铸态MnFeCoCuNix高熵合金的力学性能与断裂机理
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2021年第1期
论文作者:朱成艳 伍昊 朱和国 李向东 涂春磊 谢宗翰
文章页码:222 - 231
关键词:高熵合金;双相结构;力学性能;原位拉伸;断裂机理
Key words:high-entropy alloys; dual-phase structure; mechanical properties; in-situ stretching;fracture mechanism
摘 要:采用真空感应熔炼法制备不同Ni含量的MnFeCoCuNix高熵合金。利用X射线衍射仪、扫描电镜以及能谱仪分析材料的相组成和结构,利用万能拉伸试验机测定试样的拉伸性能。结果表明,该高熵合金体系具有双相结构。其中,FCC1相富含Fe和Co,而FCC2相富含Cu和Mn。随着Ni含量的增加,Cu的偏析减少,伴随着FCC2相的减少。在界面强化和固溶强化的共同作用下,抗拉强度先升高后降低,而伸长率略有增加。对MnFeCoCuNi0.5合金进行原位拉伸试验,发现其在拉伸断裂过程中产生明显的颈缩。在初始变形阶段,双相结构中滑移线的形态不同;在变形后期原子的再分布和溶解相的再分离使得表面滑移线更加细长和致密。
Abstract: MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys (HEAs) with different Ni contents were fabricated by vacuum induction melting. XRD and SEM-EDS were used to analyze the phase constitution and structure, and the tensile properties of the samples were determined using a universal tensile tester. The results show that the HEAs consist of a dual-phase structure, in which FCC1 phase is rich in Fe and Co, while the FCC2 phase has high contents of Cu and Mn. As Ni content increases, the segregation of Cu decreases, accompanied by the decrease of FCC2 phase. Moreover, the tensile strength of the HEAs increases first and then decreases, and the elongation increases slightly. This is attributed to the combined effect of interface strengthening and solid solution strengthening. The in-situ stretched MnFeCoCuNi0.5 alloy shows obvious neck shrinkage during the tensile fracture process. In the initial deformation stage, the slip lines show different morphologies in the dual-phase structure. However, in the later stage, the surface slip lines become longer and denser due to the redistribution of atoms and the re-separation of the dissolved phase.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31(2021) 222-231
Cheng-yan ZHU1, Hao WU1, He-guo ZHU1, Xiang-dong LI2, Chun-lei TU3, Zong-han XIE4,5
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China;
2. School of Mechanical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 211189, China;
3. School of Mechanical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China;
4. School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Adelaide, SA 5005, Australia;
5. School of Engineering, Edith Cowan University, WA 6027, Australia
Received 20 March 2020; accepted 18 September 2020
Abstract: MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys (HEAs) with different Ni contents were fabricated by vacuum induction melting. XRD and SEM-EDS were used to analyze the phase constitution and structure, and the tensile properties of the samples were determined using a universal tensile tester. The results show that the HEAs consist of a dual-phase structure, in which FCC1 phase is rich in Fe and Co, while the FCC2 phase has high contents of Cu and Mn. As Ni content increases, the segregation of Cu decreases, accompanied by the decrease of FCC2 phase. Moreover, the tensile strength of the HEAs increases first and then decreases, and the elongation increases slightly. This is attributed to the combined effect of interface strengthening and solid solution strengthening. The in-situ stretched MnFeCoCuNi0.5 alloy shows obvious neck shrinkage during the tensile fracture process. In the initial deformation stage, the slip lines show different morphologies in the dual-phase structure. However, in the later stage, the surface slip lines become longer and denser due to the redistribution of atoms and the re-separation of the dissolved phase.
Key words: high-entropy alloys; dual-phase structure; mechanical properties; in-situ stretching;fracture mechanism
1 Introduction
High-entropy alloy, also called multi- component alloy, has been rapidly developed. The original design concept focused on using five or more alloying elements in an equal or approximate atomic ratio [1,2]. Although there are many alloying elements and a large number of high-entropy alloy systems are formed, the crystal structure of high-entropy alloys is simple, which includes FCC, BCC, FCC+BCC, and even HCP [3-5]. This phenomenon can be explained by the Gibbs free energy equation △Gmix=△Hmix-T△Smix, where the mixed entropy (△Smix) and the mixed enthalpy (△Hmix) are in a competing position. At higher temperatures, the larger mixing entropy encourages the formation of a simple solid solution [6-8]. The high entropy effect does not guarantee the formation of a single-phase solid solution in multi-component alloys. Many other important factors that need to be considered [9-11], such as mixed enthalpy (△Hmix), atomic size difference (△), and valence electrons concentration (VEC). In general, HEAs with FCC structure have good plasticity but poor strength, while HEAs with BCC structure have high strength but low ductility [12-15]. The basic characteristics of HEAs can be summarized as four effects, namely, high entropy effect on thermodynamics, lattice distortion effect on structure, sluggish diffusion effect on kinetics, and “cocktail” effect on properties [16].
CANTOR et al [1] reported a five-component Fe20Cr20Mn20Ni20Co20 alloy forming a single FCC phase solid solution, termed “Cantor” alloy [17]. There have been extensive studies on modified Cantor alloys, for example, substituting for a certain element from or adding some elements to the original Cantor composition, or changing the content of some elements [18-20]. The most common alternative element is Cu. TAZUDDIN et al [21] used Cu to replace Cr, and found that the MnFeCoNiCu high-entropy alloy exhibits greater room temperature ductility while maintaining the FCC structure. SHIM et al [22], KIM et al [23], OH and HONG [24] used Cu element to substitute for Mn, Co, Ni, and Cr, respectively, and studied the microstructure stability and mechanical properties of the resultant alloys from multiple angles. The addition of elements was also explored by using Al, V, Ti, and Nb [25-27]. For example, CAO et al [28] and XU et al [29] showed that when Al was added to Cantor alloy, the fraction of BCC phase increased and the tensile strength of the alloy increased significantly as the Al content increased. Although there are a lot of studies on modified Cantor alloys [30-35], there is no research on the effect of Ni content on MnFeCoCuNi high-entropy alloys.
In this work, MnFeCoCuNix (x=0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5) high-entropy alloys were fabricated by vacuum induction melting method through changing the Ni content in the Mn-Fe-Co-Cu-Ni system. The samples were analyzed by X-ray diffractometry (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). The tensile properties were tested by universal tensile tester and the fracture mechanism was studied and ascertained by in-situ tensile testing in scanning electron microscope.
2 Experimental
The Mn particles (purity 99.99%, 3-6 mm in diameter and 5 mm in length), iron particles (purity 99.99%, 3-6 mm in diameter and 5 mm in length), cobalt particles (purity 99.9%, 3-5 mm in diameter and 5 mm in length), nickel particles (purity 99.99%, 3-6 mm in diameter and 5mm in length), copper particles (purity 99.99%, 3-6 mm in diameter and 5 mm in length) were used as raw materials. MnFeCoCuNix (x=0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5) high- entropy alloys with different Ni contents were prepared. To control the Ni content, the mass of the raw materials required for preparing 40 g of each of MnFeCoCuNix (x=0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5) high-entropy alloys was first calculated and then weighed.
All the raw materials were inductively smelted in a ceramic crucible, the molten metals were alloyed under argon gas protection. The induced current was set to be 500 A, after all particles melted, the magnetic force was used to stir molten metals for about 5 min. The liquid metal was then cast into a copper crucible and cooled down to room temperature. A series of tests were performed on the fabricated samples, such as XRD (Bruker- AXS D8 Advance), SEM (FEI Quanta 250 FEG) and EDS (FEI Quanta 250 FEG). The SEM specimens were prepared via mechanical polishing, followed by chemical etching with aqua regia (V(HCl):V(HNO3)=3:1). The area fractions of FCC1 and FCC2 phases were estimated by the Image J software. The tensile samples were wire-cut from the ingots. Three samples were prepared for each alloy and tested using a UTM/CMT 5000 electronic universal testing machine at a strain rate of 0.5 mm/min and ambient temperature.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructural characterization
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns of MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys with different Ni contents (x=0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5). The positions of the main peaks do not change as the Ni content changes, which makes clear that the crystal structure of the MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys is face-centered cubic (FCC) type. Notably, some new diffraction peaks appear at 2θ values of 42.6° and 49.6° in the XRD patterns, indicating that another phase with FCC structure is formed. Figure 1(b) shows the expanded view of the peaks with 2θ values from 47° to 53°, which reveals the splitting and broadening of the peaks. When the Ni content is relatively low, the peaks of the FCC2 phase are more obvious.
Figure 2 shows the typical microstructure of the MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys. Table 1 gives the chemical compositions of various phases measured by SEM-EDS analysis. The as-cast alloys are dendritic, in which the dendrite region A and the inter-dendritic region B are labeled. According to the EDS analysis, for the high-entropy alloys where Ni is present, the dendritic region A is rich in Fe and Co, while the inter-dendritic region B is rich in Cu and Mn. For the Ni-free high-entropy alloy, the dendrite region A is rich in Fe and Co, while the inter-dendritic region B is rich in Cu.

Fig. 1 XRD patterns of MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys with different Ni contents
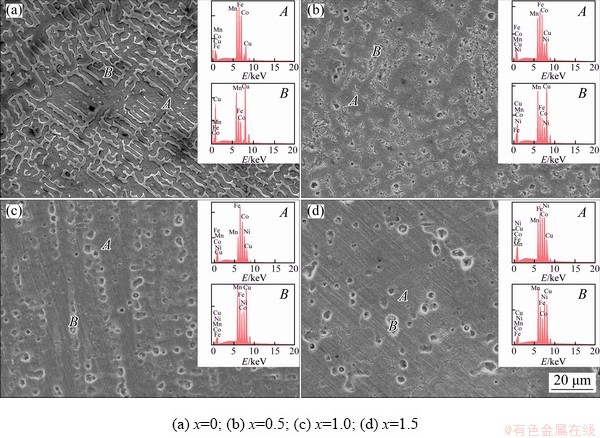
Fig. 2 SEM images of MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys
Figure 3 shows SEM images and elements mapping of MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys. When x=0, Mn is uniformly distributed in the alloy; when x=0.5, 1.0 and 1.5, Ni is relatively evenly distributed in the alloys. Moreover, when the volume fraction of one of the phases decreases, the intensity of the peaks in Fig. 1 decreases. The explanation for this phenomenon may be that as the Ni content changes, the lattice constants of the two FCC phases are adjusted to a similar value through the redistribution of different elements. This effect is not obvious in traditional alloys, but in high- entropy alloys, various elements with different atomic radii have a greater influence on the lattice constant of the developed phase due to the multi-component nature [22,36-38].
Table 1 EDS results of MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys corresponding to Fig. 2(at.%)


Fig. 3 SEM images and elements mapping of MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys with different Ni contents
The area fraction of each phase in Fig. 3 was estimated and given in Fig. 4 by using the Image J software. As the Ni content increases, the area fraction of the phase rich in Cu and Mn decreases, reflected by the reduction of the inter-dendritic region. Therefore, the phase rich in Cu and Mn corresponds to the FCC2 phase in Fig. 1, and the other phase rich in Fe and Co represents the FCC1. Combined with the EDS results in Table 1, it is shown that with the increase of Ni content, the Cu content of the region rich in Cu and Mn decreases, and the content of Mn increases. This may be explained by the mixing enthalpy (△Hmix) between different elements (see Table 2 [39]).
As shown in Table 2, the mixing enthalpy values of Cu with the four other elements are positive. Accordingly, during the solidification process, the phase rich in Fe, Co, and Ni solidifies in the dendrites first, and the Cu atoms segregate at the inter-dendrites. The mixing enthalpy between Cu-Ni is lower than that between Cu-Fe and Cu-Co. With the increase of Ni content, the high positive mixing enthalpy of Cu with other atoms decreases, and the segregation of Cu element is reduced. Similarly, the mixing enthalpy values of Mn with Co and Ni are both negative, with the mixing enthalpy of Mn-Ni reaching -8 kJ/mol. When the Ni content increases, the high negative mixing enthalpy values between Mn and other atoms increase, intensifying the segregation of Mn element. However, under the action of mixing enthalpy, the reduction of Cu segregation is greater than the increase of Mn segregation, leading to the decrease of FCC2 phase which is rich in Cu and Mn.

Fig. 4 Variation of area fraction of two phases in MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys with different Ni contents
Table 2 Mixing enthalpy (△Hmix) between different elements in MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys [39]

3.2 Tensile properties
Figure 5 shows the stress-strain curves of MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys. As x increases from 0 to 1.5, the elongations to fracture of the high-entropy alloys increase continuously, which are (42.1±0.2)%, (46.3±0.2)%, (47.5±0.2)% and (52.0±0.2)%, respectively. And the tensile strengths are (546±5), (574±5), (526±5) and (507±5) MPa, respectively. Figure 6 shows SEM images of the tensile fracture surfaces of the alloys. As revealed from the fracture surface morphology, ductile fracture occurs with dense dimples. A small number of fine particles are visible in the middle of the dimple. According to the EDS spectrum analysis in Fig. 6(d), the small protrusions are made of FCC2 phase (rich in Cu and Mn) with a columnar structure. It is worth noting that the fracture morphology is uneven, and the EDS data obtained at the failure are not accurate enough to be used as direct evidence. Therefore, it has to be compared with the EDS result in Fig. 2(b) in order to infer that the particle is FCC2 phase. During the tensile testing, the FCC2 columns are fractured, with broken ends sticking out within the dimple. As the Ni content increases, the plasticity of the high-entropy alloy increases steadily.

Fig. 5 Stress-strain curves of MnFeCoCuNix high- entropy alloys with different Ni contents
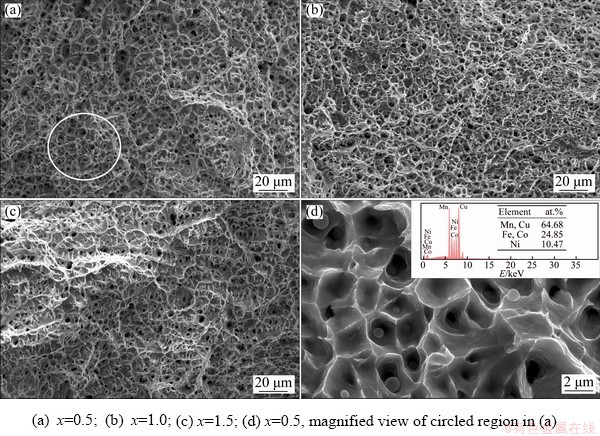
Fig. 6 SEM images showing tensile fracture surfaces of MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys
From Fig. 1, the lattice constants of the FCC1 phase in the four alloys at x=0, 0.5, 1.0 and 1.5 are 0.3595, 0.3599, 0.3600 and 0.3601 nm, respectively, and the lattice constants of the FCC2 phase are 0.3691, 0.3665, 0.3650 and 0.3625 nm, respectively. The lattice constants between the two phases get closer, with the tendency of the two phases merging into one. This is expected to promote the uniformity of the composition and structure of HEAs, leading to the increase of the plasticity. For x=0 and 0.5, the boundaries between the two phases are clear, which block the movement of dislocations. The solid solution strengthening and phase boundary strengthening effects are significant, resulting in high tensile strength. When x=0.5, the solid solution strengthening effect of the sample is higher than that of the sample with x=0, so the tensile strength increases. However, when x=1.0 or 1.5, the volume fraction of FCC2 phase decreases, and the interface strengthening effect is weakened, so the tensile strength is reduced. By calculating the atomic size difference △,

where ci, ri and rj denote the atomic fraction and atomic radii of the ith element and the jth element, respectively, the △ values of the MnFeCoCuNix (x=0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5) are 1.78%, 1.98%, 2.08% and 2.13%, respectively. As the △ increases, the lattice distortion increases, and consequently the elastic-strain energy increases [40]. This also explains the decrease in the tensile strength when x=1.0 and 1.5.
3.3 Fracture mechanism
The SEM images showing the surfaces of MnFeCoCuNi0.5 high-entropy alloys at different strains are presented in Fig. 7. When the strain is 5% (Fig. 7(a)), area-specific response appears on the surface of the material, owing to different phases in the dendrite and the inter-dendritic regions. When the strain increases to 15% (Fig. 7(b)), the boundary between the two phases becomes more obvious due to different compositions of the two phases. During the plastic deformation process, the defects, such as vacancies and dislocations, are different. The dislocations are accumulated at the two-phase interface, resulting in significant boundary between the two phases. When the strain continues to increase to 25% (Fig. 7(c)), dislocations are generated and connected in large quantities, which promote the slippage of the multilayer atoms, resulting in a small amount of slip bands. Finally, when the strain increases to 35% (Fig. 7(d)), a large amount of slip bands are formed on the surface of the material, and the sliding surface spacings of the two phases are different. The surface of the material becomes uneven, and a surface topography with ridges and grooves is formed.

Fig. 7 SEM images showing surfaces of MnFeCoCuNi0.5 high-entropy alloys at different strains
Figure 8 presents the SEM images showing crack propagation under the deformation of MnFeCoCuNi0.5 high-entropy alloys. The surface slips appear quite rough, but they are evenly distributed on the sample, which indicates excellent deformability. As can be seen from Figs. 8(a)-(c), the material produces less pronounced necking at a strain of 40%, and necking becomes more appreciable as the strain continues to increase. Notably, the necking portion comprises a large number of slip bands in different directions. This may be due to the difference in grain orientation and the change in shape resulting in different local shear forces. With a small increase in strain, the number of the slip bands is greatly increased. It can be seen from Fig. 8(d) that when the strain is 40%, micro-voids are formed in the neck portion, and the hole is the source of crack formation. As the strain further increases to 41.7% (Fig. 8(e)), the pores expand and join together to form microcracks. The cracks are produced at the slip zone junctions in different directions. When the strain is 42.5% (Fig. 8(f)), the fracture occurs, wherein the circled position is the origin of the crack formation, and the arrow represents the direction of the crack propagation. It can be seen that the cracks propagate along the slip bands. On the other hand, from the mapping of Cu element in the F and G regions as circled in Fig. 8(f), the atoms in the two phases have been redistributed as a result of the high dislocation density in the region with large deformation. Therefore, the segregation of elements in the separated two phases is reduced, and the structure of the two phases is changed.

Fig. 8 SEM images showing crack propagation in MnFeCoCuNi0.5 high-entropy alloys at different strains

Fig. 9 SEM image, and elemental mapping of Cu and Co over longitudinal section away from (a) and near (b) fracture region in as-cast MnFeCoCuNi0.5 alloy
Figure 9 shows the fracture surface and elemental mapping of Cu and Co over the longitudinal section away from and near the fracture region in the as-cast MnFeCoCuNi0.5 alloys. Note, the elemental mapping images of Mn, Fe and Ni are not shown here to save the space. From Fig. 9(a), at the position away from the fracture, the difference in mechanical response between the two phases is obvious at the small deformation. There are many large slip bands (indicated by red straight lines) in the Fe- and Co-rich phase with long and sparse slip lines. However, small slip bands (indicated by white double arrows) with short and dense slip lines appear in the Cu- and Mn-rich phase because the Cu- and Mn-rich phase contains a large amount of Cu, which is softer and has better ductility. Therefore, the slip bands produced are fine and dense. In Fig. 9(b), the necking area near the fracture is deformed to a great extent, and the large slip lines in the Fe- and Co-rich phase overcome the interface barrier between the two phases. Connecting with small slip lines in the Cu- and Mn-rich phase leads to the formation of a large number of dense and long slip bands. In addition, some micropores are formed at the interface of the two phases, similar to the micropores generated in the initial stage of crack formation. A large number of micro-voids formed during the deformation process develope into micro-cracks and continue to expand until cracks take place. Moreover, as the Ni content increases, the Cu content decreases in the soft Cu- and Mn-rich phase but increases in the Fe- and Co-rich phase. Under the large deformation, the redistribution of atoms and re-separation of dissolved phases are likely to occur [22]. The composition difference of the two phases is further reduced, and the phase interface is reduced. Dislocations are not likely to accumulate at the phase interface, and cracks are not easy to generate. So the plasticity is improved.
4 Conclusions
(1) The MnFeCoCuNix high-entropy alloys exhibit two-phase FCC structure. The FCC1 phase rich in Fe and Co forms the dendrites, while the FCC2 phase rich in Cu and Mn makes the inter-dendrites. Moreover, as the Ni content increases, the segregation of Cu element decreases, while the segregation of Mn element increases, accompanied by the reduction of FCC2 phase.
(2) With the increase of Ni content, the tensile strength of MnFeCoCuNix alloys at x=0, 0.5, 1.0 and 1.5 increases firstly from (546±5) to (574±5) MPa, and then decreases from (526±5) to (507±5) MPa, owing to the combined effect of interface and solid solution strengthening. The elongation to fracture increases slightly, which is (42.1±0.2)%, (46.3±0.2)%, (47.5±0.2)% and (52.0±0.2)%, respectively.
(3) In the initial deformation of the MnFeCoCuNi0.5 alloy, the morphologies of slip lines in FCC1 and FCC2 phases are different; one for the FCC1 is long and sparse, while one for the FCC2 is short and dense. However, in the later deformation, the high dislocation density, the redistribution of atoms and the re-separation of the dissolved phase might occur. The slip lines overcome the interface barrier and form a large number of dense and long slip bands. The MnFeCoCuNi0.5 high-entropy alloys show necking during the fracture process. First, micropores are created at the interface of the two phases, and then merge to produce micro-cracks, which extend along the slip zone until fracture.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial supports from the Jiangsu Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project, China (BE2018753/ KJ185629), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51571118), and the 2020 Extracurricular Academic Research Fund for College Students of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, China. Zong-han XIE acknowledges the support of the Australian Research Council Discovery Projects.
References
[1] CANTOR B, CHANG I T H, KNIGHT P, VINCENT A J B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 375-377: 213-218.
[2] YEH Jien-wei, CHEN Swe-kai, LIN Su-jien, GAN Jon-yiew, CHIN Tsung-shune, SHUN Tao-tsung, TSAU Chun-huei, CHANG Shou-yi. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2004, 6(5): 299-303.
[3] NONG Zhi-sheng, ZHU Jing-chuan, YANG Xia-wei, YU Hai-ling, LAI Zhong-hong. Effects of annealing on microstructure, mechanical and electrical properties of AlCrCuFeMnTi high entropy alloy [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology Materials Science, 2013, 28(6): 1196-1200.
[4] KIVY M B, ZAEEM M A, LEKAKH S. Investigating phase formations in cast AlFeCoNiCu high entropy alloys by combination of computational modeling and experiments [J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 127: 224-232.
[5] MIRACLE D B, SENKOV O N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts [J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 122: 448-511.
[6] SUN Xiao-dong, ZHU He-guo, LI Jian-liang, HUANG Jie-wen, XIE Zong-han. High entropy alloy FeCoNiCu matrix composites reinforced with in-situ TiC particles and graphite whiskers [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 220: 449-459.
[7] MANZONI A M, GLATZEL U. New multiphase compositionally complex alloys driven by the high entropy alloy approach [J]. Materials Characterization, 2019, 147: 512-532.
[8] TSAI Ming-hung, YEH Jien-wei. High-entropy alloys: A critical review [J]. Materials Research Letters, 2014, 2(3): 107-123.
[9] WANG Z J, HUANG Y H, YANG Y, WANG J C, LIU C T. Atomic-size effect and solid solubility of multicomponent alloys [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 94: 28-31.
[10] YE Y F, WANG Q, LU J, LIU C T, YANG Y. High-entropy alloy: Challenges and prospects [J]. Materials Today, 2016, 19(6): 349-362.
[11] ZHANG Y, ZUO T T, TANG Z, GAO M C, DAHMEN K A, LIAW P K, LU Z P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2014, 61: 1-93.
[12] CHEN Jian, ZHOU Xue-yang, WANG Wei-li, LIU Bing, LV Yu-kun, YANG Wei, XU Da-peng, LIU yong. A review on fundamental of high entropy alloys with promising high-temperature properties [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 760: 15-30.
[13] CHENG Hu, XIE Yan-chong, TANG Qun-hua, RAO Cong, DAI Pin-qiang. Microstructure and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNiMn high-entropy alloy produced by mechanical alloying and vacuum hot pressing sintering [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 1360-1367.
[14] FU Z Z, KOC R. Ultrafine TiB2-TiNiFeCrCoAl high-entropy alloy composite with enhanced mechanical properties [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017, 702: 184-188.
[15] ZHANG Ai-jun, HAN Jie-sheng, SU Bo, MENG Jun-hu. A novel CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy matrix self-lubricating composite [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 725: 700-710.
[16] RIVA S, TUDBALL A, MEHRABAN S. A novel high- entropy alloy-based composite material [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 730: 544-551.
[17] CANTOR B. Multicomponent and high entropy alloys [J]. Entropy, 2014, 16(9):4749-4768.
[18] PENG Jian, LI Zi-yong, JI Xin-bo, SUN Yan-le, FU Li-ming, SHAN Ai-dang. Decomposition kinetics of carbon-doped FeCoCrNiMn high-entropy alloy at intermediate temperature [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30: 1884-1894.
[19] SATHIARAJ G D, TSAI C W, YEH J W, JAHAZI M, BHATTACHARJEE. The effect of heating rate on microstructure and texture formation during annealing of heavily cold-rolled equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 688: 752-761.
[20] WANG Jian-ying, FANG Jing-hua, YANG Hai-lin, LIU Zhi-lin, LI Rui-di, JI Shou-xun, WANG Yun, RUAN Jian-ming. Mechanical properties and wear resistance of medium entropy Fe40Mn40Cr10Co10/TiC composites [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29: 1484-1494.
[21] TAZUDDIN, BISWAS K, GURAO N P. Deciphering micro-mechanisms of plastic deformation in a novel single phase fcc-based MnFeCoNiCu high entropy alloy using crystallographic texture [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 657: 224-233.
[22] SHIM S H, OH S M, LEE B J, HONG S K, HONG S I. Nanoscale modulated structures by balanced distribution of atoms and mechanical/structural stabilities in CoCuFeMnNi high entropy alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2019, 762: 138120.
[23] KIM Y K, LEE B J, HONG S K, HONG S I. Strengthening and fracture of deformation-processed dual fcc-phase CoCrFeCuNi and CoCrFeCu1.71Ni high entropy alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2020, 781: 139241.
[24] OH S M, HONG S I. Microstructural stability and mechanical properties of equiatomic CoCrCuFeNi, CrCuFeMnNi, and CoCrCuFeMn alloys [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 210: 120-125.
[25] REN B, LIU Z X, LI D M, SHI L, CAI B, WANG M X. Effect of elemental interaction on microstructure of CuCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy system [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 493: 148-153.
[26] HE Z F, JIA N, MA D, YAN H L, LI Z M, RAABE D. Joint contribution of transformation and twinning to the high strength ductility combination of a FeMnCoCr high entropy alloy at cryogenic temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2019, 759: 437-447.
[27] JO Y H, CHOI W M, SOHN S S, KIM H S, LEE B J, LEE S. Role of brittle sigma phase in cryogenic-temperature- strength improvement of non-equi-atomic Fe-rich VCrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 724: 403-410.
[28] CAO C M, TONG W, BUKHARI S H, XU J, HAO Y X, GU P, HAO H, PENG L M. Dynamic tensile deformation and microstructural evolution of AlxCrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2019, 759: 648-654.
[29] XU Jun, CAO Cheng-ming, GU Ping, PENG Liang-ming. Microstructures, tensile properties and serrated flow of AlxCrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30: 746-755.
[30] SATHIARAJ G D, PUKENAS A, SKROTZKI W. Texture formation in face-centered cubic high-entropy alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 826: 154183.
[31] JIANG Shu-yong, WANG Yu, XING Xiao-dong, ZHANG Yan-qiu. Stress-induced martensite phase transformation of FeMnSiCrNi shape memory alloy subjected to mechanical vibrating polishing [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30: 1582-1593.
[32] HAASE C, MORA L A B. Influence of deformation and annealing twinning on the microstructure and texture evolution of face-centered cubic high-entropy alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 150: 88-103.
[33] SHABANI A, TOROGHINEJAD M R. Evaluation of microstructure and texture formation during annealing of cold-rolled FeCrCuMnNi multiphase high-entropy alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30: 449-462.
[34] YIM D, SATHIYAMOORTHI P, HONG S J, KIM H S. Fabrication and mechanical properties of TiC reinforced CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy composite by water atomization and spark plasma sintering [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 781: 389-396.
[35] TAKEUCHI A, WADA T, ZHANG Y. MnFeNiCuPt and MnFeNiCuCo high-entropy alloys designed based on L10 structure in Pettifor map for binary compounds [J]. Intermetallics, 2017, 82: 107-115.
[36] LIU N, WU P H, ZHOU P J, PENG Z, WANG X J, LU Y P. Rapid solidification and liquid-phase separation of undercooled CoCrCuFexNi high-entropy alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2016, 72: 44-52.
[37] TAZUDDIN, GURAO N P, BISWAS K. In the quest of single phase multi-component multiprincipal high entropy alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 697: 434-442.
[38] DAI Shuai, WANG Feng, WANG Zhi, LIU Zheng, MAO Ping-li. Effect of Cu on microstructure, mechanical properties, and texture evolution of ZK60 alloy fabricated by hot extrusion-shearing process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30: 1511-1523.
[39] TAKEUCHI A, INOUE A. Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element [J]. Materials Transactions, 2005, 46(12): 2817-2829.
[40] ANDREOLI A F, ORAVA J, LIAW P K, WEBER H, OLIVEIRA M F, NIELSCH K, KABAN I. The elastic-strain energy criterion of phase formation for complex concentrated alloys [J]. Materialia, 2019, 5: 100222.
朱成艳1,伍 昊1,朱和国1,李向东2,涂春磊3,谢宗翰4,5
1. 南京理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,南京 210094;
2. 东南大学 机械学院,南京 211189;
3. 南京理工大学 机械学院,南京 210094;
4. School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Adelaide, SA 5005, Australia;
5. School of Engineering, Edith Cowan University, WA 6027, Australia
摘 要:采用真空感应熔炼法制备不同Ni含量的MnFeCoCuNix高熵合金。利用X射线衍射仪、扫描电镜以及能谱仪分析材料的相组成和结构,利用万能拉伸试验机测定试样的拉伸性能。结果表明,该高熵合金体系具有双相结构。其中,FCC1相富含Fe和Co,而FCC2相富含Cu和Mn。随着Ni含量的增加,Cu的偏析减少,伴随着FCC2相的减少。在界面强化和固溶强化的共同作用下,抗拉强度先升高后降低,而伸长率略有增加。对MnFeCoCuNi0.5合金进行原位拉伸试验,发现其在拉伸断裂过程中产生明显的颈缩。在初始变形阶段,双相结构中滑移线的形态不同;在变形后期原子的再分布和溶解相的再分离使得表面滑移线更加细长和致密。
关键词:高熵合金;双相结构;力学性能;原位拉伸;断裂机理
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Corresponding author: He-guo ZHU; Tel: +86-13605182940; E-mail: zhg1200@njust.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65489-9
1003-6326/ 2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier B.V. & Science Press
2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier B.V. & Science Press

