文章编号:1004-0609(2013)05-1241-07
Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D复合材料的蠕变微观组织和变形机理
田 君,石子琼,钟守炎,廖梓龙
(东莞理工学院 机械工程学院,东莞 523808)
摘 要:在温度为473~573 K、外加应力为30~100 MPa下,对硅酸铝短纤维增强AZ91D镁基(Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D)复合材料及AZ91D镁合金进行拉伸蠕变实验。通过SEM和TEM检测方法对其蠕变微观组织变化和变形规律进行研究。结果表明,当两种材料的真应力指数n=3时,蠕变速率受位错的黏滞性滑移控制;复合材料的门槛应力增大、短纤维有效的承载和传载作用导致复合材料的蠕变抗力显著增大。短纤维表面上的MgO保护层增大了短纤维的承载和传载作用;短纤维的存在阻碍了复合材料的蠕变变形,降低了蠕变变形速率,控制着整个蠕变变形过程。
关键词:镁基复合材料;蠕变;载荷传递;微观组织
中图分类号:TB332 文献标志码:A
Microstructural evolution and deformation mechanism during creep of Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D composite
TIAN Jun, SHI Zi-qiong, ZHONG Shou-yan, LIAO Zi-long
(School of Mechanical Engineering, Dongguan University of Technology, Dongguan 523808, China)
Abstract: The tensile creep tests were conducted on Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D composite and an unreinforced AZ91D matrix alloys in the temperature range of 473-573 K and stress range of 30-100 MPa. By scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy, the microstructural effects on the creep behavior of the two materials were discussed. The results show at a true stress exponent of n=3 for the two materials, and creep rate is affected by the viscosity slip control of the dislocation. The creep resistance of the reinforced material is shown to be considerably improved compared with that of the matrix alloy. The creep strengthening arises mainly from the increase of threshold stress of the composite and the effective load transfer between plastic flow in the matrix and the fibers. The MgO protective layer on the surface of short fibers can increase carrying and transferring of loads of the short fibers. The presence of short fibers can hinder the creep deformation of the composite, reduce the creep deformation rate, and control the whole creep deformation process.
Key words: magnesium matrix composite; creep; load transfer; microstructure
镁合金具有低密度、高比强度、高比刚度和易回收等优点,在航空、航天、汽车、计算机、电子、通讯和家电等行业有广泛的应用[1-3]。然而,在温度高于423 K时镁合金的抗蠕变能力较弱,这极大地限制了其高温应用[4-8]。复合材料化已成为提高合金高温蠕变性能的一种重要手段[9-12]。利用来源广泛且价格相对低廉的硅酸铝短纤维与AZ91D镁合金通过挤压铸造而得到的硅酸铝短纤维增强AZ91D镁基复合材料被证实具有较好的综合力学性能[13]。迄今为止,国内外研究者对镁基复合材料的高温蠕变性能的研究主要集中在颗粒增强或长纤维增强的镁基复合材料上,对短纤维增强镁基复合材料的高温蠕变研究较少[14]。与长纤维相比,短纤维增强镁基复合材料的制备工艺简单,制造成本较低,目前正加大对它们的开发使用。基于理论研究与实际使用的要求,有必要开展系统的有关短纤维增强镁基复合材料蠕变行为与蠕变机理的实验与理论研究。为此,本文作者对硅酸铝短纤维增强AZ91D复合材料及AZ91D镁合金在不同温度和应力条件下进行常应力拉伸蠕变实验,研究硅酸铝短纤维增强AZ91D复合材料中蠕变前后的微观组织变化和蠕变变形规律,为该材料的实际工程应用和丰富短纤维增强镁基复合材料的蠕变理论研究提供指导。
1 实验
所用复合材料由硅酸铝短纤维与AZ91D镁合金(Mg-9%Al-1%Zn-0.3%Mn,质量分数)通过挤压铸造法制备。所制备的AZ91D镁基复合材料具有良好的结合界面,复合材料的性能得到明显增强,而且其综合力学性能好。硅酸铝短纤维预制体是由随机分布的硅酸铝短纤维(Al2O3-SiO2,直径不超过5 μm,长度不超过80 μm)组成。挤压铸造后的复合材料中短纤维的体积分数为25%。为方便表达,体积分数为25%的硅酸铝短纤维增强AZ91D镁基复合材料可以写成25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D,其中下标sf表示短纤维。复合材料和AZ91D基体均于温度为473、523和573 K,外加应力为30~100 MPa下在GWT105持久测试机上进行拉伸蠕变实验,直到最终蠕变断裂。通过LVDT数据采集系统绘制蠕变曲线,利用SEM 和TEM观察材料蠕变实验前后的组织。
2 结果与分析
2.1 高温蠕变曲线
图1所示为AZ91D基体合金在473 K和不同载荷下的应变—时间(ε—t)蠕变曲线;图2所示为25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D复合材料在温度T=473 K和不同载荷下的应变—时间(ε—t)蠕变曲线。两种材料在某时刻的蠕变速率可从曲线上该时刻点的切线斜率得到。从图1和2可以看出,两种材料的蠕变曲线形状表现为典型的金属蠕变3阶段:第一阶段在瞬间产生一个初始形变量后,应变快速增加,应变速率逐渐减小,即减速蠕变第一阶段;当蠕变速率逐渐减小到一稳定值时,蠕变进入第二阶段即稳态蠕变阶段,此阶段的特点是蠕变应变随时间呈线性增加,此阶段的蠕变时间占整个蠕变时间的比例很大;第三阶段为蠕变破坏阶段,在该阶段应变速率明显增大直至材料的破坏。当应力等于或小于某一值时,试样不再发生蠕变,在应变图上表现为一段水平线,说明该材料存在蠕变门槛应力[14]。在T=473 K、σ=40 MPa时,合金的应变曲线为一段水平线;σ=50 MPa时,复合材料的应变线为一段水平线。表明AZ91D复合材料及其基体合金在此温度下存在蠕变门槛应力,基体合金的门槛应力应在40~45 MPa之间,复合材料的门槛应力应在50~70 MPa之间,复合材料的蠕变门槛应力大于基体的蠕变门槛应力。AZ91D基体在T=473 K、σ=60 MPa下的稳态蠕变时间约为12 h,AZ91D复合材料在T=473 K、σ=70 MPa的稳态蠕变时间约为100 h,所求得的复合材料的稳态蠕变速率低于基体合金的稳态蠕变速率近2个数量级。可见,在相同温度、相近外应力作用下,复合材料的抗蠕变能力远远强于基体合金的抗蠕变能力。
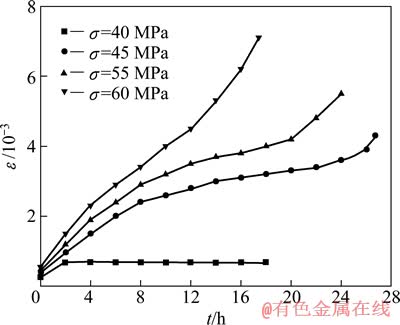
图1 AZ91D镁合金在473 K和不同载荷下的蠕变曲线
Fig. 1 Creep curves of AZ91D magnesium alloys at 473 K and different loads
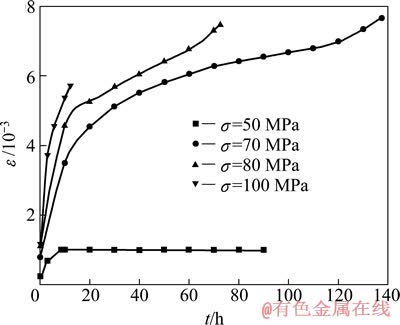
图2 25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D复合材料在473 K和不同载荷下的蠕变曲线
Fig. 2 Creep curves of 25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D composites at 473 K and different loads
2.2 蠕变门槛应力和真应力指数
金属材料如果存在蠕变门槛应力σth,当温度为定值时,金属材料的稳态蠕变速率方程可用式(1)表示[14-15]:
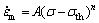 (1)
(1)
将式(1)改写成式(2):
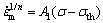 (2)
(2)
式中:A和A1为与材料和温度有关的常数;n为真应力指数;σ为外加应力;σth为门槛应力; 为稳态蠕变速率;
为稳态蠕变速率;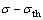 为金属材料的蠕变有效应力。
为金属材料的蠕变有效应力。
对于硅酸铝短纤维增强AZ91D镁基复合材料及AZ91D镁合金,n各取3、5和8时分别作出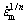 —σ关系曲线。从中选择线性关系较好的曲线,其对应的n值为真应力指数,从该图就可以获得不同温度下的真门槛应力值[14]。复合材料和基体合金线性关系最好的曲线所对应的n=3,如图3所示。
—σ关系曲线。从中选择线性关系较好的曲线,其对应的n值为真应力指数,从该图就可以获得不同温度下的真门槛应力值[14]。复合材料和基体合金线性关系最好的曲线所对应的n=3,如图3所示。
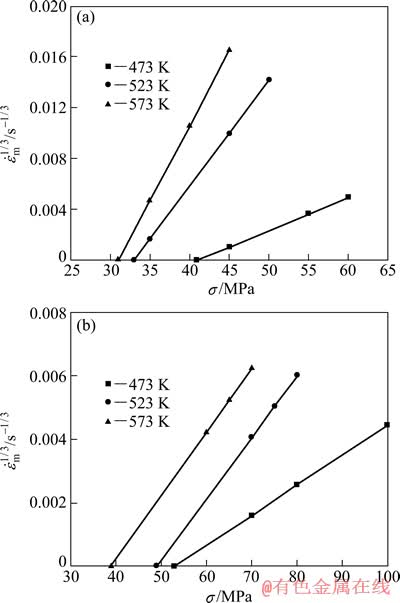
图3 AZ91D基体合金及复合材料25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/ AZ91D的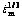 —σ关系曲线
—σ关系曲线
Fig. 3 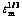 —σ curves of AZ91D alloy (a) and 25%Al2O3- SiO2(sf)/AZ91D composite (b)
—σ curves of AZ91D alloy (a) and 25%Al2O3- SiO2(sf)/AZ91D composite (b)
Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D复合材料的基体合金为AZ91D,AZ91D合金为固溶体合金,固溶体合金稳态蠕变时应力指数较小,当应力指数n为3或5时,代表固溶体合金的两种重要蠕变类型。n≤3、其典型值为3,表示蠕变行为与纯金属有很大区别,称为第一类合金型蠕变;n=4~7,其典型值为5,表示蠕变行为与纯金属类似,称为第二类纯金属型蠕变;n≥8表示稳态蠕变行为不能用幂律方程来描述[14-16]。两种材料的真应力指数n=3,表明蠕变机制与应力指数n=3的第一类固溶体合金蠕变机制相同,即蠕变速率主要受位错的黏滞性滑移控制[14]。从图3可以求出其蠕变门槛应力σth,如表1所列。从表1可以看出,在相同温度情况下,复合材料的门槛应力高于基体的门槛应力。
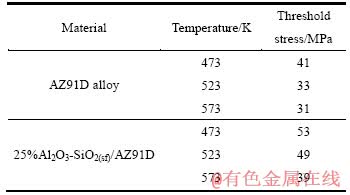
表1 AZ91D合金和25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D复合材料的蠕变门槛应力
Table 1 Creep threshold stress values of AZ91D alloy and 25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D composite
2.3 蠕变前微观组织
图4所示为AZ91D基体合金和Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/ AZ91D复合材料的金相显微组织。从图4可以看出,硅酸铝短纤维随机并均匀地分布于基体中,没有发现明显的短纤维缠结现象,复合材料组织比基体合金组织致密,而且晶粒也明显比基体合金的晶粒小。硅酸铝短纤维的加入,阻碍了基体晶粒的长大,细化了晶粒,改善了复合材料的组织,从而使复合材料得到增强。AZ91D基体合金在铸态下的相主要是α-Mg和β-Mg17Al12组成。复合材料除了基体具有的α-Mg和β-Mg17Al12两个相之外,还存在AlPO4、MgO和Al2O3·SiO2;AlPO4相来自于粘结剂焙烧后的产物;Al2O3·SiO2相来自于短纤维,是复合材料的主要相;所形成的MgO是Mg与SiO2界面反应所生成的产物,比较均匀地包围在短纤维的表面,保护了短纤维,从而起到增强作用[13]。
2.4 蠕变后的微观组织变化
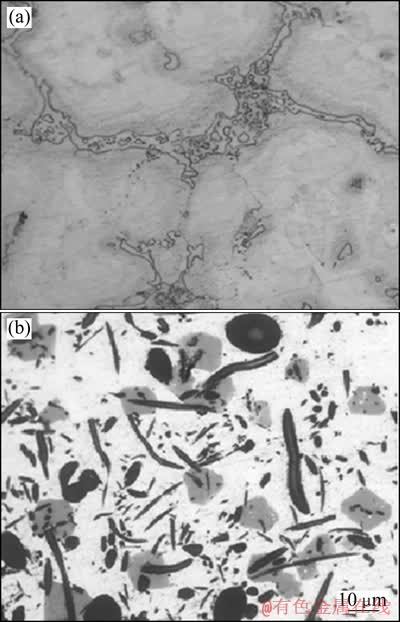
图4 AZ91D基体合金和25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D的金相组织
Fig. 4 Microstructures of AZ91D matrix alloy (a) and 25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D composite (b)

图5 AZ91D基体合金在473 K和60 MPa下蠕变后的TEM像
Fig. 5 TEM image of AZ91D matrix alloy after creep at 473 K and 60 MPa
图5所示为AZ91D镁合金在T=473 K和σ=60 MPa下蠕变后的TEM像。从图5可以看出,当在高温下发生蠕变时,过饱和的α-Mg固溶体中的溶质Al首先在晶界处发生偏聚,形成Al原子溶质气团,接着以质点形式在晶界处非连续析出薄片状或棒状β-Mg17Al12相,β-Mg17Al12相粗化变软,使AZ91D合金的抗蠕变能力下降[15, 17],这时,能对蠕变继续起抗力作用的也只能是α-Mg基体,α-Mg基体为固溶体,α-Mg固溶体中的溶质Al在晶界处偏聚形成的Al原子溶质气团通过扩散跟着位错运动,由于扩散速率比位错自由滑移速率慢,位错运动受Al原子溶质气团的拖拽。这种对可动位错的拖拽吸引作用就产生了门槛应力。图6所示为AZ91D复合材料在473 K和100 MPa下蠕变后的TEM像。从图6可清楚地看出,在高温蠕变下的复合材料纤维表面存在一层纳米颗粒,这层纳米颗粒大多数为比较均匀的MgO颗粒[13],MgO颗粒层的厚度大约为0.2 μm,由于短纤维上这层MgO颗粒使短纤维增强体覆盖一层细密纹理的MgO保护层,达到增强复合材料的效果,即增大了短纤维的承载和传载作用。在温度分别为473和573 K时,AZ91D合金的门槛应力分别为41和31 MPa,而在相同的温度下,25%Al2O3-SiO2/AZ91D复合材料的门槛应力分别为53和39 MPa。可见,在温度为473和573 K时,25%Al2O3-SiO2/AZ91D复合材料的门槛应力分别比基体的门槛应力大12和8 MPa,即复合材料的门槛应力分别比基体的门槛应力增大了29.3%和25.8%,这种门槛应力的增大作用只可能来源于硅酸铝短纤维增强体的影响。

图6 25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D复合材料在473 K和100 MPa下蠕变后的TEM像
Fig. 6 TEM image of 25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D composite after creep at 473 K and 100 MPa
由于AZ91D基体的弹性模量比硅酸铝短纤维的小,在外加载荷作用下,其基体的应变要比短纤维的大,基体中的位错无疑要受到短纤维的拖拽。这种由于基体与短纤维的应变不一致而产生的对可动位错的拖拽力就是短纤维的承载和传载作用力,这就是AZ91D复合材料的门槛应力比基体合金的门槛应力大的原因。
从图2可以看出,在T=473 K、σ=70 MPa时,25%Al2O3-SiO2/AZ91D复合材料的应变曲线比较平缓,也就是说它发生蠕变的蠕变速率较小,而它的门槛应力σth=53 MPa,外应力与门槛应力的差值为17 MPa。从图1可以看出,在T=473 K、σ=60 MPa时,AZ91D合金的应变曲线很陡,也就是说,它发生蠕变的蠕变速率很大,而它的门槛应力σth=41 MPa,外应力与门槛应力的差值为19 MPa。在相同温度下,排除了各自门槛应力之后,基体合金与复合材料的外应力接近,而其蠕变程度却相差很大,AZ91D合金的蠕变速率远大于其复合材料的蠕变速率,说明除门槛应力外,复合材料的蠕变还存在其他因素的强烈作用,这就是硅酸铝短纤维增强体在蠕变中起到了有效的承载与传载作用,使复合材料的蠕变速率下降,从而显著地提高了复合材料的抗蠕变能力。
AZ91D镁基复合材料在高温蠕变过程中,硅酸铝短纤维通过变形来进行承载与传载作用。随着蠕变变形的增大,短纤维最终表现出多处损伤、断裂和多重断裂。图7所示为硅酸铝短纤维在复合材料蠕变断裂后的SEM像。从图7可以看出,硅酸铝短纤维发生了多处损伤或断裂。硅酸铝短纤维的存在降低了复合材料的蠕变有效应力,从而提高了复合材料的抗蠕变能力,说明AZ91D镁基复合材料的增强体蠕变强化的根本原因是硅酸铝短纤维进行了有效的承载与传载作用。硅酸铝短纤维的断裂和多重断裂阻碍了位错的迁移,降低了位错运动速率,即降低了蠕变速率,使得复合材料的蠕变由位错的黏滞性滑移控制。
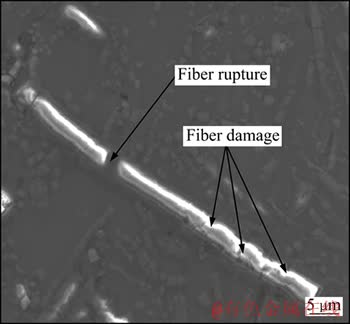
图7 在573 K和60 MPa下硅酸铝短纤维的蠕变断裂SEM像
Fig. 7 SEM image showing creep fractography of aluminum silicate short fibers at 573 K and 60 MPa
2.5 Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D复合材料蠕变过程中的应力分布
采用单纤维三维单胞模型,中心含1/4纤维,周围为基体,模型划分为成800个20节点的三维等参元,分析软件采用ANSYS,蠕变类型选为Norton型。通过计算机模拟计算,短纤维沿纤维长度方向(Z轴)的应力即轴向应力分布如图8所示,界面、基体和复合材料沿纤维长度方向(Z轴)的应力分布同理可获。为便于分析,利用计算得出的数据作出轴应力沿Z轴方向变化的关系如图9所示。从图9可以看出,短纤维最大应力出现在纤维中心处,沿Z轴正向(纤维中心指向纤维末端)轴应力渐渐减小,靠近纤维末端应力集中比较严重,此处是蠕变过程中容易发生界面脱粘的位置。界面的轴应力沿Z轴正向逐渐减小,最大应力出现在纤维中心处。基体的轴应力沿Z轴正向逐渐增大,最大应力出现在基体与短纤维末端的界面处。受载开始时,载荷是由基体通过基体与纤维的界面传递到纤维上,由于弹性模量的差异,纤维承受大部分外载,基体的蠕变变形迫使纤维拉伸,纤维应力持续增大,并在纤维中心出现应力最大值。
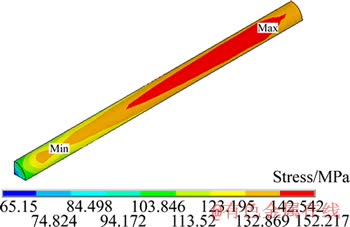
图8 25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D复合材料中短纤维在473 K和70 MPa沿纤维长度方向的应力分布
Fig. 8 Stress distribution of short fiber of 25%Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/ AZ91D in axial direction at 473 K and 70 MPa
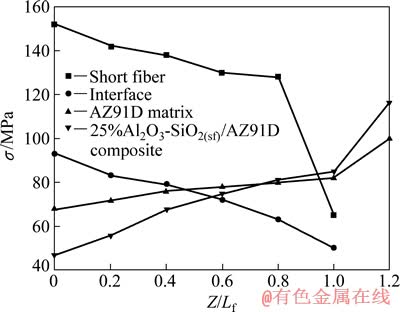
图9 纤维轴线方向的应力分布
Fig. 9 Stress distribution in axial direction (Z/Lf is relative length of short fiber)
2.6 蠕变变形规律
从复合材料蠕变后微观组织变化及应力分布的分析可知,位错控制着Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D复合材料的整个蠕变变形过程。在蠕变初期,外加载荷能够在AZ91D基体和硅酸铝短纤维之间得到很好的传递,加载到硅酸铝短纤维上的应力能够得到迅速的松弛。但由于AZ91D基体和硅酸铝短纤维具有不同的弹性模量,在外加应力的作用下,它们之间会产生应变不匹配。当应变不匹配产生的位错向基体和纤维的界面迁移时,应力从基体向纤维传递,在纤维中心处轴应力达到最大值。随着位错在界面处的堆积,位错密度逐渐增加,在纤维的周围形成工作硬化区,位错无法穿越工作硬化区。因此,纤维的存在极大地限制了位错的运动,也就阻碍了基体合金的变形,导致在蠕变第一阶段的应变速率降低。当短纤维的应变达到断裂应变时,纤维从中心开始断裂,纤维发生断裂后形成更短的亚纤维,位错运动至亚纤维端部的距离缩短,这大大提高了位错的迁移速度;当位错堆积与位错在纤维端部消失的过程达到动态平衡时,复合材料的蠕变进入稳态蠕变阶段,应变速率保持相对稳定。由于少数纤维/基体界面结合不好而存在缺陷和微裂纹,这些弱界面在蠕变中会遭到严重破坏,界面处的孔洞和裂纹在应力的作用下会逐渐扩展,导致复合材料在蠕变过程中不断变形,大部分纤维中的裂纹扩展至界面处,少数裂纹会越过界面继续扩展至基体合金中,基体中的裂纹在应力作用下继续扩展,最终发展成为宏观裂纹,导致复合材料发生断裂。
3 结论
1) 在相同温度和外加载荷下,Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/ AZ91D复合材料的稳态蠕变时间和蠕变门槛应力大于其基体合金的,稳态蠕变速率低于其基体合金的近2个数量级,表明复合材料的抗蠕变能力远强于基体合金的抗蠕变能力。两种材料的真应力指数n=3,蠕变速率主要受位错的黏滞性滑移控制。复合材料的抗蠕变能力的提高是因为蠕变门槛应力的增大和硅酸铝短纤维在蠕变中起到有效的承载与传载作用。
2) 蠕变前后微观组织分析表明,两种材料中β-Mg17Al12相粗化变软,使抗蠕变能力下降,α-Mg相中的溶质Al在晶界处偏聚形成的Al原子溶质气团对位错运动具有拖拽作用,产生蠕变抗力。复合材料中短纤维相(Al2O3·SiO2)进行有效承载与传载作用后,最终表现出多处损伤、断裂和多重断裂,它的承载与传载显著地提高了复合材料的抗蠕变能力。短纤维表面上的MgO保护层增大了短纤维的承载和传载作用。
3) Al2O3-SiO2(sf)/AZ91D复合材料的蠕变变形是由于基体与短纤维的应变不一致而产生的对可动位错的拖拽,使得基体中的位错向基体和纤维的界面迁移,在纤维的周围形成工作硬化区,位错无法穿越工作硬化区,导致蠕变变形初期的速率下降;位错堆积与位错在纤维端部消失的过程达到动态平衡时,复合材料的蠕变进入稳态蠕变阶段;弱界面在蠕变中遭到严重破坏,界面处的孔洞和裂纹在应力作用下逐渐扩展成为宏观裂纹,导致复合材料在蠕变过程中不断变形,直到最终断裂。短纤维的存在阻碍了复合材料的蠕变变形,降低了蠕变变形速率,控制着整个蠕变变形过程。
References
[1] AGHION E, BRONFIN B. Magnesium alloys development towards the 21stcentury[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2000, 350/351: 19-30.
[2] POLMEAR I J. Magnesium alloys and applications[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1994, 10(1): 1-16.
[3] 吴国华, 孙 明, 王 玮, 丁文江. 镁合金纯净化研究新进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(6): 1021-1031.
WU Guo-hua, SUN Ming, WANG Wei, DING Wen-jiang. New research development on purification technology of magnesium alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(6): 1021-1031.
[4] 田素贵, 杨景红, 于兴福. AZ31镁合金蠕变初期的变形特征[J]. 金属学报, 2005, 41(4): 375-379.
TIAN Su-gui, YANG Jing-hong, YU Xing-fu. Deformation features of AZ31 Mg alloy in initial period of high temperature creep[J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2005, 41(4): 375-379.
[5] Srinivasan A, Swaminathan J, Gunjan M K. Effect of intermetallic phases on the creep behavior of AZ91 magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(6): 1395-1403.
[6] Pekguleryuz M, Celikin M. Creep resistance in magnesium alloys[J]. International Materials Reviews, 2010, 55(4): 197-217.
[7] 张尧成, 曾 明, 郭 萍, 廖春丽, 沈保罗. AE42合金的抗压入蠕变性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(7): 1169-1175.
ZHANG Yao-cheng, ZENG Ming, GUO Ping, LIAO Chun-li, SHEN Bao-luo. Indentation creep resistance of AE42 alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(7): 1169-1175.
[8] 吴玉锋, 杜文博, 左铁镛. Mg-Al-Nd/Sr 耐热镁合金的组织结构与蠕变性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(9): 1680-1685.
WU Yu-feng, DU Wen-bo, ZUO Tie-yong. Microstructures and creep properties of heat-resistant Mg-Al-Nd/Sr alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(9): 1680-1685.
[9] Trojanova Z, Szaraz Z, Labar J. Deformation behaviour of an AS21 alloy reinforced by short saffil fibers and SiC particles[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2005, 162/163: 131-138.
[10] Dragone T L, Nix W D. Steady state and transient creep properties of an aluminum alloy reinforced with alumina fibers[J]. Acta Metall Mater, 1992, 40(10): 2781-2791.
[11] Pandey A B, Mishra R S. Steady state creep behavior of silicon carbide particulate reinforced aluminum composites[J]. Acta Metal Mater, 1992, 40(8): 2045-2052.
[12] 吕映宾, 马乃恒, 王浩伟. TiB2+SiC混杂颗粒增强的ZL109 复合材料[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(4): 602-606.
 Ying-bin, MA Nai-heng, WANG Hao-wei. ZL109 composite reinforced by hybrid particles of TiB2 and SiC[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(4): 602-606.
Ying-bin, MA Nai-heng, WANG Hao-wei. ZL109 composite reinforced by hybrid particles of TiB2 and SiC[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(4): 602-606.
[13] 田 君, 李文芳, 韩立发. Al2O3-SiO2/AZ91D镁基复合材料的挤压浸渗制备工艺及微观组织和界面的研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2009, 38(20): 53-56.
Tian Jun, Li Wen-fang, HAN Li-fa. Microstructure, interface and fabricating process of Al2O3-SiO2/AZ91D composites prepared by squeeze infiltration[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2009, 38(20): 53-56.
[14] 张俊善. 材料的高温变形与断裂[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 102.
Zhang Jun-shan. High temperature deformation and fracture of materials[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007: 102.
[15] Li Y, Langdon T G. Creep behavior of an AZ91 magnesium alloy reinforced with alumina fibers[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1999, 30: 2059-2065.
[16] Chmelik F, Lukac P, Janecek M. An evaluation of the creep characteristics of an AZ91 magnesium alloy composite using acoustic emission[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 338: 1-7.
[17] Spigarelli S, Cabibbo M, Evangelista E. Analysis of the creep behaviour of a thixoformed AZ91 magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 289(1/2): 172-181.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:广东省自然科学基金资助项目(10151170003000002)
收稿日期:2012-08-13;修订日期:2012-11-09
通信作者:田 君,副教授,博士;电话:13662847480;E-mail:841608534@qq.com