DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.09.009
超声外场下SiCp/7085复合材料界面结合机理
李畅梓,张立华,李晓谦,黎正华,李瑞卿,董方
(中南大学 机电工程学院 高性能复杂制造国家重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:采用半固态混合—机械搅拌—超声搅拌工艺制备体积分数为10%的SiCp/7085复合材料,通过扫描电镜(SEM)和能谱仪(EDS)分析制备过程中2种粒度SiC颗粒的界面结合、界面相及成分的演变规律,研究超声外场对复合材料界面结合的影响机理。研究结果表明:半固态混合—机械搅拌工艺基本实现了大粒度SiC颗粒与基体的界面结合,但在界面处生成了大量Al4C3,而对于小粒度颗粒,机械搅拌的作用效果不明显;超声外场作用下的空化效应产生高温高压,有效改善小颗粒与熔体的润湿性,并使得Mg元素在界面处富集,生成MgO和MgAl2O4等界面强化相,获得更优的结合界面。
关键词:超声外场;7085铝合金;SiCp;界面
中图分类号:TG148; TB559 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)09-2968-08
Interface bonding mechanism of SiCp/7085 composite in ultrasound field
LI Changzi, ZHANG Lihua, LI Xiaoqian, LI Zhenghua, LI Ruiqing, DONG Fang
(State Key Laboratory of High Performance Complex Manufacturing,
School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: SiCp/7085 composites with 10% (volume fraction) particle were fabricated by semi-solid mixture, mechanical stirring and ultrasonic radiation process. The evolution of interfacial combinative state, interface phase and composition between the particles of two sizes and melt during the fabrication process was investigated by SEM and EDS to research the mechanism of the ultrasonic radiation transformation interface. The results show that the semi-solid mixture and mechanical stirring process accomplish the wetting between the larger particles and melt in the main, while generate Al4C3 at the interface, but there is not remarkable improvement of wettability between the small particles and melt. As a result of ultrasonic radiation, Mg is reriched at the interface, which gives rise to the formation of interface strengthening phase MgO and MgAl2O4, the interface bonding is stronger than that of semi-solid mixture and mechanical agitation.
Key words: ultrasonic radiation; 7085Aluminum alloy; SiCp; interface
SiCp/Al复合材料具有比强度高、比刚度大、热膨胀系数小、导热性能好等特点[1],在航空航天、汽车机械、武器制造、微电子等重要科技领域具有广阔的应用前景和巨大的发展潜力,受到各国材料界的广泛关注[2]。界面作为联结基体与增强体的重要微区结构,其结合状态直接影响着复合材料的各方面性能[3],因而界面优化对于提高复合材料的性能具有重要意义。目前,SiCp/Al复合材料的制备工艺主要包括粉末冶金、喷射沉积、压力浸渗、原位反应、搅拌铸造等。其中搅拌铸造法适用性高,操作简易,便于二次加工,工业化前景更广阔。然而,在搅拌铸造制备过程中,SiC颗粒与基体间物理性能的差异、SiC颗粒表面附带的气体及杂质、搅拌过程形成的氧化膜等问题都严重阻碍颗粒与熔体的结合,致使SiC增强颗粒难以湿润,无法获得良好的界面结合效果[4],此外,高温下SiC颗粒与熔体间的化学不稳定性引发界面反应,生成的不稳定脆性相也会严重影响界面强度,进而制约材料性能的提高。高温焙烧能减少表面吸附的气体层,同时在颗粒表面形成一层非晶SiO2[5],有效改善颗粒与熔体的润湿效果,并与合金中的Mg反应生成MgO或者MgAl2O4,附着于颗粒表面,阻隔了SiC与铝合金熔体的直接接触,避免了脆性界面产物的生成,从而获得良好的界面结合[6],达到提高材料断裂韧性的效果。高能超声处理对改善颗粒与基体之间的润湿性、实现颗粒的均匀分布、降低材料的孔隙率,最终实现颗粒增强铝基复合材料的成形成性一体化制备具有重要作用[7]。关于搅拌铸造法中超声对界面结合的影响还有待进一步研究。作为复合材料制备科学领域的一项创新工艺,施加超声波外场对提高复合材料的成形质量、降低生产成本带来了前所未有的机遇,同时对制造理论和方法也提出了新的挑战。为此,本文作者采用半固态混合—机械搅拌—超声搅拌工艺制备2种不同粒度增强颗粒的复合材料,并分别对工艺过程中两者的界面结合、界面相及成分的演变规律进行分析,结合基体中元素的分布规律,研究超声外场对界面结合的影响机制。
1 实验材料及方法
1.1 实验设备
实验设备主要有:自制超声波发生器,输出频率为17~22 kHz,频率可根据负载工况实时自动跟踪,输出功率5档可调,本实验采用1 kW;超声振动系统,包括PZT压电陶瓷换能器、45号钢变幅杆和钛合金工具杆,工作端面直径为50 mm;450 W熔体搅拌器;坩埚电阻炉及温度控制仪;热电偶;浇注用铁模;高纯石墨坩埚,坩埚内径为200 mm,高度为210 mm。超声铸造实验装置示意图如图1所示。
分析设备主要有:Automet250型自动研磨机;TESCAN扫描电镜;自制电解腐蚀装置;EDS-OXFORD能谱分析仪。
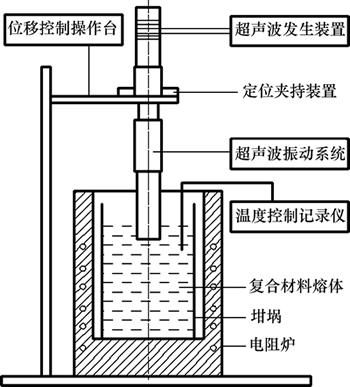
图1 超声铸造实验装置图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of ultrasonic casting experimental apparatus
1.2 实验材料与方法
本实验基体选用7085铝合金,成分见表1。
表1 实验用7085铝合金成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Composition of aluminum alloy 7085 (mass fraction) %
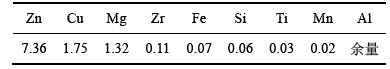
所用SiC颗粒是由SiC原矿经破碎、水洗、分级得到的磨料级绿SiC。采用超声水洗、烘干、高温氧化焙烧、过筛等预处理工艺,预处理后颗粒表面光洁如图2所示。
图2 预处理后的SiC颗粒SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM image of pretreated SiC particles
实验预设定的复合材料SiC颗粒体积分数为10%。将铝合金锭放入电阻加热炉中的石墨坩埚中进行熔炼,待完全熔化后,添加铝打渣剂并充分搅拌,使熔体充分均匀。将熔体冷却至半固态(625 ℃左右),加入预热的240号(粒径为60 μm) SiC颗粒,并搅拌,待颗粒混合均匀后,将温度保持在720~750 ℃。同时,开启机械搅拌器,持续搅拌20 min;之后将变幅杆工具头插入铝熔体中心位置预热,插入深度为25 mm[8],施振30 min。热电偶置于液面下方25 mm处。将颗粒换成400号(粒径为38 μm),重复以上实验操作。
1.3 取样方案与样品制备
分别在机械搅拌前、机械搅拌后、超声施振10 min、超声施振30 min取液面下30 mm的熔液进行铁模浇铸,水淬至室温,得到直径×长度为20 mm×50 mm的棒状样。在棒样中心处取直径×长度为20 mm×20 mm块样,块样经打磨、抛光,进行扫描电镜观察,通过电解抛光(电解液是体积分数为70%~85%的H3PO4 , 电压和电流密度分别为25 V和20~80 A/dm2,时间为4~20 min),对颗粒进行暴露处理,清洗干燥后再次进行扫描电镜观察。
2 实验结果与讨论
2.1 界面形态演变
图3所示为加入大颗粒(240号)的混合熔体在机械搅拌前、后颗粒与熔体的界面结合状态。在半固态混合过程中,颗粒逐渐被熔体包裹,实现二者初步结合,但因接触不连续,界面结合强度较弱,在制样过程中,受外部应力作用界面出现一定程度的开裂(见图3(a));经机械搅拌后,颗粒与熔体充分接触,形成的界面结合更紧密(见图3(b))。
伴随着复杂的界面反应,颗粒与熔体的润湿结合所形成的界面产物附着于界面,采用电化学抛光暴露颗粒,通过扫描电镜观察界面反应产物的微观形态,如图4所示。由图4(a)可观察到:与熔体初步接触后,大颗粒表面形成大量晶体,粒度为3~8 μm,且呈不规则状,错落分布在界面处;在机械搅拌过程中,随着界面反应的持续,界面产物在颗粒表面不断累积,最终形成一层致密的反应层,将颗粒完全包裹(见图4(b))。通过成分检测,所生成的反应产物由单一的Al4C3构成。
在半固态混合—机械搅拌过程后,大颗粒实现了与熔体的润湿结合,随后的超声搅拌过程对界面形貌无明显改变。
小颗粒(400号)与熔体结合过程如图5所示。从图5可见:通过半固态混合,颗粒逐渐分散入熔体,而颗粒表面附着大量气泡,使得颗粒无法与熔体接触(图5(a));机械搅拌后,气体层变薄,但小颗粒与熔体的润湿状况并未得到彻底改善(图5(b))。加入超声10 min,界面处气孔显著减少,熔体逐渐在颗粒表面铺展开(图5(c));当施振时间达到30 min,颗粒表面吸附的气泡基本被消除,颗粒与熔体完全结合(图5(d))。
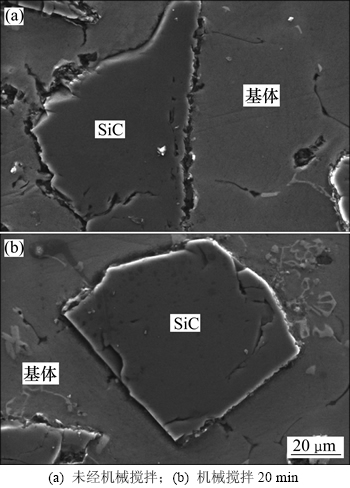
图3 240号SiCp/7085复合材料界面SEM像
Fig. 3 SEM images of interface in No.240 SiCp/7085 composites
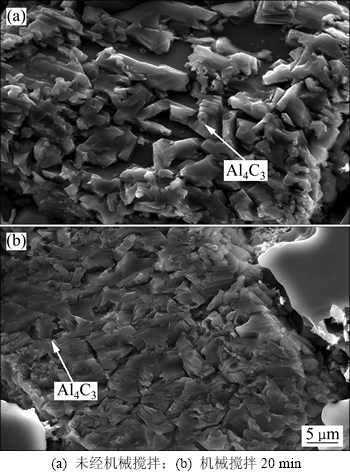
图4 240号SiCp/7085复合材料界面反应产物SEM像
Fig. 4 SEM images of reaction product interface in No.240 SiCp/7085 composites
由图5(a)和5(b)可知:半固态混合—机械搅拌工艺过程并未有效改善小颗粒的润湿状况,颗粒与熔体仍受到气体层隔绝,没有发生界面反应,颗粒表面光整,与图2所示颗粒表面特征一致;通过将超声施加于混合熔体,颗粒逐步实现与熔体润湿;超声施振时间10 min,颗粒与熔体的界面析出一层形貌规则的反应产物,粒径基本在1 μm以下。经检测,成分为MgO(颜色较暗)、MgAl2O4(颜色较亮),两者交错且均匀分布在颗粒所表面(图6(a))。继续施振,颗粒表面逐渐被微小的MgAl2O4颗粒覆盖,形成一层致密的保护层(图6(b))。
相较于大颗粒,小颗粒总表面积增加,表面能上升,与熔体润湿难度更大。此外,在半固态搅拌过程中,颗粒表面气体吸附层、搅拌卷入的气体被高温氧化产生的表面氧化层包裹,无法逸出。在机械搅拌过程中产生漩涡负压,难以有效地消除颗粒表面大量的气体吸附层和氧化膜。通过施加超声外场,小颗粒与熔体逐步结合。
2.2 基体元素分布
对界面附近基体进行EDS采点分析,位置Ⅰ和Ⅱ如图7所示,主要元素包括Al,Zn,Mg,Cu,Si和O。整合2组数据,绘制出垂直于界面路径上的Mg和O元素质量分数分布曲线。
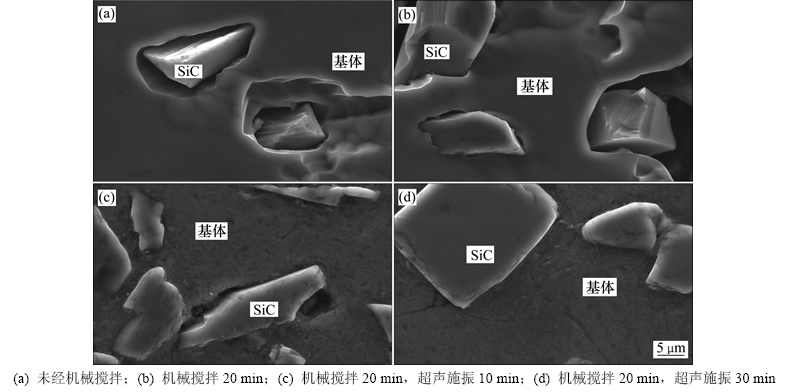
图5 400号SiCp/7085复合材料界面结合形态衍变SEM像
Fig. 5 SEM images of evolution of interface shape in No.400 SiCp/7085 composites
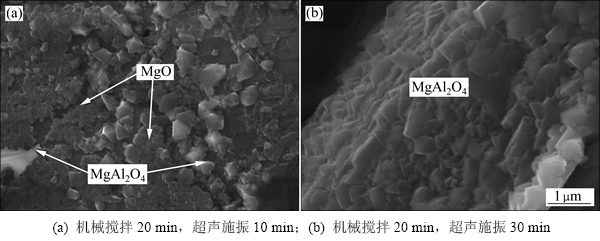
图6 400号SiCp/7085复合材料界面反应产物SEM像
Fig. 6 SEM images of interface reaction product in No.400 SiCp/7085 composites
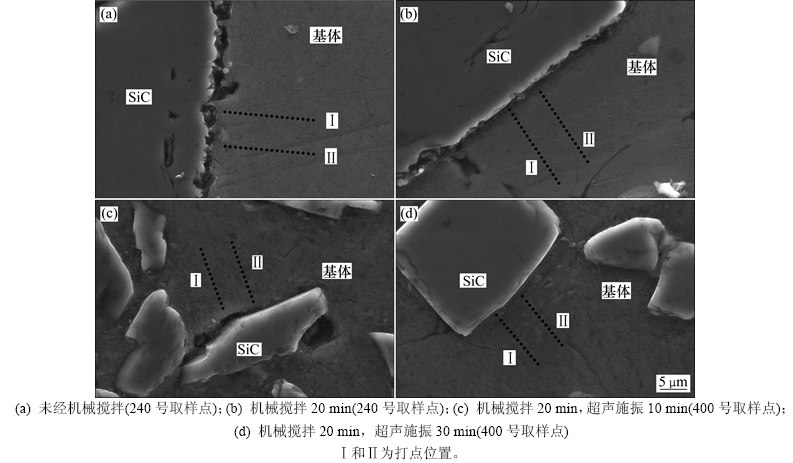
图7 EDS元素定量分析取样点
Fig.7 Positions of EDS analysis
颗粒与熔体结合时包含着多种引发界面处元素迁移的物理、化学过程,如图8所示。大颗粒半固态混合后,混合熔体中氧质量分数较高,且多集中在界面处,镁元素质量分数较低但均匀地分布在熔体中;经机械搅拌,界面附近基体中氧质量分数升高,同时,界面处的镁质量分数减小,在基体中形成1个指向界面的较小质量分数梯度。小颗与熔体结合过程的元素质量分数分布变化如图9所示。从图9可见:超声施振10 min,颗粒与熔体润湿过程中,基体中的氧质量分数快速增大,同时镁富集在界面处;持续施振,颗粒与熔体完全结合,界面及基体中氧质量分数显著下降,界面处镁质量分数也与基体的质量分数几乎持平。经对比可知:超声促进气泡与氧化物快速逸出;同时,在润湿过程中,诱发界面处Mg富集,有效实现小颗粒与熔体结合。
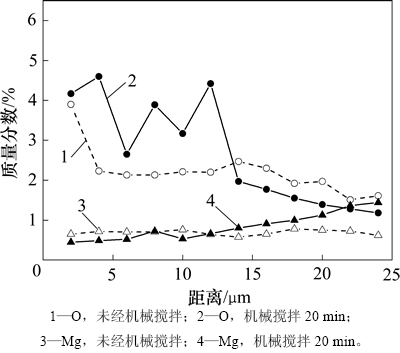
图8 240号界面Mg和O元素质量分数分布曲线
Fig. 8 Mass fraction distribution curves of Mg and O at interface of No.240 SiCp/7085 composites
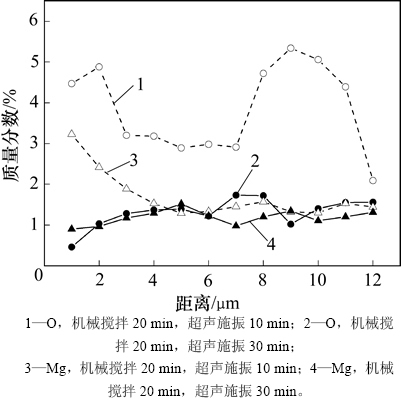
图9 400号界面Mg和O元素质量分数分布曲线
Fig. 9 Mass fraction distribution curves of Mg and O at interface of No.400 SiCp/7085 composites
3 界面结合机理分析
颗粒与熔体在结合过程中,体系中的各相属性直接决定界面润湿性。颗粒表面的原始状态如吸附气体、表面油污等均使润湿角增大;液相的性质如夹杂、气孔等会增大熔体的黏度;两相间的冶金化学反应都会对界面润湿造成影响。此外,在大气环境中,较高的制备温度使得易氧化的基体金属形成高熔点的氧化膜,包裹吸附着气体的颗粒,也会严重降低体系的润湿性。通过对颗粒进行预处理,消除颗粒表面油污,生成氧化层,减少气体吸附,既改善了润湿初始条件,又减少了脆性界面产物的生成,最终形成SiO2-Air- Oxide-Melt润湿体系。
高温下固液气三相体系中,镁存在着挥发趋势,纯镁的蒸汽压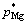 可由下式得到:
可由下式得到:
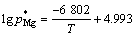 (1)
(1)
其中: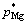 为纯镁的蒸汽压;T为热力学温度。合金中组元的蒸汽压pi与纯金属蒸汽压
为纯镁的蒸汽压;T为热力学温度。合金中组元的蒸汽压pi与纯金属蒸汽压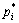 存在如下关系:
存在如下关系:
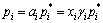 (2)
(2)
式中:pi为合金中组元的蒸汽压;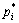 为i组元纯金属的蒸汽压;ai为合金中i组元的活度;xi为组元i在合金熔体中的摩尔分数;γi为i组元的活度系数。考虑到合金中主要元素为Al,其他合金元素质量分数较 低,将扩展的Miedema模型计算所得参数导入二元体系Wilson方程,获得的结果只依赖于组元的物性参数,既避免了实验数据的局限性,又建立了与温度的关系[9]。
为i组元纯金属的蒸汽压;ai为合金中i组元的活度;xi为组元i在合金熔体中的摩尔分数;γi为i组元的活度系数。考虑到合金中主要元素为Al,其他合金元素质量分数较 低,将扩展的Miedema模型计算所得参数导入二元体系Wilson方程,获得的结果只依赖于组元的物性参数,既避免了实验数据的局限性,又建立了与温度的关系[9]。
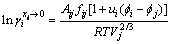 (3)
(3)
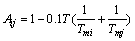 (4)
(4)
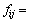
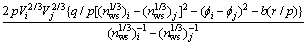 (5)
(5)
式中:f为原子接触比;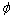 为电负性;V为摩尔体积;nws为Wigner-Seitz原胞边界处的电子密度;u,q,R和p为经验参数。对于单价或碱金属,u=0.14;对于双价金属,u=0.1;对于3价金属以及Cu,Ag和Au,u=0.07;对其他金属,u=0.04。对于参数p,由2种过渡族金属、2种非过渡族金属、1种过渡族金属和1种非过渡族金属组成的二元合金,p分别为14.1,10.6和12.3。对于参数b,由1种过渡族金属和1种非过渡族金属组成的二元液相合金,b=0.73,在其他情况下,b=0;对于r/p,当i和j分别属于过渡族金属和非过渡族金属时,r/p等于金属元素对应数值的乘积,参数的具体数值都可从文献[10]中查到。
为电负性;V为摩尔体积;nws为Wigner-Seitz原胞边界处的电子密度;u,q,R和p为经验参数。对于单价或碱金属,u=0.14;对于双价金属,u=0.1;对于3价金属以及Cu,Ag和Au,u=0.07;对其他金属,u=0.04。对于参数p,由2种过渡族金属、2种非过渡族金属、1种过渡族金属和1种非过渡族金属组成的二元合金,p分别为14.1,10.6和12.3。对于参数b,由1种过渡族金属和1种非过渡族金属组成的二元液相合金,b=0.73,在其他情况下,b=0;对于r/p,当i和j分别属于过渡族金属和非过渡族金属时,r/p等于金属元素对应数值的乘积,参数的具体数值都可从文献[10]中查到。
在Al-Mg-SiO2界面反应体系中镁的质量分数直接影响着最终的界面反应产物[10]。根据热力学理论,LEE等[11]运用Thermo-Calc软件计算得出以下结论:熔体中镁质量分数极低时,反应产物为Al2O3;当熔体中镁到达一定量(质量分数>0.007%)时,生成MgAl2O4;镁质量分数超过4%时得到的是MgO。这一结论得到施忠良等[12]实验结果的验证,此外,JEONG等[13]测得MgAl2O4和MgO产物的界面结合强度更大。实验中所用铝合金镁质量分数为1.32%,理论产物为MgAl2O4。
3.1 常规界面结合
以大颗粒与熔体结合过程为参考,对半固态混 合—机械搅拌下界面结合机理进行分析。
采用半固态搅拌添加SiC颗粒,利用半固态熔体的触变性,在黏度较大的固液两相区添加颗粒。在半固态状态下,熔体暴露在空气中,表面形成一层氧化膜,与颗粒表面气体吸附层、搅拌卷气一同混入熔体中,造成界面附近的氧质量分数偏高,影响界面润湿性。在搅拌过程中,颗粒与基体发生强烈碰撞、相互挤压,较为突出的表面率先得到活化,两者实现一定结合,避免了颗粒的上浮、团聚,但颗粒与熔体的润湿状况不理想,界面处附着大量被氧化层包裹的气泡。将混合熔体升温至液相,进行液相搅拌,充分地搅拌在界面微区产生一定的扰动,不断作用于氧化层,夹有较大气泡的氧化膜率先破裂,熔体突破气体和氧化层的隔绝,与颗粒接触;同时,破碎形成的微气泡与氧化层碎片被卷入界面附近熔体中。在熔体与颗粒接触后,界面反应发生,界面处的合金元素镁被不断消耗,熔体中的镁元素向界面处扩散,而混入熔体中的微气泡、氧化膜碎片在界面处形成1个氧化夹杂区,阻碍了合金元素镁向界面扩散,使得镁无法完全参与界面反应,在界面处生成大量脆性Al4C3。
3.2 超声界面结合
小颗粒与熔体结合过程反映了超声外场对界面的影响。在超声处理熔体时,由超声波发生器输出的高频交流电信号激振压电陶瓷片,将电能转变为超声频振动的机械能(弹性振动纵向波),通过导波工具杆直接耦合到金属熔体中。超声波在金属熔体中传播时形成的空化、声流、谐振、异质活化等诸多特殊效应,具有除气除杂、传热传质、形核细晶的作用[14]。
图10 超声润湿示意图
Fig. 10 Schematic of ultrasonic wetting
在空化泡崩溃过程中,瞬间会在极有限的空间内产生很大的压力梯度,产生各种特殊的物理、化学效应。由Noltlingk-Neppiras方程导出超声波作用下空化泡壁的运动方程,通过计算,在频率为20 kHz,功率为1 kW的超声波作用下,空化泡破灭能产生的最大压强约为1.1 GPa,最高温度约为4.8×104 K。超声润湿示意图如图10所示。空化效应在氧化层附近的熔体中形成大量的微射激流,有效破除氧化膜,其形成的微区湍流将氧化膜卷入熔体,所夹气体层不断转变成微气泡逸散至熔体中。熔体突破氧化膜和气体层,与颗粒接触,并不断在颗粒表面铺展开。卷入熔体中的氧化膜在超声持续施振下破碎成颗粒状,散入熔体中。
已知制备工艺是在常规大气压强下进行,经计算,当T=1 000 K时,pMg≈20.8 Pa。显然难以满足Mg在气泡—熔体两相界面充分挥发逸出的条件,因此,在机械搅拌大颗粒界面润湿过程中未出现界面Mg元素富集的现象。而当超声作用于熔体时,会在熔体中产生较大的正负压强[15]。空化泡壁面(气液界面)存在多种交换机制,其中包括空化运动过程中气体的扩散[16]。参照李晓谦等[17]对超声输入功率为1 kW、温度为720 ℃的空化泡动力学数值模拟结果,空化核在负压强的作用下体积膨胀,内部最小压强达0.2 Pa,形成较高真空度,满足空化泡壁面处镁挥发的条件(p<pMg≈20.8 Pa)。空化泡膨胀过程中充分吸收气态镁,经周期正负压强作用不断长大,与附着于界面处的气泡结合时[18],所吸收的Mg在界面处释放,造成界面镁质量分数提高,见图11。较高的镁质量分数提高了润湿体系的初始粘着功[9],更有利于润湿,界面反应所得产物为MgO。持续施振,在超声除气除杂的效应下,微气泡与气泡一起从熔体中净化出去,熔体中氧质量分数显著降低。随着界面附着的气泡减少,空化泡向界面逸散的趋势减弱,界面处Mg在反应中被不断消耗,界面镁质量分数降低,最终界面产物转变成MgAl2O4。
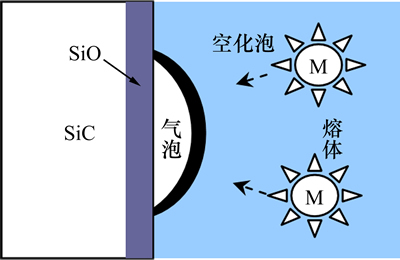
图11 超声空化作用下Mg在界面处的富集
Fig. 11 Enrichment of Mg in interface under action of ultrasonic cavitation
4 结论
1) 在半固态搅拌—机械搅拌工艺过程中,颗粒与熔体的润湿并不完全。此外,受氧化膜、表面吸附气体层、卷入气体等因素的影响,界面附近形成一定厚度的氧化夹杂区,阻碍了镁向界面处扩散,使其无法充分参与界面反应,致使界面生成大量的Al4C3,严重影响界面结合。
2) 在超声外场作用下,界面附近熔体中产生大量空化泡,在破灭过程中形成的高温高压作用使得氧化膜破碎,并随微区紊流和气体一同逸散入熔体,原本被气体层、氧化膜包裹的小颗粒逐步实现与熔体润湿。同时,熔体中的镁以气态形式被空化泡吸收逸散至界面附近,提高了界面附近熔体的Mg质量分数,便于熔体在颗粒表面铺展,形成初始界面增强相MgO。随着超声施振继续,颗粒与熔体完全结合,熔体中镁分布逐渐均匀,MgO最终转变为更稳定的MgAl2O4。
参考文献:
[1] IZCILER M, MURATOGLU M. Wear behaviour of SiC reinforced 2124 Al alloy composite in RWAT system[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 132(1/2/3): 67-72(6).
[2] CUI Y, WANG L F, REN J Y. Multi-functional SiC/Al composites for aerospace applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2008, 21(6): 578-584.
[3] 杨旭刚. 复合材料界面[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2010: 6-8.
YANG Xugang. Composite interfaces[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2010: 6-8.
[4] LIU G W, MUOLO M L, VALENZA F, et al. Survey on wetting of SiC by molten metal[J]. Ceramics International, 2010, 36(4): 1177-1188.
[5] ZHANG H W, GENG L, GUAN L N, et al. Effect of SiC particle pretreatment and stirring parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of SiCp/Al-6.8Mg composites fabricated by semi-solid stirring technique[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 528(1): 513-518.
[6] SHI Z L, ZHANG D, WU R J, et al. The interfacial characterization of oxidized SiCp/2014Al composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2001, A303: 46-53.
[7] LIU Z, HAN Q, LI J. Ultrasound assisted in situ technique for the synthesis of particle reinforced aluminum matrix composites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2011, 42(7): 2080-2084.
[8] 李晓谦, 蒋日鹏, 张立华, 等. 超声施振深度和冷却方式对纯铝凝固组织的影响[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2008, 28(4): 290-293.
LI Xiaoqian, JIANG Ripeng, ZHANG Lihua, et al. Effects of depth and method of cooling upon applying ultrasonic vibration on the solidification structures of pure aluminum[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2008, 28(4): 290-293.
[9] 房鑫. SiC/Al复合材料界面反应与粘着功理论预测研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学材料科学与工程学院, 2013: 20-22.
FANG Xin. Thoeretical prediction of interfacial reaction and work of adhesion in SiC/Al composites[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University. School of Material Science and Engineering, 2013: 20-22.
[10] MCLEOD A D, GABRYEL C M. Kinetic of the growth of spinal, MgAl2O4, on alumina particle in aluminum alloys containing magnesium[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1992, 23(4): 1279-1283.
[11] LEE J C, AHN J P, SHI Z L, et al. Methodology to design the interfaces in SiC/Al composites[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A: Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 2001, 32(6): 1541-1550.
[12] 施忠良, 顾明元, 刘俊友, 等. 氧化的碳化硅与铝镁合金之间的界面反应[J]. 科学通报, 2001, 46(14): 1161-1165.
SHI Zhongliang, GU Mingyuan, LIU Junyou, et al. The interfacial reaction between oxidized SiC and Al-Mg alloy[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(14): 1161-1165.
[13] JEONG J H, KIM Y, LEE J C. Mechanical properties of 2014Al/SiC composites with oxidized SiC particles[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A: Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 2003, 34(6): 1361-1369.
[14] 蒋日鹏, 李晓谦, 李开烨, 等. 超声对铝合金凝固传热与组织形成的影响与作用机制[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(10): 3807-3813.
JIANG Ripeng, LI Xiaoqian, LI Kaiye, et al. Effect of ultrasonic on heat transfer and microstructure formation of aluminum alloy during solidification and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(10): 3807-3813.
[15] 潘蕾, 陶杰, 陈照峰, 等. 高能超声在颗粒/金属熔体体系中的声学效应[J]. 材料工程, 2006(1): 35-42.
PAN Lei, TAO Jie, CHEN Zhaofeng, et al. Acoustic effect of high intensity ultrasonic in particle/metal melt[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2006(1): 35-42.
[16] DUBUS B, VANHILLE C, POZUELO C C, et al. On the physical origin of conical bubble structure under an ultrasonic horn[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2010, 17(5): 810-818.
[17] 李晓谦, 邓静, 林森. 7050铝合金超声空化气泡动力学数值模拟[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2013, 33(5): 395-399.
LI Xiaoqian, DENG Jing, LIN Sen. Dynamics numerical simulation of ultrasonic cavitation bubble in 7050 aluminum alloy[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2013, 33(5): 395-399.
[18] HAMILTON M F, ILINSKII Y A, MEEGAN G D, et al. Interaction of bubbles in a cluster near a rigid surface[J]. Acoustics Research Letters Online, 2005, 6(3): 207-213.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2015-10-10;修回日期:2015-12-24
基金项目(Foundation item):国家重点基础研究发展计划(“973”计划)项目(2010CB731706,2012CB619504);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51575539) (Projects(2010CB731706, 2012CB619504) supported by the National Basic Research Development Program (973 Program) of China; Project (51575539) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:张立华,教授,硕士生导师,从事金属基复合材料研究;E-mail: zhanglihua@163.com