EDS). All the samples reported here were as-cast.
3 Results
The microstructures of M951 alloy with various Y or Zr contents are shown in Fig. 1. It can be seen that the secondary dendrite spacings are all 100-150 μm. The similarity in secondary dendrite spacings indicates that the solidification situations are roughly the same. As shown in Fig. 1(a), no eutectic colony can be observed. With increasing Zr and Y contents, appreciable eutectic colonies present at the vicinity grain boundaries, which are given in Figs. 1(b), (c) and (d). It can be seen from Fig. 2 that trace elements exert a significant impact on the eutectic volume of the superalloy. The eutectic volume steadily increases with the rise of Zr or Y contents. In particular, when Y content exceeds 0.013%,or Zr content exceeds 0.04, the eutectic volume increases drastically.
Powders extracted from alloys with various levels of trace elements were examined by SEM and XRD. As shown in Fig. 3, the powder actually consists of two phases, the major phase of MC carbides, and very minor M3B2 borides. The carbide morphologies are presented in Fig. 4. As shown in Fig. 4(a), in the low level Zr and Y-free alloy, the MC carbide is predominantly needle or platelet-shaped. While learned from Fig. 4(b) and Fig. 4(c), for those alloys containing appreciable level of Zr or Y, discrete blocky carbide particles are predominant.
The difference in the metallic element content of MC will directly affect the morphology of carbides. Figure 5(a) shows that the platelet-like carbide contains primarily Nb and C, which means that M in MC is predominantly Nb. By contrast, the blocky carbide contains appreciable Y and Zr contents (Fig. 5(b)). This results have good repeatability. The compositions of carbides in varied shape are listed in Table 1, and each composition represents an average of 5 carbides. As illustrated in Table 1, the Nb mass fraction in platelet- like MC carbide is about 72%. As for those discrete blocky carbides, their Nb component drops notably, with a remarkable rise of Zr content. Also, it is clear that the MC carbides are not simply NbC or ZrC, but a compound of MC (M=Nb,Zr,Cr,Ni,Y). It is indicated that some of Nb atoms in MC carbides are substituted by Zr. The average Y content of carbides in 0.017% Y alloy is 1.4%, which is much higher than that of bulk material. Thus, the modification in carbide morphology may be related to its chemical composition modification.
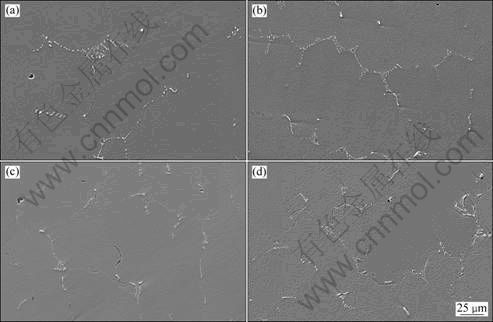
Fig. 1 Microstructures of M951 alloy with various Y or Zr contents: (a) Zr and Y free; (b) 0.04%Zr; (c) 0.014%Y; (d) 0.017%Y
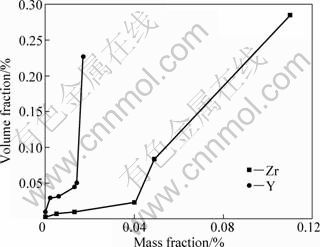
Fig. 2 Eutectic volume in alloys with various Y or Zr contents
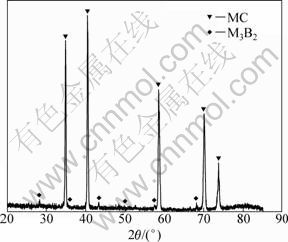
Fig. 3 XRD pattern of extracted phases
Table 1 Compositions of carbides in varied shape

4 Discussion
From the above results, it is clearly shown that the addition of Zr or Y to the M951 alloy has the following effects upon microstructure: 1) the γ + γ′ eutectic volume in superalloy drastically increases with increasing Zr or Y content; 2) the needle-and platelet-like carbides are modified to a blocky particulate morphology.
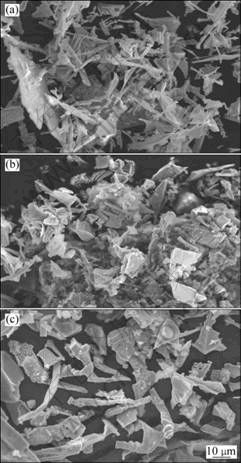
Fig. 4 Carbide morphologies in alloys with 0.005% Zr (a), 0.11% Zr (b) and 0.017% Y (c)
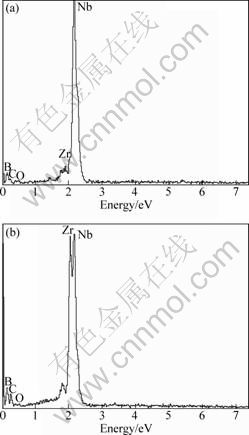
Fig. 5 EDS patterns of carbides in platelet-like shape (a) and discrete blocky-like shape (b)
Besides Zr and Y, it was reported that Hf also has a significant influence on eutectic colonies [11]. It can be seen that Zr, Y and Hf have larger atomic radii than others. The atomic radii of Zr, Y and Hf are 1.60 ?, 1.80 ?, 1.59?, respectively. In contrast, the atomic radii of other main elements used in superalloy range from 1.24 ? to 1.47 ?[12]. The large atoms in the melt make them harder for the diffusion of other elements, such as Al, which means a smaller diffusion coefficient DL. Furthermore, Zr is found to be enriched in the final solidified regions. Thereby, segregation of the eutectic elements in the mushy zone was aggravated. An effective distribution coefficient, ke, can be described by the following equation:
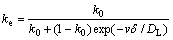 (1)
(1)
where k0 is the equilibrium distribution coefficient; v is the solidification or growth rate; δ is the thickness of boundary layer in the melt; DL is the diffusion coefficient.
Under solidification conditions in which v and δ are constant, a smaller DL leads to a greater ke. The residual melt with the concentration reaching the eutectic point, can be described as the following equation:
 (2)
(2)
where fL is the fraction of residual melt; cE is the concentration of eutectic melt; c0 is the original concentration of melt.
For Ni-Al system, k0<1, and ke is between k0 and 1. Here cE and c0 are assumed to be constant, cE>c0. Judging from above equation, a greater ke results in larger fraction of melt whose concentration reaches cE, which is apt for eutectic formation. So, introducing elements with large atomic radii into nickel-based superalloy will promote formation of γ + γ′ eutectic.
The morphology of primary MC carbide may be influenced by the solidification processing [13,14] and alloy composition [15,16]. In the present study, the solidification parameters are the same, thus the cooling rates for all the alloys studied are assumed to be identical. By comparing the compositions of carbides with various morphologies, it is evident that carbides rich in Zr and Y always are in blocky morphology, while those carbides with needle- or platelet-like ones are primarily rich in Nb. Therefore, the appreciable Zr and Y components in MC are directly relevant to morphology modification. As listed above, Zr, Y and Hf have larger atomic radii; meanwhile, those elements are strong MC carbide formers [17].
For carbides with high Zr or Y content, an enhanced distortion in MC particle during solidification leads to a reduction of driving force. Furthermore, the statistical lattice constant in modified carbides is larger than that of the carbides in the matrix alloy. As seen from Fig. 6, the peak (311) of MC is shifted to a smaller angle. The peaks of Zr and Y modified carbides are broadened. This result confirms our conclusion. MC has an orientation relationship of  with
with 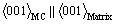 , with the matrix in nickel-based superalloy [18,19]. Additionally, the Bravais unit of MC lattice is greater than that of the matrix. Therefore, the lattice misfit of the MC and matrix interface is improved by doping the trace elements. This leads to the higher energy due to the greater strain energy. Consequently, the driving force for the MC carbide formation decreases. As a result, the size of carbide in modified alloy appears to be smaller than that of unmodified alloys. It is generally accepted, with identical volume, a carbide in blocky shape has smaller surface than that in platelet- or needle-like ones. To minimize the surface energy, the carbide is apt to form carbides in blocky like rather than that in platelet- or needle-like ones.
, with the matrix in nickel-based superalloy [18,19]. Additionally, the Bravais unit of MC lattice is greater than that of the matrix. Therefore, the lattice misfit of the MC and matrix interface is improved by doping the trace elements. This leads to the higher energy due to the greater strain energy. Consequently, the driving force for the MC carbide formation decreases. As a result, the size of carbide in modified alloy appears to be smaller than that of unmodified alloys. It is generally accepted, with identical volume, a carbide in blocky shape has smaller surface than that in platelet- or needle-like ones. To minimize the surface energy, the carbide is apt to form carbides in blocky like rather than that in platelet- or needle-like ones.
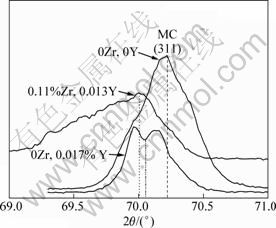
Fig. 6 XRD pattern of MC with various Zr and Y contents
5 Conclusions
1) The eutectic volume in M951 superalloy increases noticeably with increasing Zr or Y content. The matrix alloy is almost eutectic free, while the eutectic volume fraction is 0.23% for 0.017%Y alloy and 0.29% for 0.11%Zr alloy.
2) Primary carbide morphology is modified by the two dopants. It is found that carbide in blocky shape tends to have higher Zr or Y contents. The average Zr content of discrete blocky carbides is 39.2%, which is much higher than that of platelet-like carbide. Much of the Nb atoms in MC are substituted by Zr or Y. The atomic radius of Zr or Y is larger than that of Nb, consequently, the composition modification of MC leads to a larger lattice constant of carbide.
References
[1] CAO W D, KENNEDY R. Role of chemistry of In718 type allvac?718TM alloy development [C]//GREEN K A, POLLOCK T M, HARADA H, HOWSON T E, REED R C, SCHIRRA J J,WALSTON S. Superalloy 2004. Warredale, PA: TMS, 2004: 91-99.
[2] HUANG H E, KOO C H. Effect of zirconium on microstructure and mechanical properties of cast fine-grain CM247LC superalloy [J]. Mater Trans, 2004, 45: 554-561.
[3] ZHOU P J, YU J J, SUN X F, GUAN H R, HU Z Q. Role of yttrium in the microstructure and mechanical properties of a boron-modified nickel-based superalloy [J]. Scripta Mater, 2007, 57: 643-646.
[4] LIU C T, WHITE C L, HORTON J A. Effect of boron on grain-boundaries in Ni3Al [J]. Acta Metall, 1985, 33: 213-229.
[5] GUO J T, LI H, SUN C, WANG S H, REN D D, XIONG L Y. Behavior of boron in poly-monocrystalline Ni3Al and its effect at room and high temperature [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1992, 152: 120-125.
[6] KHADKIKAR P S, VEDULA K, SHARBEL B S. The role of boron in ductilizing Ni3Al [J]. Metall Trans A, 1987, 18: 425-428.
[7] BLAVETTE D, DUVAL P, LETELLER L, GUTTMAN M. Atomic-scale APFIM TEM investigation of grain boundary microchemistry in Astroloy nickel base superalloys[J]. Acta Mater, 1996, 44: 4995-5005.
[8] JOHNSON W C, DOHERTY J E, KEAR B H, GIAMEI A F. Confirmation of sulfur embrittlement in nickel alloys [J]. Scripta Metall, 1974, 8: 971-974.
[9] SCHUMANN E, YANG J C, GRAHAM M J. Direct observation of the interaction of yttrium and sulfur in oxidized NiAl [J]. Scripta Mater, 1996, 34: 1365-1370.
[10] HOU Jie-shan, CONG Pei-juan, ZHOU Lan-zhang, QIN Xue-zhi, YUAN Chao, GUO Jian-ting. Effect of Hf on microstructure and mechanical behavior of hot corrosion resistant Ni-based superalloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(5): 945-953. (in Chinese)
[11] KOVTAL P S, VENABLES J D, CALDER R W. The role of hafnium in modifying the microstructure of cast nickel-base superalloys [J]. Metall Trans A, 1972, 3: 453-458.
[12] DEAN J A. Lange’s handbook of chemistry[M]. 15th ed. New York: McGraw- Hill Co, 1998.
[13] LIU L, SOMMER F. Effect of solidification conditions on MC carbides in a nickel-base superalloy IN738 LC [J]. Scripta Met Mater, 1994, 30: 587-591.
[14] YU Zhu-huan, LIU Lin, ZHAO Xin-bao, ZHANG Wei-guo, ZHANG Jun, FU Heng-zhi. Effect of solidification rate on MC-type carbide morphology in single crystal Ni-base superalloy AM3 [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20: 1835-1840.
[15] CUTLER E R, WASSON A J, FUCHS G E. Effect of minor alloying additions on the carbide morphology in a single crystal Ni-base superalloy [J]. Scripta Mater, 2008, 58: 146-149.
[16] HUANG X B, ZHANG Y, LIU Y, HU Z Q. Effect of small amount of nitrogen on carbide characteristics in unidirectional Ni-base superalloy [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 1997, 28: 2143-2147.
[17] STRRINK M J, CAMA H, THOMSON R C. MC carbides in the Hf containing Ni based superalloy MarM002 [J]. Scripta Mater, 1998, 38: 73-80.
[18] CHEN Q Z, JONES C N, KNOWLES D M. Effect of alloying chemistry on MC carbide morphology in modified RR2072 and RR2086 SX superalloys [J]. Scripta Mater, 2002, 47: 669-675.
[19] LIU J L, JIN T, YU J J, SUN X F, GUAN H R, HU Z Q. Effect of thermal exposure on stress rupture properties of a Re bearing Ni base single crystal superalloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 527: 890-897.
Zr和Y对铸态M951镍基高温合金显微组织的影响
周鹏杰1,2,于金江2,孙晓峰2,管恒荣2,胡壮麒2
1. 江苏科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,镇江 212003;
2. 中国科学院 金属研究所 高温合金研究部,沈阳 110016
摘 要:应用光学显微镜、扫描电镜、电子探针和X射线衍射研究Zr和Y对镍基高温合金铸态组织的影响。结果表明,随着镍基合金中Zr和Y含量的增加,合金中的γ+γ′共晶数量明显增多。同时,随着Y和Zr含量的增加,合金的初生MC碳化物形貌也发生明显变化,由针状或片状转化为以孤立的块状为主。XRD衍射测试发现,加入一定量的Zr和Y后,MC 碳化物的晶格常数变大。电子探针结果表明,针状或片状碳化物主要含Nb和C,而块状的碳化物则平均含有39.2%Zr和39.6%Nb。这两种元素对铸态显微组织的影响可以归结于它们所具有的原子尺寸效应。
关键词:钇;锆;碳化物;镍基高温合金;显微结构;凝固
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Project supported by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, China
Corresponding author: ZHOU Peng-jie; Tel: +86-511-84426291; Fax: +86-511-84407381; E-mail: zhoupengjie@126.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61361-7